Chapter 18: Amino Acids
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are the principle classes of Biomolecules?
proteins, carbs, lipids, and nucleic acids
What are the building blocks of proteins?
amino acids
What functional groups are characteristic of an a-amino acid?
-NH2 amino, -COOH carboxylic acid, -R side chain
Which type of -R side chains are hydrophilic?
basic, acidic, and polar
Which a-amino acid is achiral?
glycine
Which type of -R chains are hydrophobic?
nonpolar
What kind of reaction can take place within an amino acid?
acid-base
Which part of an uncharged amino acid is acidic?
-COOH group
Which part of an uncharged amino acid is basic?
-NH2 group
What is the name for the resulting molecule of an amino acid which undergoes an acid-base reaction?
dipolar ion
What happens to the -COOH group of an amino acid after an acid-base reaction?
loses an H+ ion to become -COO-
What happens to the -NH2 group of an amino acid after an acid-base reaction?
gains an H+ ion to become -NH3+
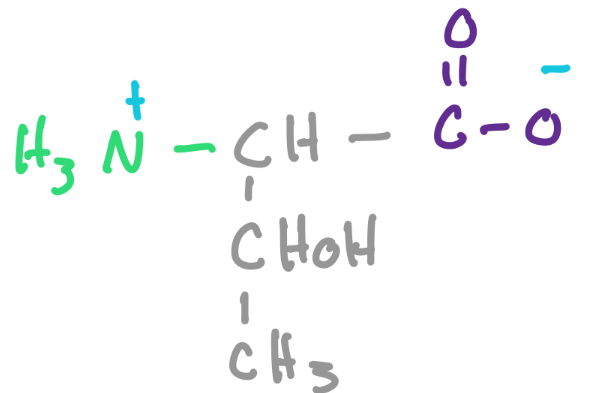
