Serology Quiz 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus)
Chronic inflammatory disease; multi-organ involvement (skin, joints, kidney, lungs, CNS)
Tissue damage is due to ab/ag complexes in the renal glomeruli, skin, and choroid plexus of the brain
Anemia: 50% leukopenia
Decrease in 25-50% platelet count
Elevated ESR
Negative ANA, rules out SLE
Specific for SLE: anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm: titers will rise in active disease and fall in remission, useful in monitoring disease
AntiSSA Ags are associated with the neonatal SLE syndrome
Drug induced SLE
Associated with long term ingestion of several drugs: procainamide, hydralazine, anticonvulsants, chlorpromazine
Antibodies to histones are present
Milder form of Lupus: homogenous ANA pattern due to anti-histone antibodies and absence of anti-dsDNA
Raynaud's Syndrome
Vasoconstriction on extremities
Associated with the antinuclear antibody (RNP)
Ribonucleoprotein (anti-RNP)
Sjorgren's Syndrome
Chronic inflammatory disease
Strong association with HLA-C, HLA-DR3
Middle aged to elderly women
Autoantibodies: 90% rheumatoid factor
ANA: anti-LA
Definitive diagnosis: biopsy of labial salivary gland
Scleroderma
Cyanosis, puffy face, hard skin, atrophy, GI symptoms, lung, heart arrhythmias
2 forms of the disease: Progressive diffuse and systemic CREST
Calcinosis: bone formation
Raynaud: vasoconstriction of hands/feet
Esophageal involvement
Sclerodactyly: skin on fingers harden
Telangiectasia: spider veins
ANA
Centromere pattern due to ACA (Anticentromere antibody)
Nucleolar pattern can also be seen in diffuse type of organ involvement
Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
Deficient insulin production due to immune destruction of the B cells of the pancreas
Direct result of congenital Rubella
Juvenile onset
Immunoglobulin binds to tissue receptor for insulin - prevent biological action of insulin
HLA-DR3 and - DR4, HLA-DQw8 Ags: genetic susceptibility
CD4 T-lymphocyte
