AP Chem Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Particles
1/57
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms

What is the atomic number of zinc?
30

What is the atomic symbol for zinc?
Zn

What is the average atomic mass of zinc?
65.38g

How many protons does zinc have?
30

How many neutrons does Zn-65 have?
35
The number of protons in an element is equal to its ____
atomic number
The number of electrons in a neutrally-charged element is equal to ____
the number of protons
The number of neutrons in an element is equal to ____
mass number - number of protons
Gases are at standard temperature and pressure when pressure is ___atm and temperature is ____K
1, 273
When a gas is at STP, one mole of gas always occupies ___L
22.4
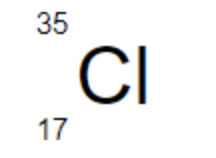
The number of protons in Cl-35 is ___
17
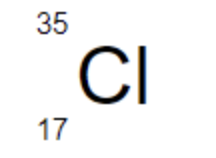
The number of neutrons in Cl-35 is ____
18
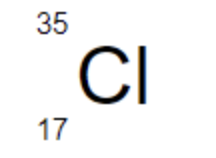
The mass number of Cl-35 is ___
35
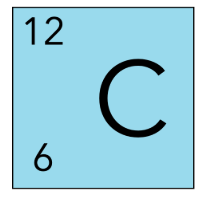
The number of neutrons in C-12 is ____
6
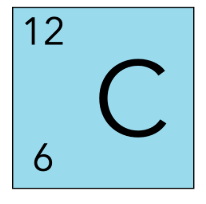
The mass number of C-12 is ___
12
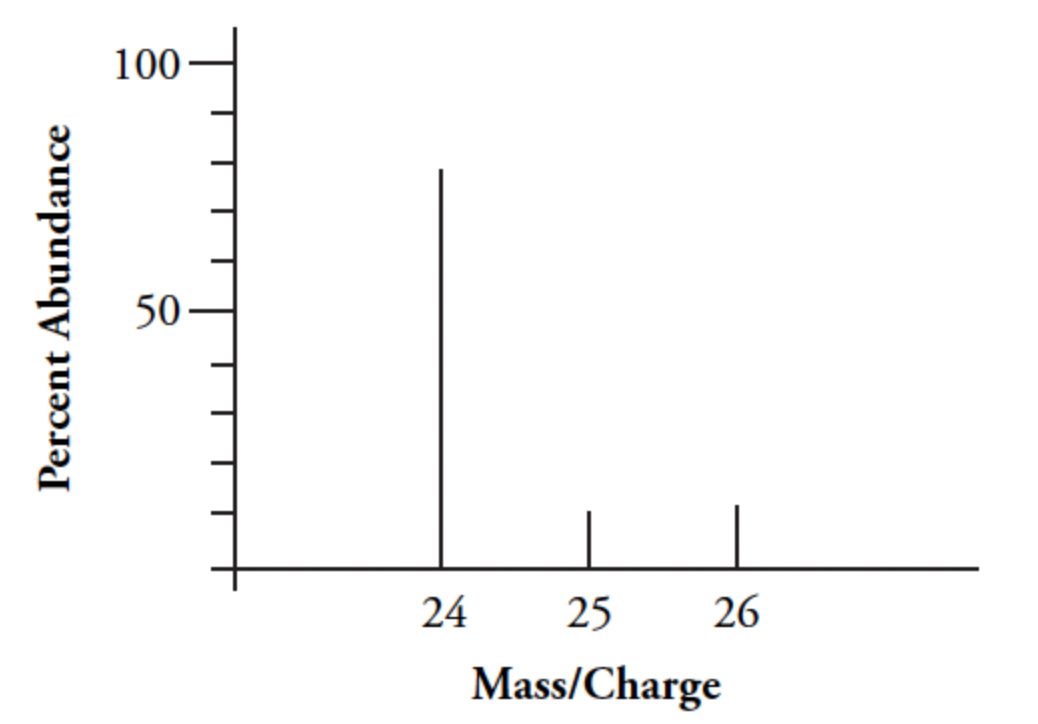
According to the graph, what is the most abundant isotope of magnesium?
Mg-24
Ions collide with a metal plate. Electrons are transferred from the metal to the ion, producing a current and thus a signal to a computer.
Detection
Ions are attracted to the negative side of an electromagnetic field causing separating of the mixture based on mass and charge.
Deflection
Electrons are knocked off sample particles to form (mostly) +1 ions.
Ionization
Ions move through a series of charged plates to form a narrow beam of high speed particles with equal kinetic energy.
Acceleration
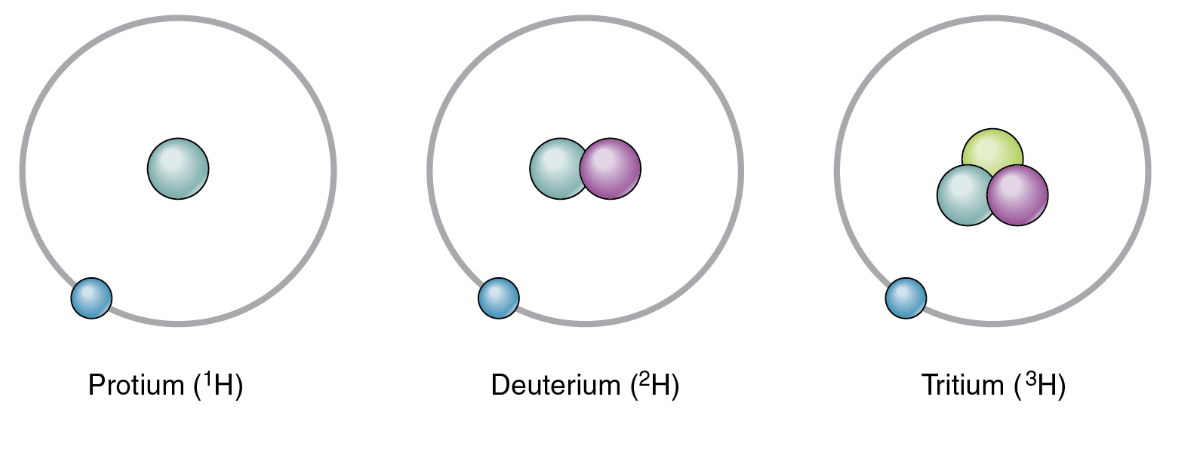
If the average atomic mass of hydrogen in nature is 1.0070, which isotope must have a higher percent composition in nature?
