Chapter 9 - Agriculture
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
dietary energy consumption
the amount of food that an individual consumes, measured in kcal or calories
2
New cards
intensive subsistence, wet rice dominant
East Asia + South Asia
3
New cards
intensive subsistence, not wet rice dominant
East Asia + South Asia
* rely on wheat, oats, legumes, corn, etc.
* rely on wheat, oats, legumes, corn, etc.
4
New cards
pastoral nomandism
Southwest Asia + North Africa + Central Asia + East Asia
* herding of domesticated animals in dry climates where planting crops is impossible
* herding of domesticated animals in dry climates where planting crops is impossible
5
New cards
shifting cultivation
Latin America + S.S. Africa + Southeast Asia
* farming technique where crops/people shift from one field to another frequently
* farming technique where crops/people shift from one field to another frequently
6
New cards
plantation
Latin America + S.S. Africa + South Asia + Southeast Asia
* large commercial farm in a developing country specializing in 1-2 crops
* Generally owned by North Americans/Europeans
* large commercial farm in a developing country specializing in 1-2 crops
* Generally owned by North Americans/Europeans
7
New cards
mixed crop and livestock
U.S. Midwest + central Europe
8
New cards
dairy
U.S. + Canada + Europe
9
New cards
grain
U.S. + Canada + Europe
10
New cards
livestock ranching
North America + Latin America + Central America + South Pacific + S.S. Africa
11
New cards
mediterranean
Med. Sea areas + Western U.S. + Southern Chile/Africa
12
New cards
commercial gardening
U.S. + Australia
13
New cards
crop rotation
the practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year to avoid exhausting the soil
14
New cards
paddy
area used for growing rice
15
New cards
transhumanance
seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pasture areas
16
New cards
slash and burn
land is cleared by slashing vegetation and burning debris
17
New cards
frequent relocation
crops are grown on a cleared field for a few years until soil nutrients have been depleted before leaving it alone for years
18
New cards
aquaculture
(aquafarming) the cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions
19
New cards
Trade and Assistance Act of 1954
sells grain at low interest and gives grants to those in need
20
New cards
desertification
human actions causing land to deteriorate in a desert like condition
21
New cards
second agricultural revolution
began in the U.K. in the 1600s, increased productivity through the improvement of livestock breeding and crop rotation
22
New cards
forest fallow
fields are cleared and utilized for up to 2 years and left fallow for more than 20 years, long enough for the forest to grow back
23
New cards
bush fallow
fields are utilized and cleared for up to 8 years and left fallow for up to 10 years, long enough for small trees and bushes to grow back
24
New cards
short fallow
fields are cleared and utilized for perhaps 2 years and left fallow for up to 2 years, long enough for wild grasses to grow back
25
New cards
annual cropping
fields are used every year and rotated between legumes and crops
26
New cards
green revolution
the invention and rapid diffusion of more productive agricultural techniques during the 1970s and 80s
27
New cards
Norman Borlaug
important person in the green revolution, helped invent miracle seeds
28
New cards
conservation tillage
a method of soil cultivation that reduces soil erosion and runoff
29
New cards
no tillage
leaves all of the soil undisturbed, and the entire residue of the previous year’s harvest is left untouched
30
New cards
ridge tillage
a system of planting crops on ridge tops
31
New cards
rural settlement
clustered, dispersed, linear
32
New cards
friction of distance
movement occurs with some cost proportional to the distance traveled
33
New cards
land settlement
long lots, metes and bounds, township and range
34
New cards
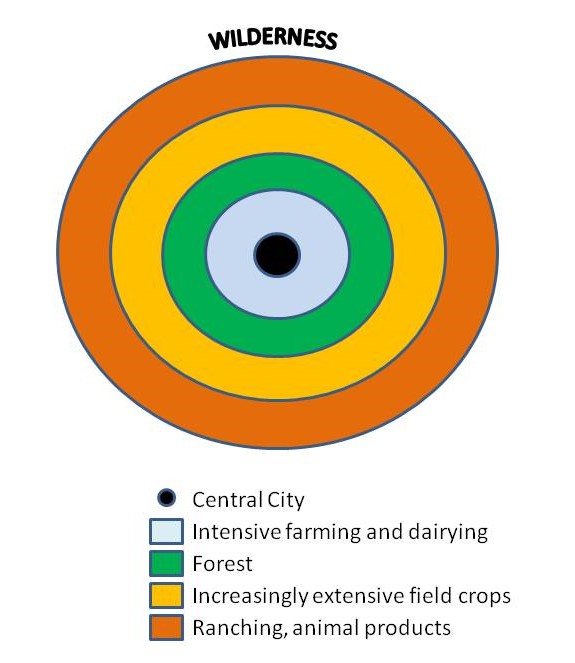
Von Thunen’s model