2.04-2.06 Alternating & Direct Current
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
Power, Current, and Voltage relationship (for power formula)
Power = Current x Voltage
P = I x V
P = I x V
2
New cards
Power, Current, and Voltage relationship (for current formula)
Current = Power / Voltage
I = P / V
I = P / V
3
New cards
Power, Current, and Voltage relationship (for voltage formula)
Voltage = Power / Current
V = P / I
V = P / I
4
New cards
Power is … , current is … , voltage is … Therefore power can also be considered as …
rate of doing work (transferring energy), rate of flow of charge, energy transferred per unit charge passed, rate of energy transferred for charge
5
New cards
Energy transferred, power, and time relationship (for energy formula)
Energy transferred = Power x Time
E = P x t
E = P x t
6
New cards
Energy transferred, power, and time relationship (for power formula)
Power = Energy transferred / Time
P = E / t
P = E / t
7
New cards
Energy transferred, power, and time relationship (for time formula)
Time = Energy transferred / Power
t = E / P
t = E / P
8
New cards
Energy transferred = … , and power = …, therefore we can also say that energy transferred = …
power x time, current x voltage, current x voltage x time (E = I x V x t)
9
New cards
Power
Rate of energy transferred per second; rate of work done.
It’s equal to energy transferred/time or work done/time
It’s equal to energy transferred/time or work done/time
10
New cards
Rate
Something/time
11
New cards
Electrical power of a component/appliance depends on the … and … flowing through it, and is measured in … (…)
current, voltage, Watts, W
12
New cards
1 Watt =
1 Joule/second
1W = 1J/s
1W = 1J/s
13
New cards
Energy transfers involved in a battery
Chemical energy of battery → transferred to electrical energy to the component and surroundings
14
New cards
… is done when … flows through the circuit and is … to the … being transferred
Work, charge, equal, energy
15
New cards
What happens when charge flows through a resistor?
Charge flows through resistor → thermal energy transferred (making it hot) because electrons flowing collide with the lattice of atoms in the metal conductor → provides resistance. Collisions → atoms vibrate more → conductor heats up (used by electrical heaters/ovens/stoves/toasters/ kettlers, etc)
16
New cards
Relationship between energy supplied by battery and energy transferred to all circuit components and why?
Conservation of energy → Energy supplied by battery = Energy transferred to all circuit components
17
New cards
Thermistor
Temperature-dependent resistor.
↑ Temperature → ↓ Resistance
↓ Temperature → ↑ Resistance
Temperature ∝ 1/Resistance (inversely proportional)
↑ Temperature → ↓ Resistance
↓ Temperature → ↑ Resistance
Temperature ∝ 1/Resistance (inversely proportional)
18
New cards
LDR
Light-dependent resistor
↑ Light intensity → ↓ Resistance
↓ Light intensity → ↑ Resistance
Light intensity ∝ 1/Resistance (inversely proportional)
↑ Light intensity → ↓ Resistance
↓ Light intensity → ↑ Resistance
Light intensity ∝ 1/Resistance (inversely proportional)
19
New cards
Diodes
Semiconductor device or electric component that only allows current to flow in 1 direction.
20
New cards
LED
Light-emitting diode, diodes that only light up when current flows through them when placed in the correct direction.
21
New cards
What can lamps and LEDs do in a circuit?
Acts as visual indicator of current flowing in a circuit.
Lighted LED/lamp → Current is present → Circuit working
LED/lamp not lighted → Current is absent → Circuit may be broken
Lighted LED/lamp → Current is present → Circuit working
LED/lamp not lighted → Current is absent → Circuit may be broken
22
New cards
Light-dependent circuit components have … pointing … from their …
arrows, towards, circuit symbol
23
New cards
Light-emitting circuit components have … pointing … from their …
arrows, away, circuit symbol
24
New cards
Fuse
Safety device that cuts off electricity flow if current is too high (can cause electrical fires) due to a fault or surge.
25
New cards
How do fuses work?
Fuses are glass cylinders containing a thin metal wire which heats up and melts if the current is too high → gap in circuit created and current cannot flow anymore → protects circuit/device from damage or preventing a fire. Fuses have different current ratings (e.g. 3A, 5A, 13A, etc.), the rating indicates the current at which or over which the fuse will melt. They should only be slightly higher than the current used by the device in the circuit. To be safe always select a fuse with a current rating that is the next size up (greater than) the circuit current but is as close to the circuit current as possible (e.g. 4A circuit → use 5A fuse, using 13A fuse is useless as fire or damage may occur before 13A is reached to melt the fuse).
26
New cards
Circuit breakers
Electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage due to a current that is too high. They have an automatic electromagnet switch that breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a specific threshold.
27
New cards
Are circuit breakers or fuses better? Why?
Circuit breakers are better than fuses because they can be reset and reused. They’re also faster than a fuse. However, fuses are cheaper than circuit breakers.
