hismt: fundamentals of information systems
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
information system
arrangement of data (information), processes, people, and information technology that interact to collect, process, store, and provide as output the information needed to support the organization
2
New cards
They support business operations
three vital roles of IS in an organization:
to speed up our transactions in any organization. If we are going to put it in the healthcare sector, specifically in the laboratory, this is where we request lab tests for the patients.
to speed up our transactions in any organization. If we are going to put it in the healthcare sector, specifically in the laboratory, this is where we request lab tests for the patients.
3
New cards
They support managerial decisions
three vital roles of IS in an organization:
In decision making of managers, this will be coming from the reports that can be extracted from the information systems
In decision making of managers, this will be coming from the reports that can be extracted from the information systems
4
New cards
It can provide strategic competitive advantage
three vital roles of IS in an organization:
It gives you a competitive advantage if you already have information systems.
It gives you a competitive advantage if you already have information systems.
5
New cards
health information system
refer to any system that “captures, stores, manages or transmits information related to the health of individuals or the activities of organizations that work within the health sector.
6
New cards
patients
The stakeholders of the hospitals are ____
7
New cards
information technology
is a contemporary term that describes the combination of computer technology (hardware and software) with data and telecommunications technology
8
New cards
models in IT
Define the way we learn about the world, interpret what we see and apply our knowledge to effect change, whether that is through our own actions or using technology such as a computer
9
New cards
hardwarre
physical components of the computers
any digital device
any digital device
10
New cards
software
Collective term for computer programs, which are sets of instructions to computer hardware.
11
New cards
system software
operating systems such as windows and ios. They manage the operations of the hardware
12
New cards
application
software designed for specific tasks.
13
New cards
database
Collections of interrelated data that are shared by many units and contribute to productivity and efficiency
14
New cards
query
Database is a place where your data is collected, stored, and retrieved through a ___ or asking one or more specific criteria
15
New cards
big data
term used for a truly massive amount of data that can be collected and analyzed
16
New cards
variety, volume, velocity
big data contains: greater ____, increasing ____, high rate of ____
17
New cards
data
- basic facts
- raw alpha-numeric values that we obtain from acquisition methods
- objective
- has no meaning
- unprocessed
- quantifiable
- anything and everything
- raw alpha-numeric values that we obtain from acquisition methods
- objective
- has no meaning
- unprocessed
- quantifiable
- anything and everything
18
New cards
information
- data with context
- is when your data is processed, organized, and structured / processed data
- should be objective
- has meaning
- processed
- quantifiable
- stats and infographics
- is when your data is processed, organized, and structured / processed data
- should be objective
- has meaning
- processed
- quantifiable
- stats and infographics
19
New cards
knowledge
- processed information with meaning
- it is unique to each individual because there’s a difference in interpreting and assigning meaning to the information
- subjective
- meaning with a specific purpose
- processed and understood
- not quantifiable
- answers to questions
- it is unique to each individual because there’s a difference in interpreting and assigning meaning to the information
- subjective
- meaning with a specific purpose
- processed and understood
- not quantifiable
- answers to questions
20
New cards
action; the authority and capacity
How you put ___ into that knowledge you need past experience, insights, how you interpret information but also you should have ___ to implement a decision
21
New cards
knowledge base
Collection of rules can be thought of as a database containing elements of knowledge
22
New cards
ontology
Set of concepts understood in a knowledge base and how these concepts are arranged meaningfully
rules in knowledge base will be used here
explains the entities in your knowledge base
give meaning to the rules
rules in knowledge base will be used here
explains the entities in your knowledge base
give meaning to the rules
23
New cards
classification and explanation
Ontology seeks the ___ of entities in your knowledge base
24
New cards
rules of inference
This is when there’s already logic
Specify how a knowledge base can be applied to a database
Specify how a knowledge base can be applied to a database
25
New cards
No Computer Interpretation
In 100% of their interpretative model, human is the one doing it.
It is possible that they don’t have an information system.
It is possible that they don’t have an information system.
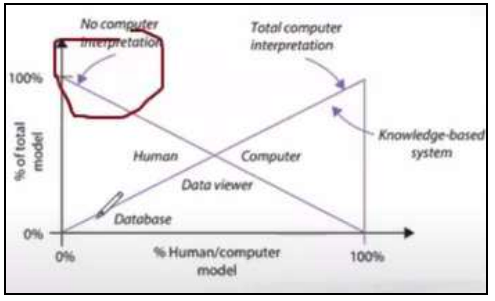
26
New cards
100% Total Computer Interpretation
computers solely are the ones interpreting the data
based on the rules entered, hence basing on the KNOWLEDGE BASED SYSTEM
based on the rules entered, hence basing on the KNOWLEDGE BASED SYSTEM
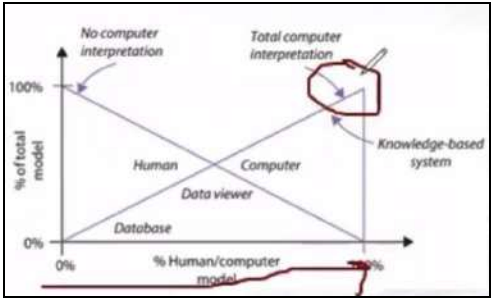
27
New cards
shared burden
The best method would be if there is a ___ between humans and computers in interpretation.
