Bio 006 - 8LB : Plant Organs: Leaves, Stems, Roots
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Calvin Cycle
A series of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis where CO2 is converted into G3P.
stroma
Location of Calvin Cycle
Carbon Fixation
The process where Rubisco puts CO2 together with RuBP to form 3-phosphoglycerate.
Rubisco
An enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin Cycle.
3-phosphoglycerate
The product formed from the fixation of CO2 with RuBP.
C3 Plants
Plants that undergo typical photosynthesis, examples include rice, wheat, and soybeans.
Stomata
Open during the day and closed at night for gas exchange.
__________ in C3 Plants
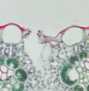
Guard Cells
Cells that control the opening and closing of stomata.
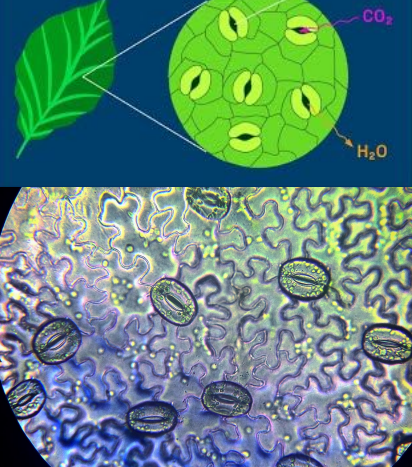
CAM Plants
Plants adapted to dry conditions, such as cacti and pineapples, that open stomata at night.
Stomata are closed during the day to prevent water loss
Conservation water
C4 Plants
Plants adapted to hot regions with intense sunlight, examples include grasses and corn.