H-1
If the average atomic mass of boron in nature is 10.81 amu, which isotope must have a higher percent composition in nature?
B-11
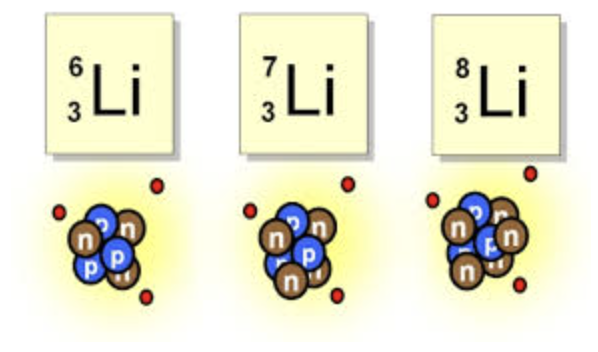
Isotopes of the same element have different numbers of ___
Neutrons
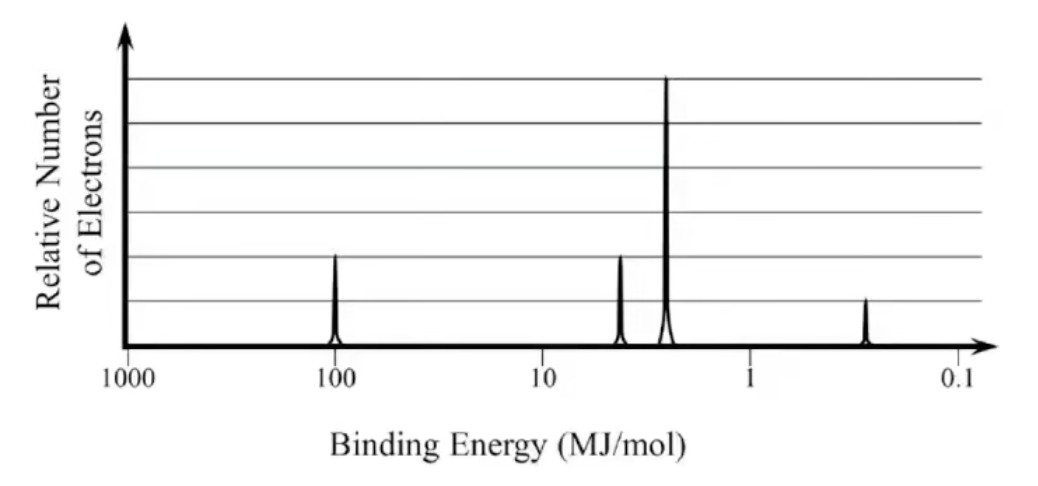
What element is this?
Na
Higher number of protons means….
Greater attractive force
A close valence electron means…
Greater attractive force
The _____ electron configuration refers to the arrangement of the electrons in the lowest available energy levels
ground state
An ___ electron configuration refers to a situation in which at least one of the electrons has moved up to a higher energy level
excited state
As electrons get closer to the nucleus, binding energy ___
increases
Does N or O have a higher binding energy?
O
A greater attractive force means a ____ atomic radius
smaller
A closer valence electron means a ___ atomic radius.
larger
When two ions have the same number of protons, the one with the smaller atomic radius has ___ electrons in its outermost shell
less
The force that pushes electrons apart due to their like charges is called…
electron-electron repulsion
As you move from left to right across a horizontal row on the periodic table, atomic radius values tend to ___ from left to right, and first ionization energy values tend to ___ from left to right.
decrease, increase
As you move from top to bottom down a vertical column on the periodic table, atomic radius values tend to ___ from top to bottom, and first ionization energy values tend to ___ from top to bottom.
increase, decrease
After an elements valence electrons are removed, the electrons following require a much ___ amount of ionization energy
larger
The higher the electronegativity value for an element is, the ___ the attraction for electrons.
greater
The greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, the ___ polar the bond is.