What is the name of an amino acid with dipolar ions which cancel out to a neutral charge?
zwitterion
What does a zwitterion do in an Acidic solution (low pH)?
-COO- accepts a proton
What does a zwitterion do in a Basic solution (high pH)?
-NH3+ loses a proton
What part of a zwitterion is basic?
-COO- group
What part of a zwitterion is acidic?
-NH3+ group
How do multiple amino acids link togehter?
peptide bonds
How does a peptide bond form?
-NH2 amino group of one amino acid bonds to the -COOH of another amino acid
What other molecule forms from a peptide formation?
H2O
What are the original amino acids in a peptide chain called?
residues
Which residue gets named first for in a peptide?
N-terminal amino residue
Which residue gets named second in a peptide?
C-terminal residue
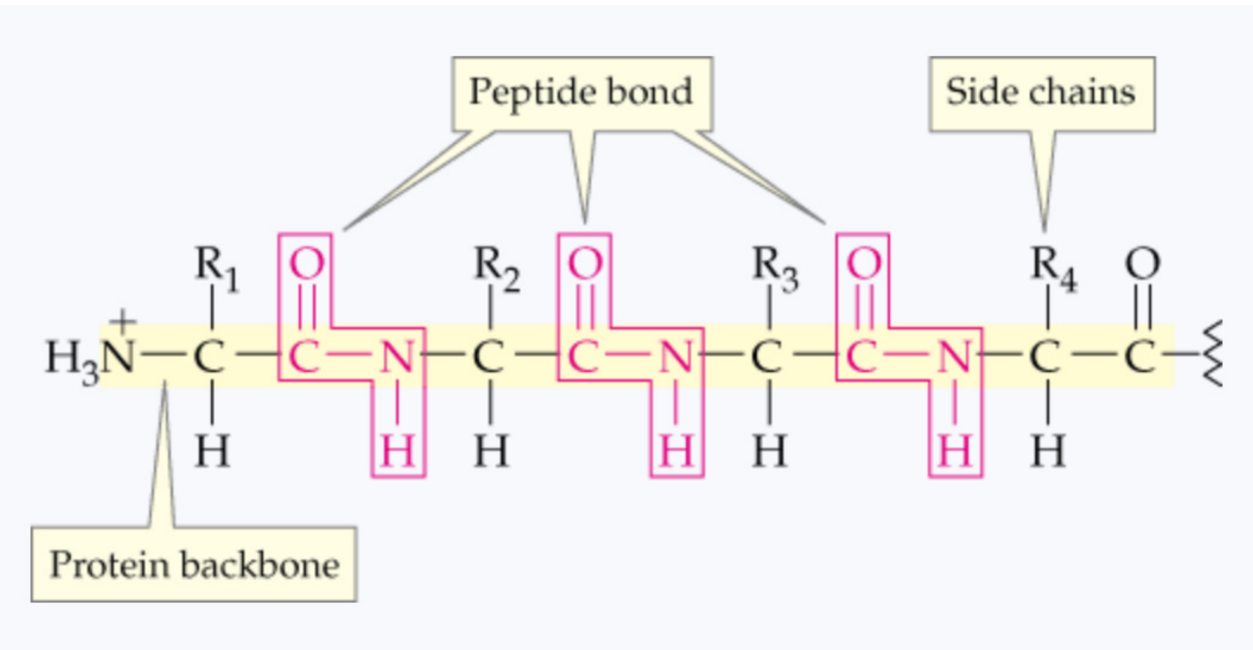
What forms the backbone of a primary protein structure?
alternating peptide bonds and alpha carbons
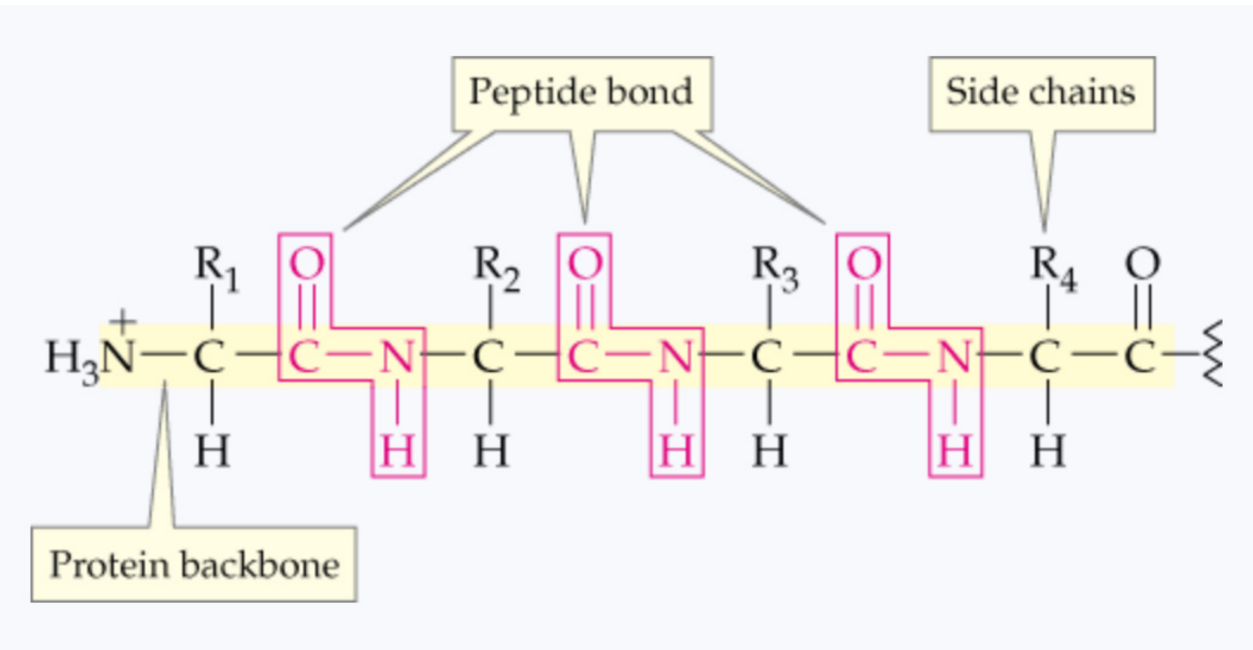
What is a linear line of amino acids connected with peptides called?
