Keplers Laws (1)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
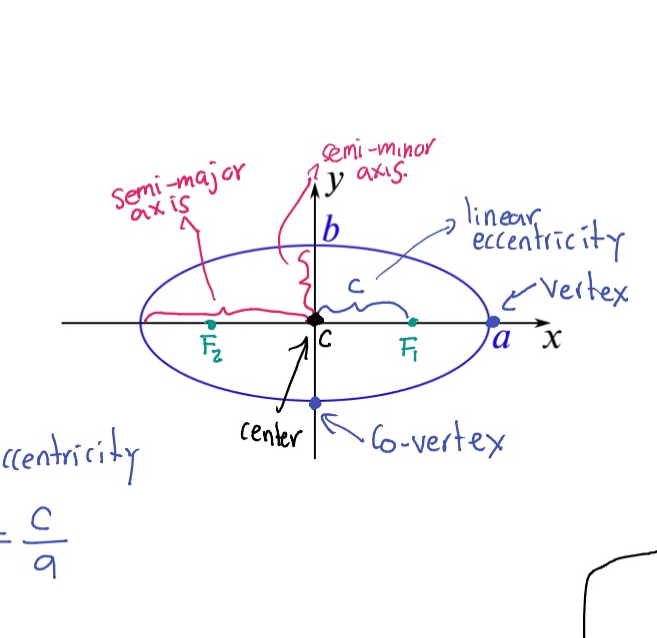
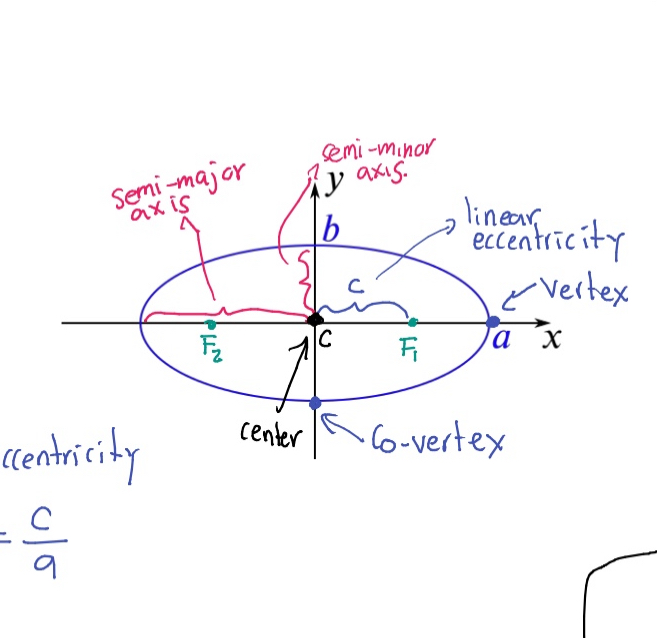
Semi-major axis
The longest diameter of an ellipse, dividing it into two equal halves.
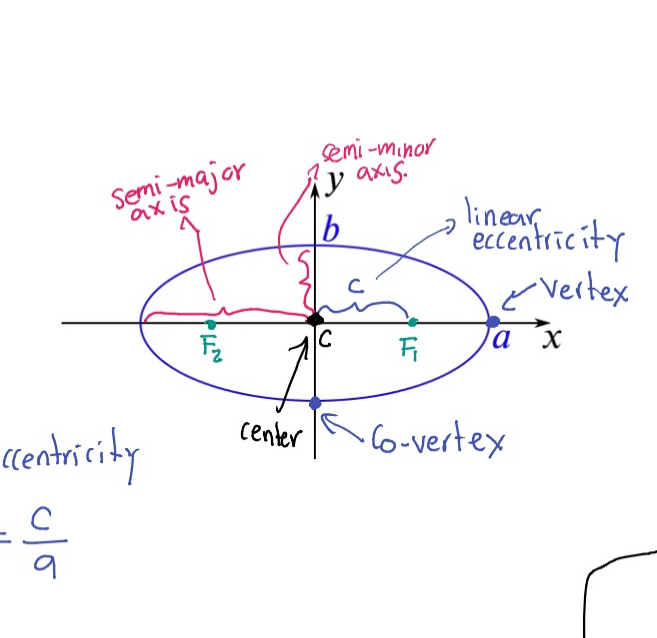
Semi-minor axis
The shortest diameter of an ellipse, perpendicular to the semi-major axis.
