Lab 2: Osteology: The Axial Skeleton (Excluding Head/Face and Foramen Chart)
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
axial skeleton
consists of 80 bones
5 major functions of skeletal system
1. support
2. movement
3. protection
4. storage of minerals
5. protection of blood cells
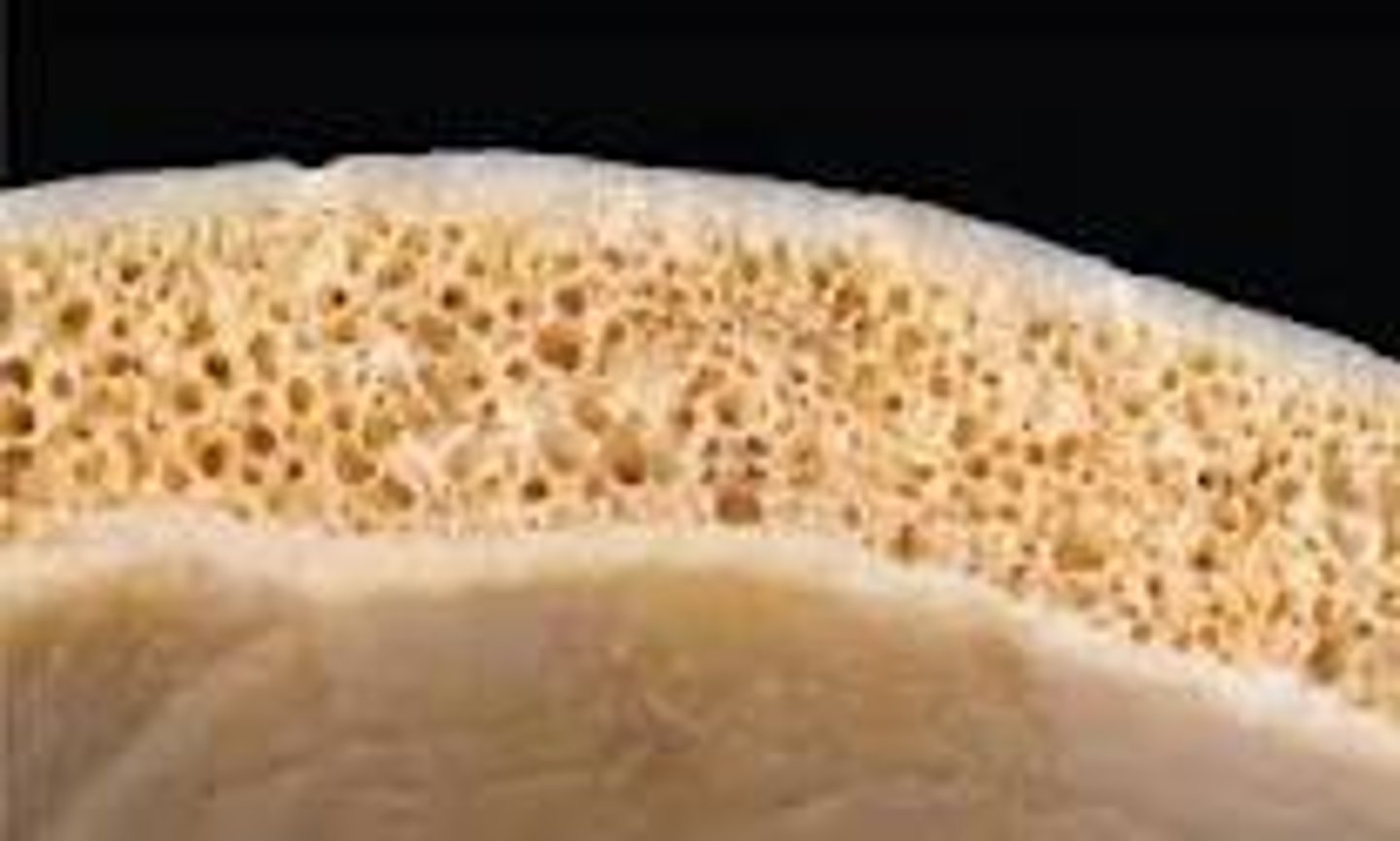
compact bone
looks smooth and homogeneous
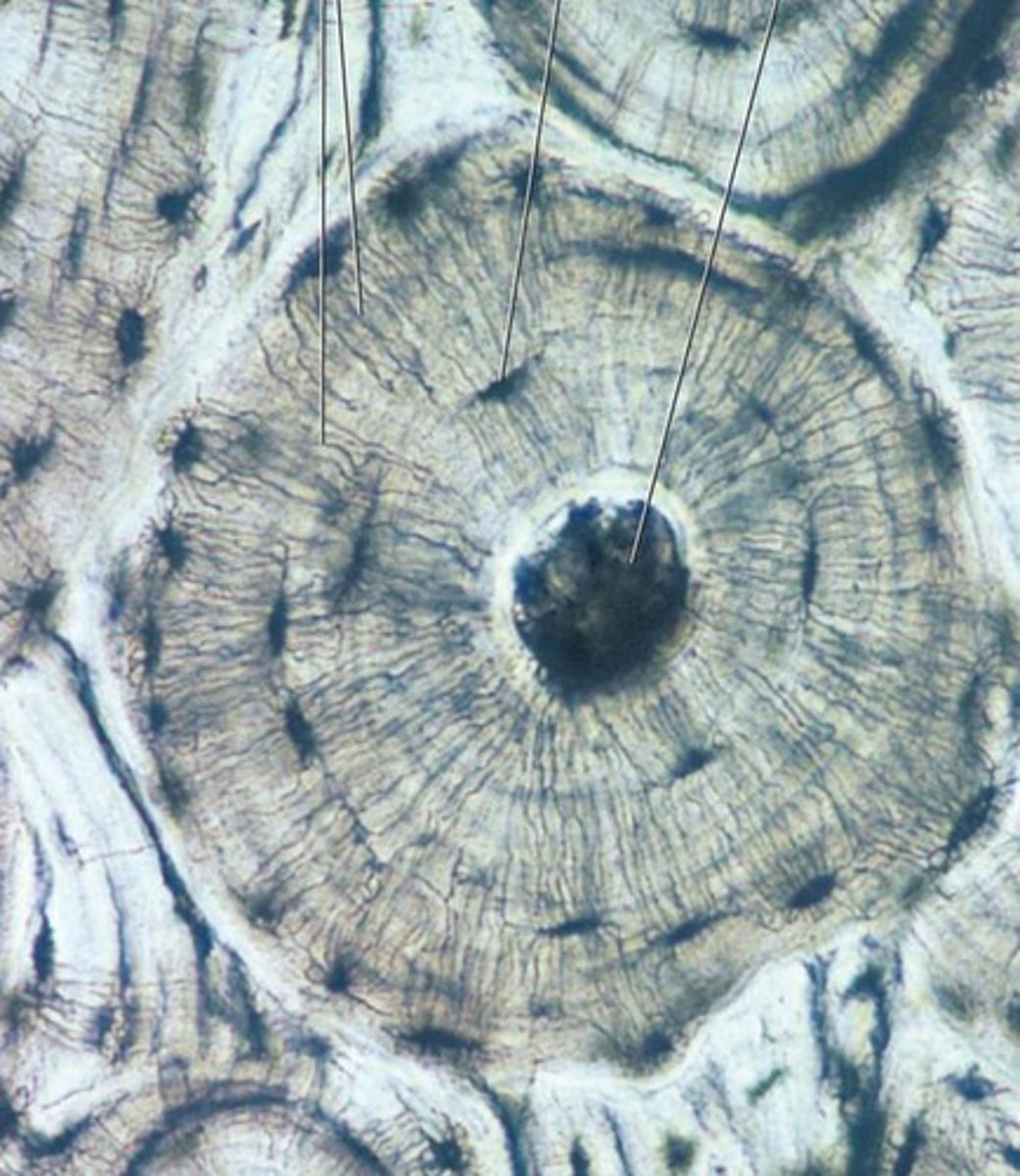
spongy bone