more
The measure of the magnitude of a dipole is called the …
dipole moment
Whenever two electrical charges of opposite sign are separated by a distance, a ___ is generated.
dipole
In general, the greater the difference in electronegativity, the ___ the magnitude of the dipole moment
greater
The atoms of the ___ ordinarily do not form chemical bonds or share electrons with other atoms.
noble gases
The most electronegative element on the periodic table is…
Flourine
As you move from left to right across a horizontal row on the periodic table, electronegativity values tend to ___ from left to right.
increase
As you move from top to bottom down a vertical column on the periodic table, electronegativity values tend to ___ from top to bottom.
increase
The smaller the atomic radius is, the ___ the electronegativity value is.
greater
The larger the atomic radius is, the ___ the electronegativity value is.
smaller
The greater the attraction is between an atom and an added electron, the more ___ the value of ΔE is.
negative
The more negative the value of ΔE is, the ___ the electron affinity is.
greater
The energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to form a negatively charged anion.
electron affinity
In general, ___ energy is released when a nonmetal atom gains an electron than when a metal atom gains an electron.
more
The likelihood that two elements will form a chemical bond is determined by the interactions between the valence electrons and ___ of elements.
Nuclei
Elements in the same column of the periodic table tend to form ___ compounds.
analogous
Typical charges of atoms in ionic compounds are governed by the number of valence electrons and predicted by their ___ on the periodic table.
location
What are the diatomic elements?
Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F
What element is tetratomic? (occurs with 4 atoms)
P
What element is octatomic? (occurs with 8 atoms)
S