Mixed connective tissue disease
Diffuse tissue disease that doesn’t fall into one disease category
Joint pain, stiffness, esophageal dysfunction, progressively worsening.
75% leukopenia; deforming arthritis
ANA: 50% low titer RF/high titer of anti-RNP, anti-ssDNA
Distinguish from SLE: absence of multiple anti-SM and anti-ds-DNA
Ankylosing spondylitis
Males have a more progressively severe form than females who have a greater involvement of peripheral joints and cervical spine
Fibrolysing and ossifying process of the ligaments and synovial capsules in bone
Lumbar pain and limited lumbar motion
Prostatitis, conjunctivitis, aortic valve disease, upper lobe pulmonary fibrosis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Affects the synovium and articular surface of multiple joints with varying degrees of systemic involvement
High incidence in elderly and females 20-40 years old
Joint swelling, morning stiffness, weight loss, fatigue, low grade fever
RF: rhematoid factor (also found in infections)
Circulating immune complexes consist of immunoglobulins and complement, and RF
ANA: 14-28% of pts
RA latex agglutination detects mostly IgM RF
Felty's syndrome
RA associated with splenomegaly and leukopenia, prone to bacterial infections
HLA-DR4 found in 95% of patients
High titer of RF assay
+ANA
Juvenile RA and HLA typing
Joint swelling, Still's disease: +HLA-DR5
40%: +HLA-DRw6
Girls <6 years: +HLA-Dw5 and +HLA-DR5
Boys <6 years: +HLA-B27
20%: +HLA-DR4
ANA: positive only in few cases
Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune disorder of the CNS
Formation of lesions (plasques) in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord → progressive destruction of the myelin sheath of axons
Closely associated with inheritance of a particular HLA molecule coding for the beta chain DR(DRB1*1501)
Oligoclonal bands seen on CSF Electrophoresis
Myasthenia gravis (MG)
Autoimmune disease that affects the neuromuscular junction, characterized by weakness and fragility of skeletal muscles