composed of small trabeculae (tiny beams and struts) of bone with lots of open spaces
4 bone classifications (gross anatomy)
long, short, flat, and irregular
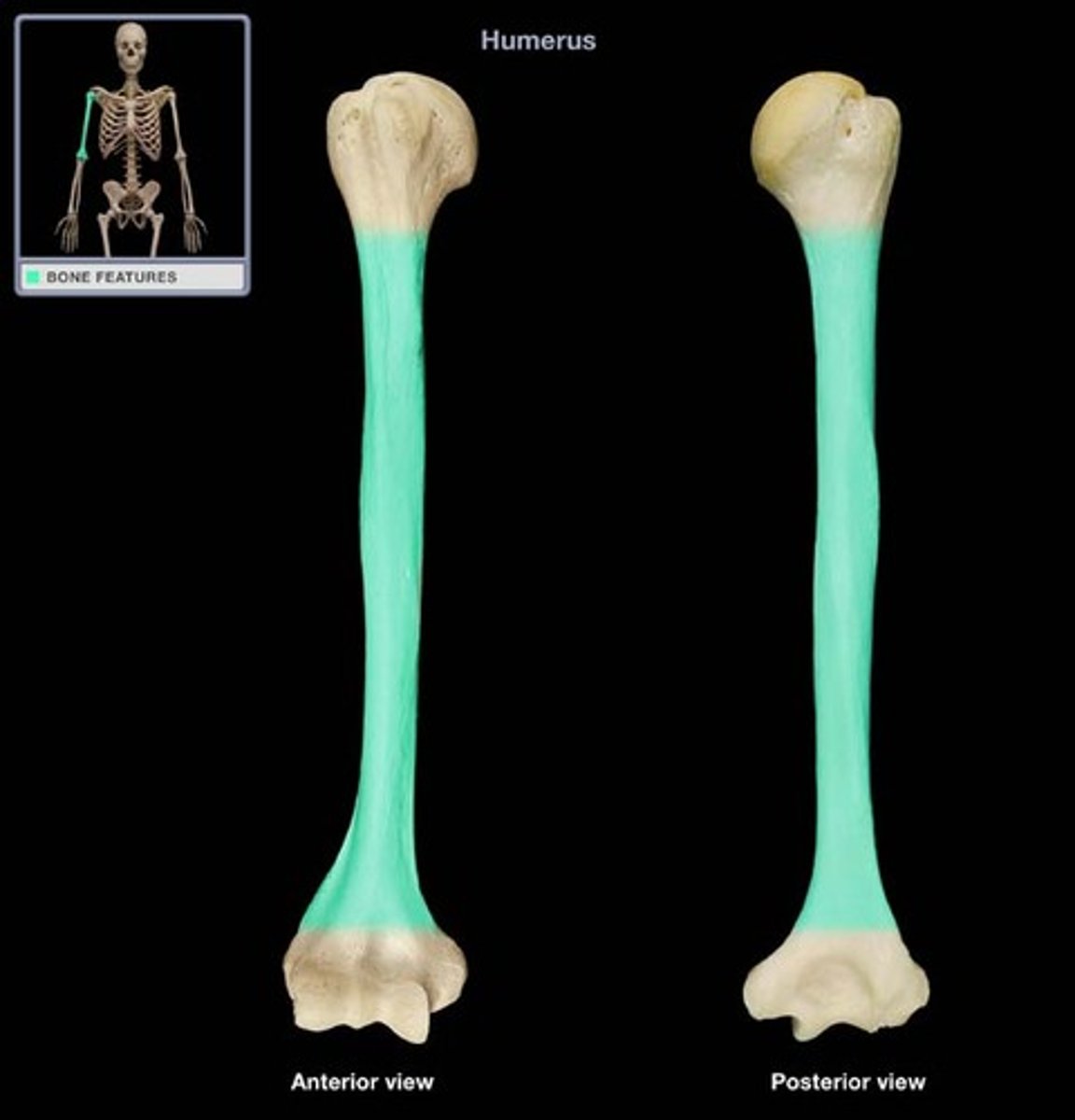
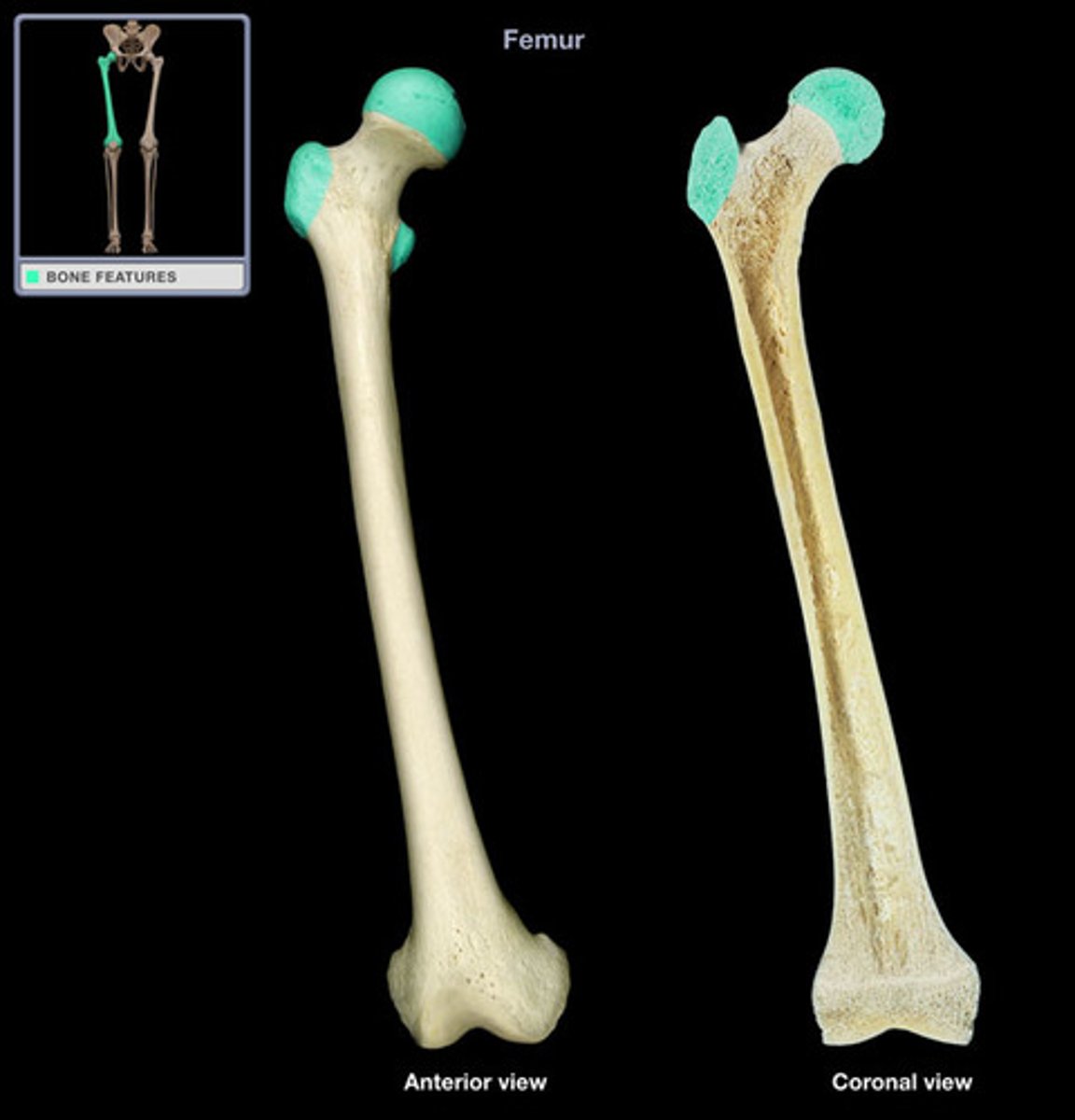
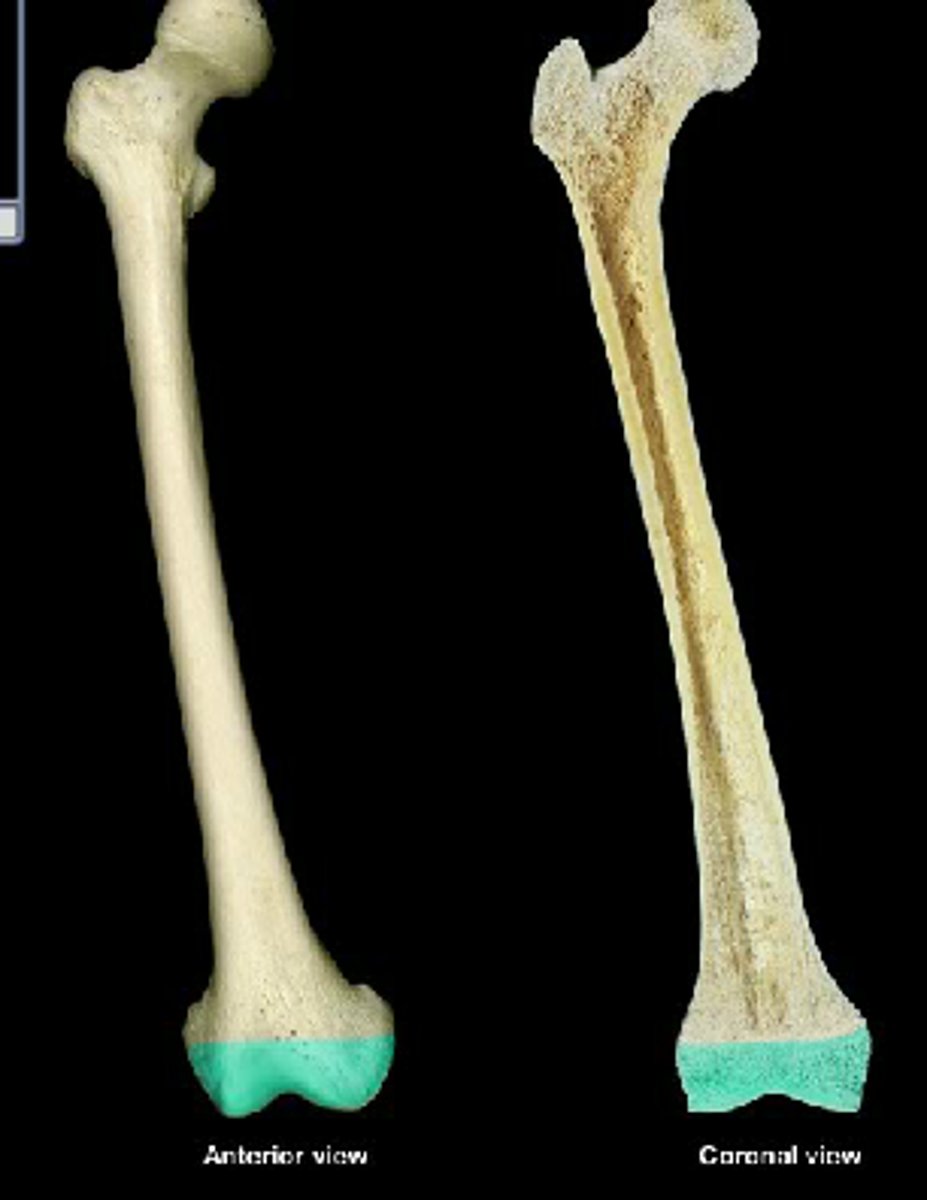
long bones
- longer than they are wide
- generally consist of a shaft with heads at either end
- primarily composed of compact bone
short bones
