ANFS475 Exam 4 - Final, Veterinary Biochem Exam 4
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
The number of high energy phosphate bonds required for ubiquitin attachment to a condemned protein is _______________
a) Zero
b) One
c) Two
d) Four
Two
In the process of transamination that transfers an amino group from an amino acid to aspartate, _______________ is recycled.
a) Alpha-ketoglutarate
b) Glutamate
c) Aspartate
d) Oxaloacetate
Alpha-ketoglutarate
The urea cycle uses a total of _______________ high energy phosphate bonds.
a) Zero
b) One
c) Two
d) Four
Four
If an individual has deficient tyrosine levels, the production of _______________ will be negatively impacted.
a) L-DOPA
b) Dopamine
c) Norepinephrine
d) Epinephrine
e) All of the options
All of the above: L-DOPA, Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Epinephrine
_______________ is the primary fuel for the brain.
a) Glucose
b) Galactose
c) Pyruvate
d) Oxaloacetate
Glucose
Glut2 and Glut4 primarily allow transport of _______________.
a) Glucose
b) Galactose
c) Pyruvate
d) Oxaloacetate
Glucose
If bicarbonate (HCO3-) levels are lower than normal, production of _______________ is affected.
a) Purines
b) Pyrimidines
c) Both purines and pyrimidines
d) Neither purines or pyrimidines
Both purines and pyrimidines
Purines include _______________.
a) Adenine & Guanine
b) Cytosine & Uracil
c) Cytosine & Thymine
d) Thymine & Uracil
Adenine & Guanine
If quinone is blocked from undergoing oxidation-reduction cycling, production of _______________ is affected.
a) Purines
b) Pyrimidines
c) Both purines and pyrimidines
d) Neither purines or pyrimidines
Pyrimidines
Uric acid is broken down to _______________.
a) Urea
b) Ammonium (NH4+)
c) Allantoin
d) All the options
All of the above: Urea, Ammonium (NH4+), and Allantoin
If an individual has deficient ascorbate (Vitamin C) levels, the production of _______________ will be negatively impacted.
