CompTIA A+ 220-1201 (3.7 - Multifunction Devices)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Multifunction devices
• Multifunction devices (MFD)
- Printer
- Scanner
- Fax (yes, really)
- Network connection
- Phone line connection
- Print from web
• A lot of things can go wrong
- You're going to fix them
Unboxing a device
• These can be large devices
- Make sure you have enough room
- Stay out of walkways
• Check the area
- Power
- Network
- Accessibility
Printer drivers
• Specific to a printer model
• Get this exactly right
• Get the right operating system drivers
- Windows 10, Windows 11
- Get the right version of the operating system
- 32-bit drivers are very different than 64-bit drivers
• You can't mix and match drivers
- It's a very specific task
PCL or PostScript
• PCL (Printer Command Language)
- Created by Hewlett-Packard
- Commonly used across the industry
• PostScript
- Created by Adobe Systems
- Popular with high end printers
• Make sure the drivers match the printer
- PCL printer, PCL driver
- PostScript printer, PostScript driver
- Wired device sharing
Firmware
• The internal "operating system" of the multifunction device
- Starts the system
- Connects to the network
- Interprets the incoming data stream
- Runs the printing process
• Update the firmware to avoid any incompatibilities
- And probably fix a few bugs
• Get the latest firmware from the device website
- Install from a stable platform and power source The most common connector
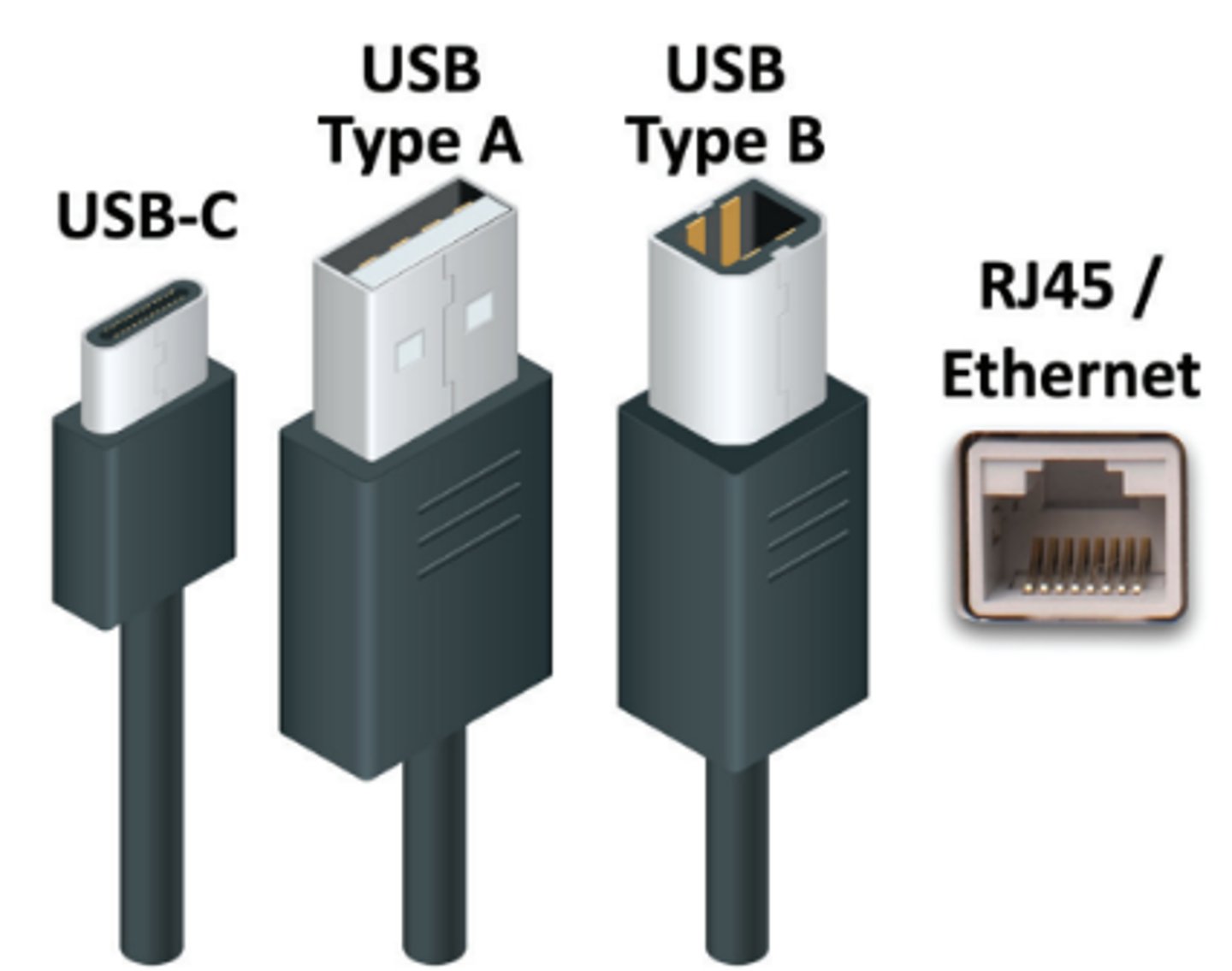
Wired device sharing
• USB
- The most common connector
- USB Type B on the printer,
USB Type A on the computer
- Or, USB-C everywhere
• Ethernet - RJ45 connector
• May include more than one option
Wireless device sharing
• Bluetooth - Limited range
• 802.11 Infrastructure mode
- Many devices using an access point
• 802.11 Ad hoc mode
- No access point
- Direct link between wireless devices
Sharing the printer
• Printer share
- Printer is connected to a computer
- The computer shares the printer
- Computer needs to be running
• Print server
- Print directly to the printer
- Jobs are queued on the printer
- Jobs are managed on the printer
- Web-based front-end
- Client utility
Configuration settings
• Duplex
- Save paper
- Print on both sides of the page without manually
flipping over the paper
- Not all printers can do this
• Orientation
- Portrait vs. Landscape
- The paper doesn't rotate
- The printer compensates
• Tray settings
- Printers can have multiple trays
- Plain paper, letterhead, etc.
- Choose the correct tray in the print dialog
• Quality
- Resolution / Color, greyscale / Color saving
Printer security
• User authentication
- Everyone can print
- Set rights and permissions
- Printing vs. managing the printer
• Badging
- Authenticate when using the printer
- Your job doesn't print until you use your
employee badge
- Quick and easy
• Audit logs
- Cost management
- Security monitoring
- Event Viewer / System Events
- May be built into the printer or print server
• Secured prints
- Printer must support secure printing
- Define a passcode
- Use the passcode at the printer
Flatbed scanner
• Different form factors
- All-in-one multifunction device
- Standalone flatbed
• May include an ADF
- Automatic Document Feeder, multiple pages
Network scan services
• Scan to email
- Scans are sent to your inbox
- Large scans can fill up your mailbox
• Scan to folder
- Using SMB (Server Message Block)
- Send to a Microsoft share
• Scan to cloud
- Cloud storage account
- Google Drive, Dropbox, etc