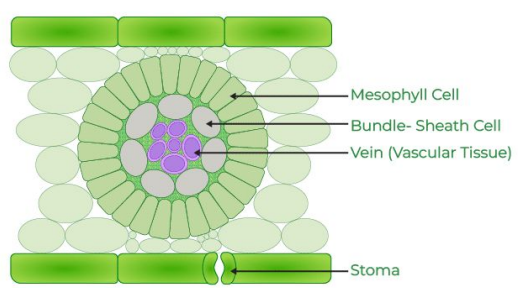
Stomata
Partially close during the day if sunlight is very intense.
__________ in C4 Plants
Bundle Sheath Cells
Cells in C4 plants that receive the 4-carbon molecule and drop off CO2 for the Calvin Cycle.

Mesophyll Cells
Cells in C4 plants where the initial reaction occurs to form the 4-carbon molecule.
Mesophytic
medium conditions for moisture —→ C3
Xerophytic
survives on very little water (think 'zero water') —→ CAM
Hydrophytic
high water conditions, including growing directly in the water —→ C3/C4
Adaxillary
upper surface of the leaf (top)
Abaxillary
lower surface of the leaf (bottom)
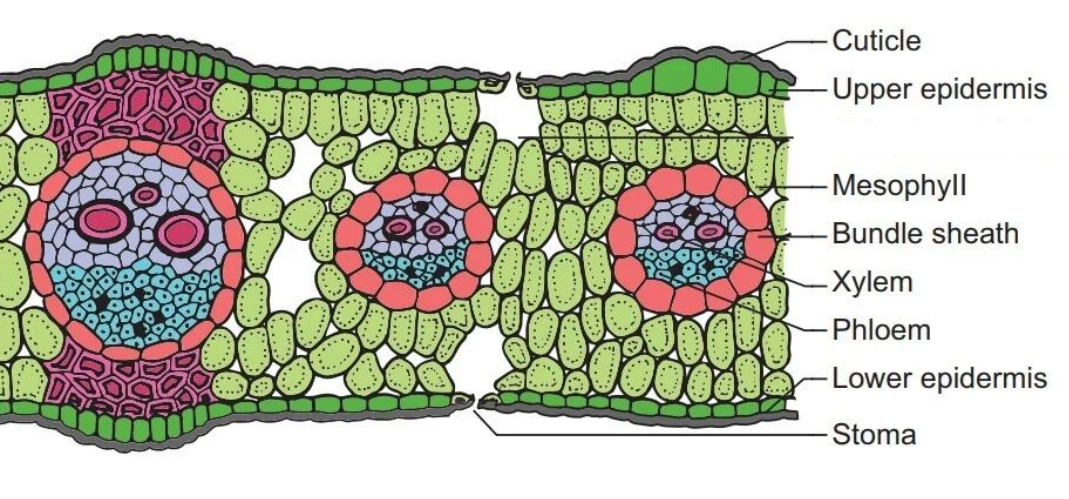
Monocot Leaf
monkey face vascular bundles
spread out all over in stems
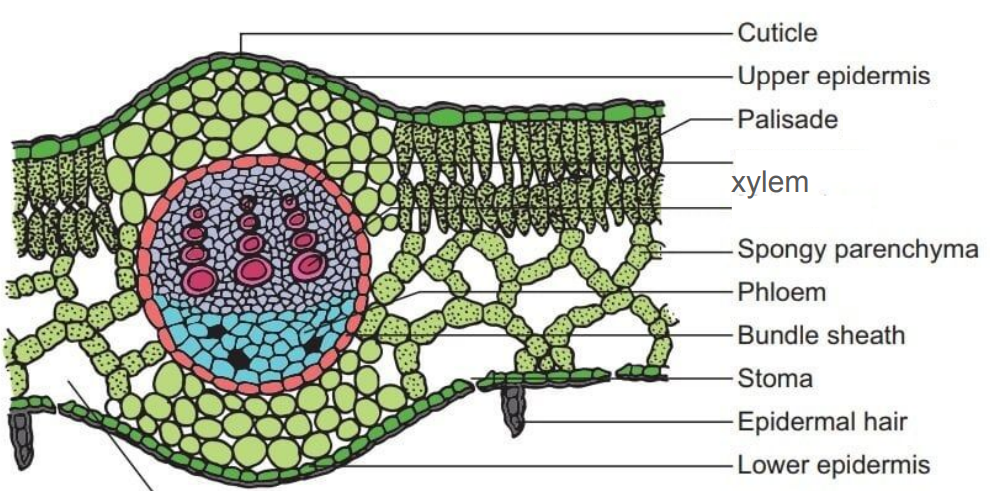
Eudicot Leaf
xylem in parallel lines
candy corn
circle around edge in stems
Lateral Roots
Roots coming off of taproot
Anchor plants
Absorb water/ nutrients
note: Remember —→ Eudicots

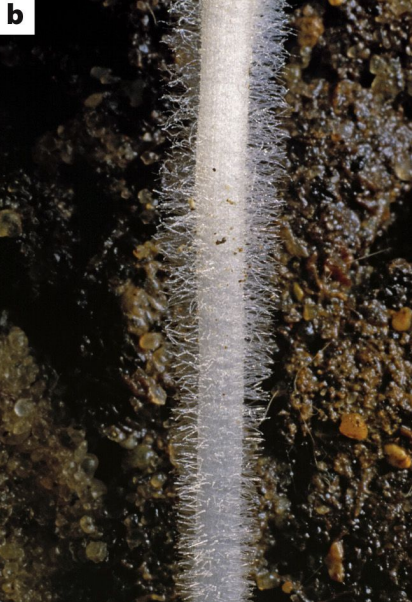
Root hairs
Only 1 cell wide! Found on BOTH taproots and fibrous roots (eudi & mono)