- roughly cube shaped
- contain more spongy bone than compact bone
flat bones
- generally flattened along a major aspect of their geometry, but can be curved
- two wafer-like layers of compact bone between a layer of spongy bone
irregular bones
do not fit into the other major 4 categories due to their morphology, vertebra
periosteum
- what encapsulates the bone
- tough fibrous membrane that appears glossy
- covers the compact bone surface
- composed of 2 layers
- outer fibrous layer where muscle tendons and bone ligaments attach
- inner cellular layer that produces osteoblasts
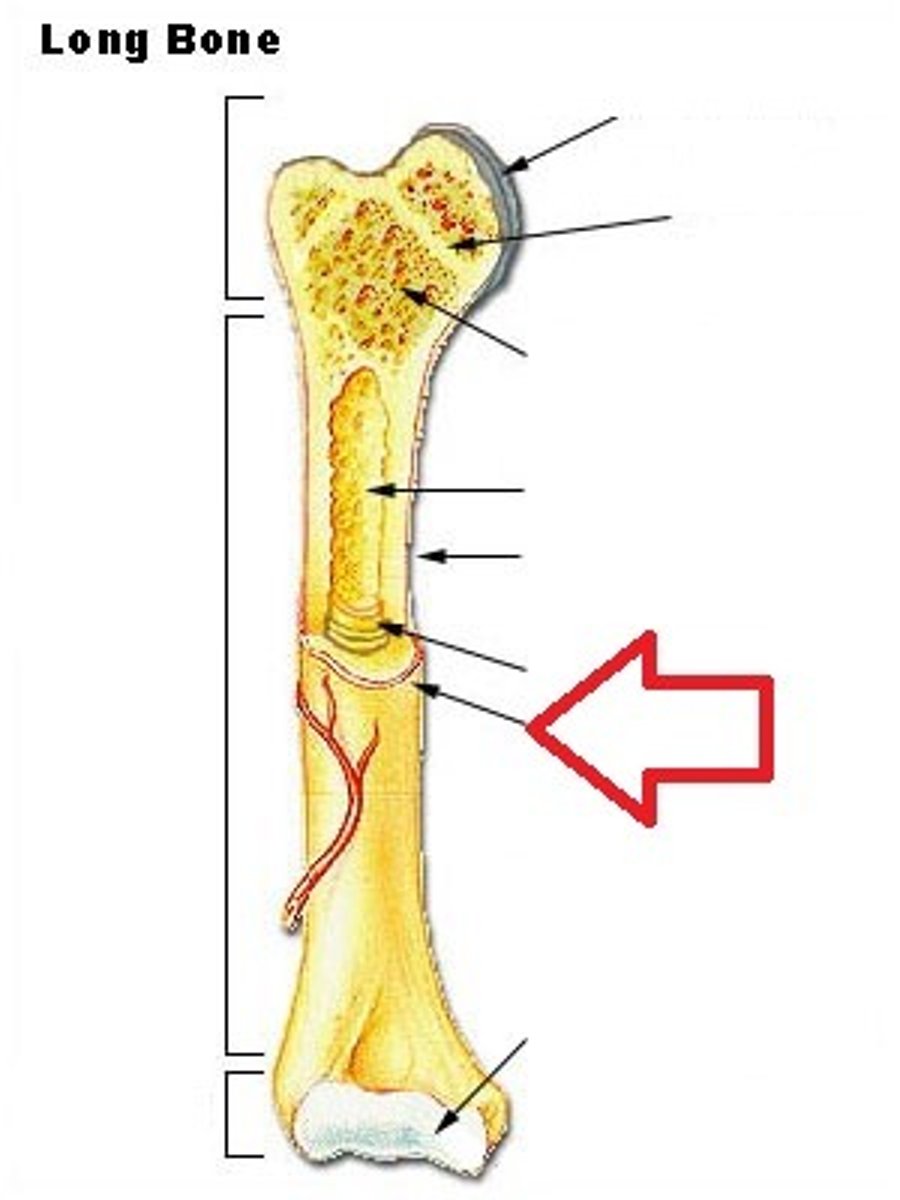
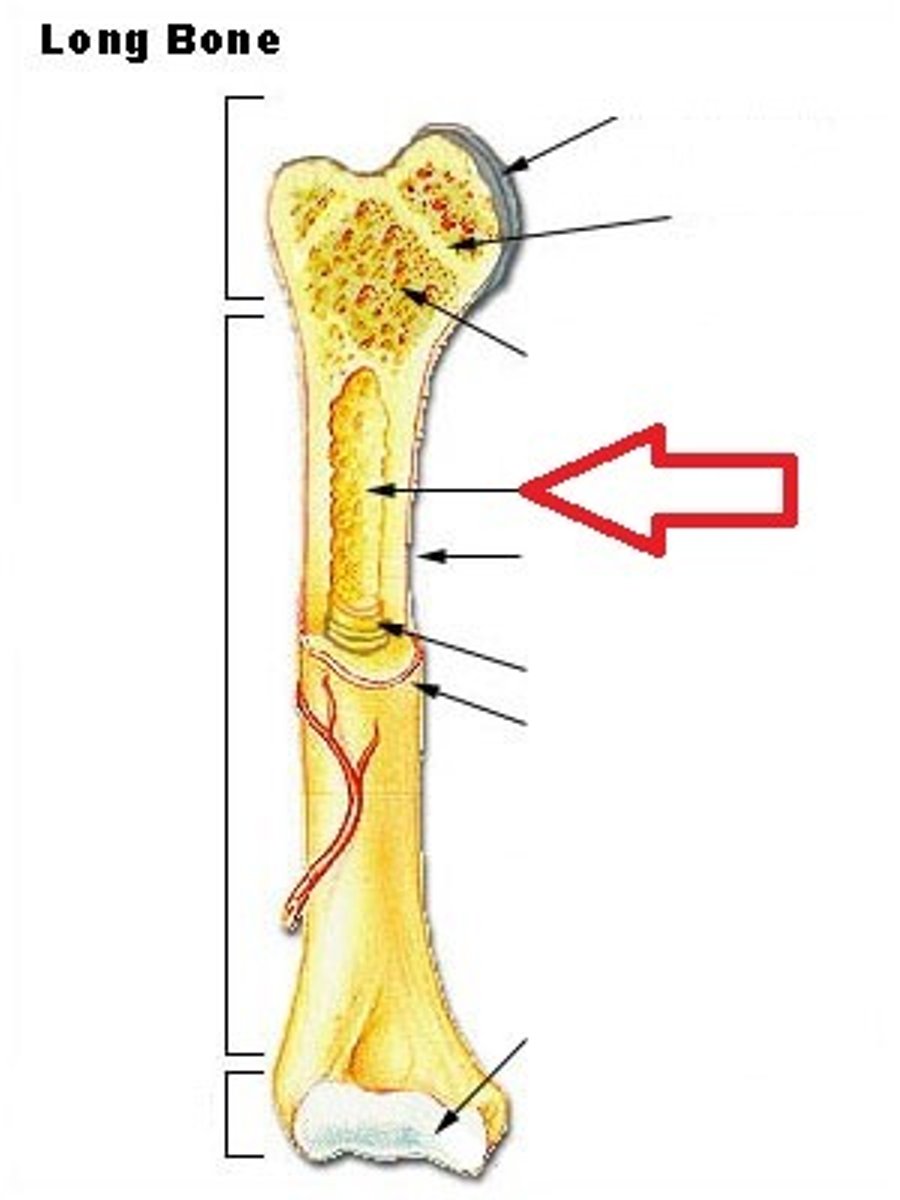
diaphysis
- long, central shaft of the bone
- wall is made of compact bone
- inside is hollow
proximal epiphysis
on the end of the long bone closest to the trunk of the body
distal epiphysis
