Physics 3 - Harmonics - Module 5
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
The frequency the crystal likes to ring at
What is the resonant frequency
one-half wavelength
What is the calculation of the resonant frequency
Resonant/center frequency
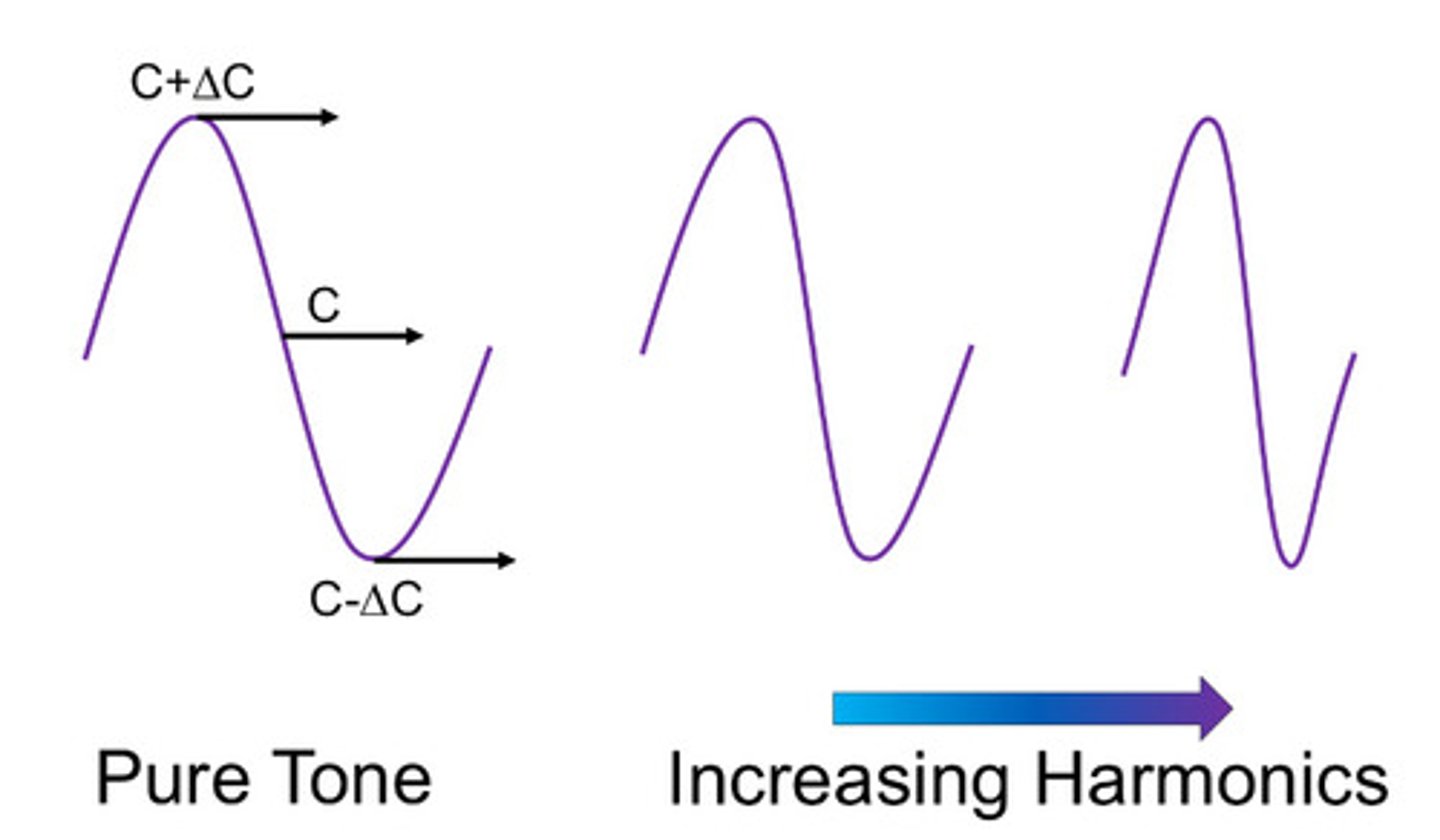
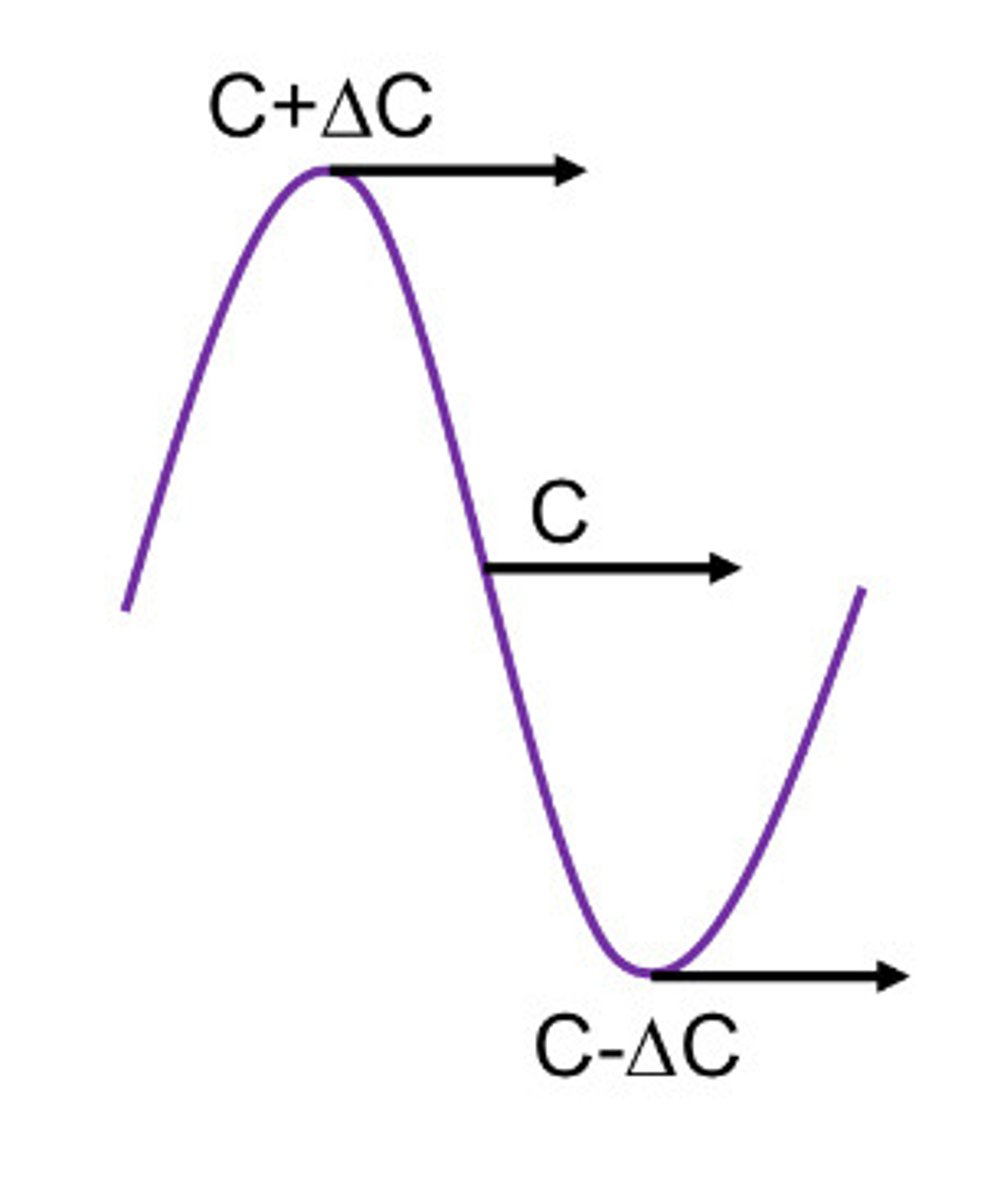
What does this image represent
Compressibility
What has the most impact on the speed of the wave
Sine wave
What is the increase and decrease of density shown in
Change in stiffness
Changing in density =
Change in intensity
Change in stiffness=
Increase in density means an increase in stiffness which will increase the intensity of
Explain how an increase in density will increase the intensity
Decrease in density means and increase in compressibility which causes a decrease in intensity
Describe how a decrease in density results in a decrease in intensity
Decrease in intensity
Increased in compressibility =
Wave distortion
As sound travels through tissue with changes of stiffness it will result in:
False, it is random
T/F: the process of wave distortion is linear
True
T/F: every time we emit sound we get a non linear process
More options for frequencies that we can ring at
What does damping material give us
Beam dynamics or the result of the wave propagating through tissue
What is harmonics
HD TV
What is harmonic comparative to
Fundamental frequency
What is the frequency that we are driving at