a) L-DOPA
b) Dopamine
c) Norepinephrine
d) Epinephrine
e) Both norepinephrine and epinephrine
Both norepinephrine and epinephrine
An example of an essential amino acid is _______________.
a) Glutamate
b) Glutamine
c) Threonine
d) Tyrosine
Threonine
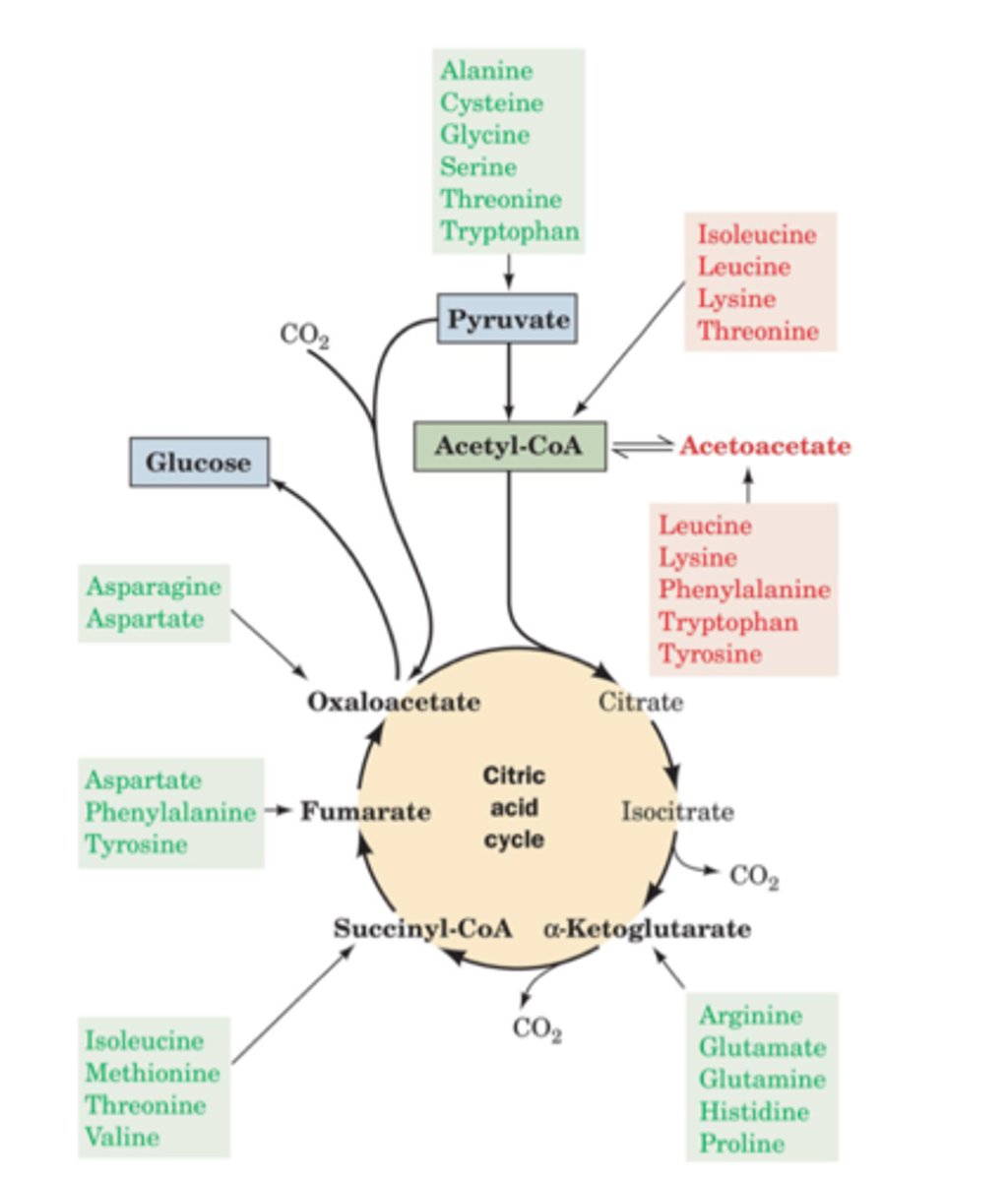
If asparagine and aspartate are deficient, production of _______________ is negatively affected in the TCA cycle.
a) Oxaloacetate
b) Citrate
c) Fumarate
d) Both oxaloacetate and citrate
Both oxaloacetate and citrate
If aspartate, phenylalanine, and tyrosine are deficient, production of _______________ is enhanced in the TCA cycle.
a) Oxaloacetate
b) Succinyl-CoA
c) Fumarate
d) Both oxaloacetate and fumarate
Succinyl-CoA
In the fasted state, hormones secreted by the pancreas affect the _______________.
a) Adipose tissue
b) Muscle
c) Liver
d) Both adipose tissue and liver
e) All the listed organs
Both adipose tissue and liver
If you are hungry, your body secretes _______________.
a) Neuropeptide Y
b) Ghrelin
c) PYY3-36
d) Both neuropeptide Y and ghrelin
Both neuropeptide Y and ghrelin
How many ATP are required for production of IMP from R5P?
a) Two
b) Four
c) Six
d) Eight
Six
How many ATP are required for production of UMP from Glutamine?
a) Two
b) Four
c) Six
d) Eight
Two
If PRPP levels are lower than normal, production of _______________ is affected.
a) Purines
b) Pyrimidines
c) Both purines and pyrimidines
d) Neither purines or pyrimidines
Both purines and pyrimidines
Pyrimidine is broken down to _______________.
a) Acetyl-CoA
b) Malonyl-CoA
c) Uric acid
d) Urea
Malonyl-CoA
What are the 10 essential amino acids?
The 10 essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine, arginine
What animal species can remove free nitrogen as ammonia (toxic) using a lot of water and very little energy?
Fish
What animal species can remove free nitrogen as urea (moderately toxic) using some water and a moderate amount of energy?
