3.8 - Amino acids, Proteins + DNA
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is an Amino Acid?
Molecules with a central Carbon atoms, bonded directly to an amine group, carboxylic acid group, hydrogen atom and changeable “R” group
What 2 properties does the “R” group in an amino acid dictate? (how)
Size → Larger R group increases amino acid size
Polarity → R group can contain atoms that induce different IMFs (Hydrogen bonding, Permanent Dipole-Dipole etc)
How many amino acids does the body use?
Of these how many are essential (non-dietary)
Of these how many are non-essential (dietary)
21:
9 essential
12 non-essential
What type of isomerism do the Amino acids in our body observe?
What is the exception?
Optical Isomerism:
20 amino acids observe Optical isomerism, bar glyceine → since its “R” group is a hydrogen
***NAMING AMINO ACIDS IN CHEM NOTES 1***
***NAMING AMINO ACIDS IN CHEM NOTES 1***
What is a Zwitterion?
A molecule containing both positive (NH3+) and negative (COO-) charged groups of an amino acid, resulting in no overall electrical charge
In what conditions do Zwitterions exist?
Neutral conditions → for example: amino acids in water
What is the trend of Mp + Bp of Zwitterions? (why)
Tend to have High Mp + Bp:
The oppositely charged COO- and NH3+ have a strong attraction to eachother - requiring large amounts of energy to overcome the ionic force
When drawing zwitterions which groups change to their ions?
Rule of THUMB for this
NH2 and COOH groups directly bonded to the central Carbon atoms change to their ions:
R groups that contain amine or carboxyl groups dont change to their ions
Which group changes for the following conditions in an Amino acid:
Acidic conditions
Alkaline conditions
Acidic conditions = COOH group is kept (Amine group is turned ionic)
Alkaline conditions = NH2 group is kept (Carboxyl group is turned ionic)
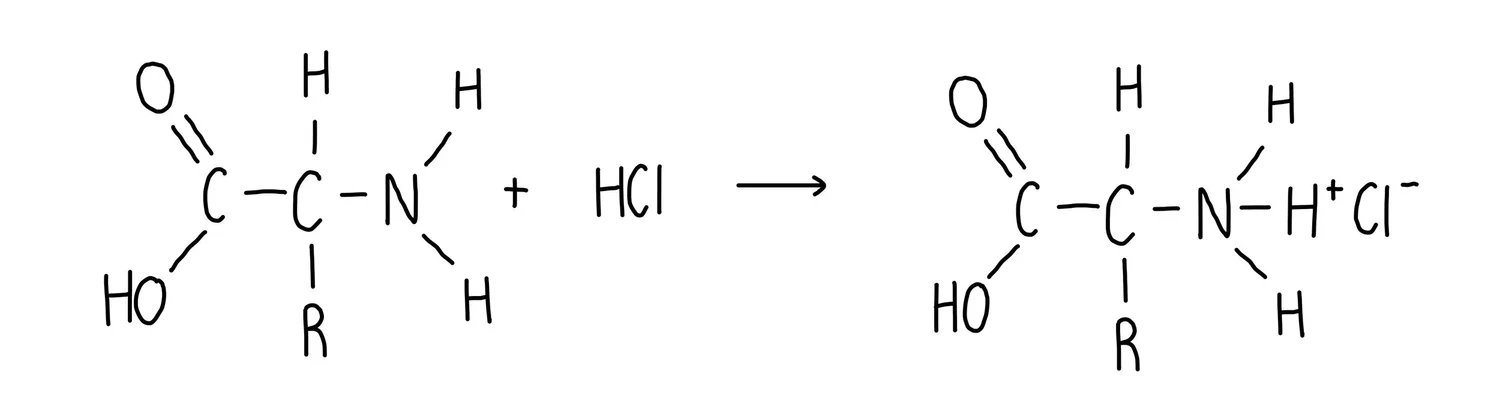
What is the general equation for an Amino acid + Acid?
Amino acid + Acid → Amino acid salt
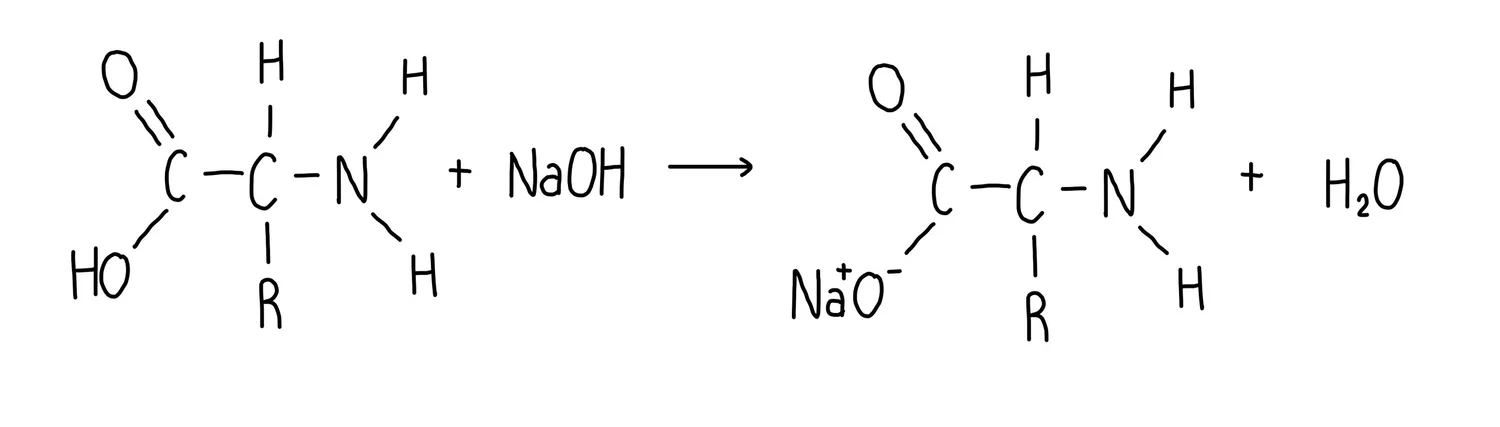
What is the general equation for an Amino acid + Base?