primary protein structure
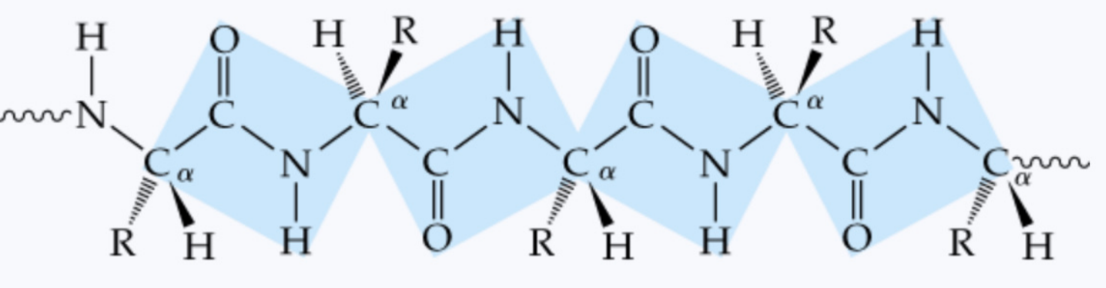
What are the flat, rigid blocks containing Cα–C(=O)–N–H–Cα in a protein chain?
planar units
How many atoms does a planar unit contain?
6
What does a proteins function depend on?
order of amino acids
How to find the number of arrangements of a certain number of amino acids?
=n!
What two forms do secondary protein structures take?
a-helix and B-sheet
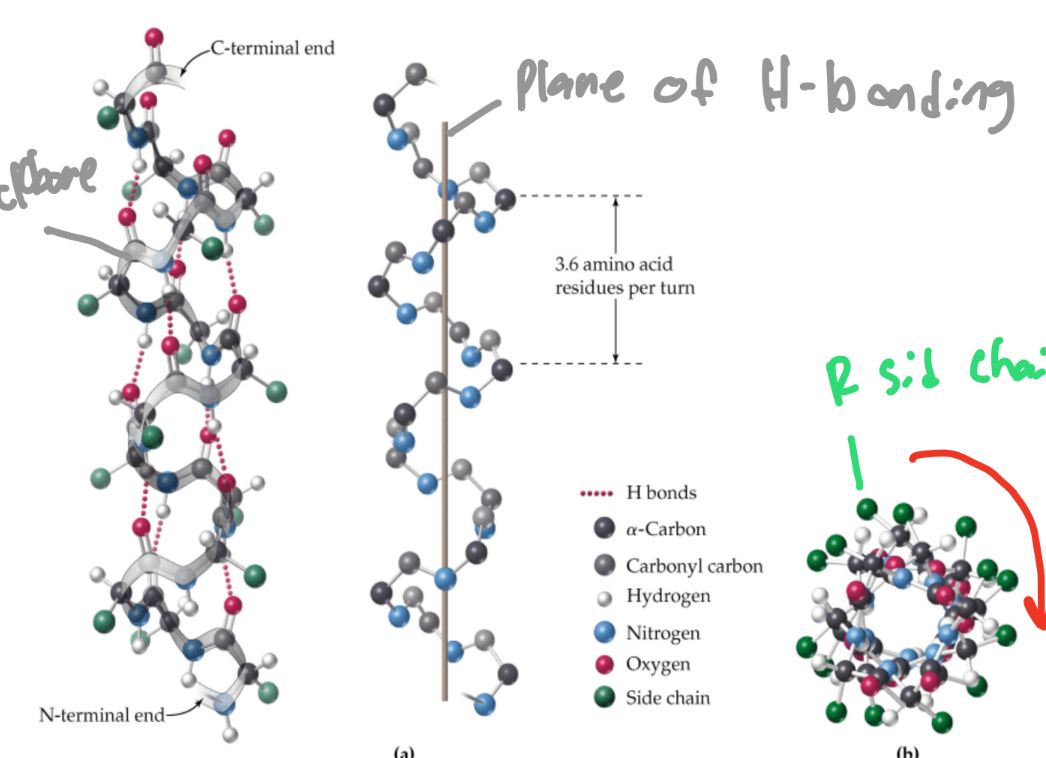
What is a single protein chain coiled clockwise by many hydrogen bonds?