on the end of the long bone furthest from the trunk of the body
articular cartilage
a layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the place where the epiphysis articulates with another bone
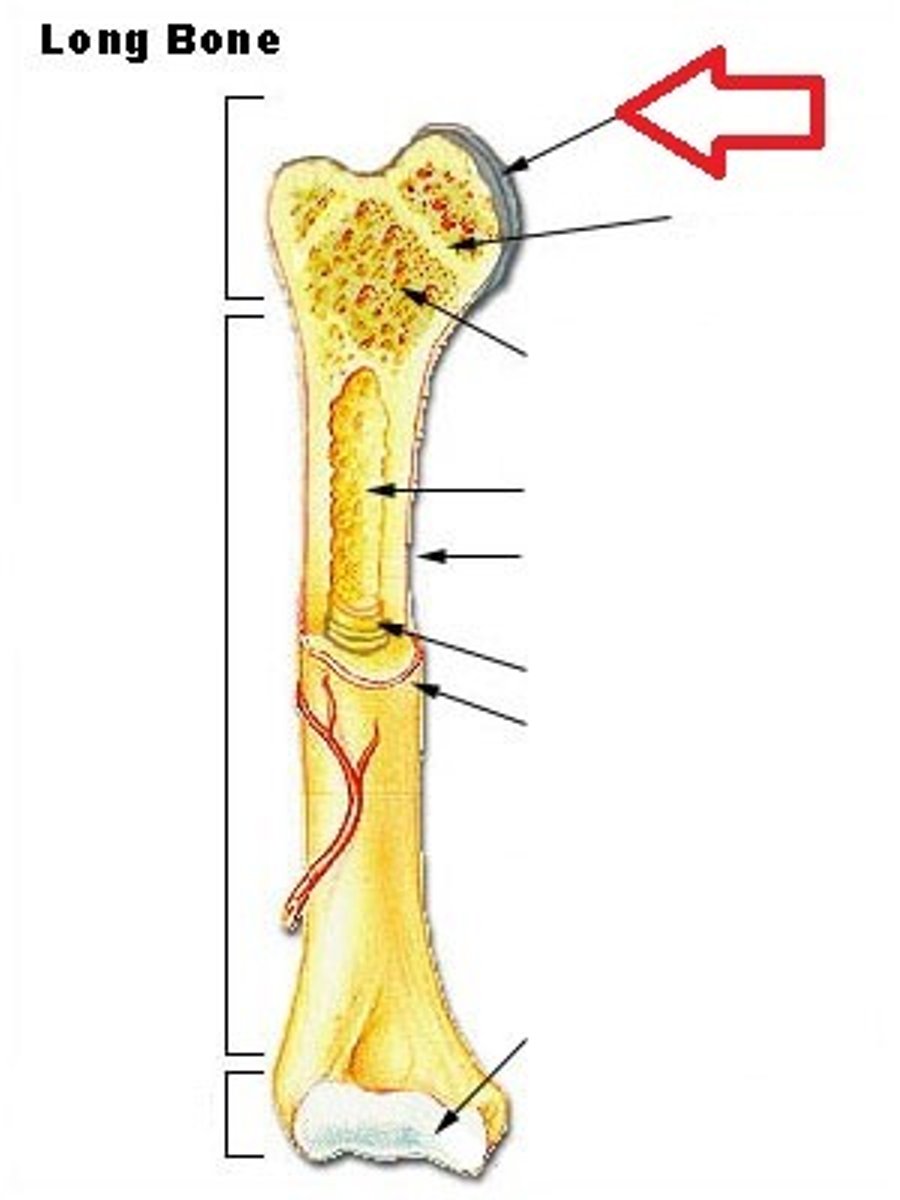
marrow (medullary) cavity
the hollow interior of the diaphysis that contains yellow marrow
yellow marrow
high concentration of lipids within the medullary cavity
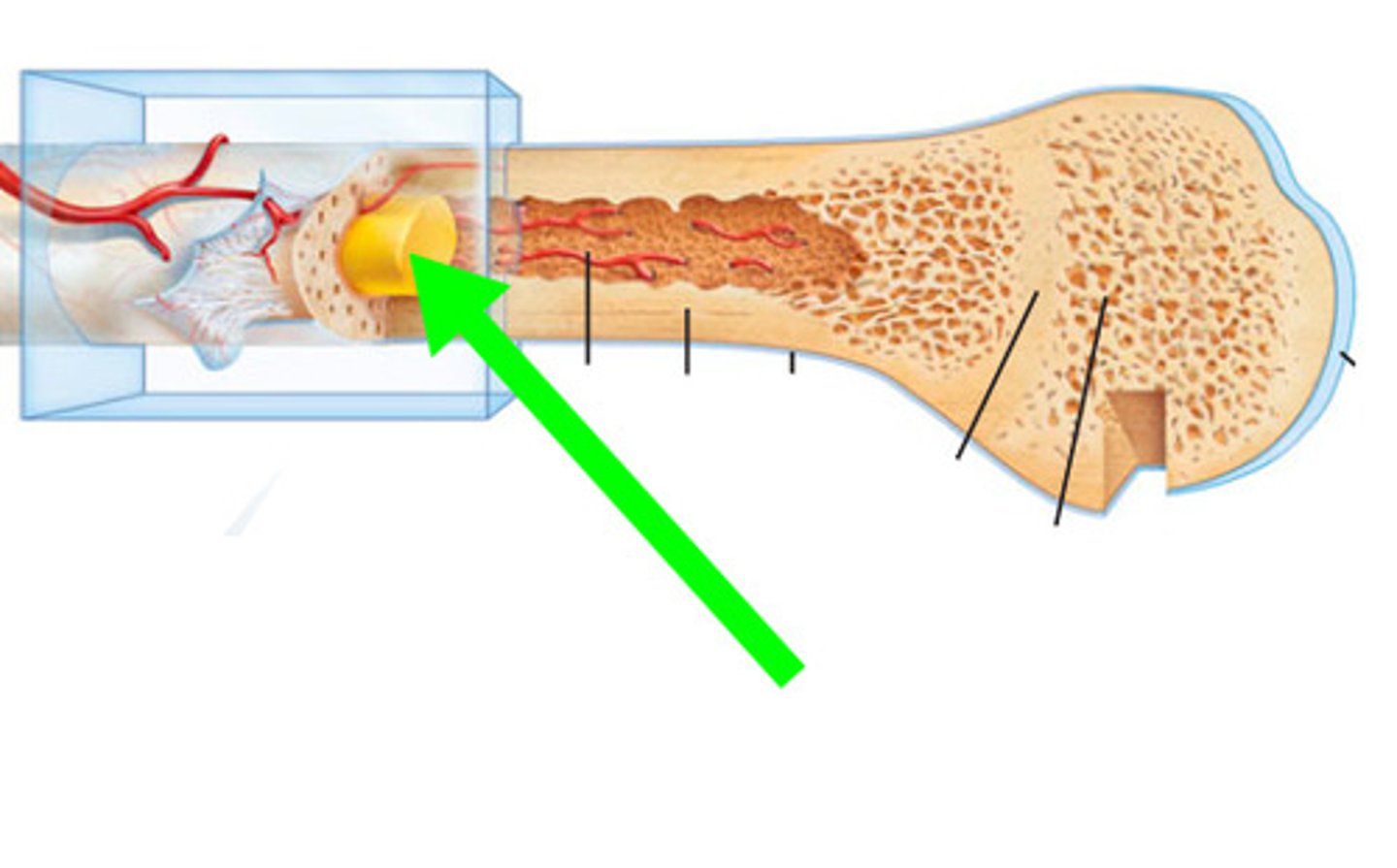