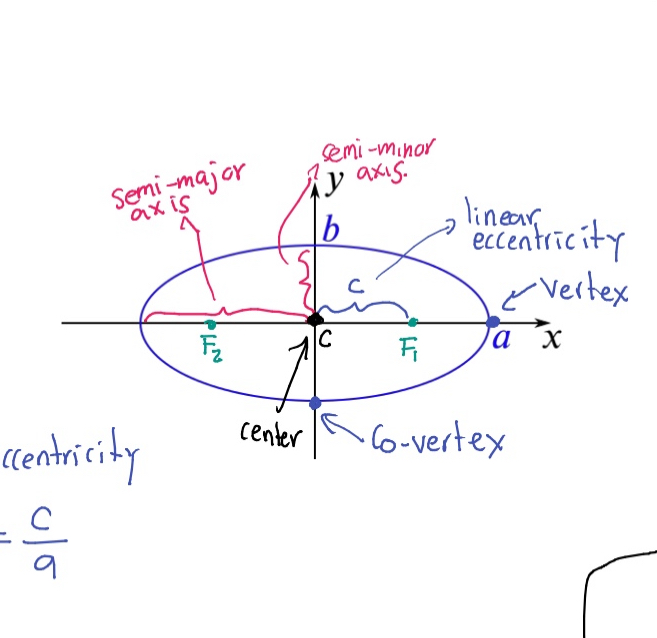
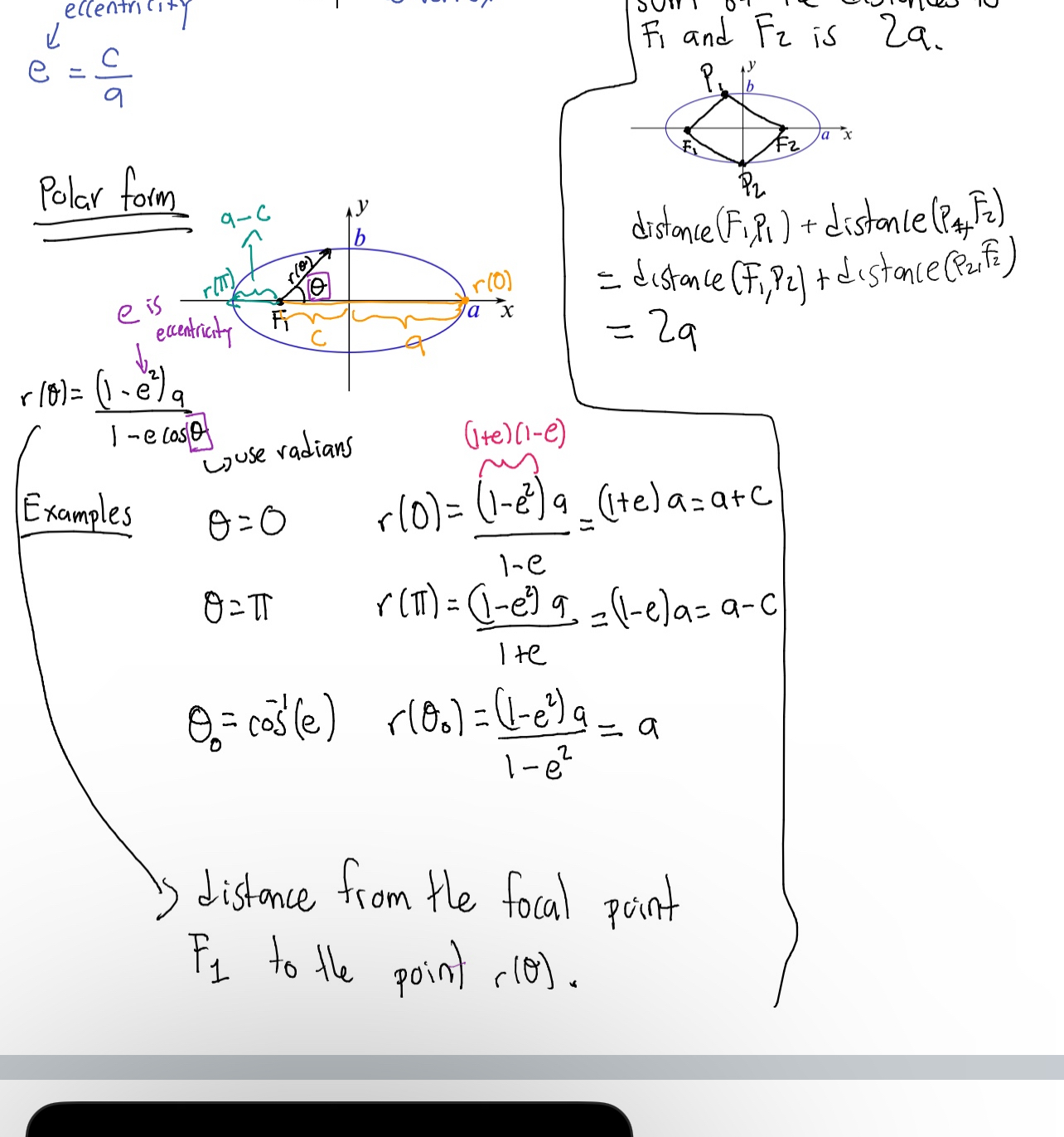
Eccentricity (e)
A measure of how much an ellipse deviates from being circular, calculated as e = c/a where c is the distance from the center to a focus and a is the semi-major axis.
