General Chemsitry II Chapter 11
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hybridization + Valence Bond Theory + Molecular Bond Theory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the Valence Bond Theory in simple terms?
Energetically favorable orbitals of atoms will remain together through covalent bonds
Why does atoms potential energy become negative as they get closer together and positive as they get further apart?
Energy (work) is being released to attract the atoms, making the change negative. When they are too close, repulsive forces cause energy (work) to be absorbed and separate the atoms, making the change positive.
Potential energy is energy waiting to be used. Energy going in is positive, and energy leaving is negative.
How does bond length, influenced by the balance of attractive and repulsive forces, contribute to the bonding type of atoms?
The balance between repulsive and attractive forces determines bond length. Bond length determines bond strength and the distance that influences orbital overlap and stronger electrostatic attractions.
Example: Covalent bonds are strong bonds = shorter bond lengths and higher bond order
Why are shorter bond lengths stronger and longer bond lengths weaker?
Shorter bond lengths contribute to greater orbital overlap and electron pair sharing, bringing intermolecular forces closer together and stabilizing them.
Remember, bond order is inversely related to bond length.
Why does an atom’s potential energy become negative as it gets closer to another atom and positive as it gets further?
Energy (work) must be used to separate the atoms again, taking energy out of the volt and making it negative. When atoms join, energy is released and put back into the volt making potential energy positive.
How does the potential energy change contribute to the bonding type?
Potential energy change equals a change in orbital overlapping due to bond length changes, which in turn can destabilize and weaken the bonds contributing to covalent bonding.
Why is bond length determined when repulsive and attractive forces are balanced?
It’s the midpoint between bond separation and joining and represents energy equilibrium
How does the effective nuclear charge contribute to unique atom combinations?
ENC influences atom size and electronegativity, which in turn influences which atoms bond together
How does overlapping orbitals contribute to specific atom combinations?
Unpaired orbitals overlap, each contributing electrons to fill the orbital and decrease energy
How do you know which orbital will overlap?
It will be the orbital with the unfilled valance.
Why is the s orbital spherical and in no specific direction?
Its quantum number (l) being 0 allows it to have a wavefunction of spherical symmetry and its magnetic quantum number (m) being 0 means it has no dipole movement
Why is the p orbital lobed and mutually perpendicular?
The lobe of one p orbital must overlap with the other to ensure constructive interference.
What are hybrid orbitals?
The mixing of two or more nonequivalent atomic orbitals of the same atom
Why does AX2 have a sp hybridization?
The steric number of = 2, meaning that there are 2 orbitals being occupied by electrons.
Electrons go in order from lower energy to higher
#’s before orbital indicate which level not which type
List the orbitals in order
s, p p p, d d d d d…..
Why does hybridization not occur in isolated atoms or diatomic molecules?
Hybridization is the joining of two different atomic orbitals that are together and covalently bond.
Yes or No? Do hybrid orbitals share the same shape and orientation from their original atomic orbitals? Why?
No, it is the mixing of two nonequivalent atomic orbitals creating a whole new atomic orbital.
Why is the number of hybrid orbitals equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were mixed.
Orbital conservation which is useful in predicting reactions.
How do you determine the bond order?
pairs of electrons shared/ pairs of atoms
Why is hybridized orbitals shape and orientation important?
They specifically maximize overlap with other orbitals for their electrons to be closer.