Antibody-mediated damage to acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle → progressive muscular weakness
Goodpasture's Syndrome
Presence of an autoantibody to the glomerular basement membranes, resulting in injury to the glomerulus that progresses rapidly to renal failure
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Diffuse non-tender enlargement of the thyroid gland, increased TSH, normal T3/T4, eventually becomes hypothyroid
94% have titer of 1:100 of the anti-thyroid microsomal Ab : Microsomal >1:6400
Graves Disease
Diffuse enlargement of thyroid (hyperplasia), tachycardia, characteristic eye symptoms include: infiltrative ophthalmopathy (exophthalmos)
TSI Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins bind to the thyroid cells and stimulate thyroid activity (hyperthyroid)
GI Tract disease
86% have Abs against gastric parietal cells lipoprotein cytoplasmic component
Type I: B12 blockin, prevents IF binding
Type II: IF binds, but precluded by intestinal
Liver disease
Non-infectious inflammation in the bile ducts, disease manifests initially as a painless jaundice with itching
70% have ANA mixture of speckled, homogenous, anticentromic, nuclear membrane patterns
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Chron’s disease and chronic ulcerative colitis are distinct forms
ANCA (anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody) are autoantibodies directed against the intracellular components of PMNs
Straining of ANCA with proteinase 3 generates fluorescent patterns: c-ANCA, p-ANCA
Organ-Specific
Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
Multiple Sclerosis: CNS
Myasthenia gravis: neuromuscular junctions
Goodpasture's Syndrome: kidneys and lungs
Hasimoto's Thyroiditis: thyroid
Graves Disease: thyroid
Liver disease: liver and bile ducts
Autoimmune Liver Disease: liver and bile ducts
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
GI Tract Disease: Celiac, Autoimmune gastritis - organ specific, IBD - systemic