True
T/F: you can still scan with harmonics turned off but we just wont get back the other harmonics frequency (will just get back the fundamental frequency)
Harmonic frequencies
What is produced due to the ultrasound beam going through wave distortion
2x the amplitude
What is the amplitude of harmonic frequencies usually
Will have more energy to get back, will have a stronger signal
What is the significance of the harmonic frequency being 2x the amplitude
Resonate more
Because harmonic are 2x the amplitude that can:
There is not just a west harmonic that comes back, there is the 2nd, 3rd, and so on
Explain how many harmonic waves we get back
1st and 2nd one only
Which harmonic wave that we get back do we use
As frequency increase, absorption also increases so the harmonic waves past the 2nd one are attenuated too much
Why do we only use the 1st and 2nd harmonic wave
True
T/F: harmonics happens naturally and every time that we scan. The button on the machine just determines how we use it
Since harmonics happens all the time, harmonics still occurred with older machines but we just didn't know what to do with it until later (so there wasn't a button on the machine)
Explain how harmonics was or wasn't used in the past on older machines
Intensity of the beam, distance travel, and the nature of the tissue
What 3 things does the wave distortion depend on
Linear
Fundamental waves are:
Non-linear
Harmonic frequencies are:
Due to dependencies (intensity of the beam, the distance travelled, and the nature of the tissue)
Why is harmonic frequencies non linear
Bc no dependant on anything
Why are fundamental frequencies linear
The most intense part of the beam
What part of the beam is harmonics best produced by
No, will be random and slightly different
Do we get back the exact same range of frequencies with harmonics
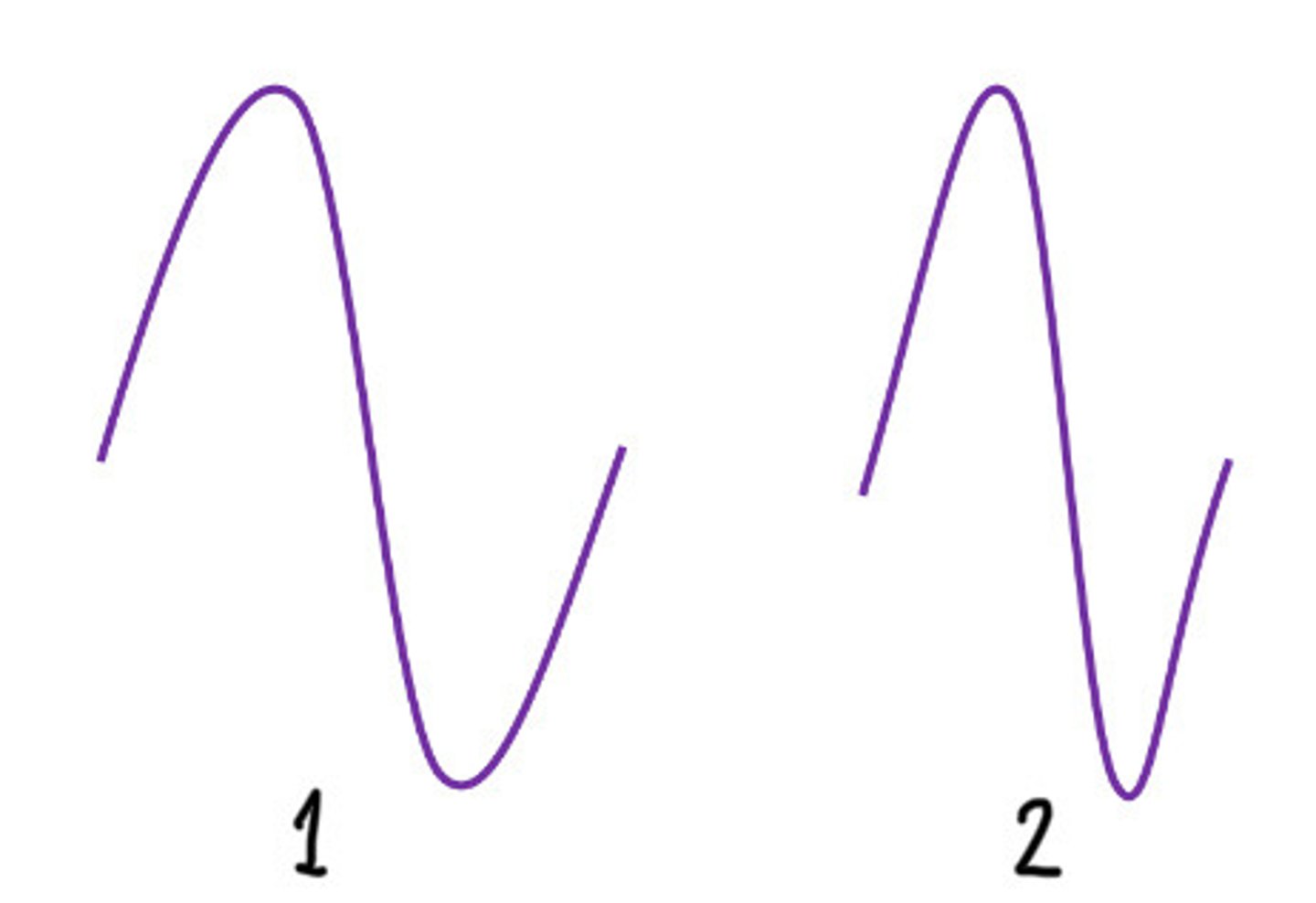
High pressure: tissue compressed and high velocity (because more dense)
Describe the top wave

Low pressure: tissue expanded and lower velocity (bc more compressible)
Describe the bottom wave

Starting with fundamental frequency and compressing into harmonic frequency
What does this image show
2
Which has the most harmonics
Pure tone
What does this image represent
Harmonic beam is narrower, grating lobes are eliminated, and reverb is reduced or eliminated
What are the 3 ways that harmonics improves the image
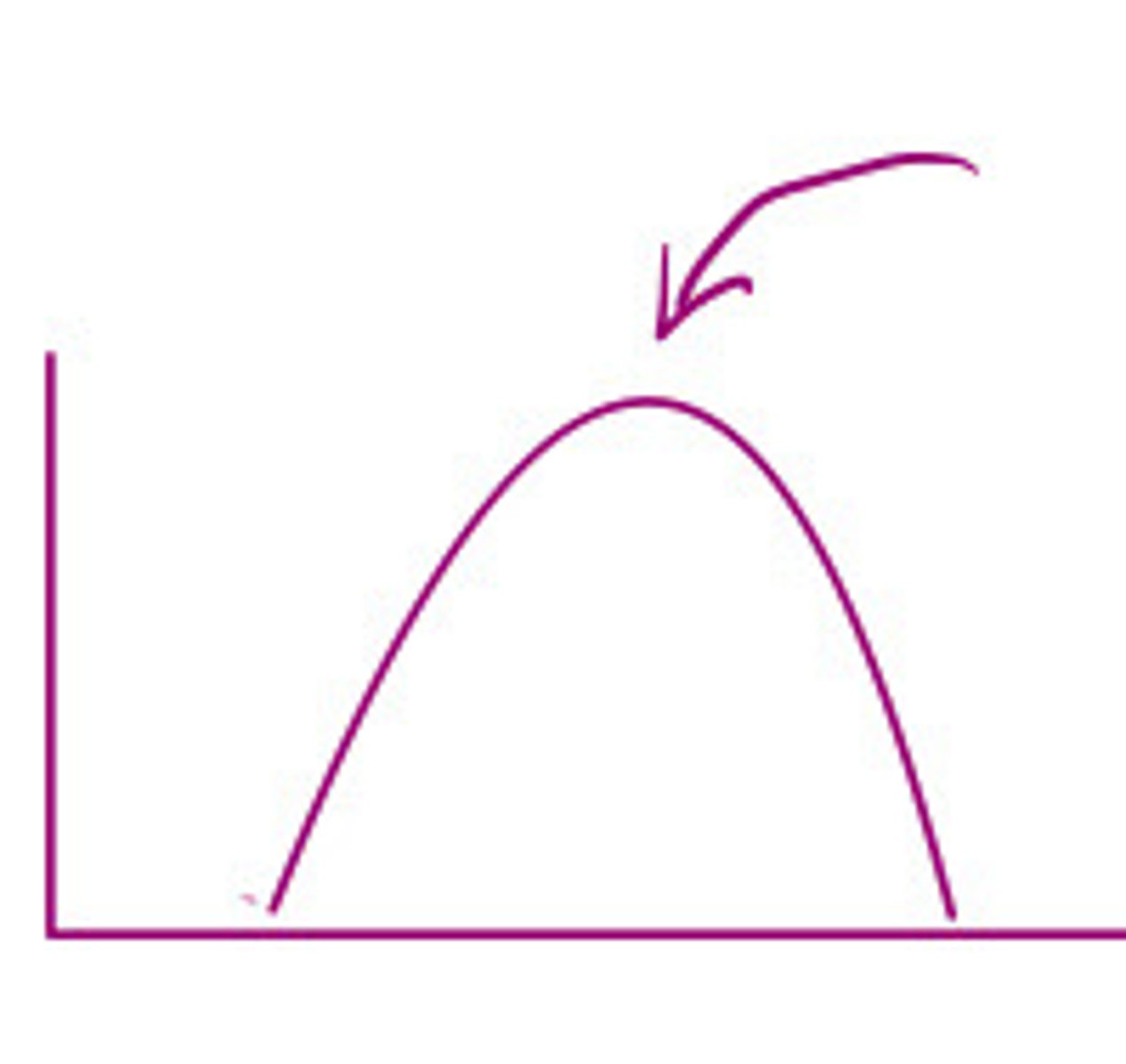
The most intense part of the beam
Where is harmonics the best
Where harmonics is the best
What does this image represent

Improve lateral resolution and a little improvement in elevational resolution
What improves due to harmonics coming from the narrowest part of the beam
Adipoziation (less cross talk) and subdicing (cut the crystals to less than a wavelength but still act as 1)
What are 2 other things that reduce grating lobes