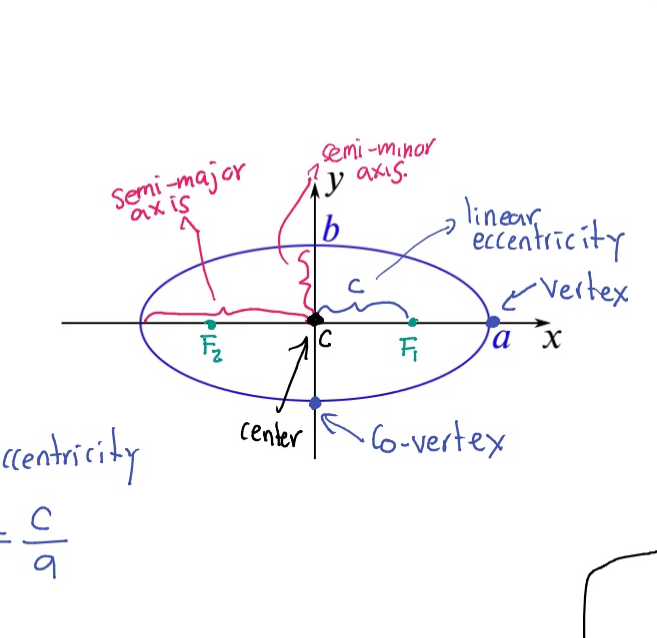
Vertex (of an ellipse)
The point where the ellipse intersects the major axis.
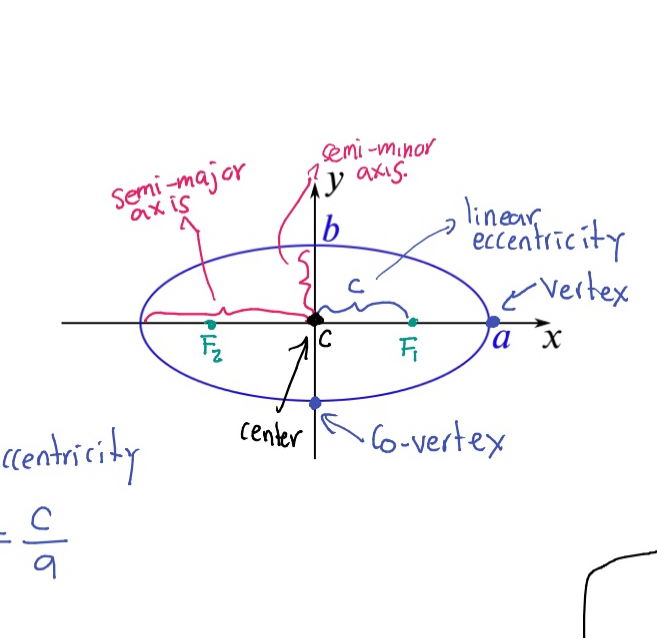
Co-vertex
The point where the ellipse intersects the minor axis.