a-helix
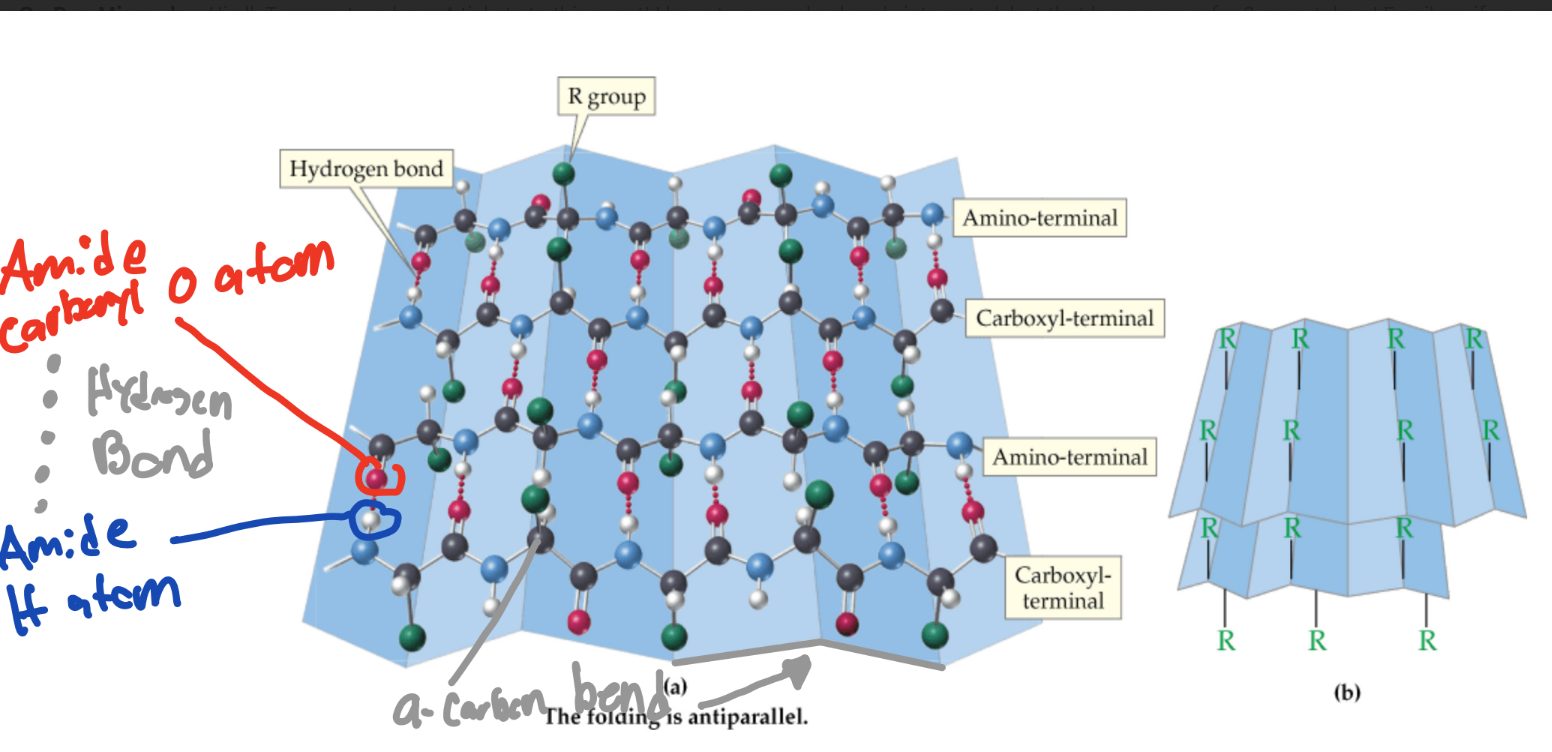
What are multiple straight neighboring protein chains hydrogen bonded together called?