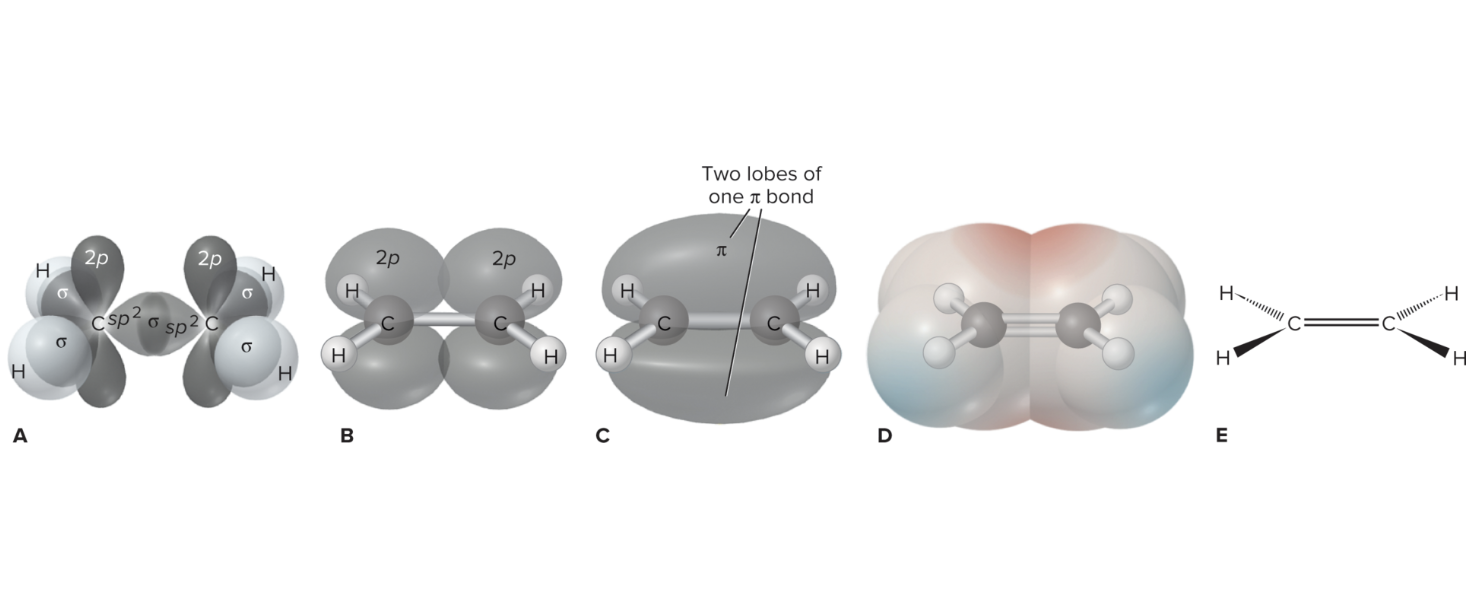
How do you know that the p orbital of carbon in ethylene is unhybridized?
…….
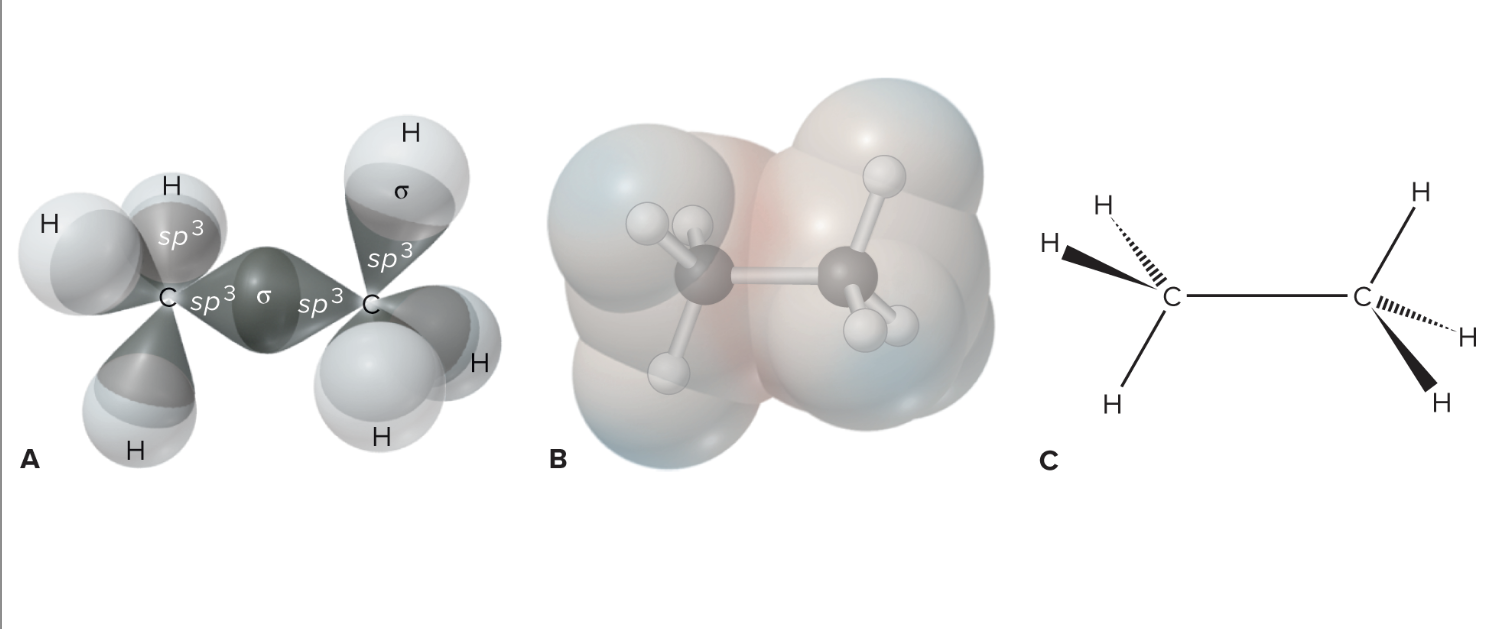
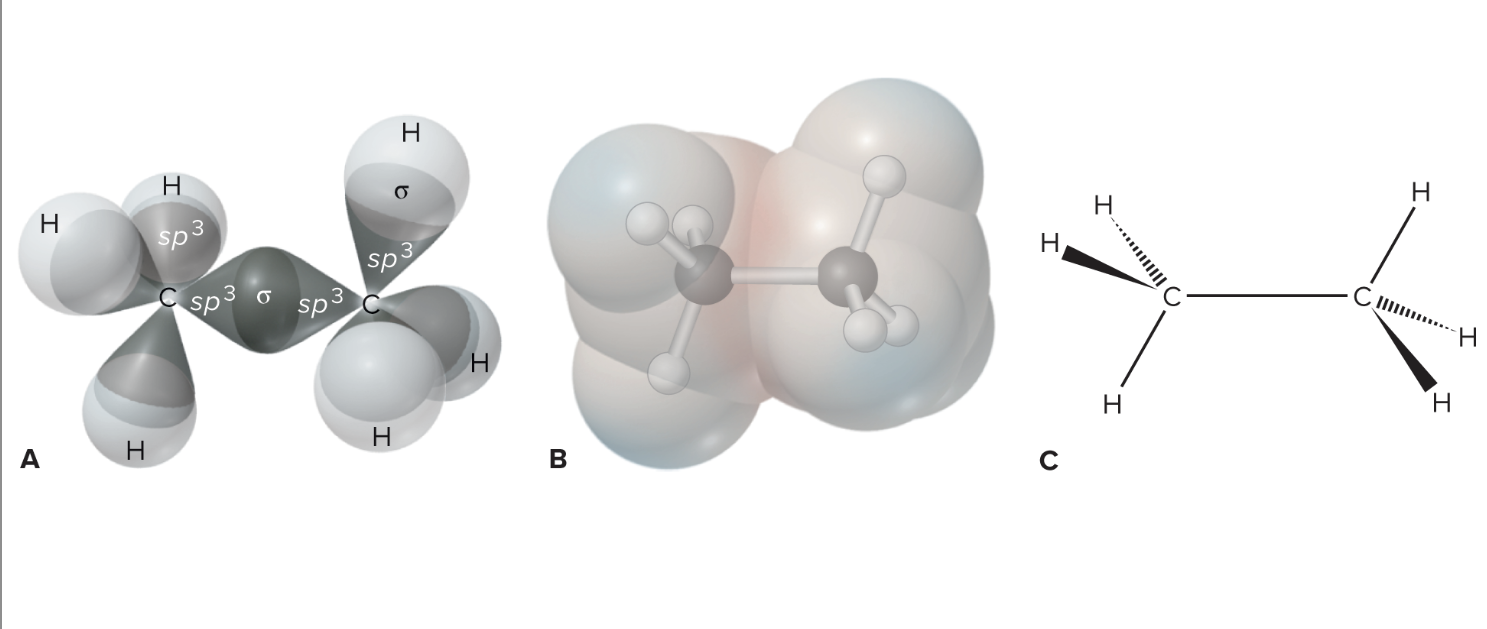
What is a sigma bond?
Sigma Bonds: End-to-end overlapping bonds between atoms with the highest electron density and share two electrons
Why do pi bonds overlap side to side with unhybridized p orbitals?
What is a Pi Bond?
Pi Bonds: Side-to-side overlapping bonds between atoms, consisting of two delocalized electrons