Bc harmonics only picks up the intense part of the beam and grating lobes are the weaker sides of the beam
Explain how harmonics decreases grating lobes
Bc the beam needs to be more powerful with harmonics, and at first we didn't know if it was too powerful or not for OB scanning (later found out it was okay to use harmonics with OB)
Explain why when harmonics first came out it was not used on OB scans
Cystic structures bc getting a narrower and more intense beam= better lateral and elevational resolution
What is an example of something that would be more resolved with harmonics
Beam gets gradually more intense until it is the most intense at the middle and then fans out, gradually becoming less intense
Describe the intensity of the beam as it travels down
Near field, weak harmonics
What is 1 and what are the harmonics like here
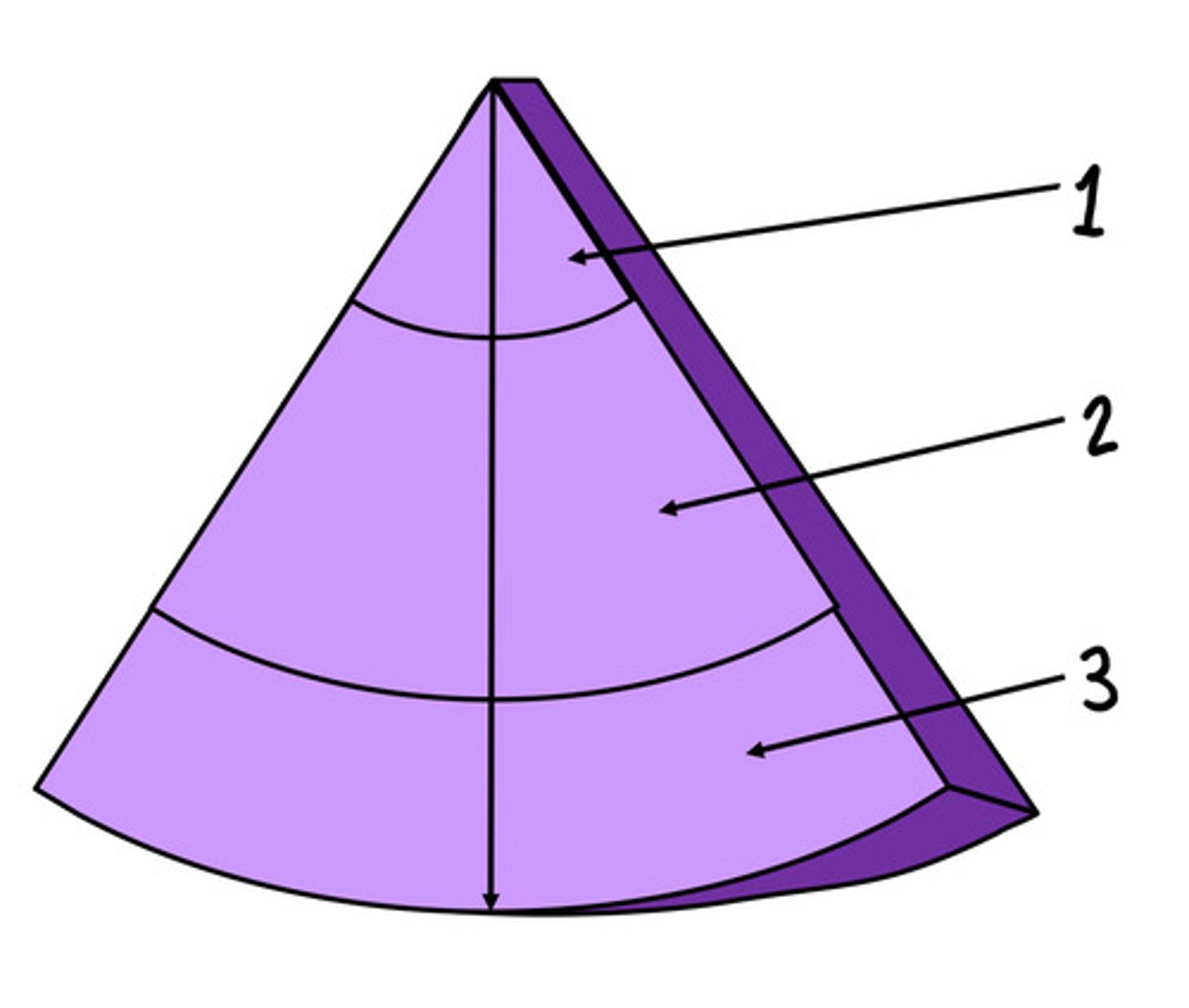
Mid field, the best harmonics
What is 2 and what are the harmonics like here
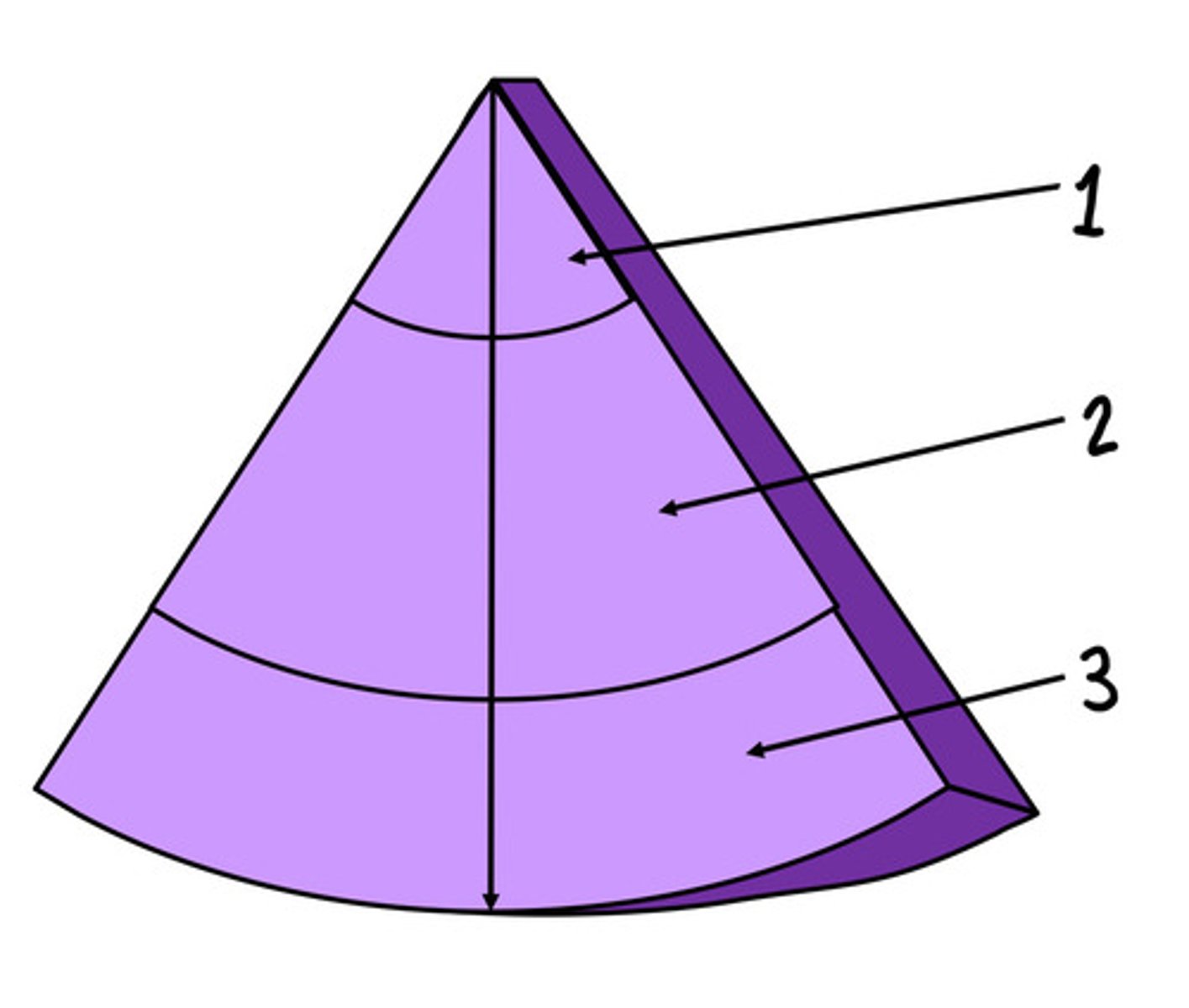
Far field, harmonics are attenuated faster than they are produced (no/worse harmonics)
What is 3 and what are the harmonics like here
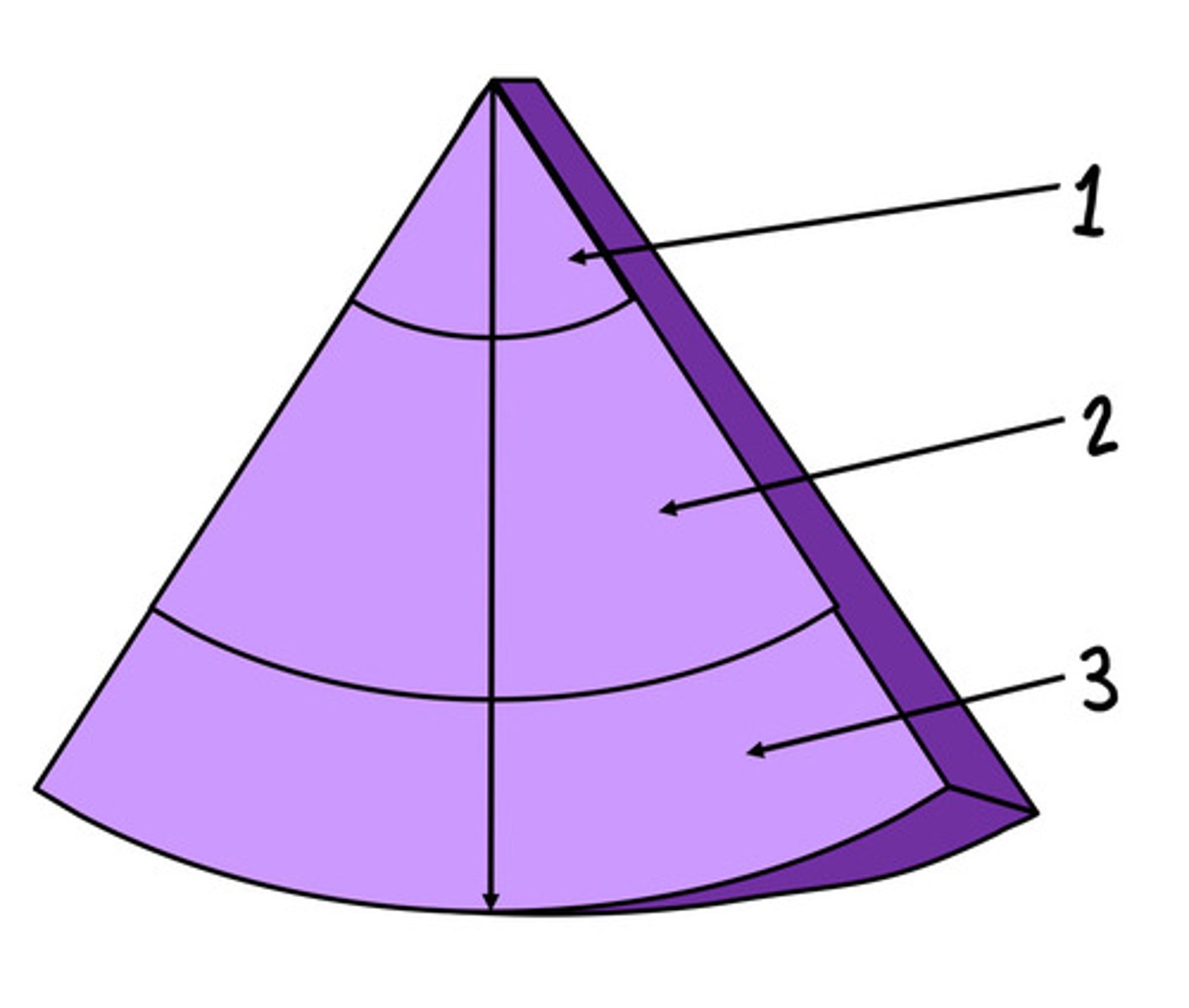
There is not a lot of harmonics at the near field bc in order to get harmonics the wave need to propagate and distort (not enough time for this in the near field)
Explain why harmonics is the best at the near field/why harmonics decreases reverberation