B-sheet
What atoms bond together to make B-sheets?
amide carbonyl O atoms and amide amino H atoms
Which type of protein are secondary protein structures responsible for?
fibrous proteins
The sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds in the polypeptide chain; for example, Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr
primary protein structure
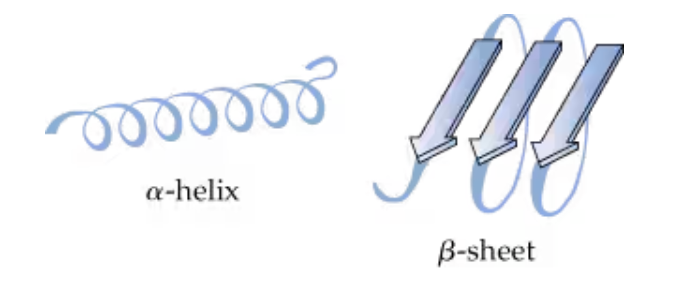
The arrangement in space of the polypeptide chain, which includes the regular patterns of the α-helix and the β-sheet formations
secondary protein structure
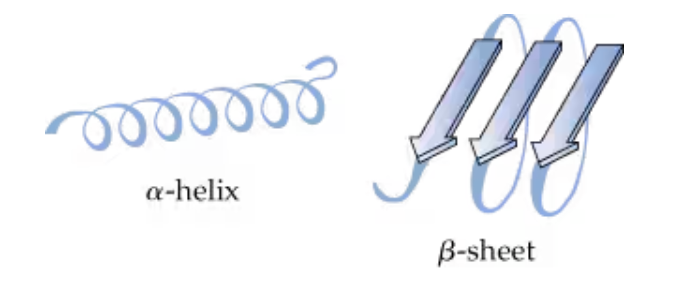
What forces hold a secondary protein structure together?
hydrogen bonds between backbone acid residues
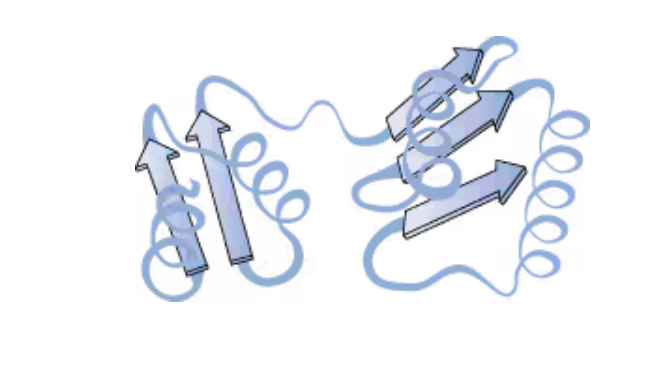
The folding of a single protein chain into a specific three-dimensional shape held together by noncovalent interactions
tertiary protein structures
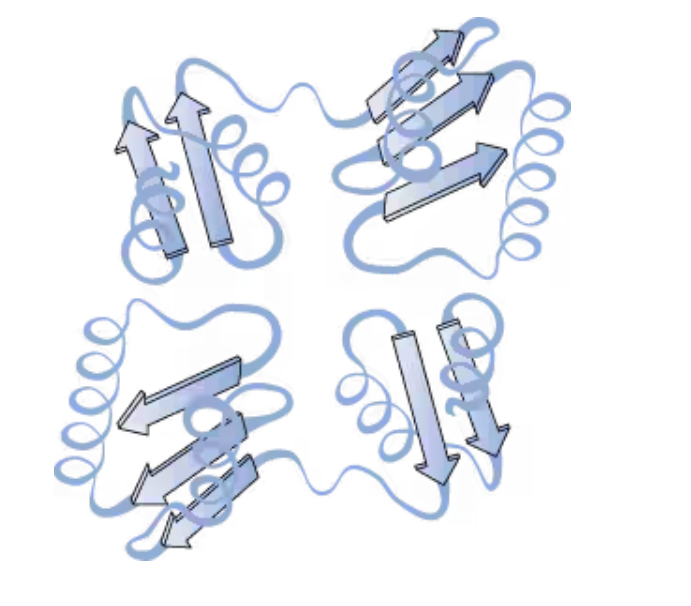
Two or more protein chains assembled in a larger three-dimensional structure held together by noncovalent interactions
quaternary structure
Which class of proteins are tough, insoluble, and composed of fibers and sheets?