28
New cards
people and procedures
The most neglected but most important components of information systems
29
New cards
people
○ information systems professionals and users
○ analyze organizational information needs
○ design and construct information systems
○ write computer programs
○ operate the hardware and maintain software
○ without the intervention of people, no one would input the rules and make sure that the system is tailored fit to the organization
○ analyze organizational information needs
○ design and construct information systems
○ write computer programs
○ operate the hardware and maintain software
○ without the intervention of people, no one would input the rules and make sure that the system is tailored fit to the organization
30
New cards
procedures
○ rules for achieving optimal and secure operations in data processing
○ include priorities in dispensing software applications and security measures
○ required so that the people who run the system would know that there is knowledge to follow
○ include priorities in dispensing software applications and security measures
○ required so that the people who run the system would know that there is knowledge to follow
31
New cards
telecommunications
○ communication over distance
○ primarily communication of bits representing many forms of data and information
○ when you use a hardware with a software inside and have connections
○ can be through wires, ethernet cables, fiber optics, wireless wifi
○ primarily communication of bits representing many forms of data and information
○ when you use a hardware with a software inside and have connections
○ can be through wires, ethernet cables, fiber optics, wireless wifi
32
New cards
networks
○ combination of devices including hardware connected to each other through one of the communication media (cables, radio waves, etc.)
33
New cards
Local Area Network (LAN)
types of networks:
within a specific area
within a specific area
34
New cards
Wide Area Network (WAN)
types of networks:
more dispersed
more dispersed
35
New cards
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
types of networks:
within the city
within the city
36
New cards
Executive Information Systems (EIS)
types of information systems:
■ highly individualized
■ often custom-made
■ highly individualized
■ often custom-made
37
New cards
Management Information Systems (MIS)
types of information systems:
■ sales management systems
■ inventory control systems
■ budgeting systems
■ personnel/human resources management systems
■ sales management systems
■ inventory control systems
■ budgeting systems
■ personnel/human resources management systems
38
New cards
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
types of information systems:
■ computer supported cooperative work systems
■ logistics systems
■ financial planning systems
■ computer supported cooperative work systems
■ logistics systems
■ financial planning systems
39
New cards
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
types of information systems:
■ payroll systems
■ order processing systems
■ reservation systems
■ payment or funds transfer systems
■ payroll systems
■ order processing systems
■ reservation systems
■ payment or funds transfer systems
40
New cards
Process Control Systems (PCS)
types of information systems:
monitor and control physical processes
monitor and control physical processes
41
New cards
Operations Support Systems
types of information systems:
○ roles include processing business transactions, controlling industrial processes, supporting enterprise communications and collaborations, and updating corporate databases efficiently
○ e.g. Sales and Inventory Systems, Accounting Systems, Result Retrieval and Printing (LIMS)
○ roles include processing business transactions, controlling industrial processes, supporting enterprise communications and collaborations, and updating corporate databases efficiently
○ e.g. Sales and Inventory Systems, Accounting Systems, Result Retrieval and Printing (LIMS)
42
New cards
Management Support Systems
types of information systems:
○ provides information and support for decision making by all types of managers
○ usually involve infographics
○ e.g. Sales Analysis, Product Performance, Inventory, Competitor Analysis, Product Pricing
○ provides information and support for decision making by all types of managers
○ usually involve infographics
○ e.g. Sales Analysis, Product Performance, Inventory, Competitor Analysis, Product Pricing
43
New cards
Management Information Systems
types of information systems:
○ under Management Support
○ used to extract reports for inventory levels
■ e.g. amount of arabica coffee available
○ data acquired here is analyzed to make sound decisions
○ under Management Support
○ used to extract reports for inventory levels
■ e.g. amount of arabica coffee available
○ data acquired here is analyzed to make sound decisions
44
New cards
Specialized Processing Systems
types of information systems:
○ can support either operations or management applications
○ e.g. Human Resource Management, Customer Problem Resolution Systems
○ can support either operations or management applications
○ e.g. Human Resource Management, Customer Problem Resolution Systems
45
New cards
systems development life cycle (SDLC)
conceptual model where project management of the information system is presented
46
New cards
plan
systems development life cycle (SDLC):
● Review project requests
● Prioritize project requests
● Allocate resources
● Identify project development team
Conduct a feasibility study when problems arise
● Review project requests
● Prioritize project requests
● Allocate resources
● Identify project development team
Conduct a feasibility study when problems arise
47
New cards
analyze
systems development life cycle (SDLC):
● Conduct preliminary investigation
● Perform detailed analysis activities
- Study current system
- Determine user requirements
- Recommend solution
Get information, and analyze the information based on the need and develop a functional requirement for the system.
