Chpt 1: Role of Financial Markets and Institutions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Financial market
a market in which financial assets (securities) such as stocks and bonds can be purchased or sold.
Funds are transferred in this when one party purchases financial assets previously held by another party.
Financial markets tranfer funds from…
those who have excess funds to those who need funds.
Surplus units
participants who receive more money than they spend (such as investors)
Deficit units
Participants who spend more money than they receive (such as borrowers)
Securities
represent a claim on the issuers
Debt Securities
debt incurred by the issuer
also called credit or borrowed funds
Equity Securities
Represent equity or ownership in the firm
Accommodating Corporate Finance Needs
The financial markets serves as the mechanism whereby corporations (acting as defcit units) can obtain funds from investors (acting as surplus units).
Accommodating Investment Needs
Financial institutions serves as intermediaries to connect the investment management activity with the corporate finance activity.
Primary Market
Facilitate the issuance of new securities
Secondary Markets
Facilitate the trading of existing securities, which allows for a change in the ownership of the securities
Liquidity
The degree to which securities can be easily be liquidated (sold) without a loss of value
if a security is illiquid, investors may not be able to find a willing buyer for it in the secondary market and may have to sell the security at a large discount just to attract a buyer
Securities can be classified as…
Money market securities
Capital market securities
Derivative securities
Money Market Securities
Facilitate the sale of short-term debt securities by deficit units to surplus units
Debt securities that have a maturity of one year or less
Capital Market Securities
Facilitate the sale of long-term securities by deficit units to surplus units
What are capital market securities?
Bonds
Mortgages
Mortgage-backed Securities
Stocks
What’re bonds?
Long-term debt securities issued by the Treasury government agencies, and corporations to finance their operations
What’re Mortgages
Long-term debt obligations created to finance the purchase of real estate
What’re mortgage-backed securities
Debt obligations representing claims on a package of mortgages
What’re stocks?
Represent partial ownership in the corporations that issued them
Derivative Securities
Financial contracts whose values are derived from the values of underlying assets
What’s speculation?
Allow an investor to speculate on movements in the value of the underlying assets without having to purchase those assets
What’s risk management
Financial institutions and other firms can use derivative securities to adjust the risk of their existing investments in securities
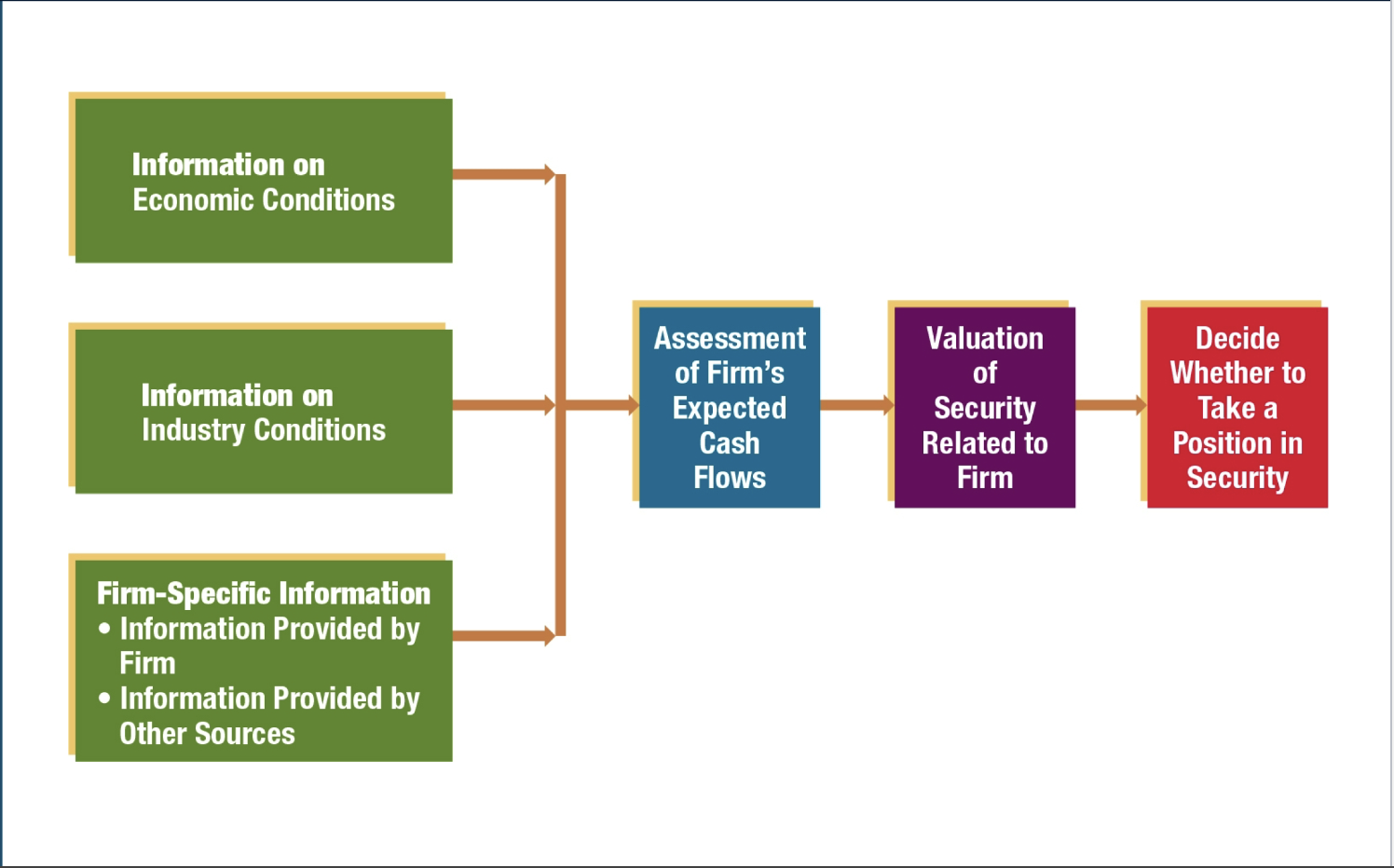
Impact of information of valuation
Estimate future cash flows by obtaining information that may influence a stocks future cash flow
use economic or industry information to value a security
Use published opinions about the firms management to value a security
Impact of Behavioral Finance on Valuation
Various conditions can affect investor psychology. Behavioral finance can sometimes explain the movements of a securities price.