Increase surface area for absorption
Absorb water/ nutrients

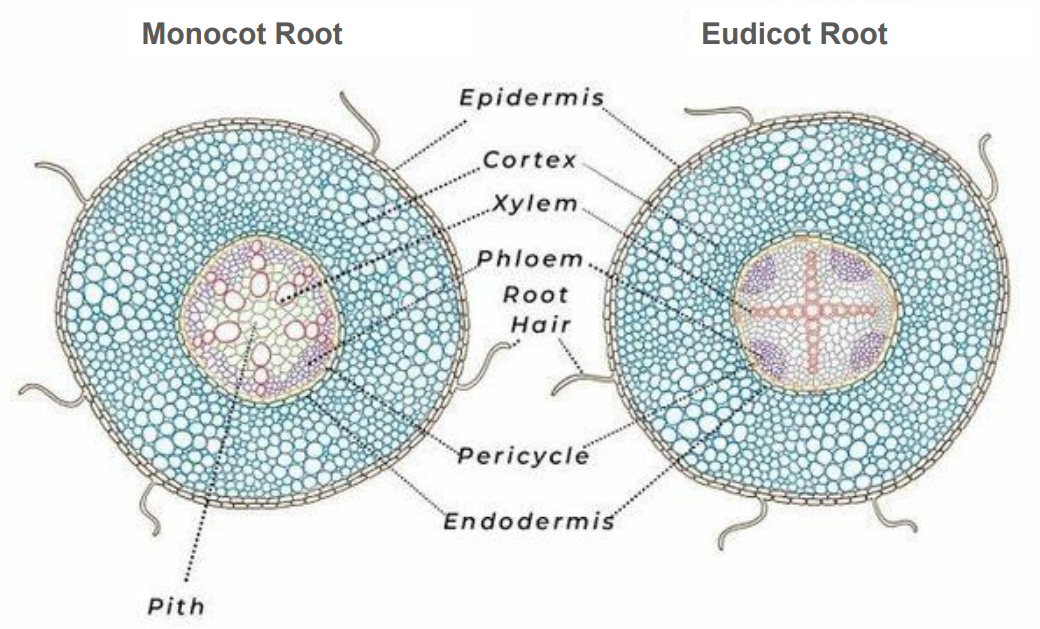
Epidermis
outermost layer, 1 cell thick
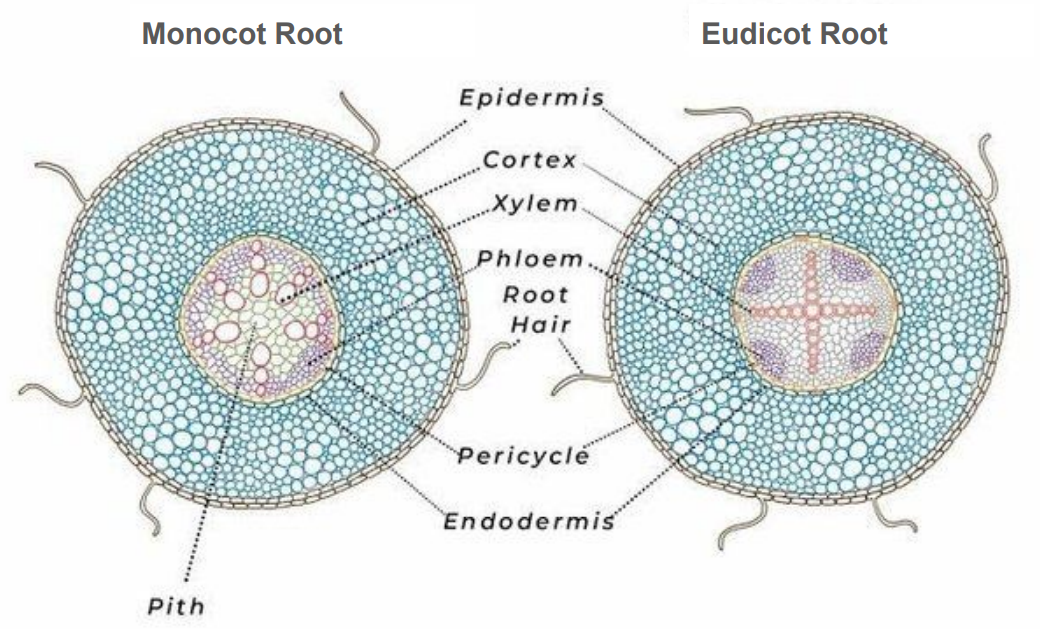
Cortex
Parenchyma, thick layer

Starch grains
Purple dots in cortex
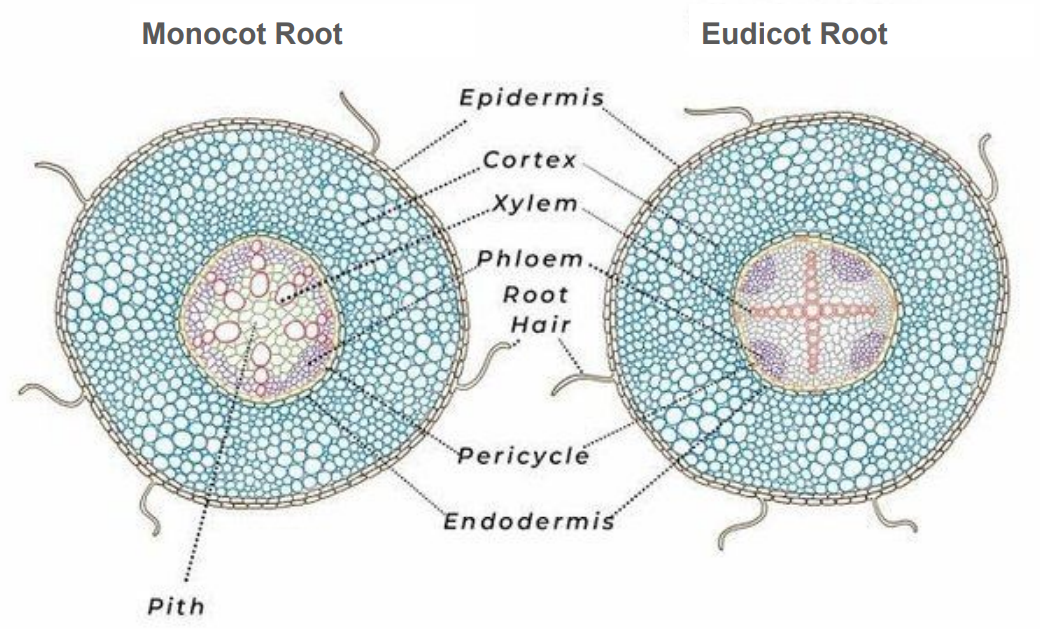
Endodermis
inner layer of cortex

Casparian strip
around endo cells
Vascular cylinder (stele)
central part of the root containing xylem and phloem
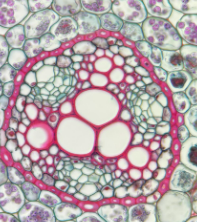
Pericycle
outermost layer of cylinder
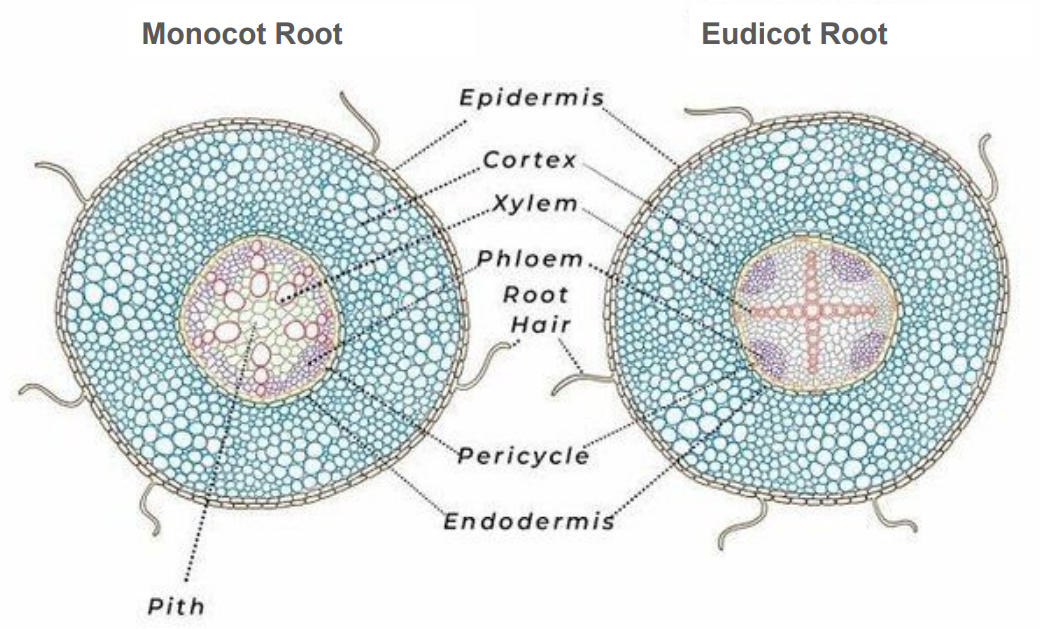