fibrous proteins
Which class of proteins are water-soluble and have chains folded into compact shapes
globular proteins
Which class of proteins only contain amino acid residues?
simple proteins
Which class of proteins include one or more non–amino acid units?
conjugated proteins
Which class of proteins are the functional shape (secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure) in which it exists naturally in living organisms?
native proteins
Which class of proteins are soluble and move through the body in extracellular fluid such as blood. An example is serum albumin?
mobile proteins
Which class of proteins are soluble and remain inside a cell. An example is hemoglobin?
cellular proteins
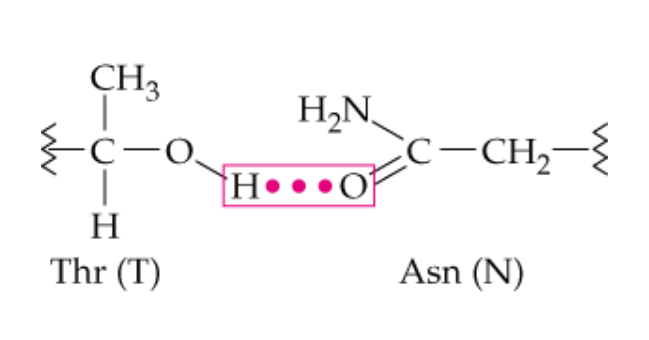
name this noncovalent side chain interaction
hydrogen bonding
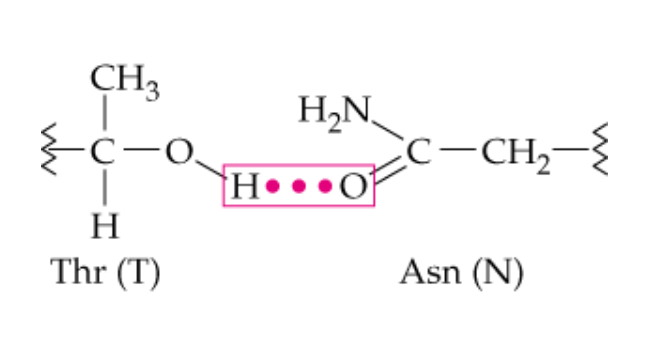
What type of side chains can hydrogen bond with each ohter?