Amino acid + Base → Amino acid (basic) salt + Water
Are Zwitterions soluble in water? (why)
Yes:
The unlike charges of the polar water molecules and ionic amine and carboxyl groups attract to form ion dipole forces, making it soluble
What type of bond forms to make protiens between Peptides?
Peptide link (a specific type of amide link)
What are the 3 types of Protein structures?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Describe the Primary Protein structure (+ display)
Peptide links form between amino acids:
- - - glu-ala-ser-glu-cyt- - -
2 types of Secondary Protein structures (+ describe)
Alpha Helix chain = H-Bonds between different points of the peptide links negative carboxyl group and positive amine group
Beta pleated sheet = “ ⬆ ”
How is the Tertiary Protein structure formed?
The bending and winding of a proteins secondary structure
What 4 factors effect Tertiary Structure? (how)
H-Bonding (in R groups)
Ionic interactions between NH3+ and COO-
Disulfide Bonds between Cysteine units (strong bonding)
VDW (When amino acids are large enough, form noticeable Dipole-Dipole forces)
Give the summary of Bonding that occurs in:
Primary Proteins
Secondary Proteins
Tertiary Proteins
Primary Proteins = Covalent
Secondary Proteins = H-Bonding of R groups
Tertiary Proteins = R group IMF interaction (H-Bonding, Ionic interactions of Amine and Carboxyl ion groups, DiSulfide bonds)
What type of Polymerisation reaction do Amino acids undergo between eachother?
Condensation polymerisation (+ water byproduct)
Give the conditions in the Hydrolysis of Proteins into its Amino acids (2 conditions)
How to identify the reactants that form the Polymer
24 hr reflux
6M HCL
When identifying the amino acids that make up the peptide link, we use the same method as Amides to find the reactants that formed it
Enzymes
Enzymes
What are Enzymes?
Stereospecifc proteins that catalyse metabollic reactions without being used up/changed. Their active sites are complimentary to a specific substrate that binds to it to form an “enzyme-substrate” complex
How does an Enzymes active site form?
The folding of a polypeptide chain - Tertiary structure
What part of the Amino Acid/Substrate binds to the substrate? (how)
The “R” group of a substrate attract to the active site of the complimentary enzyme via IMFs:
H-Bonding
VDW
Ionic
Give + explain an example where enzymes work biologically
Prevention?
Bacterium Enzymes:
React with substrates to form products that contribute to the formation/regen of its cell wall
Prevention = Use of inhibitors
How do Inhibitor molecules work?
They bind with + prevent the enzyme reacting with the substrate, preventing cell wall formation + bursting the bacterium to prevent it from multiplying
What are the 3 requirements of Inhibitors?
Must not be a shape which is complimentary to enzymes which play a role in key reactions in the body
Must be stereospecific
Must be made up of 100s of amino acid residues
What makes Inhibitors?
Computers
Describe the layout of a DNA molecule

What does the reaction between Phosphates + Sugars form?
Sugar-Phosphate + Water
***HOW TO PAIR BASES + SUGARS IN IRL FC***
***HOW TO PAIR BASES + SUGARS IN IRL FC***
What is a Nucleotide?
The sugar-phosphate-base molecule
How many bonds form between bases?
(List the base pairs + Number of bonds)
A-T → 2 bonds
G-C → 3 bonds
What is the Anti-Cancer drug we’re required to know:
Shape
Bond angles + Co-ordinate number
Describe structure
Cisplatin:
Square Planar
90o - Coordinate Number = 4
2 NH3 on the same side /// 2 Cl on same side
What does Cisplatin do? (explain)
Cisplatin triggers programmed cell death, by causing a kink in the Cancerous DNA chain, preventing enzymes from interacting with DNA. Preventing cell division + DNA unwinding
(EXTRA QUESTION)
How does Cisplatin attach to the Cancer DNA?
Cisplatin enters a cell where its Cl ligands undergo substitution for H2O molecules → forming “Cis-diamminediaquaplatinum(II)” which then locates 2 guanine bases in the cancer DNA. Replacing the waters with the Nitrogen of these bases