BCM.01- ATOMS
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Explain how gold leaf experiment was evidence for the nuclear model of the atom
originally, plum pudding model would suggest that alpha particles would only slightly deflect due to randomly placed and diffuse positive charges. In the experiment, some alpha particles bounced back and were deflected a lot. hence shows positive charge is concentrated in middle of atom and that the atom I mainly empty space as most alpha particles went straight through
Describe the atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and know their relative masses and charges
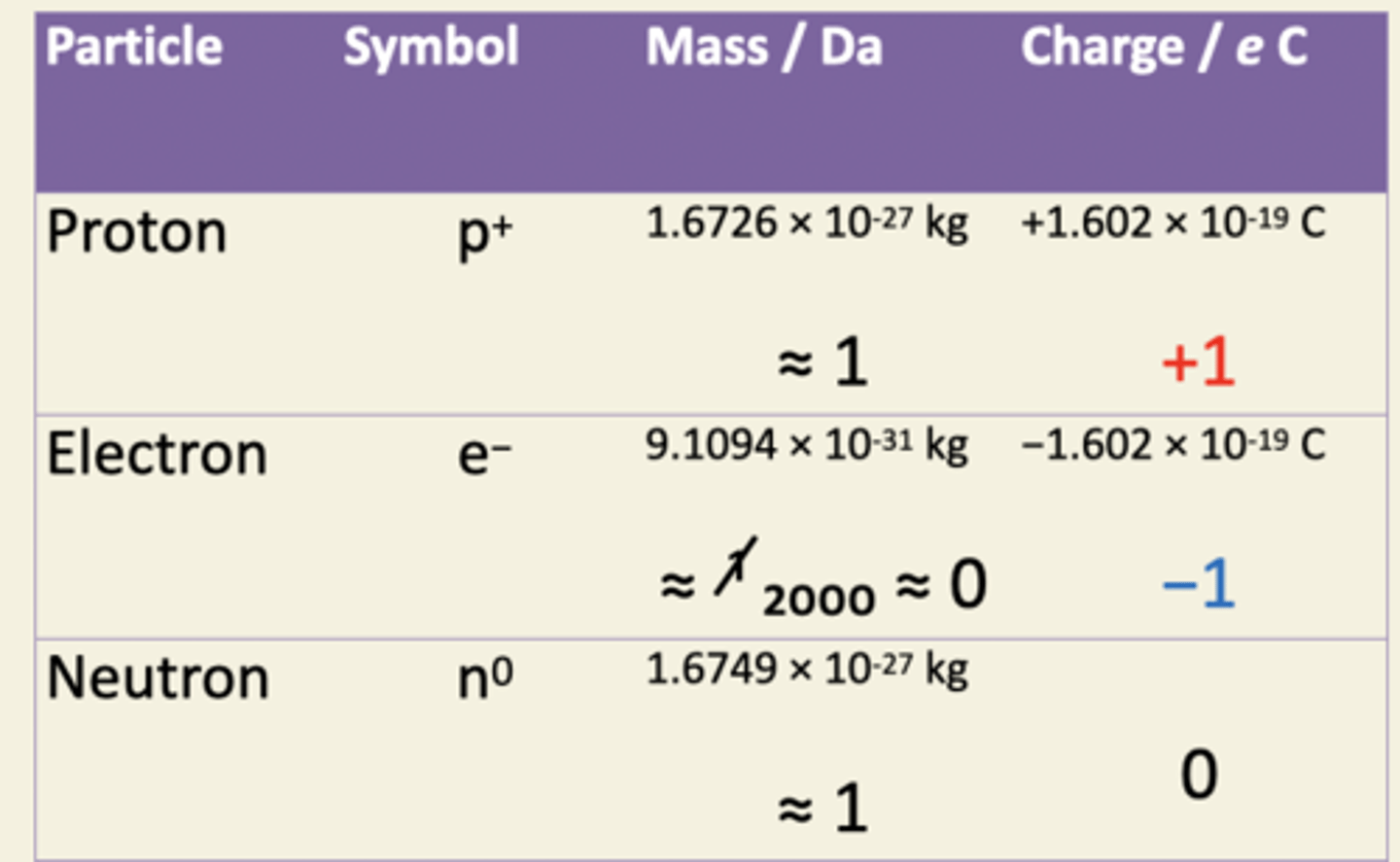
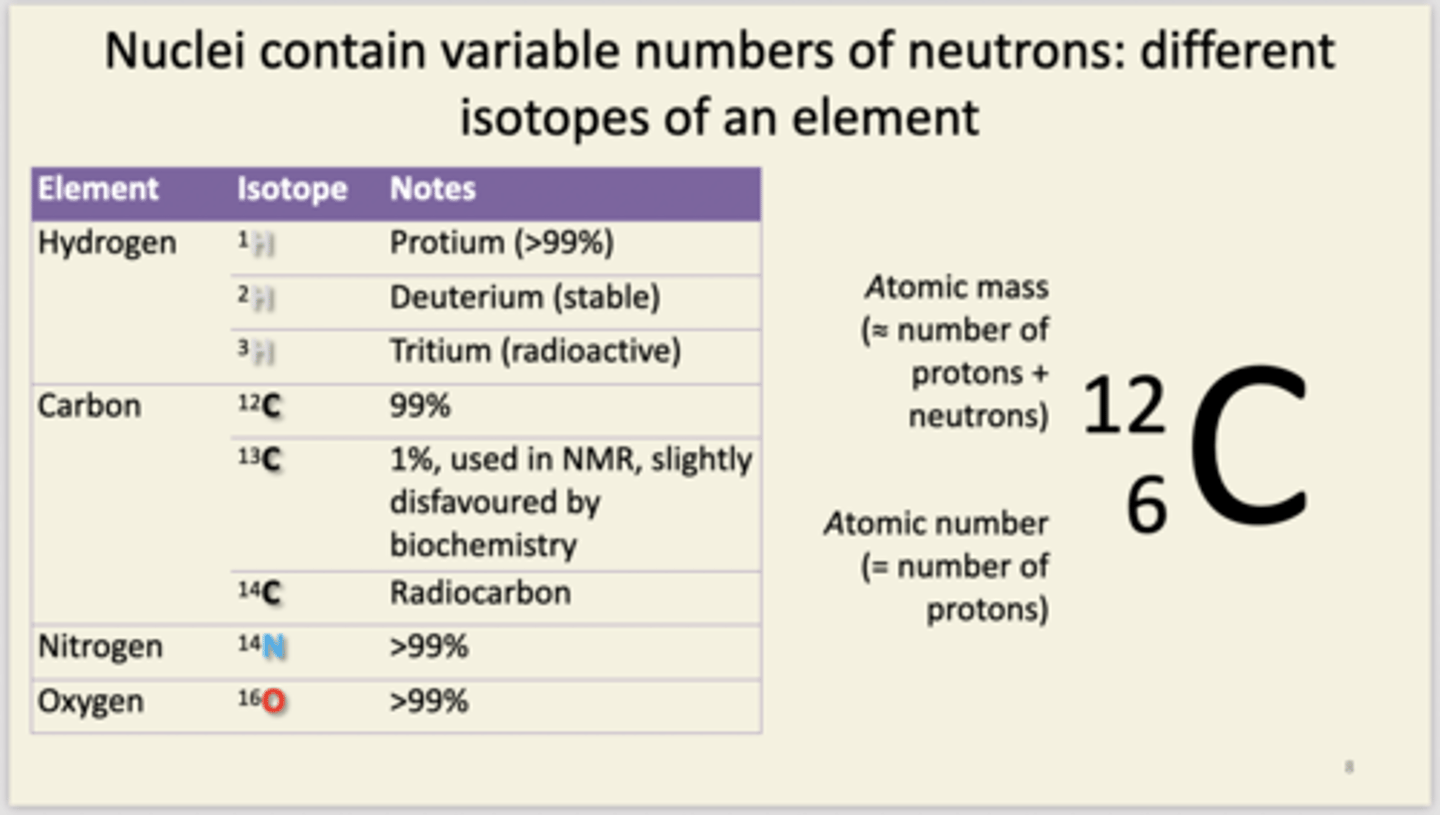
know the atomic numbers and relative masses of H,C,N and O. recall properties of important isotopes( also the other important elements)
Different elements differ by the number of protons in their nucleus. nucleon number = atomic mass. number of protons = atomic number. H = 1,1 C = 6,12 N = 7,14 O = 8,16 S and P are important for biochemicals like protein and nucleic acids. Some alkali metals Na and K and halogens Cl are used for electrolytes.