Systemic Autoimmune
SLE
Drug induced SLE
Sjogren's Syndrome
Scleroderma
Mixed connective tissue disease
Ankylosing spondylitis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Felty's syndrome: complication of RA
Raynaud's Syndrome: Primary - not autoimmune, Secondary - systemic diseases
Juvenile RA: depends on subtype
Cause of tissue injury in autoimmune disorders
Autoimmunity: Breakdown of the immune system in its ability to discriminate between self and non-self
Autoantibodies complex with patient's own DNA
Immune complexes are deposited in vascular systems in organs and tissues
Immune-mediated tissue injury from action of complement
Latex Agglutination (Agglutination)
Ex. Assays for rheumatoid factor (RA), Rubella, CRP
Particulate test Ags that have been absorbed onto latex beads react with Abs. When Ag/Ab/Latex particle complex forms, agglutination is seen as visible clumps
Haemagglutination (Agglutination)
Using RBCs in viral testing
-Ex: Rubella
Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI):
Pt serum with Rubella Ab + incubation with Rubella Ag = agglutination
When chick RBC is added, no agglutination occurs (pos. reaction)
Passive hemagglutination (PHA): human RBC coated with soluble Rubella virus Ag will agglutinate in the presence of Rubella Ab
After dilution with phosphate buffer and adding Ag-RBC, incubate at RT for 2 hours
RBC button at bottom of well = neg
Agglutination = pos
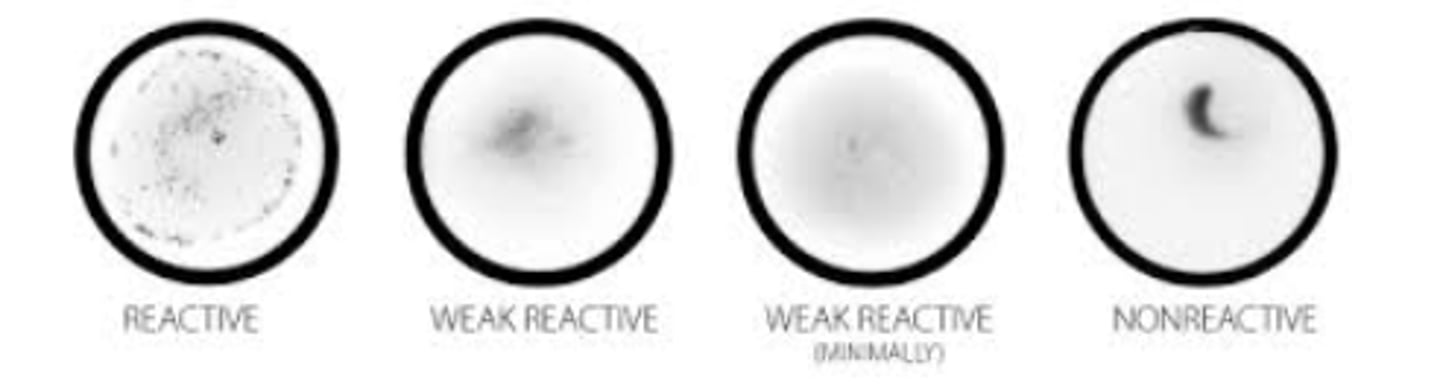
Flocculation tests (Agglutination)
VDRL or RPR (Non-treponemal tests)
Precipitate of fine particles that is microscopic (VDRL) or macroscopic (RPR-uses charcoal)
Reactive = med to large clumps
Weak Reactive = small clumps
Nonreactive = no clumps; tail when swirling
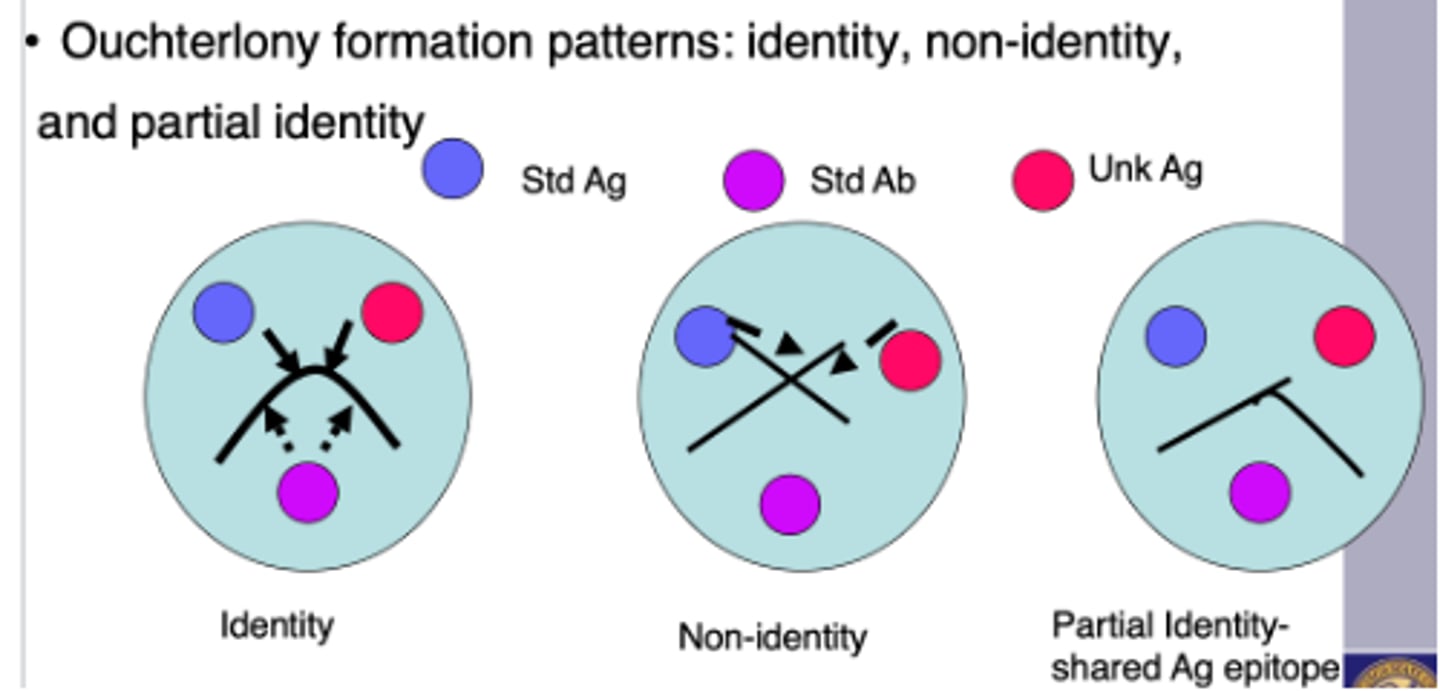
Double immunodiffusion (Ouchterlony formation)
(1) Fusion of the lines at their junction to form an arc represents serological identity or the presence of a common epitope
Looks like a sad face ☹️