28
New cards
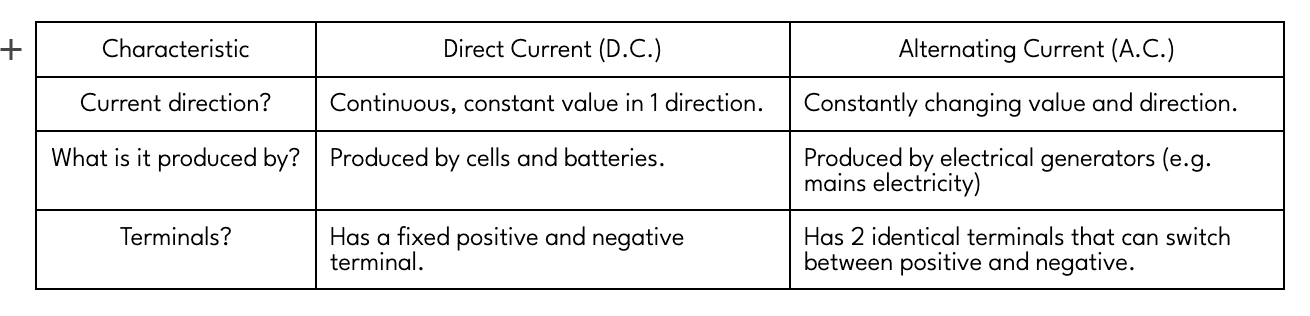
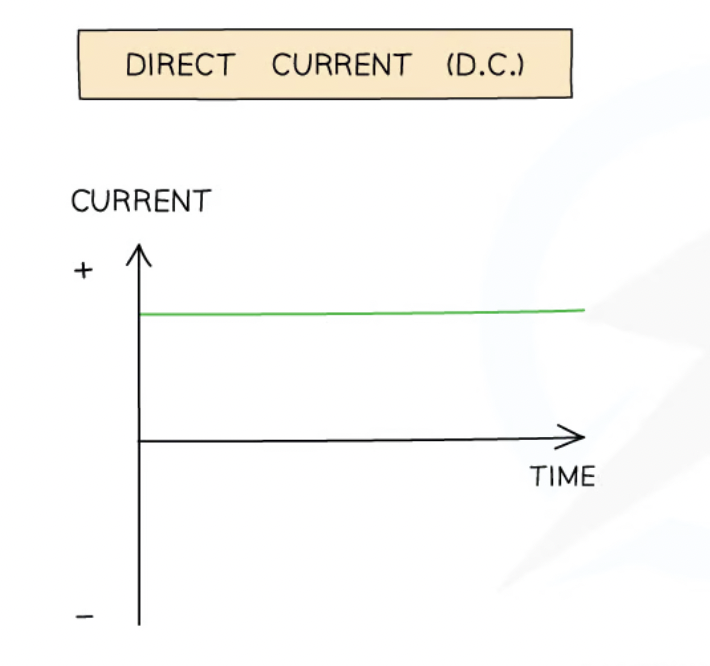
Direct Current (D.C.)
Steady current constantly flowing in the same direction in a circuit from positive to negative, and which has the same value.
D.C. power supplies (e.g. batteries and cells) have fixed positive and negative terminals → voltage (potential difference) across a cell in a D.C. circuit travels in 1 direction only → current is either positive OR negative, only 1 NOT both.
D.C. power supplies (e.g. batteries and cells) have fixed positive and negative terminals → voltage (potential difference) across a cell in a D.C. circuit travels in 1 direction only → current is either positive OR negative, only 1 NOT both.
29
New cards
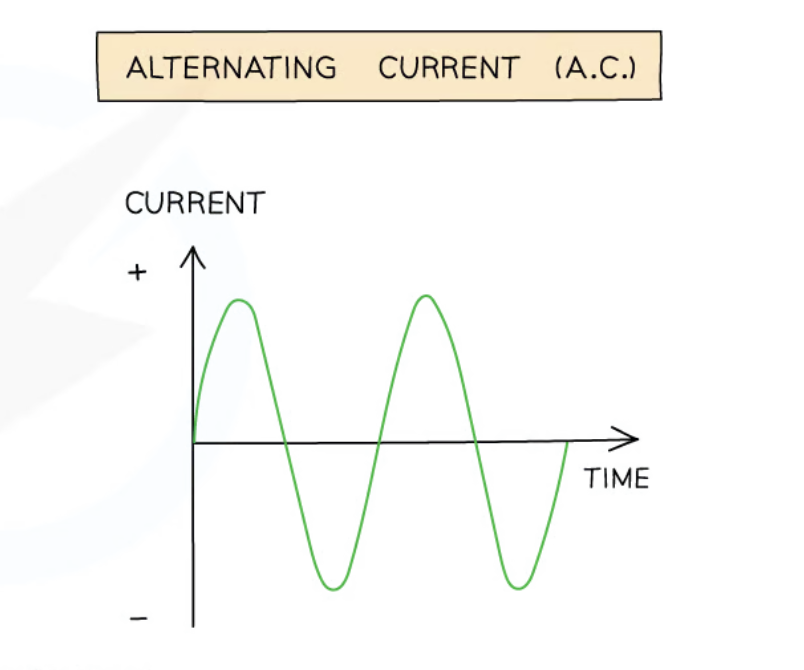
Alternating Current (A.C.)
Current that continuously changes its direction, going back and forth around a circuit, and which can have varying values.
A.C. power supplies (e.g. electrical generators and mains electricity) have 2 identical terminals that switch between positive and negative → current can hence be positive OR negative (can be 1 of both) depending on which direction it’s flowing in at that time.
A.C. power supplies (e.g. electrical generators and mains electricity) have 2 identical terminals that switch between positive and negative → current can hence be positive OR negative (can be 1 of both) depending on which direction it’s flowing in at that time.
30
New cards
Frequency of alternating current is the …
number of times the current changes direction back and forth per second.
31
New cards
What is the approximate frequency and voltage of mains electricity in the UK?
50Hz frequency
230V voltage
230V voltage
32
New cards
Fill in this D.C. vs A.C. comparison table
33
New cards
D.C. graph
34
New cards
A.C. graph