Ch6: Drugs and their Influences
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are Agonists?
Substances that mimics or enhances the effect of a neurotransmitter.
What are Antagonists?
Substances that operate against the effect of a neurotransmitter.
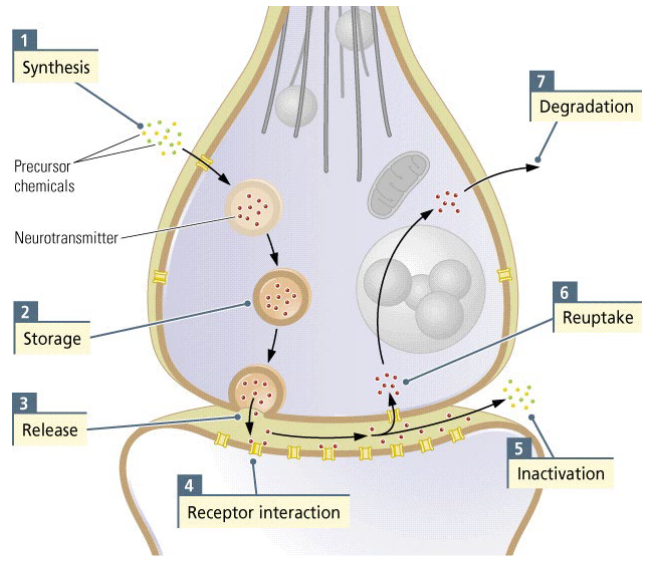
What are the 7 ways in which drugs can influence the synapse?
Synthesis
Storage
Release
Receptor interaction
Inactivation
Reuptake
Degradation
What are the examples of Drug activation on Acetylcholine synapse??
Ach synapse between motor neurons and muscles.
Ach agonists excite muscles → increase muscle tone.
Ach antagonists inhibit muscles → decrease muscle tone.
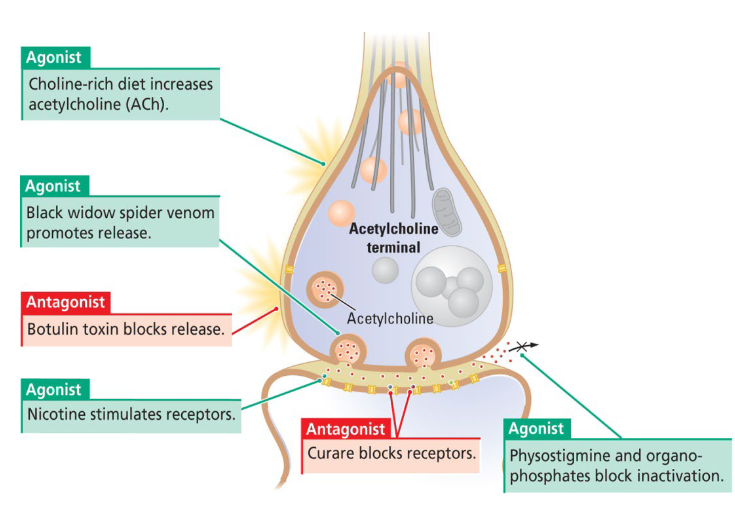
What does a Choline-rich diet do on the Acetylcholine synapse?
Agonist: choline-rich diet increases acetylcholine (Ach).
What impact does Black window spider venom have on Acetylcholine synapse?
Agonist: black widow spider venom promotes release.
What impact does Botulin have on the Acetylcholine impact?
Antagonist: botulin toxin blocks release.
What impact does Nicotine have on Acetylcholine synapse?
Agonist: nicotine stimulates receptors.
What impact does Curare have on Acetylcholine synapse?
Antagonist: curare blocks receptors.
What impact does Physostigmine and organo-phosphates have on Acetylcholine synapse?
Agonist: physostigmine and organo-phosphates block inactivation.
What are Psycholeptics?
Substances that inhibit psychological functions.
What are examples of Psycholeptics?
Sedatives and hypnotics (barbiturates, alcohol)
Anxiolytics (benzodiazepines)
Antipsychotics (chlorpromazine, haloperidol (haidol)
Mood regulators (lithium)
What are Psychoanaleptics?
Substances that stimulate psychological functions.
What are examples of Psychoanaleptics?
Antidepressants (MAO-inhibitators, TCAs, SSRIs)
Stimulants (Amphetamine, cocaine, caffeine, nicotine).
What are Psychodysleptics?
Substances that disorganize psychological functions.
What are examples of Psychodysleptics?
Narcotic analgesics (Morphine, heroin)
Hallucinogens (LSD, mescaline, marijuana)