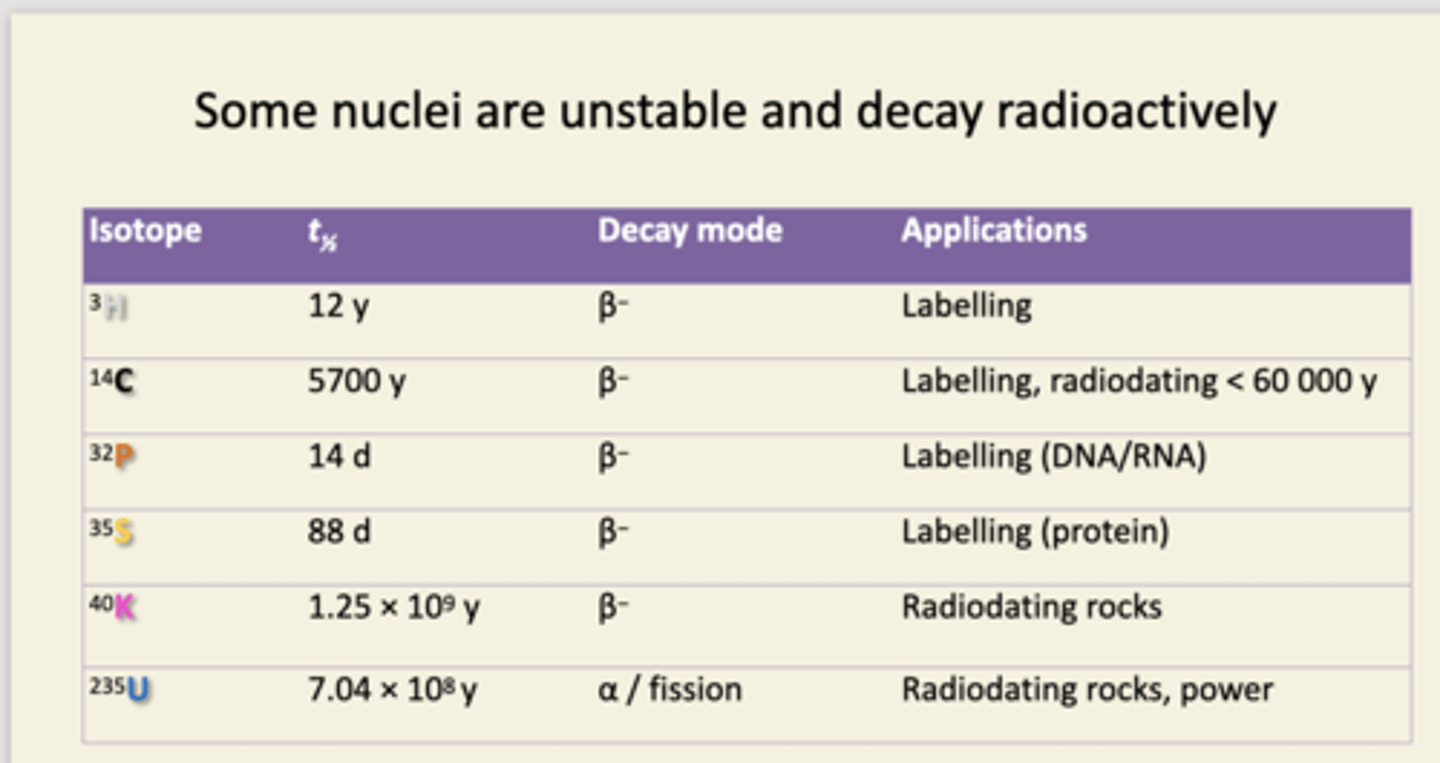
name some important radioisotopes used in biochemistry and their applications
The first 4 isotopes were used for radioactively labelling biochemicals. safer options now. Fluorescent tags track larger molecules as they move through cells.