Mammals
What animal species can remove free nitrogen as uric acid using very little water, but a lot of energy? (highly toxic)
Birds, reptiles
What amino acids break down into pyruvate?
Alanine, cysteine, glycine, serine, and threonine
What amino acids break down into oxaloacetate?
Asparagine and aspartate
How is alpha-Ketoglutarate produced?
By the degradation of arginine, glutamate, histidine, and proline
What amino acids are converted into Succinyl-CoA?
Isoleucine, methionine, threonine, and valine
7 amino acid degradation products in the Citric Acid Cycle
Pyruvate, Acetyl-CoA, Alpha-Ketoglutarate, Succinyl-CoA, Fumarate, Oxaloacetate, and Glucose
Norepinephrine leads to the production of UCP ____, which is the uncoupling protein involved in the electron transport chain and oxidative phsophorylation.
1
In the Nitrogenase-Catalyzed N2 Reduction cycle, how many ATP are produced in each cycle, and collectively?
2, 16 total (meaning there are 8 cycles between Ferrexoin and Fe-Protein)
For every 2 ammonia that are fixed, _____ ATP are utilized, making this a high energy process.
16
Glucokinase is regulated by ________ while Hexokinase is not.
Insulin
Glucokinase is only accessible to cells in the ___________ and __________. Hexokinase is available to all other cells.
Pancreas, liver
Glucokinase has a _______ binding capacity and can respond _______ than Hexokinase, but is _______ efficient.
higher binding capacity, responds quicker, less efficient
Proteins involved in response to physiological activity typically have _______ halflives than enzymes involved in structural roles.
a) Longer
b) Shorter
c) Similar
d) Changes based on the individual
Shorter
Half-life as a general rule: Structural proteins > Proteins involved in normal physiological processes >Proteins involved in immediate responses like fight or flight.
Degradation of proteins _______________ ATP.
a) Requires
b) Does not require
c) Generates
d) Depends on the protein
Requires
Amino acid catabolism produces _______________ and _______________ as immediate products.
a) NH3, CO2
b) NH3, Glucose
c) NH3, Carbon skeleton
d) NH3, Urea
NH3 and Carbon skeleton
Atmospheric N2 is converted to N-containing biomolecules via _______________.
a) Nitrite
b) Nitrate
c) Ammonia
d) The process of denitrification
Ammonia
Pyruvate can be produced from the following biomolecules:
a) Amino acids
b) Carbohydrates
c) Fatty acids
d) Both amino acids and carbohydrates
Both amino acids and carbohydrates
ATP is stored in the following form:
a) GTP
b) Phosphocreatine
c) Glucose
d) Fatty acids
Phosphocreatine
Cats cannot metabolize carbohydrates well because they lack _______________.
a) Insulin
b) Hexokinase
c) Glucokinase
d) Both hexokinase and glucokinase
Glucokinase
The movement of lactate between the liver and muscle is referred as _______________.
a) Urea cycle
b) AMPK cycle
c) Glucose-Alanine cycle
d) Cori cycle
Cori Cycle
If glycine levels are lower than normal, production of _______________ is affected.
a) Purines
b) Pyrimidines
c) Both purines and pyrimidines
d) Neither purines or pyrimidines
Purines
The following molecules provide feedback inhibition for pyrimidine biosynthesis in E. coli.
a) UDP
b) UTP
c) CTP
d) Both CTP and UTP
CTP
Lipid digestion, absorption, and transport uses lipoproteins. The first lipoprotein type to
be employed is _______________.
a) HDL
b) Chylomicrons
c) VLDL
d) LDL
Chylomicrons
Lipids are stored predominantly in which type of cells?
a) HDL
b) Chylomicrons
c) Adipose cells
d) Muscle cells
Adipose Cells
During lipid digestion, lipids are acted upon by bile acids which allows for their
breakdown by lipases. Which organ produces bile acids?