Main bang artifact (reverberation artifact right at the top of the image)
What type of reverberation artifact does harmonics greatly reduce/eliminate
Superficial structures
What exams or structures may it be helpful to turn off harmonics due to it not going through enough distortion in the near field
Could also result in main bang, so have to decide which is better
Although turning off harmonics may help with visualization of superficial structures, what do you risk by turn it off
Turn harmonic frequency down or turn it off for more penetration and visualization of the far field (remember, lower frequency=better penetration)
Explain what adjustments you can make to the harmonics to get a better visualization of the far field
Bandpass filtration
What was developed to allow us to use harmonics to our advantage
Eliminates the fundamental frequency and allow the harmonic signal to pass through the beam former
What does the Bandpass filtration do
Beam former
What most the harmonic signal pass through in order for us to make use of
Tuning a radio to accept only the frequency that you want to hear
What is the Bandpass filtration analogous to
Will have a narrower beam which is better for fitting through the ribs and also helps resolve the cystic structures in the heart (atria, ventricles, vessels)
Explain why harmonics greatly assists the resolution of echoes
Bandpass filtration
What was the first method for us to be able to use harmonic signal
Pulser inversion
What was the 2nd method used for us to be able to use the harmonics signal
Wide range of frequencies that can come out of the machine
Wider bandwidth =
Shorter pulse, shorter SPL which = better axial resolution
What does a wider bandwidth mean for pulse lengthier and SPL and resolution
Axial
What resolution is improved with a wider bandwidth
The fundamental frequency and the second harmonic bandwidths must fit within the overall transducer bandwidth without overlapping
What is required for Bandpass filtering to work
Makes the bandwidth narrower
what is the major disadvantage of Bandpass filtering
Longer pulses and longer SPL which = bad axial resolution
What does a narrower bandwidth result in
If they were to overlap then when the machine deletes the fundamental frequency it would also be deleting the portion of the harmonic frequency which would result in missing information
Explain why the fundamental and second harmonic bandwidths can not overlap with Bandpass filtering to work
How Bandpass filtering works
What does this image represent
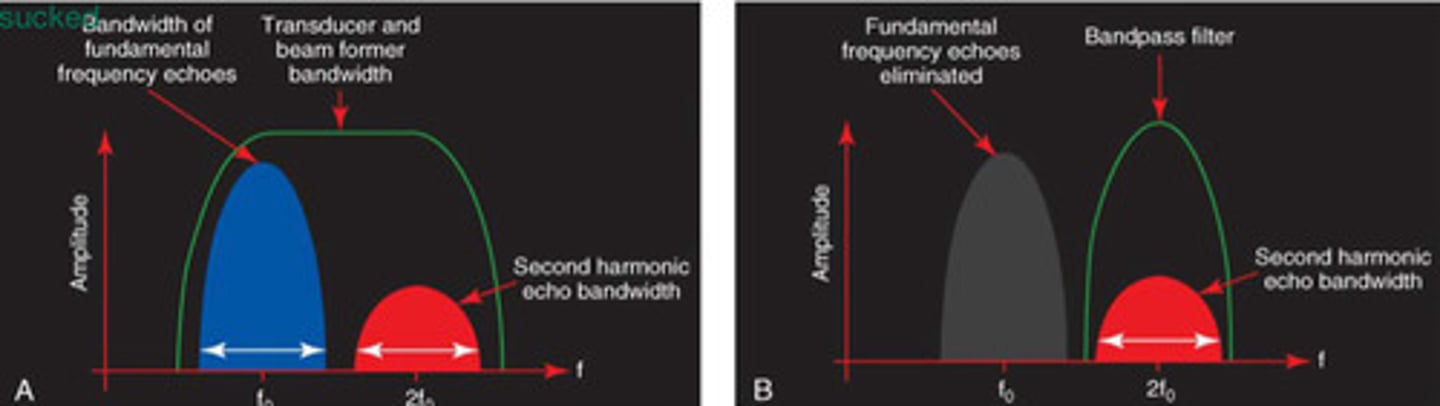
Axial resolution is our best resolution so Bandpass filtering would actually make the image worse bc decreasing axial resolution
Why is having a narrower bandwidth so bad
If we want to first 2 and get back 4, the 2 and 4 would have to fit in the bandwidth without overlapping