(2) a pattern of crossed lines demonstrates
two separate reactions and indicates that the compared antigens share no common epitopes
Looks like ❌
(3) fusion of two lines with a spur indicates partial identity. In this last case, the two antigens share a common epitope, but some antibody molecules are not captured by antigen and travel through the initial precipitin line to combine with additional epitopes found in the more complex antigen. Therefore, the spur always points to the simpler antigen
Electrophoretic immunodiffusion
Radial immunodiffusion (RID):
-Pt IgG diffuses across agar with Ab incorporated with Anti-IgG/M/A
-Outside the zone of equivalence, precipitin ring forms (diameter is proportional to Pt Ig concentration)
Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP): separation of proteins into bands
Immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE): separation of proteins as Ab placed in trough running parallel to electrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis is a double-diffusion technique that incorporates electrophoresis to enhance results
Complement inactivation (Complement fixation)
Complement fixation: complement is used as a reagent: complement is "fixed" within Ag/Ab complex formed
Uptake of complement is an indicator of the Ag/Ab formation
Lack of hemolysis indicates complement has reacted with the test Ag/Ab complex
Hemolysis of indicator SRBC coated with hemolysin, indicates that complement is not fixed into Ag/Ab complex
RIA (Labeling)
Radioactive labels with known emission properties
Uses: mostly used for trace elements in blood like hormones and serum proteins or elements too small to be detected otherwise
One reactant (Ag or Ab) is radio labeled
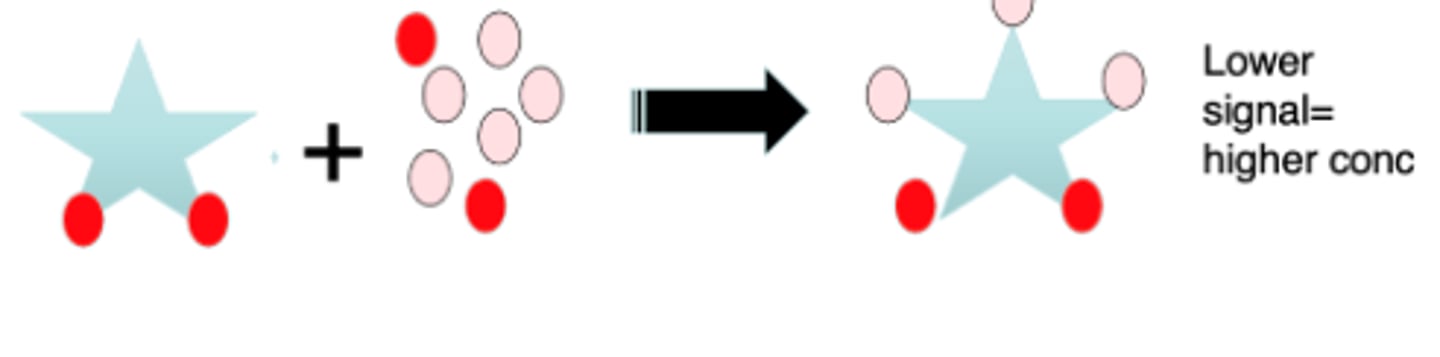
Competitive: usually Ag is labeled – “tracer”
Less signal = more concentrated
Non-competitive: Ab is labeled
Directly proportional
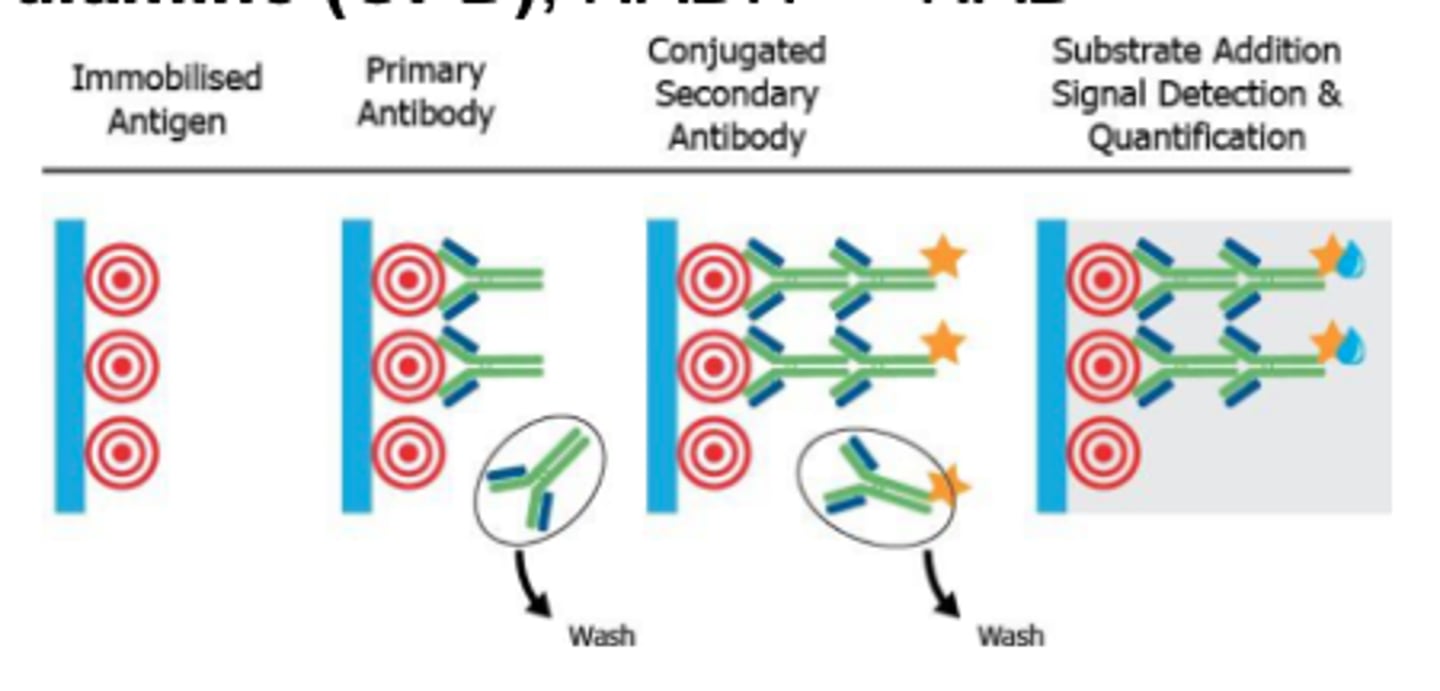
EIA/ELISA (Labeling)