● Conduct preliminary investigation
● Perform detailed analysis activities
- Study current system
- Determine user requirements
- Recommend solution
Get information, and analyze the information based on the need and develop a functional requirement for the system.
48
New cards
design
systems development life cycle (SDLC):
● Acquire hardware and software, if necessary
● Develop details of system
What hardware do we need? Can you let me know the specs? What model do we need for the system?
● Acquire hardware and software, if necessary
● Develop details of system
What hardware do we need? Can you let me know the specs? What model do we need for the system?
49
New cards
develop/implement
systems development life cycle (SDLC):
● Develop programs, if necessary
● Install and test the new system
● Train users to Convert new system
This is when we already acquire the hardware. Next, we train the ones who will use this, modify the system and convert the old system to the new system.
● Develop programs, if necessary
● Install and test the new system
● Train users to Convert new system
This is when we already acquire the hardware. Next, we train the ones who will use this, modify the system and convert the old system to the new system.
50
New cards
maintain/suppoirt
systems development life cycle (SDLC):
● Conduct post-implementation system review
● Identify errors and enhancements
● Monitor system performance
We have a post-implementation review. Which among these do not fit the system? Despite the presence of the system, it takes 1.5 hours to get the results instead of 1 hour? Why do we have to manually type the results?
● Conduct post-implementation system review
● Identify errors and enhancements
● Monitor system performance
We have a post-implementation review. Which among these do not fit the system? Despite the presence of the system, it takes 1.5 hours to get the results instead of 1 hour? Why do we have to manually type the results?
51
New cards
database model
Refers to the general logical structure in which records are stored within a database and the method used to establish relationships among the records
52
New cards
Hierarchical and Network Model
database model:
Oldest models; they are still used in some databases but are no longer used in the newly constructed databases because they turn obsolete
Oldest models; they are still used in some databases but are no longer used in the newly constructed databases because they turn obsolete
53
New cards
Relational and Object-oriented models
database model:
Most used models; widely used; used by most of the databases are designed by them
Most used models; widely used; used by most of the databases are designed by them
54
New cards
No- SQL and Data Warehouse
database model:
Rooted from the relational and object-oriented models
Rooted from the relational and object-oriented models
55
New cards
Object-oriented models
- stores data as objects
- provides class hierarchy
- complex
- not wide adopted
- can store graphics, images, or videos
- provides class hierarchy
- complex
- not wide adopted
- can store graphics, images, or videos
56
New cards
Relational data base
- stores data as tables, columns, rows
- no class hierarchy
- simple
- standard models are available
- cannot store graphics, images, or videos
- no class hierarchy
- simple
- standard models are available
- cannot store graphics, images, or videos
57
New cards
Object - oriented database
○ Access data at a more granular level
○ As objects (each piece of information is an object)
○ Complex because it can store graphics, images, or videos
○ As objects (each piece of information is an object)
○ Complex because it can store graphics, images, or videos
58
New cards
Relational database
○ The entire table would need to be locked to update one row.
○ Process data as tables
○ Simple because graphics, images, or videos cannot be added
○ A database structured to recognize relations between stored items of information
○ Process data as tables
○ Simple because graphics, images, or videos cannot be added
○ A database structured to recognize relations between stored items of information
59
New cards
Object database management system (ODBMS)
a database management system (DBMS) that supports the modeling and creation of data as objects
60
New cards
NO-SQL database
- provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.
- focuses on scalability, performance, and high availability therefore, the downfall is that it is less functional compared to relational database.
- focuses on scalability, performance, and high availability therefore, the downfall is that it is less functional compared to relational database.
61
New cards
great quantities of data is important
No SQL will be used when
62
New cards
data warehouse
- system used for reporting and data analysis
- central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources
- central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources
63
New cards
reduce redundant data and to save storage space
relational database:
tables and joins are complex since they are normalized (for RDMS). why?
tables and joins are complex since they are normalized (for RDMS). why?
64
New cards
Relational modeling techniques
relational database:
entity
entity
65
New cards
write operation
relational database:
optimized for?
optimized for?
66
New cards
analysis queries
relational database:
low performance for?
low performance for?
67
New cards
to reduce the response time for analytical queries.
data warehouse:
The tables and joins are simple since they are denormalized. why?
The tables and joins are simple since they are denormalized. why?
68
New cards
modeling techniques are used for the data warehouse design
data warehouse:
data
data
69
New cards
read operations
data warehouse:
optimized for?
optimized for?
70
New cards
analytical queries
data warehouse:
high performance for?
high performance for?