a) Stomach
b) Gallbladder
c) Small Intestine
d) Liver
Liver-produces bile acids;
the gallbladder stores them
Triacylglycerols are broken down by lipases, and the products are absorbed by the
_______________.
a) Stomach
b) Gallbladder
c) Intestine
d) Liver
Intestine
______________ carries acyl groups across the mitochondrial membrane.
a) ATP
b) NADH
c) FADH2
d) Carnitine
Carnitine
FAD utilized for beta-oxidation of fatty acyl-CoA is replenished through
_______________.
a) Ketogenesis
b) CAC
c) ETC
d) Oxidative Phosphorylation
ETC
Beta-oxidation of fatty acyl-CoA occurs in _______________.
a) Cytosol
b) Peroxisome
c) Glyoxysome
d) Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in _______________.
a) Cytosol
b) Peroxisome
c) Glyoxysome
d) Mitochondria
Cytosol
Each round of mitochondrial beta-oxidation produces _______________.
a) Acetyl-CoA
b) NADH
c) FADH2
d) All of the above
All of the above: Acetyl CoA, NADH, FADH2
The following is an example of ketone bodies
a) Acetone
b) Acetoacetate
c) Malonate
d) Both a) and b)
both Acetone and Acetoacetate
The immediate precursor to cholesterol biosynthesis is _______________.
a) Ketone bodies
b) Triacylglycerols
c) Fatty acids
d) Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Fatty acid synthesis begins with the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to generate
_______________.
a) Acetyl-CoA
b) Malonyl-CoA
c) HMG-CoA reductase
d) Succinate
Malonyl-CoA
Cholesterol synthesis is regulated by the activity and amount of
_______________.
a) Acetyl-CoA
b) Malonyl-CoA
c) HMG-CoA reductase
d) Succinate
HMG-CoA reductase
The LDL receptor keeps circulating cholesterol _______________.
a) Constant
b) Low
c) High
d) Has no effect
Low
Lipases break down ______ and are produced by the __________.
fat molecules broken down
pancreas produces lipases
Chylomicron
a lipoprotein produced in the mucosal cell of the intestine; transports Triacylglycerides out of the intestines and into the lymphatic vessels
Triacylglycerides
3 Carbon chain with oxygen attached to each, and 3 lipids. Broken down by bile, a soap-like hydrophobic & hydrophilic enzyme
Lipases act on the lipid-water interface
act on the hydrophilic part of the lipid molecule
Overall urea cycle reaction
NH3+HCO3- + Aspartate---->>> Urea + Fumarate
uses 3 ATP
Produces 2 ADP
What is tryptophan broken down into?
acetoacetate
What does degradation of leucine and lysine yield?
acetyl coa and acetoacetate
What yields fumarate and acetoacetate
phenylalanine and tyrosine
What are the nonessential amino acids
alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, Glutamine, glycine, proline serine tyrosine
amino acid derived hormones
epinephrine and norepinephrine
Seratonin
GABA
Histamine
How is ammonia incorporated into amino acids
by glutamate synthesis
Where can Brain get energy?
Ketone bodies and glucose
Where is Hexokinase used?
in glycolysis
Where is glucokinase found?
present in liver
- can only work in glucose, requires a high level of glucose for activation which allows for a lot of storage of glucose
What brings together the different metabolic pathways?
Glucose 6 phosphate
Glucose Alanine Cycle
the cycle in which alanine is released from the muscle and is converted to glucose in the liver where it is broken down to remove free ammonia
Hormonal control in a fed state
insulin acts on adipose liver and muscle
GLUT4 activity
takes in glucose from the blood to reduce glucose
in fasted state Pancreas secretes_____ and adrenal Gland secretes___________
Pancreas secretes glucagon to Liver and adipose tissue
Adrenal gland secretes epinephrine to adipose tissue, liver and muscle
effects of AMPK on liver
increases glycolysis
increases fatty acid oxidation
decreases glycogen synthesis
decreases gluconeogenesis
effect of AMPK on muscle
inhibits glycogen synthesis
increases fatty acid oxidation
Diabetes may be caused by
-insufficient production of insulin
-insensitivity to its presence
What causes gout?
high levels of uric acid
What are purines broken into?
Uric Acid
In fatty acid biosynthesis, _______________ is an electron donor.
NADPH