polar -R chains
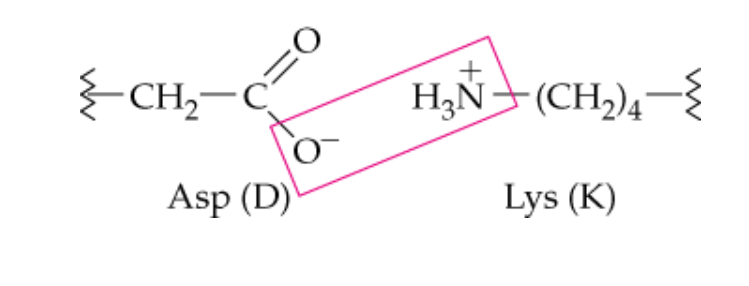
name this noncovalent side chain interaction
ionic attraction (salt bridges)
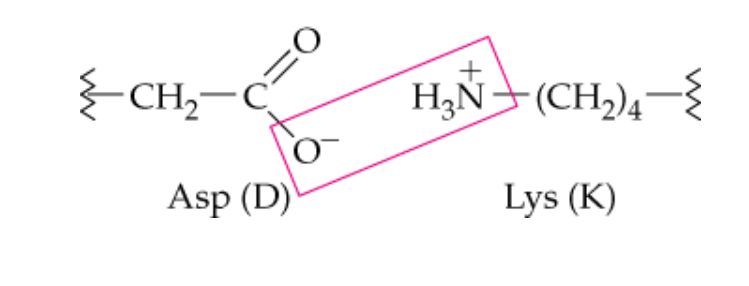
What type of side chains are involved in ionic attraction (salt bridges)
ionized acidic and basic -R groups
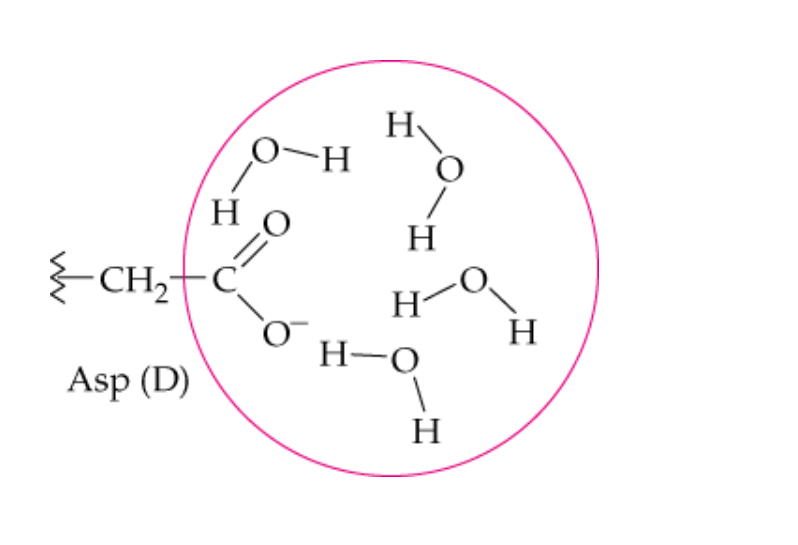
name this noncovalent interaction of a side chain
hydrophilic hydrogen bonding
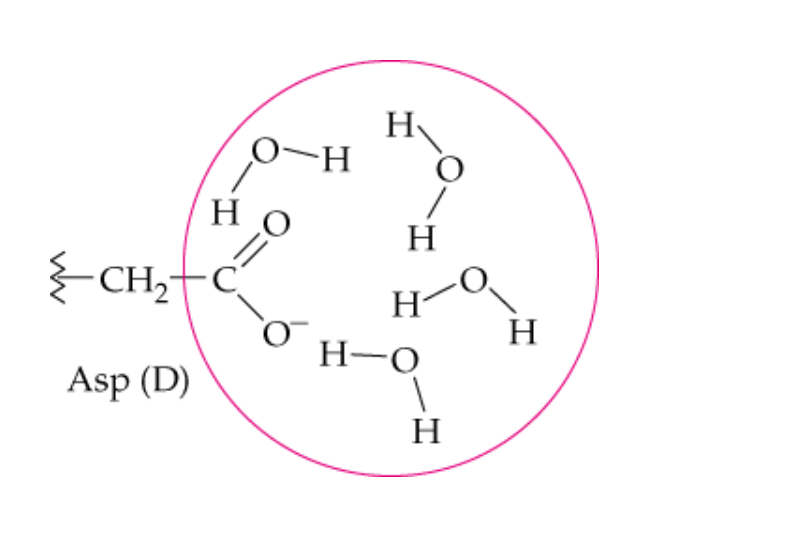
Which side chains will form hydrophilic bonds with water?
