4 - Moral Hazard - The Value of Information (Unfinished)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does the variable z denote
Information about effort or other factors that influence the outcome (e.g. oil price, weather, flipping a coin etc)
Equations for the market value of company j (2)
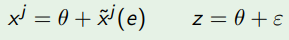
What does x̃ʲ(e) stand for
Non-verifiable effect of CEO's effort on firm j's value
What does θ stand for
Non-verifiable market conditions affecting all firms
What does z stand for
Noisy but verifiable measure that is informative about θ
Example of z
The performance of other companies
Utility of a risk-neutral principal
B(x-w) = x-w
Utility of a risk averse agent
U(w)-v(e)
How is the probability of (xᵢ, zₖ) if e=eᴴ notated
pᵢₖᴴ
How is the probability of (xᵢ, zₖ) if e=eᴸ notated
pᵢₖᴸ
Probability table for (xi,zk) when e is eH or eL
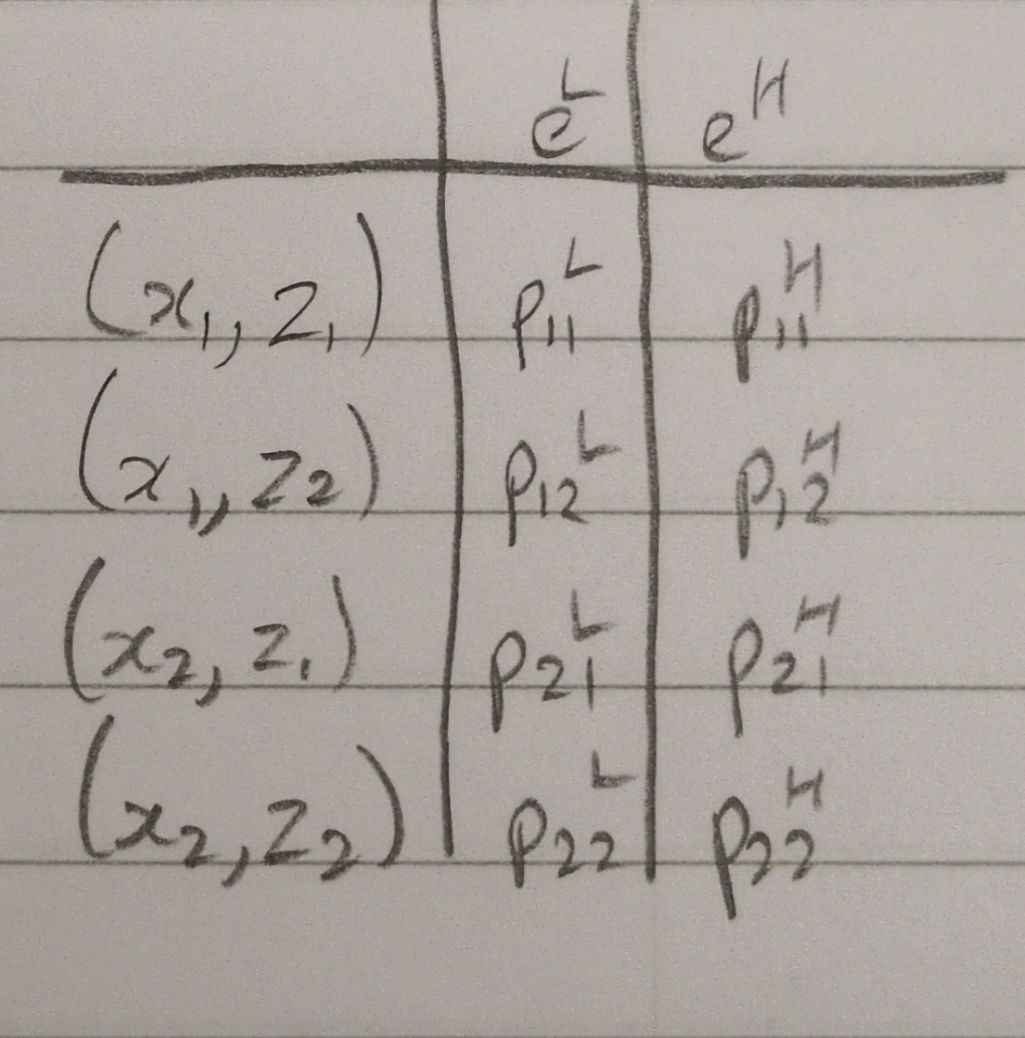
How are wages notated when adding the additional variable z
wᵢₖ = w(xᵢ, zₖ)
How can low effort be implemented in this model
A fixed wage
What does the agent do with effort cost if the wage is fixed
The agent minimises effort cost
What property does the IR constraint have when there is a profit-maximising fixed wage
The IR constraint is binding
What is the profit-maximising fixed wage when implementing low effort in this model
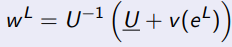
When solving the principal’s maximation problem for high effort, what is the IR constraint
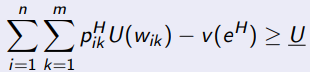
When solving the principal’s maximisation problem for high effort, what is the IC constraint
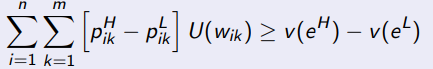
When solving the prinicipal’s maximisation problem for high effort, what are you maximising
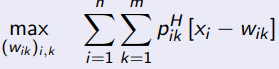
What is the principal’s maximisation problem with high effort
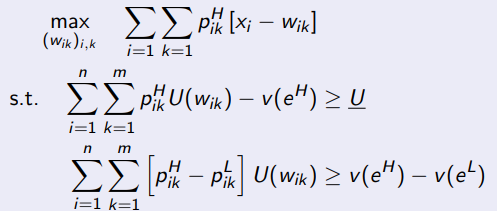
What is the difference with the principal’s maximisation problem for high effort now that z has been introduced?