Behavioral Finance
The application of psychology to make financial decisions
Uncertainty Surrounding Valuation of Securities
Limited information leads to uncertainty in the valuation of securities
Securities Act of 1933
Was intended to ensure complete disclosure of relevant financial information on publicly offered securities and to relevant fraudulent practices in selling these securities
Securities Act of 1934
Extended the disclosure requirements to secondary market issues
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
Required that firms provide more complete and accurate financial information
Financial markets vary across the world in terms of…
Degree of financial market development
Volume of funds transferred from surplus to deficit units
International Integration of Financial Markets
Under favorable economic conditions, the international integration of financial markets allow governments and corporations easier access to finding from creditors or investors in other countries to support their growth.
Role of Foreign Markets
International financial transactions normally require the exchange of currencies. The foreign exchange market facilitates this exchange.
Financial institutions are needed to resolve the limitations caused by __________ such as limited information regarding the creditworthiness or borrowers
market imperfections
Role of depository institutions
Depository institutions accept deposits from surplus units and provide credit to deficit units through loans and purchases of securities
Role of depository institutions
Offer liquid deposit accounts to surplus units
Provide loans of the size and maturity desired by deficit units
Accept the risk on loans provided
Have more expertise in evaluating creditworthiness
Diversify their loans among numerous deficit units
What are some Role of Depository Institutions?
Commercial Banks
Savings Institutions
Credit Unions
Commercial Banks
The most dominant type of depository institution
Transfer deposit funds to deficit units through loans or purchase of debt securities
Federal Fund Market- facilitates the flow of funds between depository institutions
Savings Institution
Also called thrift institutions and include Savings and Loans (S&L’s) and Savings Banks
Concentration on residential mortgage loans
Credit Unions
Nonprofit organizations
Restrict business to CU members with a common bond
What’re some Non-depository Institutions?
Finance Companies
Mutual funds
Securities firms
Insurance companies
Pension Funds
Finance Companies
Obtain funds by issuing securities and lend to individuals and small businesses
Mutual Funds
Sell shares to surplus units and use the funds received to purchase a portfolio of securities
Securities Firms
Provide a wide variety of functions in financial markets (Broker, underwriter, dealer, advisory)
Insurance companies
Provide the insurance policies that reduce the financial burden associated with death, illness, and damage to property.
Charge premiums and invest in financial markets
Pension Funds
Manage funds until they are withdrawn for retirement
Systemic Risk
The spread of financial problems among financial institutions and across financial markets that could cause a collapse in the financial system