endosteum
lines the medullary cavity
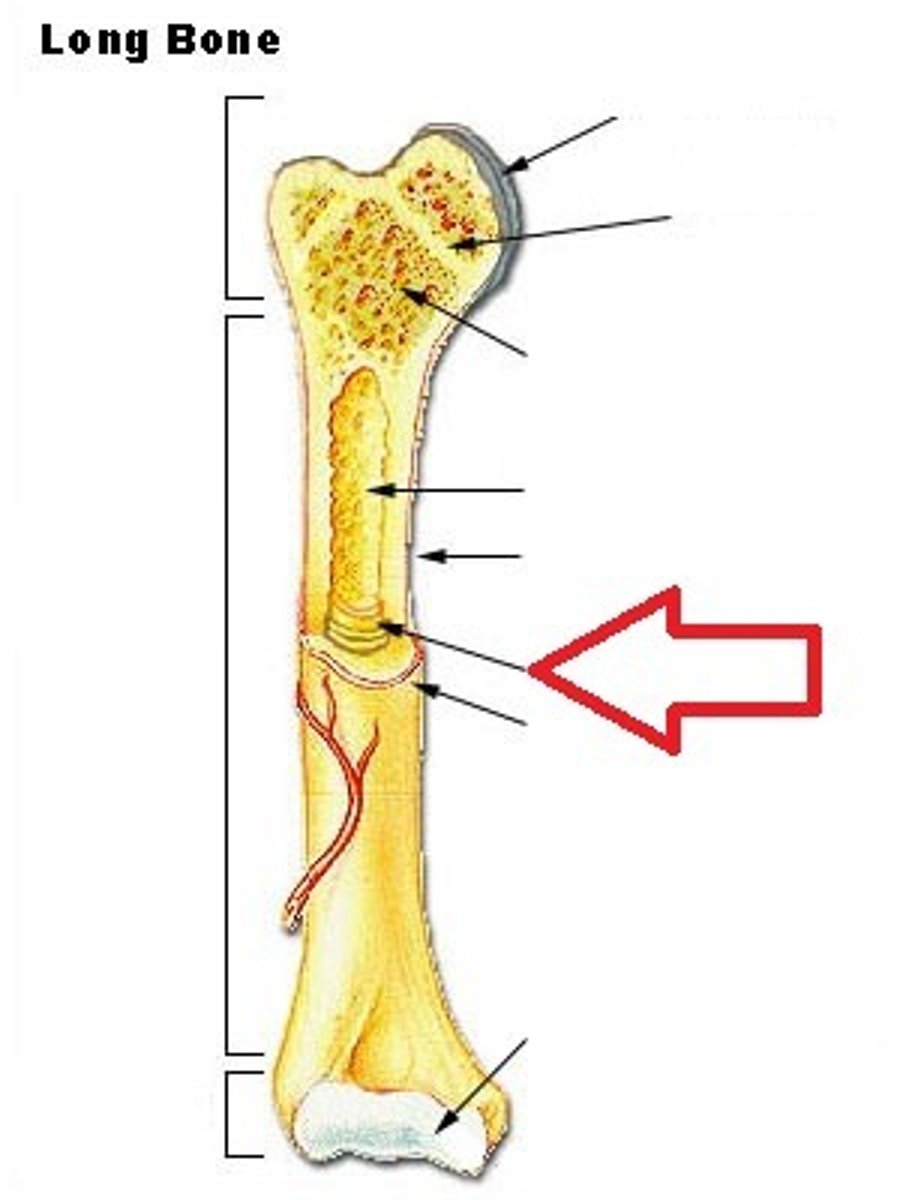
metaphysis
the space between the diaphysis and either epiphysis

epiphyseal line
- formation indicates bone growth/bone transition from juvenile stage to adult stage
- bony remnant of the growth plate
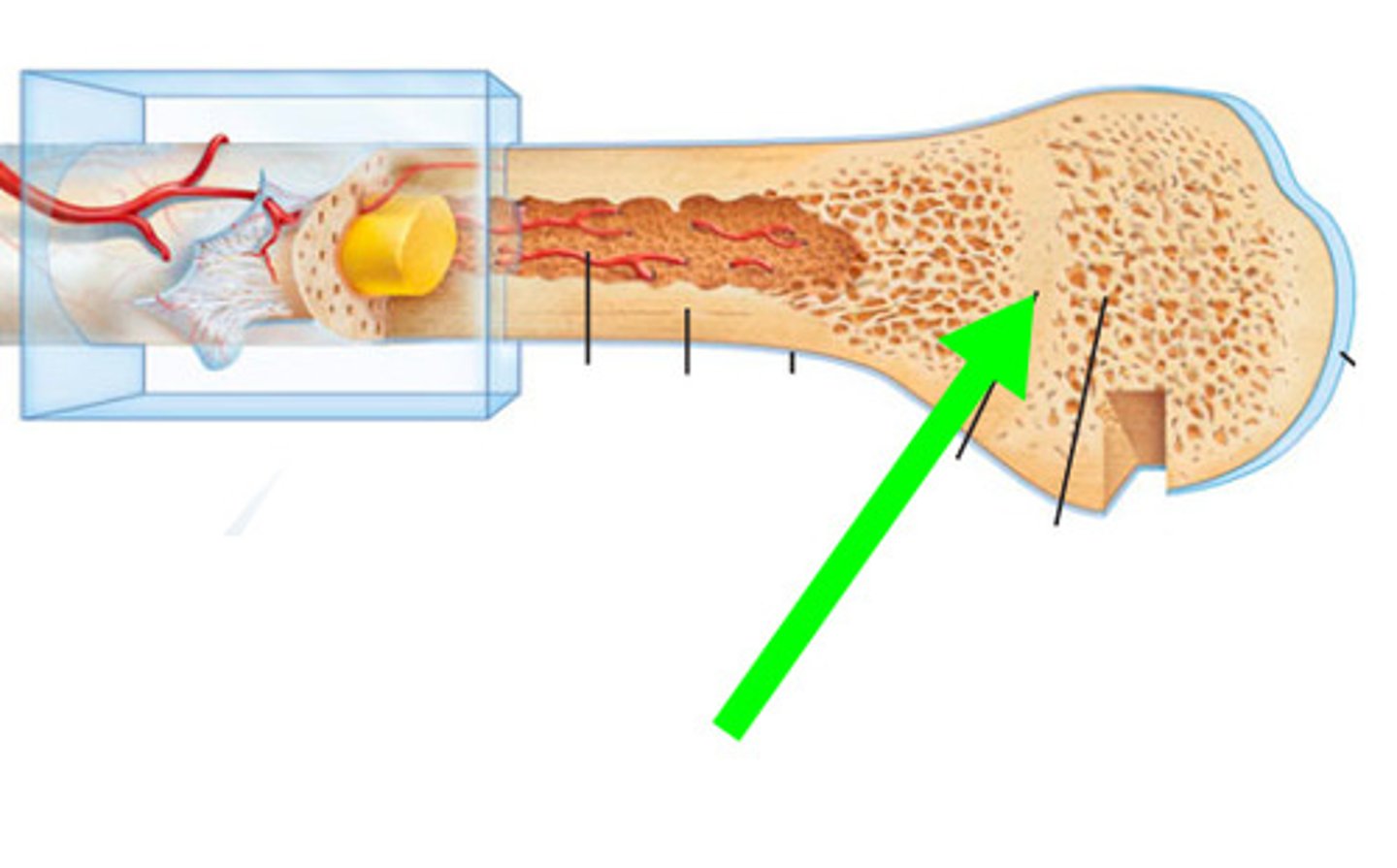
bone growth stops
when the cartilage of the epiphyseal plate disappears and is replaced by the bone...