polar and charged -R groups
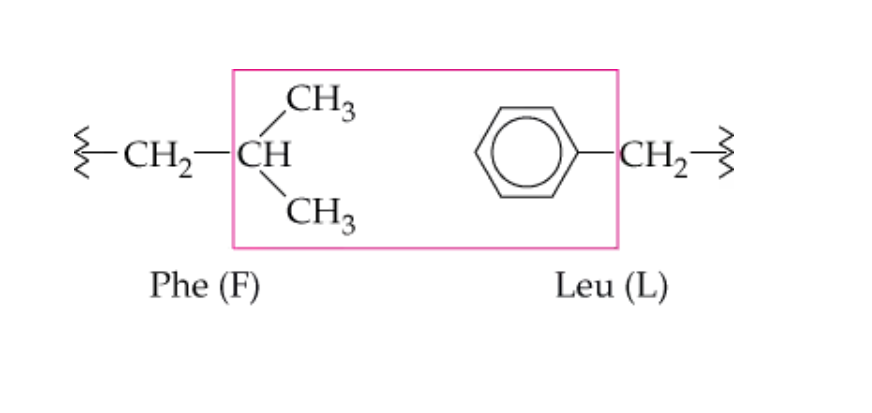
Which side chain perform hydrophobic interactions?
nonpolar/alkyl -R chains
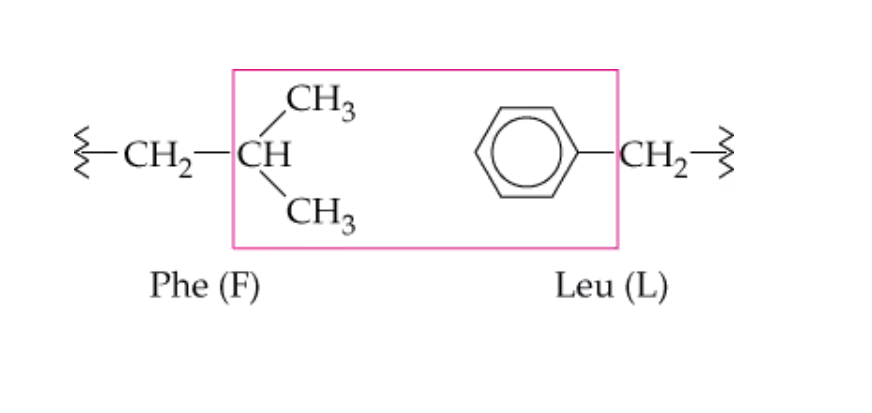
name this noncovalent side chain interaction
hydrophobic interactions
Name the one covalent side chain interaction of amino acid side chains?
disulfide bonding
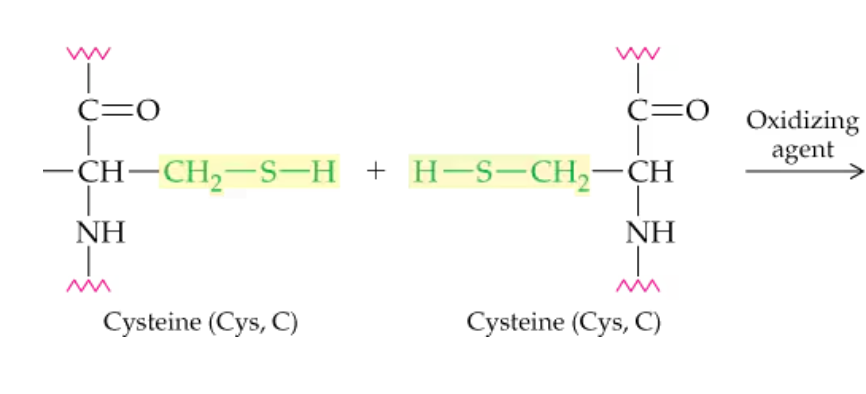
What type of interaction is this?
covalent disulfide bond
What happens when a disulfide bond occurs in the same chain?
creates a loop
What do the 5 amino acid side chain interaction determine
tertiary protein structure
The loss of secondary, tertiary or quaternary protein structure due to disruption of noncovalent interactions and/or disulfide bonds that leaves peptide bonds and primary structure intact
denaturation
How are proteins broken down?
hydrolysis
hydrolyzes a peptide bond on the carboxyl-terminal side of aromatic amino acids
chymotrypsin
hydrolyzes peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of lysine and arginine
trypsin