Ex. horseradish peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, glucose-6-PD, beta-galactosidase
Common substrate: orthophenylene diamine (OPD), NADH → NAD
Controls must be included in assay: 3 negative + 2 positive
Absorbance greater than or equal to cutoff of the negative control is reactive
If positive, repeat the EIA and send for confirmatory test (Western Blot, IFA)
Enzyme catalyzes substrate molecules and amplifies the signal
Enzyme activity may be monitored directly or coupled with co-enzyme action → colored product, measured photometrically
FIA (Labeling)
Common labels: Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), rhodamine isothiocyanate
Uses: DFA assays for bacterial or viral detection
Compounds that absorb radiant energy at higher wavelength and emit radiant energy at a lower/longer wavelength
MEIA: microparticle EIA
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA test)
Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody (FTA-ABS): fluorescence detected on microscopic slides, visual evaluation of Ag/Ab complex formation
Fluorescence polarization (FPIA): fluorescent labelled antigen competes with patient antigen for limited number of antibody-binding sites; inverse ratio between patient antigen and amount of polarization – homogenous assay
Chemiluminescent Labels
Common labels: Acridinium esters, luminol, ruthenium derivatives, nitrophenyl oxalates
Uses: cardiac markers, vitamin D level, total IgE
Organic compounds emit a photon of light in response to a chemical reaction, as they revert to their ground state
PCR (Molecular diagnostic)
Extracted DNA from an organism such as Chlamydia allows for amplification by PCR
Low levels of specific DNA sequences are amplified using oligonucleotides or primers (small portions of a single DNA strand) and enzymes
Western Blot (immunoblot)
EIA reaction is used to detect the bang (HIV testing)
Ag material is electrophoresed for separation and blotted to a nitrocellulose membrane
Membrane is incubated with specific Ab, Ag/Ab complex is a band