Explain the bandwidth requirements using a C6-2 transducer
More absorption and scatter
Increase in frequency =
Turn down the frequency of harmonics to get better penetration instead of turning it off so you still have the benefits of harmonics
Instead of turning harmonics completely off when you want more penetration, what is an adjustment that you can make
Pulse inversion
How can we maintain the axial resolution while still getting the benefits of harmonics (less reverb, improving lateral resolution, get ride of main bang and grating lobes)
A technique that can filter out the fundamental and leave only the harmonic signal while maintaining a wide bandwidth
Explain what pulse inversion is
A pulse is sent out followed by the inverse of that pulse
Describe in laymen's terms what is happening with pulse inversion
When the first pulse and inverted pulse are added together they will cancel each other out bc they are the SAME (ex/ if you send out 2 you will get 2 back bc fundamental echoes are not dependent on anything)
Describe what happens with pulse inversion on fundamental echoes (why it doesn't work with fundamental frequencies)
Destructive interference
What is it called when the fundamental echoes cancel each other out
Harmonics is NOT LINEAR so we will get back a random number (that is close to double of what we sent out). When these are added together, they will NOT cancel each other out bc they are not the exact same
Explain why pulse inversion works with harmonics
False, we do NOT get destructive interference bc they wont be the same number
T/F: when we apply pulse inversion to harmonics we get total destructive interference
Bc the echoes are slightly out of phase so wont cancel each other
Explain why pulse inversion works with harmonics in laymen's terms
True
T/F: without harmonics, pulse inversion would just cancel the pulses out and there would be no signal
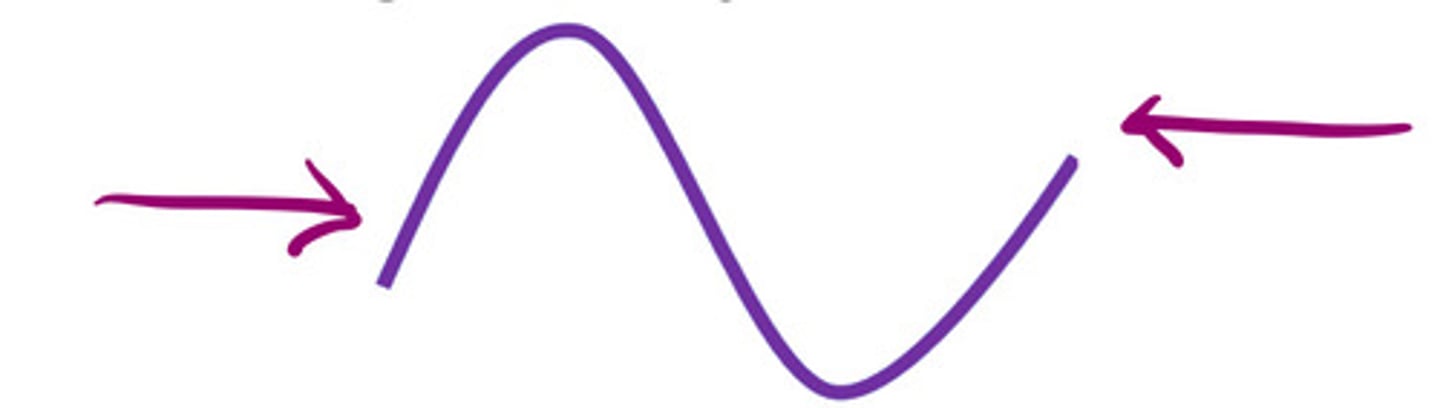
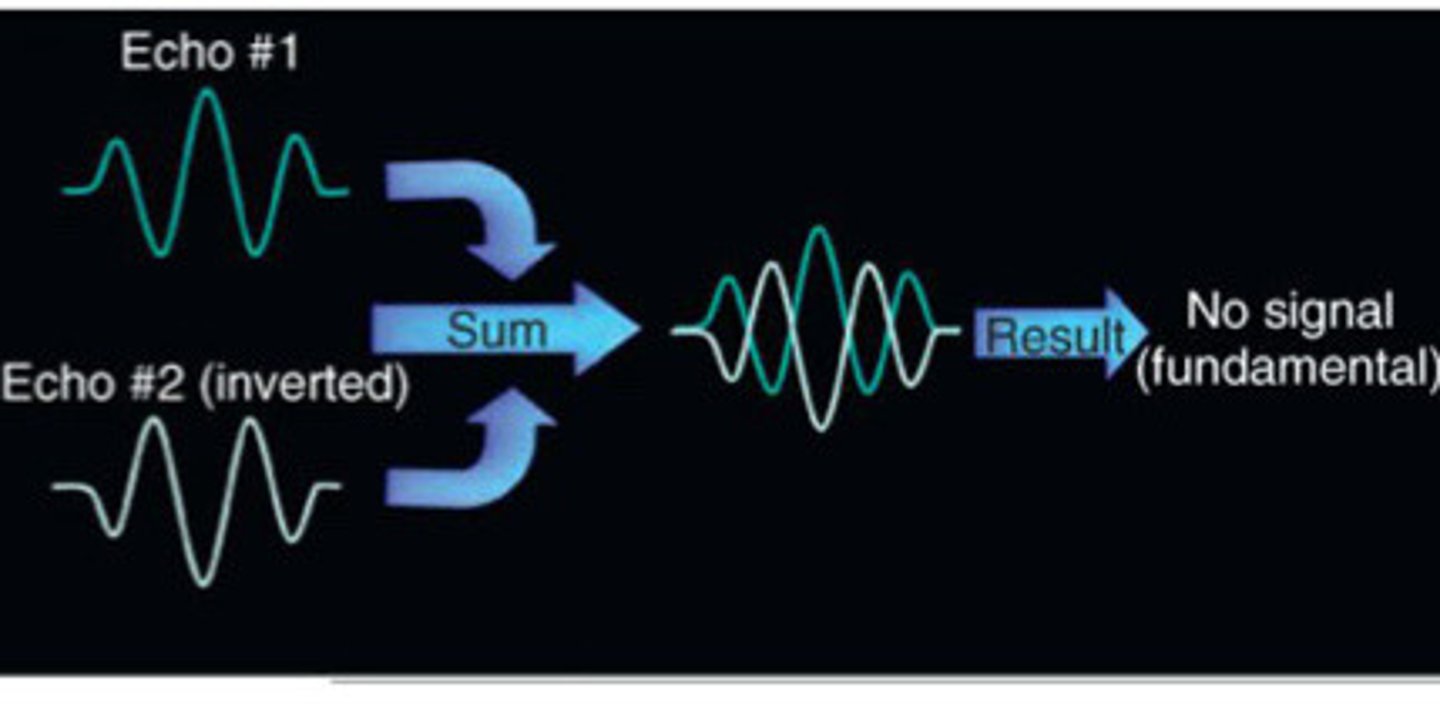
Pulse inversion with fundamental frequency
What does this image represent
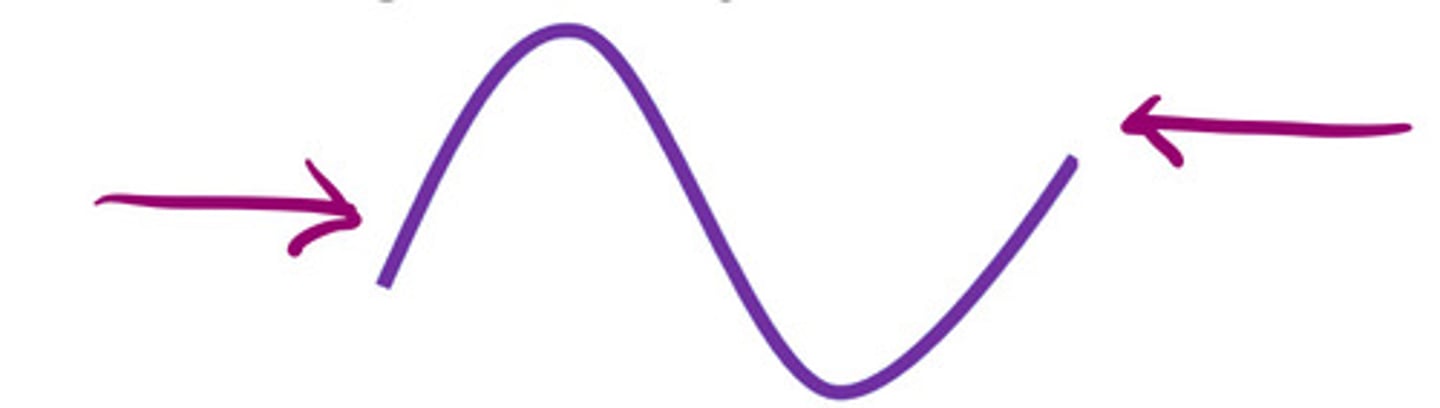
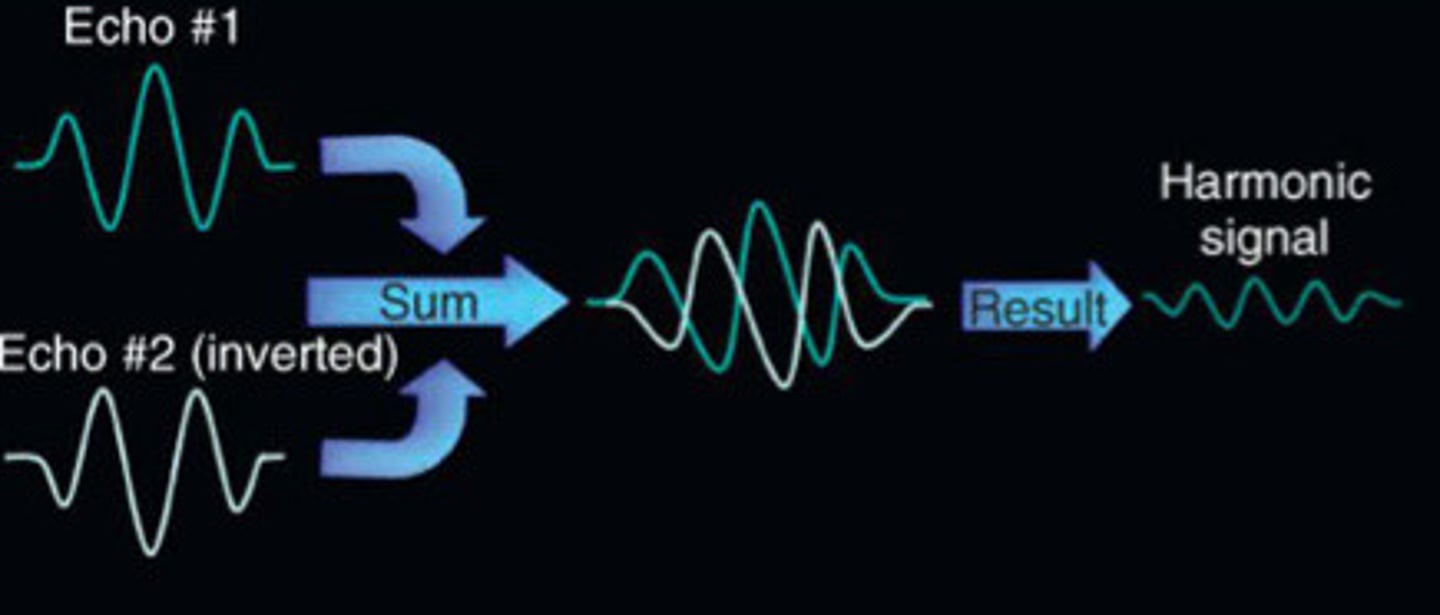
Pulse inversion with harmonics
What does this image represent
Keep pulse short, gets all the benefits of harmonics, while not sacrificing the axial resolution
What is the benefits of pulse inversion
Decreases temporal resolution
What is the disadvantage of pulse inversion
Bc now we have to send out 2 pulse in order to inverse and add them together
Why does pulse inversion decrease the temporal resolution
Yes!! The little bit of decrease of temporal resolution is worth the better resolution we get from harmonics
Is pulse inversion still worth it even though it decreases the temporal resolution
Harmonics
What is define by the decrease in the distance between peak refractable pressures
Harmonics
The distance between peak refractional pressures=