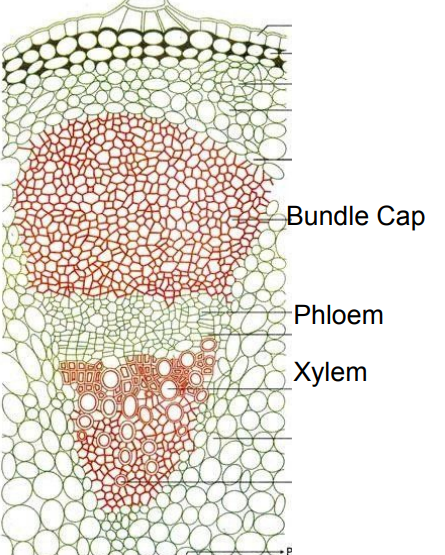
Xylem
circle in monocot root, cross/star in center of eudicot root
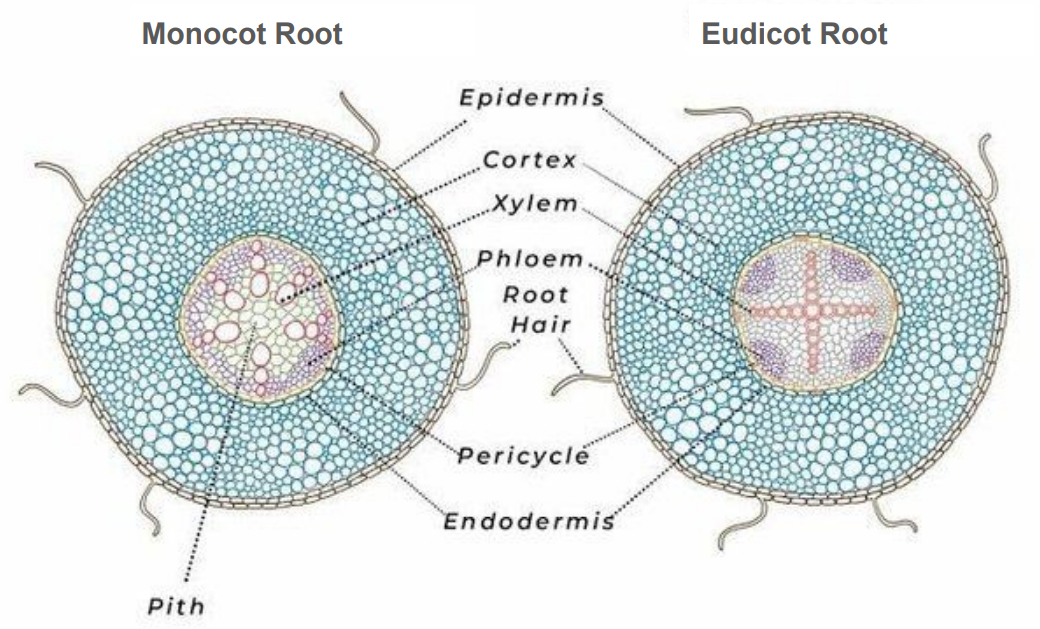
Phloem
lines edges of cylinder in monocot root, in rounded pockets to sides in eudicot root
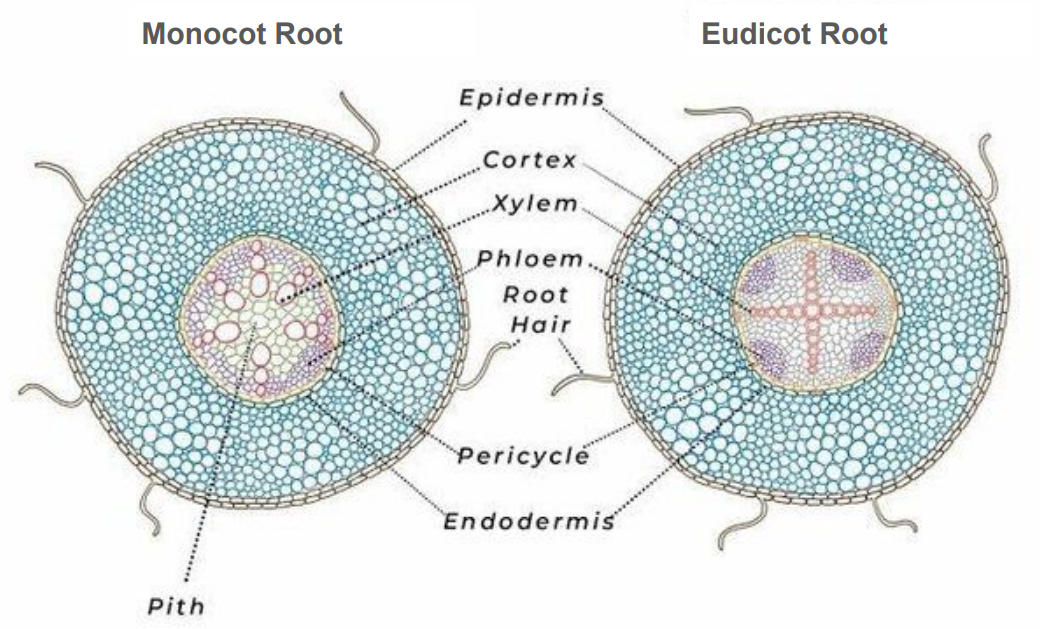
Pith
Parenchyma, very center core in monocot root, absent in eudicot root
Sclerenchyma
type of ground tissue providing support
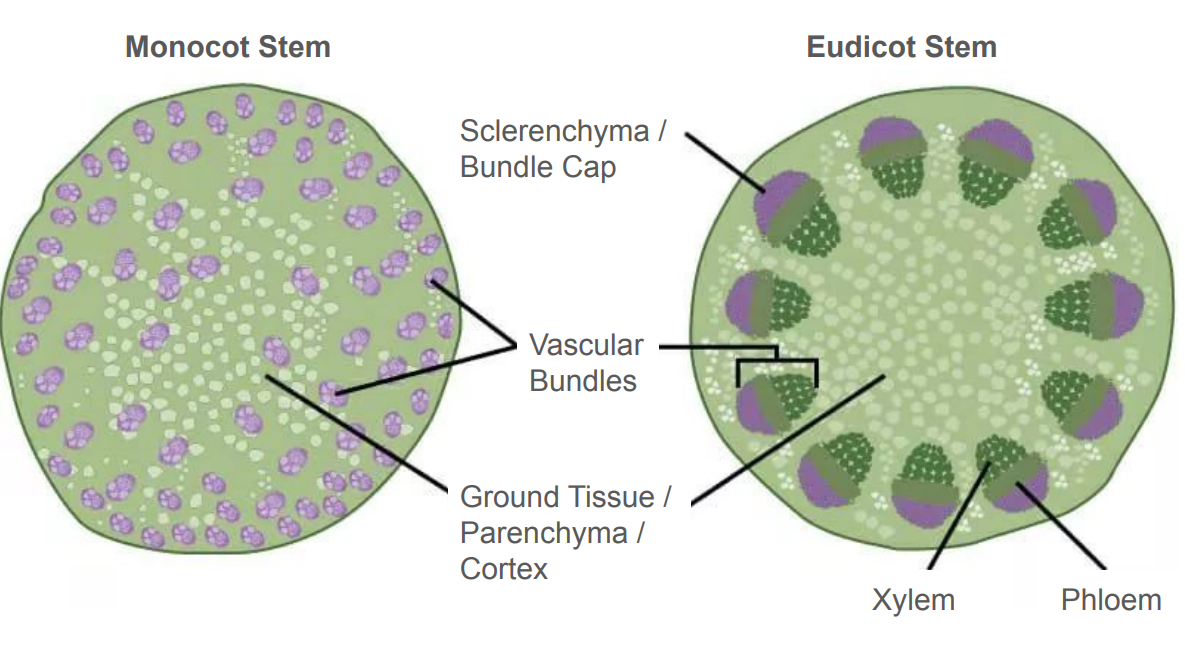
Bundle Cap
Sclerenchyma, top of vascular bundles in eudicot stems
Vascular cambium
circle that splits xylem and phloem in eudicot
