Anatomy Ch. 5 - 2 (Axial Skeleton)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
How many Vertebrae are present before birth? How many fuse?
33, 9
How many vertebrae make up the cervical
7
How many vertebrae make up the thoracic
12
How many vertebrae make up the lumbar
5
Primary curvatures
curves of thoracic and sacral regions, present when born.
Secondary curvatures
curves of cervical and lumbar
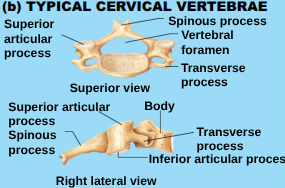
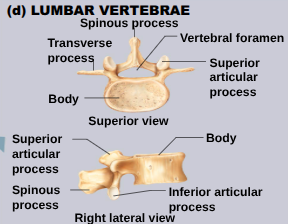
Vertebrae Body (Centrum)
disc-like and weight bearing part, that sits anteriorly in the column.
Vertebral arch
formed from the joining of all posterior extensions (lamina and pedicle)
Vertebral foramen
canal through which the spinal cord passes
Transverse Processes
two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
spinous process
single projection arising from the posterior aspect of the cerebral arch (the 2 laminae fused together)
superior and inferior articular processes
paired projects lateral to the vertebral foramen, allowing a vertebra to form joints with adjacent vertebrae.
Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)
Smallet, have small holes
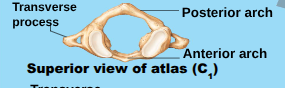
Atlas (C1)
no body, superior surfaces of its transverse processes contain large depression that reive the occipital condyles of the skull.
Axis (C2)
has a large upright process, the odontoid process (or dens) which acts as a pivot for the rotation of the atlas and skull.

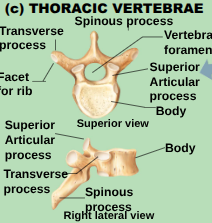
Thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12)
larger than the cervical vertebrae. Body is heart-shped and has two costal demifacets (articulation surfaces) on each side that reviece the heads of the ribs. Spinous process is long and hooks.
Lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
Have massive, block like bodies and short hatched-shaped spinous processes. Most stress of the spine occurs here, so they are the sturdiest.
Sacrum
Formed from the fusion of 5 vertebrae.
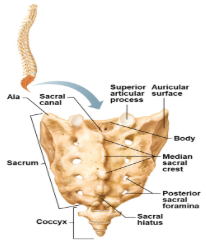
What does the Sacrum superiorly and inferiorly articulate with?
Superiorly articulates with L5, and inferiorly with the coccyx.
What articulates laterally with the hip bones forming the sacroiliac joints?
alae
The median sacral crest
Lies on its dorsal midline, aremnant of the fusion of the 5 vertebrae
Coccyx
Tailbone, formed from the fusion of 3-5 small vertebae.
Sternum (breastbone)
Flat bone, easy site for a bone marrow aspiration since it is a site of
hematopoiesis and is close to the surface of the body.
How many ribs are there (true and false)?
True ribs- pairs 1-7, false ribs- pairs 8-12.
True vs. false ribs
True attach directly to the sternum by costal cartilages
False attach indirectly or not at all to the sternum
What is special about pairs 11 & 12?
Floating ribs, do not attach anteriorly at all.
Cervical vs. Thoracic vs. Lumbar
Cervical- small, highly mobile, special holes (transverse forming).
Thoracic - medium, heart-shaped bodies, connect to ribs, less mobile.
Lumbar - largest, kidney-shaped, thickest, bearing most weight with wide, short processes for strength.
Scoliosis
Abnormal lateral curvature
Kyphosis
exaggerated thoracic curvature (convex)
Lordoisis
exaggerated lumbar curvature (concave)
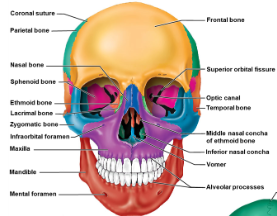
Paranasal sinuses
Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity
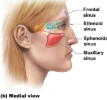
Functions of paranasal sinuses
Lighten the skull, amplify sounds made as we speak.
Name the 4 paranasal sinuses
Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoidal, maxillary
Hyoid bone
Closely talked to mandible and temporal bones. Does not articulate with another bone.

Fetal skull is ___ body length compared to adult skull, which is ___ body length
1/4, 1/8
Fontanels
fibrous membranes connecting the cranial bones. Convert to bone within 24 months after birth
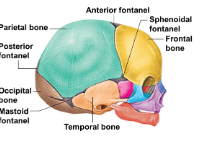
Name the 8 cranial bones that make up the Adult skull
Frontal bone, occipital bone, ethmoid bone, sphenoid bone, parietal bones (pair), temportal bones(pair).
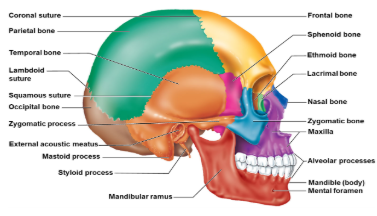
Name the 14 facial bones that make up the Adult skull
Maxilae (pair), palatine bones (pair), lacrimal bones (pair), zygomatic bones (pair), ansal bones(pair), vomer bone, inferior nasal concahe (pair), mandible.