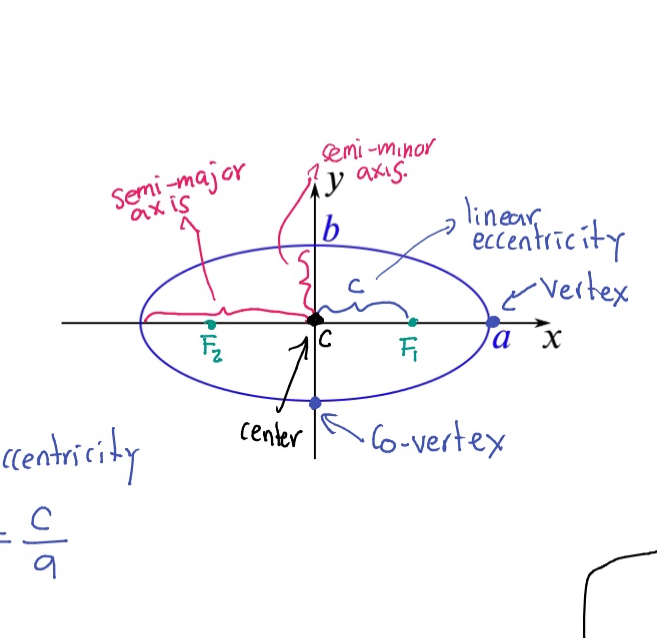
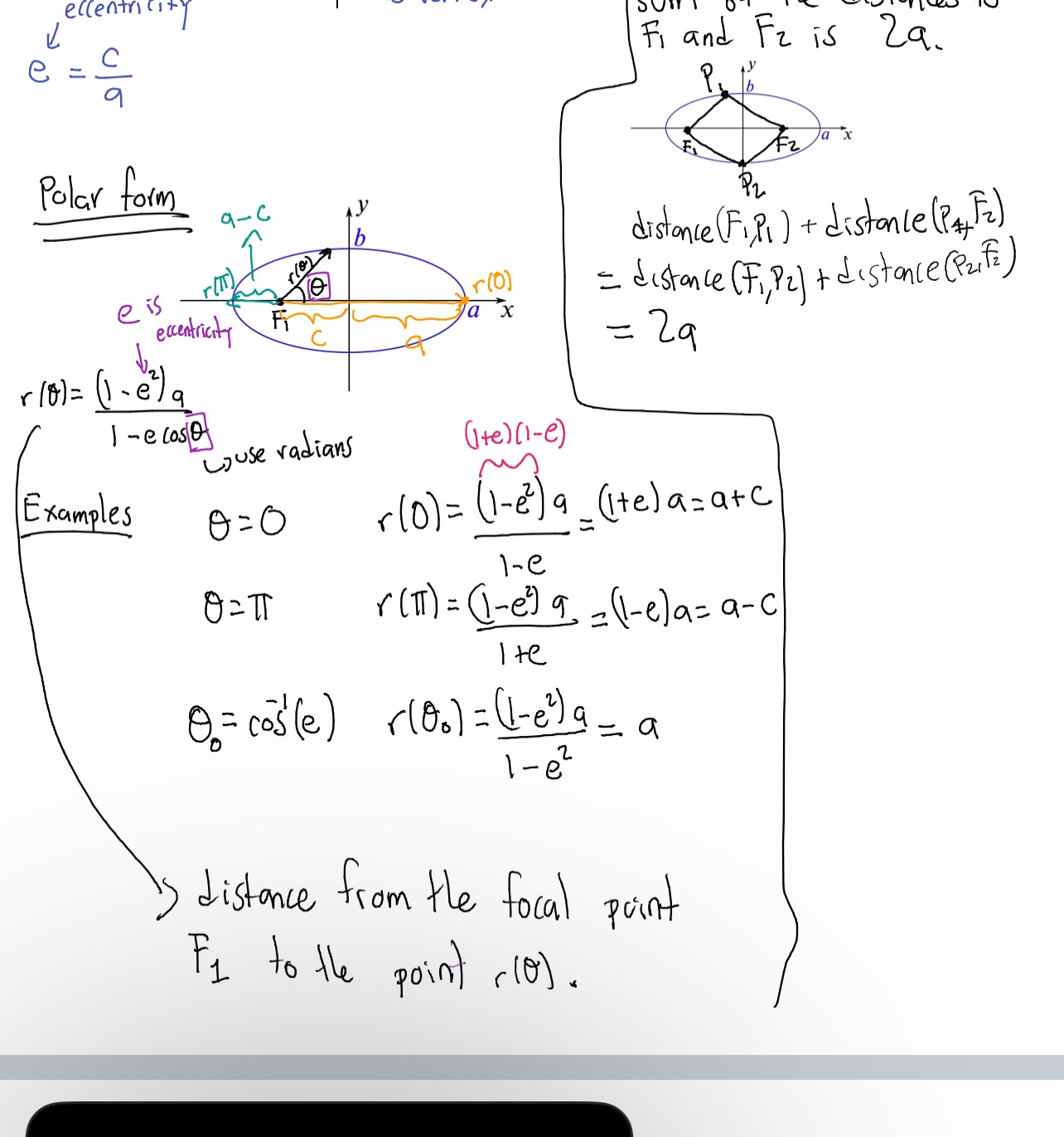
Ellipse
A set of points in a plane, the sum of whose distances from two fixed points, called foci, is constant.