Interfascicular cambium
between bundles
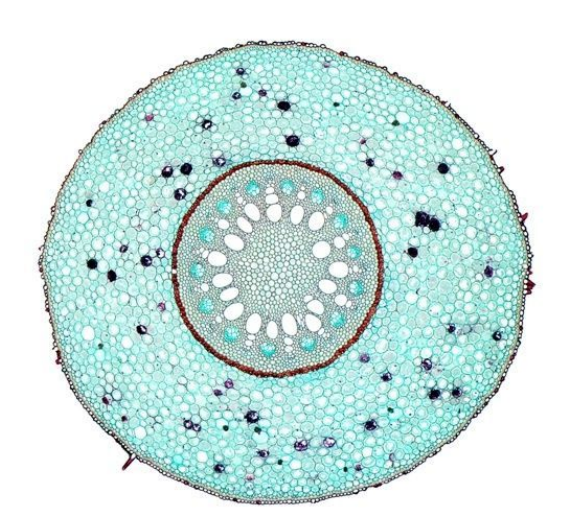
Monocot root
Identify image
Eudicot Root
Identify image
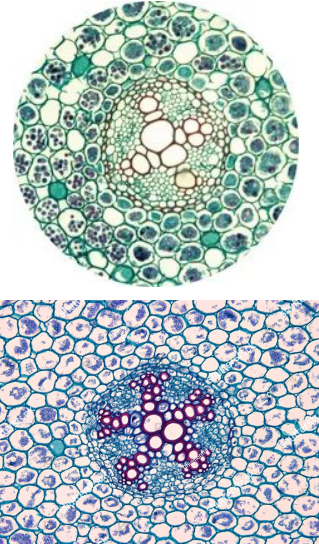
Eudicot Stem
Identify image
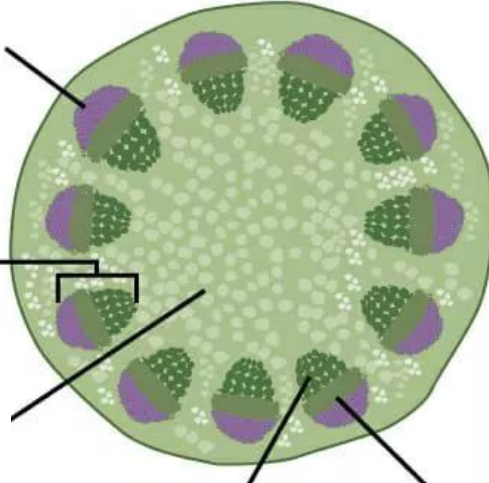
Monocot Vascular Bundle
Identify image (hint: monkey face)
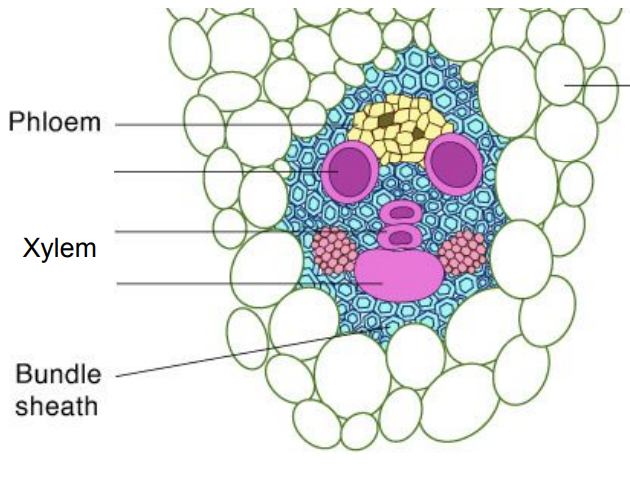
Eudicot Vascular Bundle
Identify image (hint: layered/candy corn)
leaves
flat and skinny
stems
circular, NO “layer”/ring of cortex (only background)
roots
circular, thick ring of cortex