cortex of the bone
- compact bone layers of the flat bones
- broken into external and internal tables
external and internal tables
are thick in order to provide strength for the bone
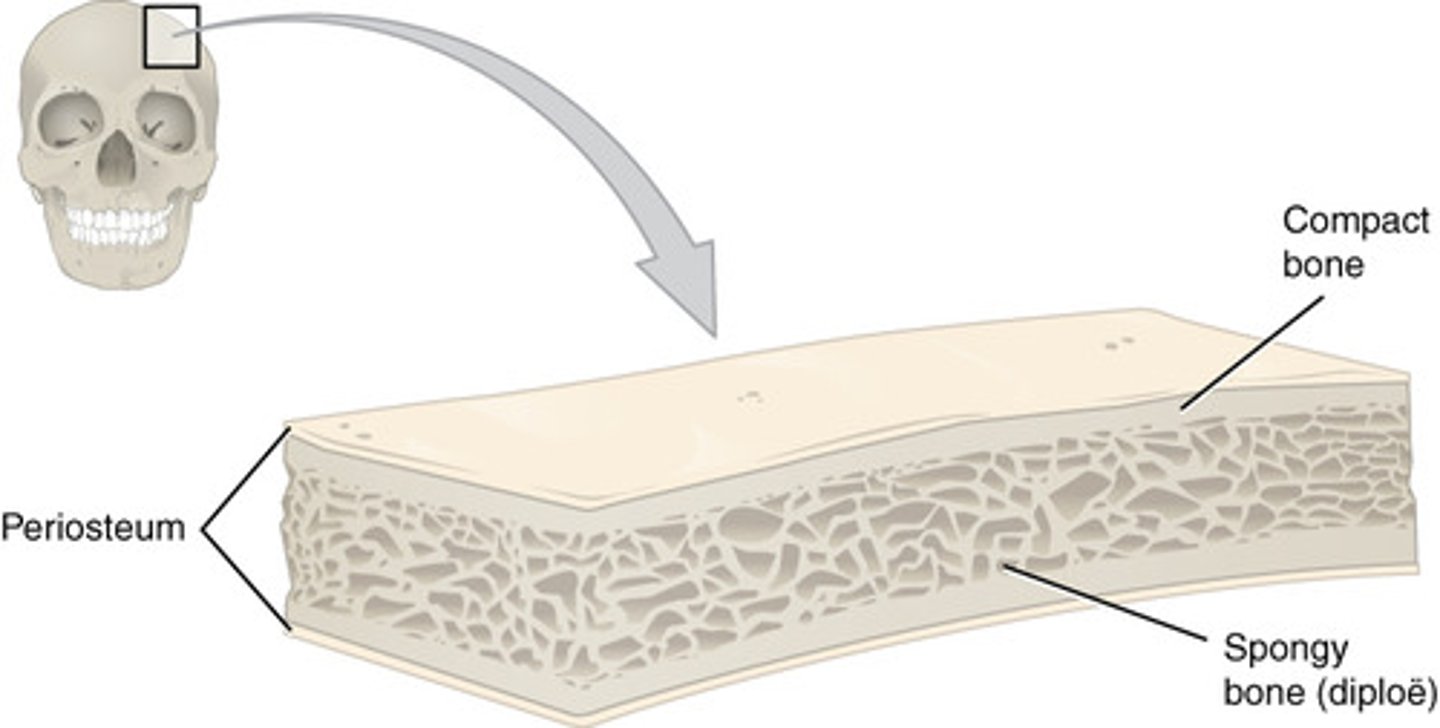
diploe
spongy bone between the external and internal tables in a flat bone that is filled with red marrow

red marrow
type of loose connective tissue that is made up of stem cells from which all blood cells arise
bone markings
reveal where bones form joints with other bones, where muscles, tendons, and ligaments were attached, and where blood vessels and nerves pass
projections and depressions
two categories of bone markings
projections
processes that grow out from the bone and serve as sites of muscle attachment or help form joints
