4.4.2.4 Radioactive contamination
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
Last updated 2:03 PM on 12/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
what can ionising radiation do
increase the risk of cancer in humans
2
New cards
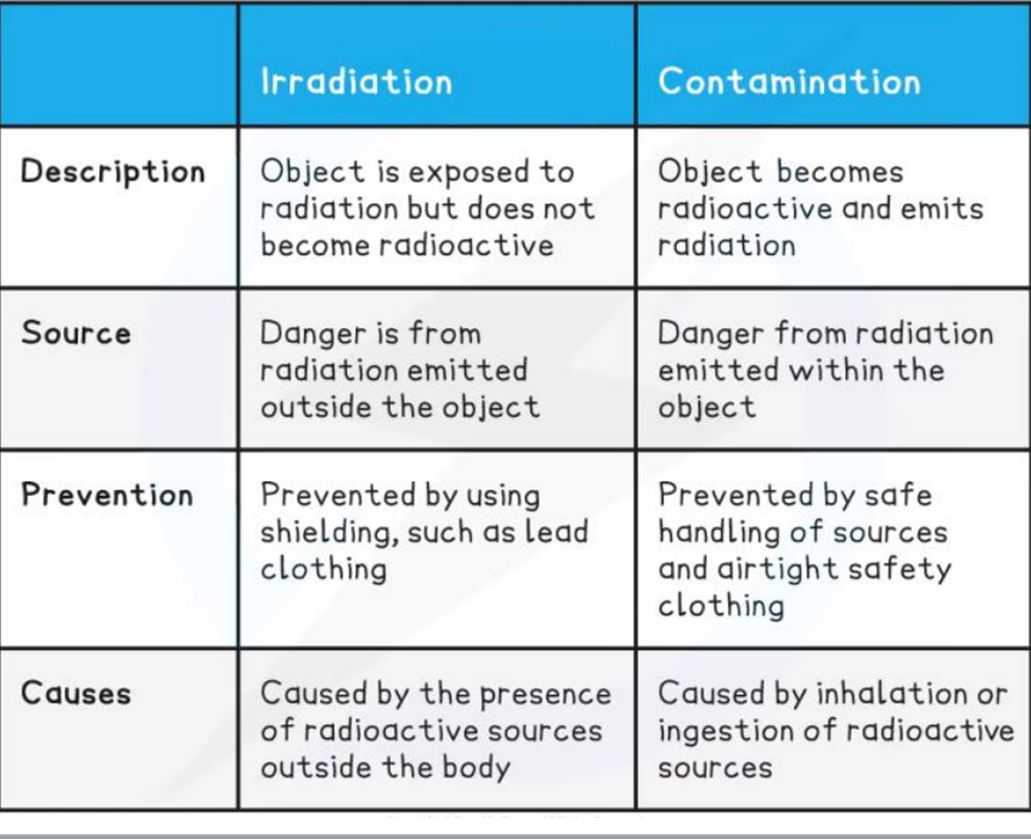
irradiation
exposing an object to nuclear radiation (alpha, beta, gamma or neutrons)
\
o Lasts only for a short period of time
o The source emits radiation, which reaches the object Exposing an object to nuclear radiation, but does not make it radioactive
o E.g. radioactive dust emitting beta radiation, which “irradiates” your skin o Medical items are irradiated sometimes to kill bacteria on its surface, but not to make the medical tools themselves radioactive
\
o Lasts only for a short period of time
o The source emits radiation, which reaches the object Exposing an object to nuclear radiation, but does not make it radioactive
o E.g. radioactive dust emitting beta radiation, which “irradiates” your skin o Medical items are irradiated sometimes to kill bacteria on its surface, but not to make the medical tools themselves radioactive
3
New cards
uses of irradiation
sterilisation- objects that cannot be heated
place object to be sterilised into a wrapper to stop bacteria entering
place object near a radioactive isotope that emits gamma radiation
that’s inside a lead shield to protect workers from radiation
withdraw internal shield allowing gamma radiation to irradiate the object
the gamma radiation kills any bacteria present
when an object is irradiated like this the object does not become radioactive- that’s because the object comes into contact with the radiation but nit the radioactive isotope itself
place object to be sterilised into a wrapper to stop bacteria entering
place object near a radioactive isotope that emits gamma radiation
that’s inside a lead shield to protect workers from radiation
withdraw internal shield allowing gamma radiation to irradiate the object
the gamma radiation kills any bacteria present
when an object is irradiated like this the object does not become radioactive- that’s because the object comes into contact with the radiation but nit the radioactive isotope itself
4
New cards
precautions when working with radioactive isotopes
shielding to stop radiation
gloves can protect against alpha radiation as it has a low penetrating power
use a lead apron for beta and gamma radiation as they are more penetrating
led walls, screen made of led-glass
radiation monitor- can measure how much radiation has been received, if the person has received too much radiation, we can stop them from working with radioactive isotopes
gloves can protect against alpha radiation as it has a low penetrating power
use a lead apron for beta and gamma radiation as they are more penetrating
led walls, screen made of led-glass
radiation monitor- can measure how much radiation has been received, if the person has received too much radiation, we can stop them from working with radioactive isotopes
5
New cards
what is radioactive contamination
when unwanted radioactive isotopes end up on other materials, this is called contamination
hazardous as the radioactive atoms decay and emit ionising radiation
\
o Lasts for a long period of time
o The source of the radiation is transferred to an object Radioactive contamination is the unwanted presence of radioactive atoms on other materials – the hazard is the decaying of the contaminated atoms releasing radiation o E.g. radioactive dust settling on your skin (your skin becomes contaminated)
hazardous as the radioactive atoms decay and emit ionising radiation
\
o Lasts for a long period of time
o The source of the radiation is transferred to an object Radioactive contamination is the unwanted presence of radioactive atoms on other materials – the hazard is the decaying of the contaminated atoms releasing radiation o E.g. radioactive dust settling on your skin (your skin becomes contaminated)
6
New cards
alpha radiation
can be very dangerous- strongly ionising but easily stopped by dead cells on the skin surface. Alpha emitters can be dangerous if inhaled or swallowed (dust or food)
alpha particles crash into living cells and damage dna
alpha particles crash into living cells and damage dna
7
New cards
beta radiation
quite ionising and can penetrate skin into the body
8
New cards
gamma radiation
weakly ionising. can penetrate body but likely to pass straight through
9
New cards
peer review
Scientific Reports Published need to be peer reviewed
If they are on the effects of radiation on humans, peer review is essential
If initial studies got measurements wrong, safety levels based on the study may cause people to die.
If they are on the effects of radiation on humans, peer review is essential
If initial studies got measurements wrong, safety levels based on the study may cause people to die.
10
New cards
summary