Southern Blot (immunoblot)
Fragments detected using radioisotope (single stranded DNA fragments and radiography)
Specimen DNA is fragmented using restriction enzymes and separated by using restriction enzymes and separated by electrophoresis and blotted onto nitrocellulose membrane
Nephelometry
Quantitation of immunoglobulins
Light scattering application used to detect Ag/Ab complexes
Distribution of Rayleigh light scatter which is symmetrical in forward and backward direction
More light scatter = higher concentration of Ag/Ab complex
Competitive assay
Higher specificity
Competition occurs between a labeled Ag and unlabeled Ag for a limited number of binding Ab sites
Labeled Ag + unlabeled Ag + limited Ab = Ag/Ab labeled + Ag/Ab unlabeled + free labeled Ag
Amount of Ag is indirectly related to the amount of label signal
Less bound labeled Ag indicates more antigen present in sample reacting with the limited Ab sites
EMIT (Enzyme Multiplied Immunoassay Technique)
Competitive Assay
Automated method commonly utilized for drug detection
Patient's urine sample contains the unlabeled drug metabolite that competes with a labeled drug metabolite. Only the unbound enzyme-label drug is left to react with the substrate.
Measure drug level which is directly proportional to enzyme activity detected.
Non-competitive assay
higher sensitivity and specificity
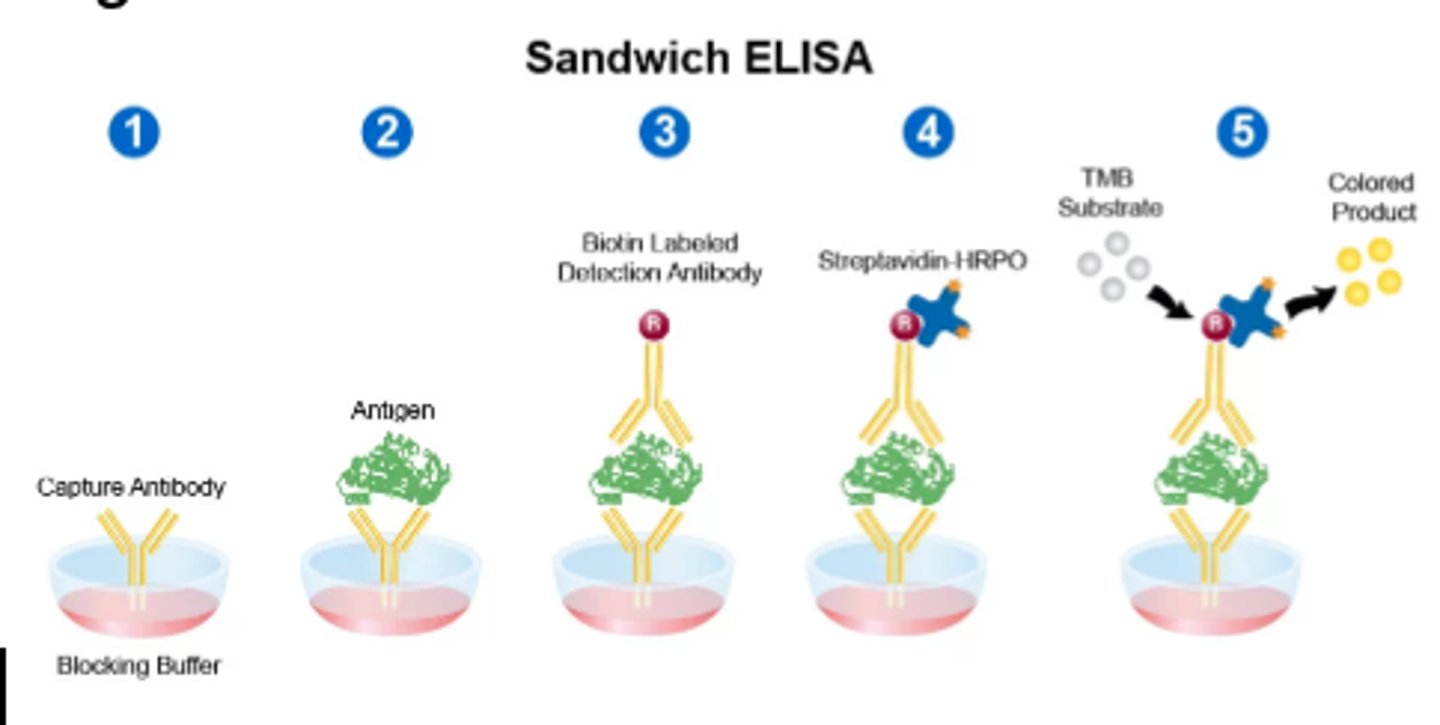
Sandwich assay: Analyte is sandwiched between two highly specific antibody reagents
Two step process, utilizes wash steps to isolate the sandwich complex and remove excess unbound labels
Concentration of labeled Ag is directly proportional to bound Ab
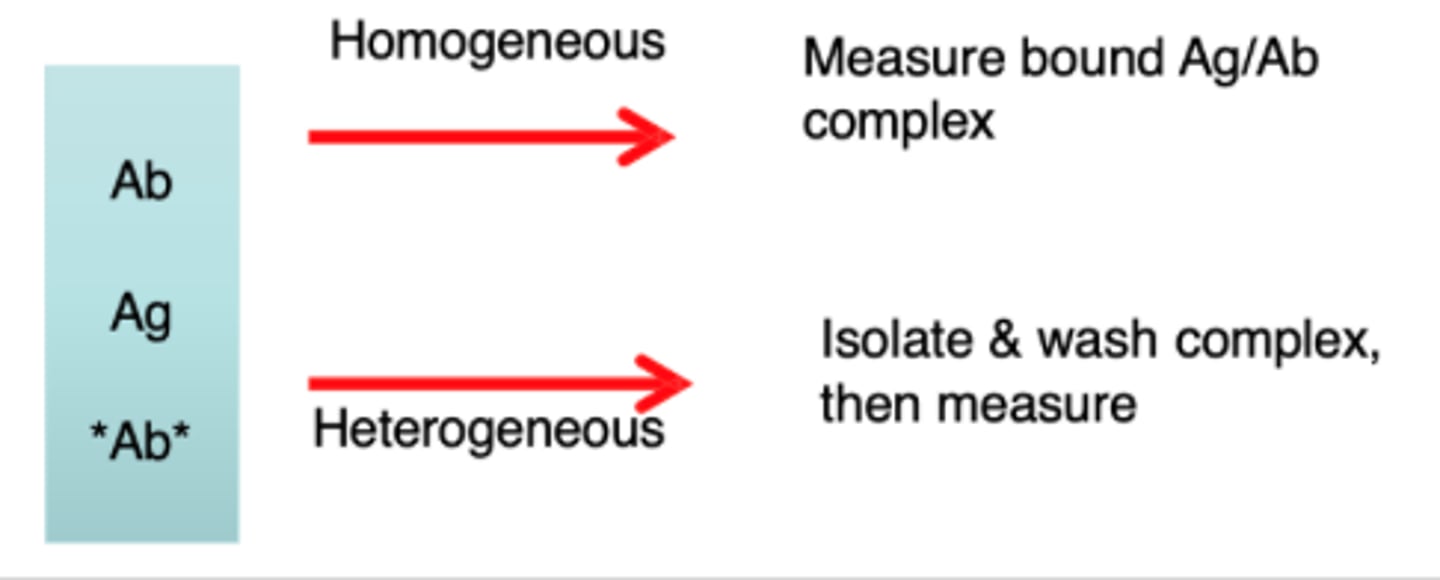
Homogenous and Heterogenous Immuno assay
Homogenous and Heterogenous Immuno assay
Homogenous: do not require separation, limited washings
Heterogenous: require separation or washing of bound Ag/Ab complexes on solid phase
Solid phase: fixed receptor sites, immobilized on a surface such as wells or beads