It is the same problem except that the probabilities and wage are now dependent on i and k
What is the first order condition for the optimal wage schedule for high effort
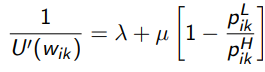
When does the optimal schedule depend on the realisation zk
If for some i and some k≠l, wik≠wil
What is the likelihood ratio in this model
LRik = pikL / pikH
When is the signal z useless
If for all xi, LRi1 = LRi2 = … = LRim
When is the likelihood ratio independent of zk for all xi and LRi1 = LRi2 = … = LRim?
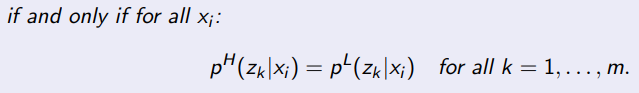
What does pH(zk|xi) stand for
The conditional probability of signal zk, given effort is eH
What is the value for pH(zk|xi)
pikH / ∑mpilH
What does pL(zk|xi) stand for
The conditional probability of signal zk, given effort is eL
Lemma’s condition
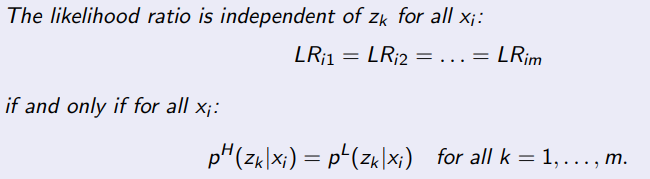
Interpretation of Lemma’s condition
Suppose we observe xi, Lemma’s condition is satisfied if for both levels, the distribution of signals zk are the same, conditional on xi
Example of Lemma’s condition being satisfied
Given firm j’s performance is xij, we expect the same results of an audit, no matter what effort the CEO has chosen (So an audit would be useless)
When does the optimal wage schedule for high effort not depend on z
If for some i,k: pH(zk|xi)≠pL(zk|xi)
When the optimal wage schedule for high effort depends on z, how can we learn additional information about the effort
We can learn additional information about the effort from z even if x has already been observed
When does the optimal wage schedule for high effort not depend on z
If for all i,k: pH(zk|xi) = pL(zk|xi)
When the optimal wage schedule for high effort does not depend on z, how can we learn additional information about the effort
All the information about the effort that is contained in z, is already contained in x
When the optimal wage schedule does not depend on z, what is x called
A sufficient statistic for z with respect to e
When solving for the optimal wages, what is most efficient when using the utility equations (for example when U(w)=√w)
Keep it in terms of U and not w (Eg. U1=√w1, U2=√w2, and solve with these)
When a certain z leads to effort not making a difference to the probability of outcome, what happens to agency cost
The agency cost is reduced as including weather information reduces the cost of implementing high effort
Equation for the performance of a company
p = a + δo + u
What does a stand for in the equation for the performance of a company
Effort
What does o stand for in the performance of a company equation
Some observable factor (oil price, exchange rates, industry performance)
Equation for optimal compensation
y = α + β(p-δo)
What represents observable luck
δo
What does β>0, mean for incentives in the optimal compensation equation
You are incentivised to keep p-δo>0
When the market condition is the worse one, how can the difference in probablities of the low outcomes for high and low effort
The high effort reduces the probability of the low outcome by the difference (Assuming pH<pL)
Equivalent condition
Conditional on xi, the distribution of z is identical for eH and eL