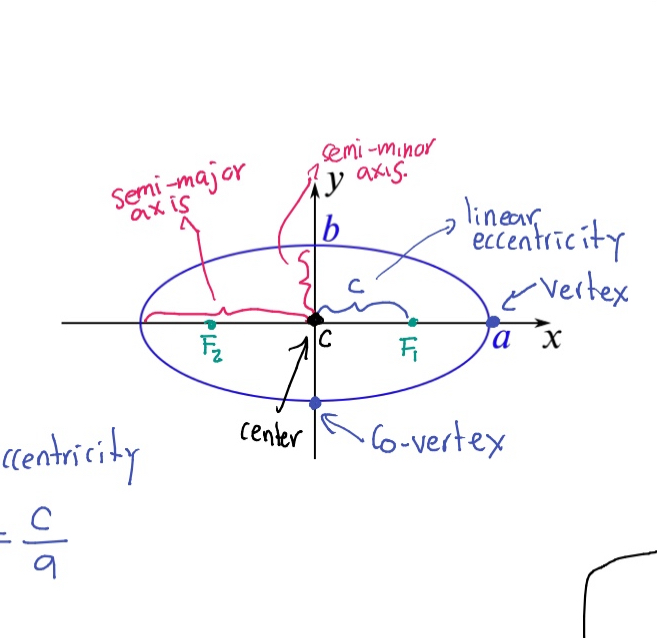
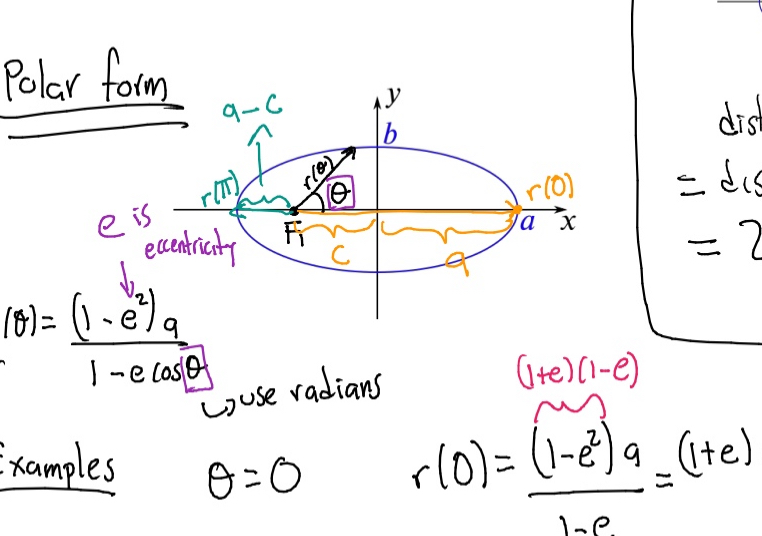
Polar form of an ellipse
Expressions that represent the distance r of a point on an ellipse from a focus as a function of the angle θ: r(θ) = (1 - e²) a / (1 - e cos(θ)).
Area approximation
A method of estimating the area enclosed by an ellipse, often simplified using the area of a circle.
Foci (F₁, F₂)
The two fixed points used to define an ellipse.
For small angles in ellipse area approximation
Using the formula involving angle y, where small angle approximations apply to compute area.