Bacterial Cell Structure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Cell envelop
Encloses the cytoplasm and internal structures of the cell
Bacterial cell envelop includes:
Plasma membrane, cell wall, periplasmic space, glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
polysaccharide outer layer outside the bacterial cell wall that aids in protection, adhesion, and virulence
Components of animal plasma membrane
phospholipids bilayer
cholesterol
proteins
carbohydrate
Bacterial plasma membrane
retains the cytoplasm and separates the cell from its enviroment
selectively permeable barrier
contains transport systems used for nutrient uptake, waste excretion, and protein secretion
location of a variety of crucial metabolic processes
contains special receptor molecules
Bacterial membrane structure
lipid bilayer in which proteins floats
Asymmetry of most membrane lipids

Cell wall
maintains shape, helps protect cell from osmotic lysis and toxic materials, may contribute to pathogenicity
Gram positive cell walls
Composed primarily of a thick layer of peptidoglycan

Gram negative cell walls
Composed primarily of a thick layer of peptidoglycan, outer membrane composed of lipids, lipoproteins, and LPS

Peptidoglycan
mesh-like polymer that forms the bacterial cell wall, composed of alternating sugar derivatives (NN-acetylglucosamine [NAG] and NN-acetylmuramic acid [NAM]) cross-linked by short peptides
LPS (lipopolysaccharide)
covers almost the entire outer surface of the gram-negative outer membrane
acts as protective barrier, potent endotoxin, immune recognition molecule
LPS causes severe inflammation and sepsis by stimulating Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)
LPS consists of ?
lipid A
core polysaccharide
O side chain (O antigen)
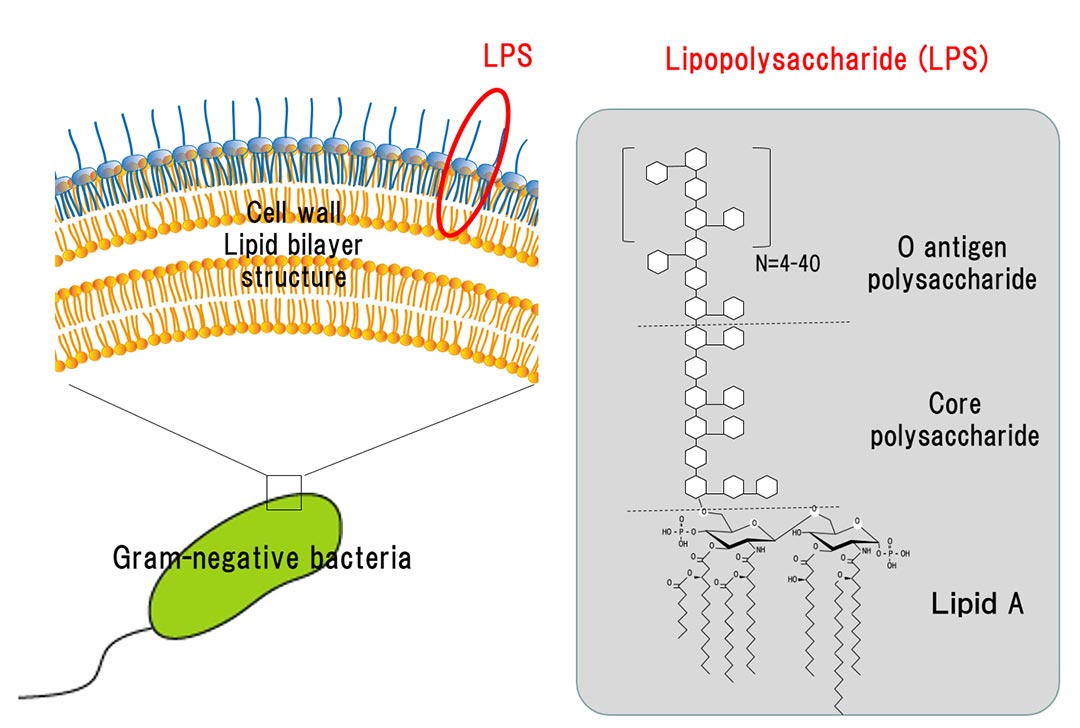
Lipid A
endotoxic component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that anchors this molecule within the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria
it serves as the primary activator of the host immune system (via TLR4) during infection, with its structure (acyl chains/phosphate groups) determining its toxicity
recognize by TLR4/MD2 receptors
Core polysaccharide
acts as a structural bridge,
covalently linking the hydrophobic Lipid A (embedded in the membrane) to the outermost O-antigen
the core is divided into an inner part containing KDO (3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid) and heptose, and an outer part with hexoses, often phosphorylated to stabilize the membrane
O antigen (O-polysaccharide)
outermost layer
consisting of repeating sugar units
it acts as a primary barrier against host immune defenses (complement-mediated killing, phagocytosis) and serves as a major target for antibody recognition
determines serotype
LPS triggers inflamation

Slime layer
loose, unorganized, and easily removed layer of extracellular material (mainly polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids) that surrounds some bacterial cells. It functions in bacterial adherence to surfaces, protection against dehydration, entrapment of nutrients, and evasion of immune cell
Biofilm
protective, slimy communities of bacteria (and other microbes) that stick to surfaces, encased in a self-produced glue called Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS), allowing them to thrive, resist antibiotics, and cause infections like dental plaque, cystic fibrosis lung infections, or catheter infections
Three types of external structures
fiambre, pilli and flagella
Fiambre
short, thin, hairlike
composed of fimbrilin protein
primary involved in attachment to surfaces
biofilm formation
important virulence factor in pathogenis bacteria
Pilli
hair-like protein appendages
composed mainly of pilin protein
used in transfers of DNA to other cells and in cell adhesion
Conjugation
specific type of pilus, called F pilus or sex pilus, is important in the transfer of DNA between bacterial cells
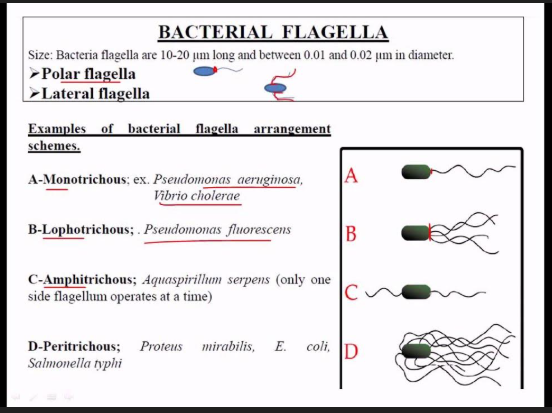
Flagella
responsible for bacterial mobility
attached to the cell by a basal body that holds a long rotali
Structure of flagella
Filament: external helical structure
Hook: flexible connector
Basal body: motor embedded in cell envelope
Flagellar arrangement
Chemotaxis
movement towards a chemical attractant or away from a chemical repellent