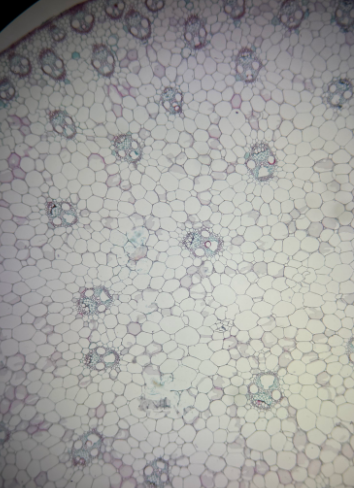
dicot syringa leaf
Identify the image
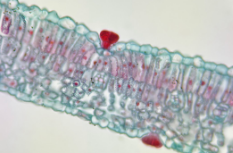
syringa leaf
What part of the leaf is this?
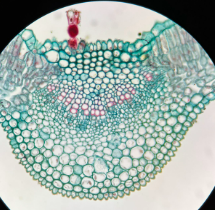
monocot zea mays leaf
Identify the image
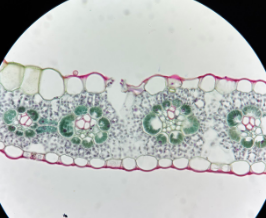
dicot oleander leaf
Identify the image
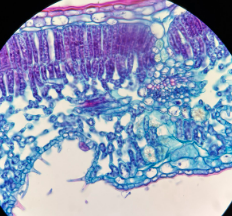
dicot ranunculus root
Identify the image
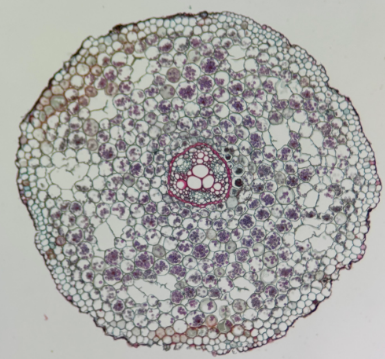
smilax herbacea root
Identify the image
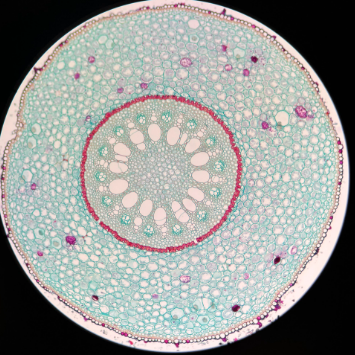
monocot zea mays stem
Identify the image