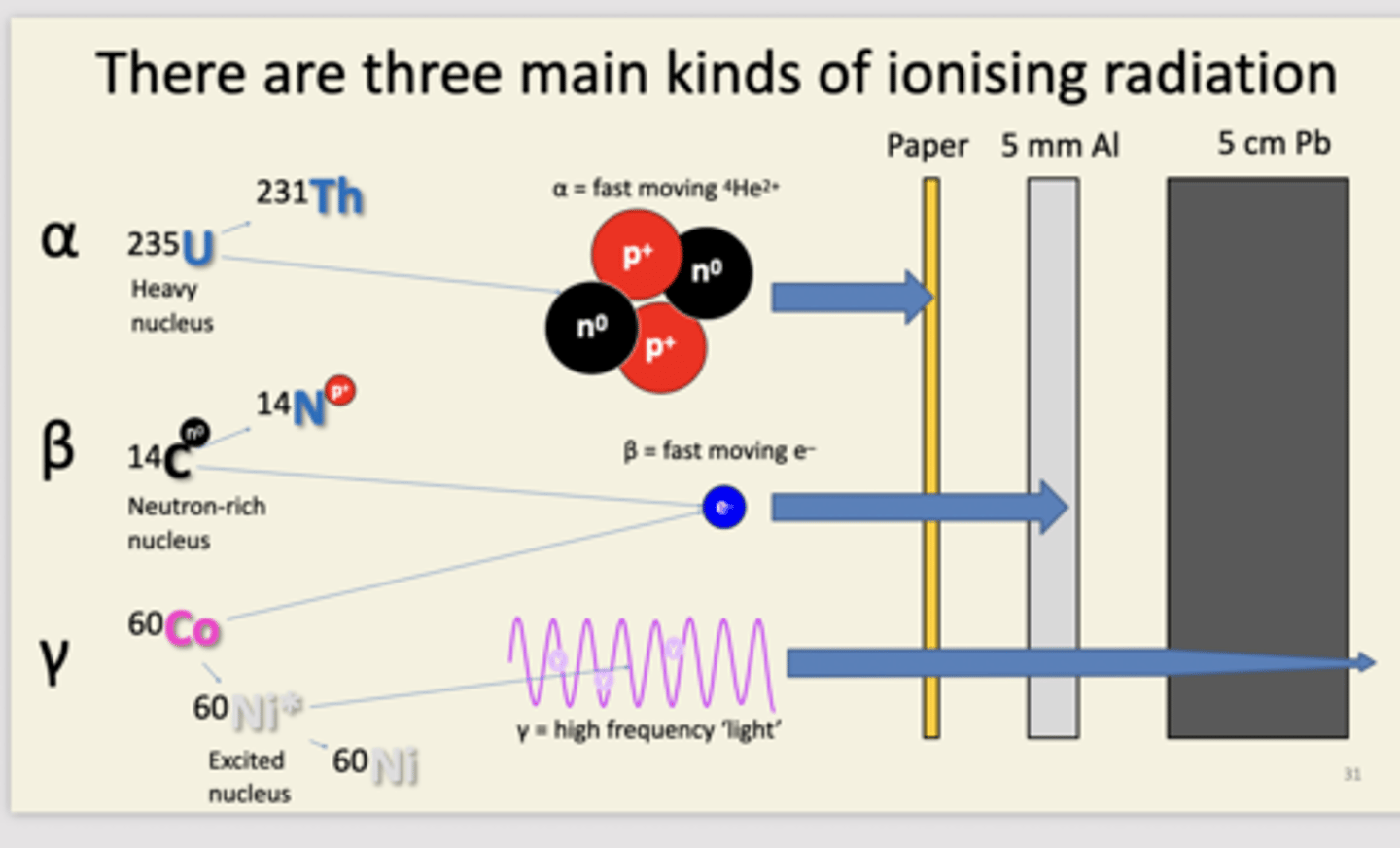
name the three types of radioactive decay
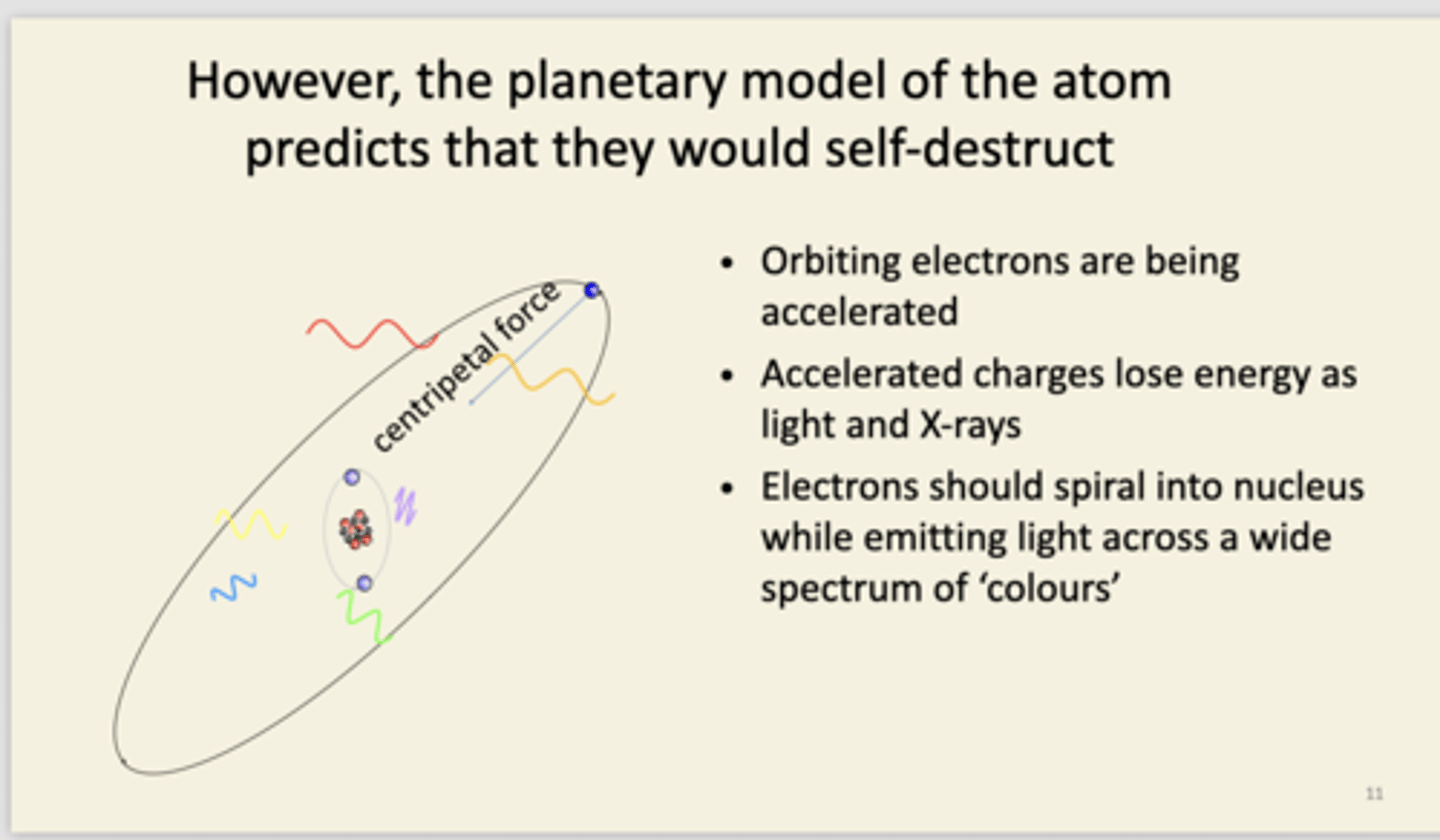
explain the planetary model and its limitations
small central nucleus with electrons orbiting. it is misleading. number of electrons = number of protons. Limitations are seen in diagram. shows the planetary model is unstable and that atoms shouldn't exist. Nothing in planetary model to stop an electron from being at any distance away from nucleus. As there are no orbit constraints, excited atoms should emit light across wide portions of the spectrum and not discrete lines we see. No constraints on the orbit means now constraints on the lowest energy - into centre of nucleus
Use molar mass to convert between masses and amounts (moles), and be able to determine molar mass from a chemical formula

what is the van Der Waals radius
The van der Waals radius is the radius of an imaginary ‘hard’ sphere of electron orbits around an atom’s nucleus. The closest that two atoms can approach each other is the sum of their van der Waals radii.
what is the dilution equation
C1V1=C2V2 amount taken from stock = amount in working solution