depressions
indentations or openings in the bone that often serve as conduits for nerves and blood vessels
tuberosity
large rounded projection
crest
narrow ridge of a bone; usually prominent
trochanter
very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
line
narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
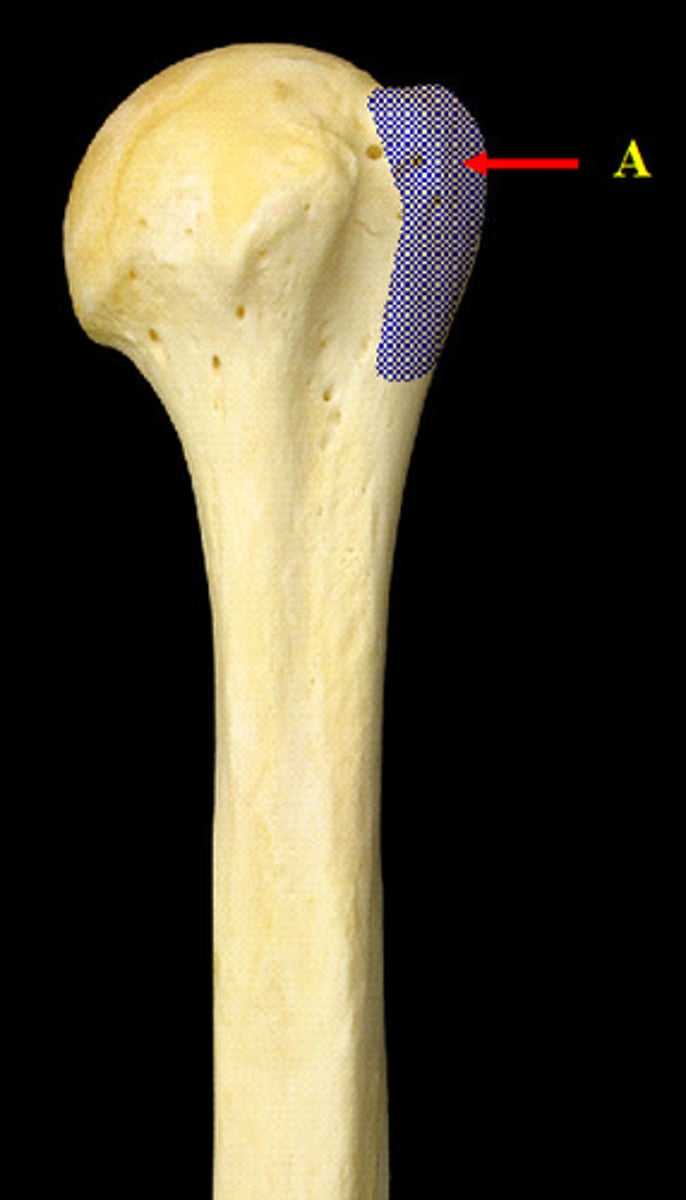
tubercle
small rounded projection or process
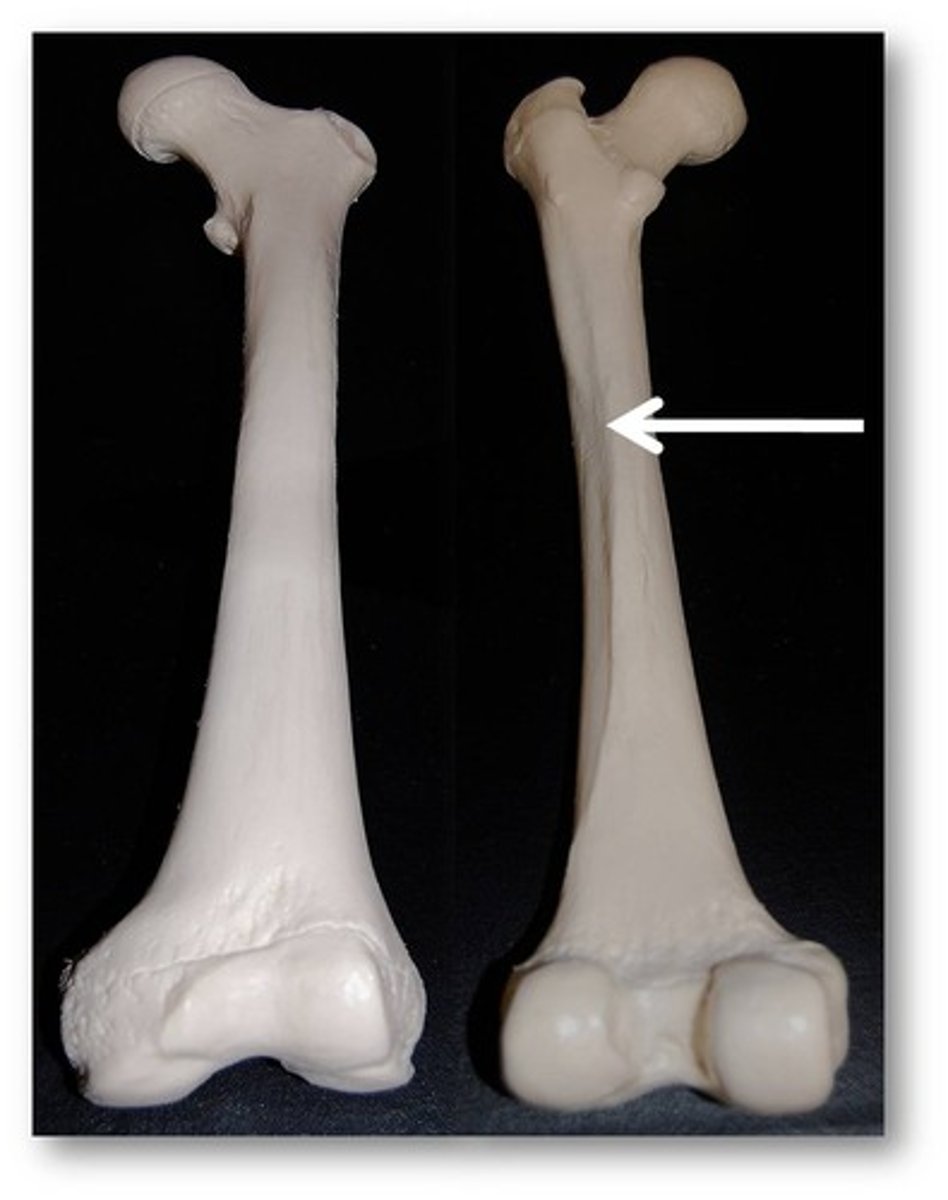
epicondyle
raised area on or above condyle
spine
sharp, slender often pointed projection
process
any bone prominence
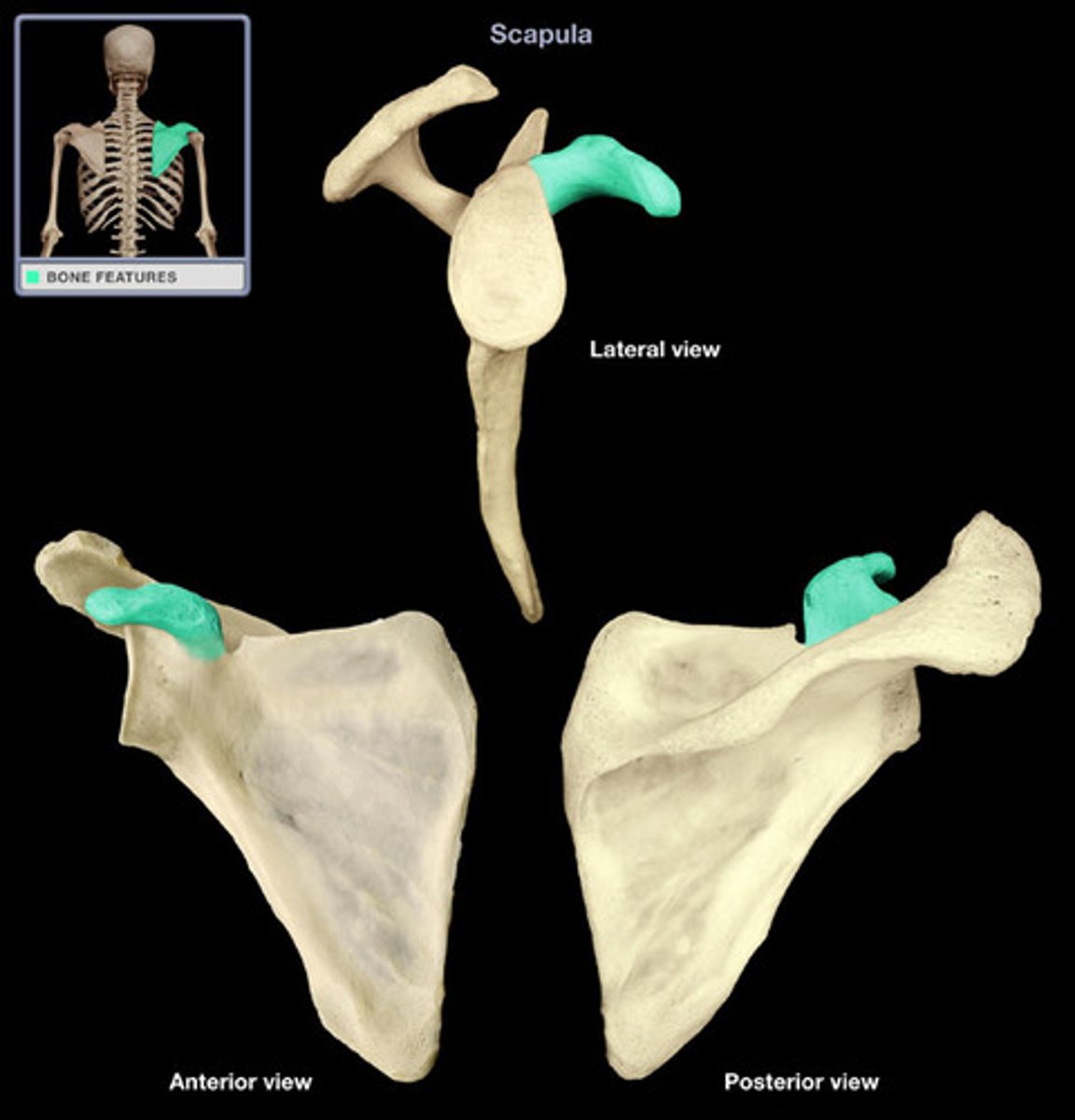
projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attachment
tuberosity, crest, trochanter, line, tubercle, epicondyle, spine, process
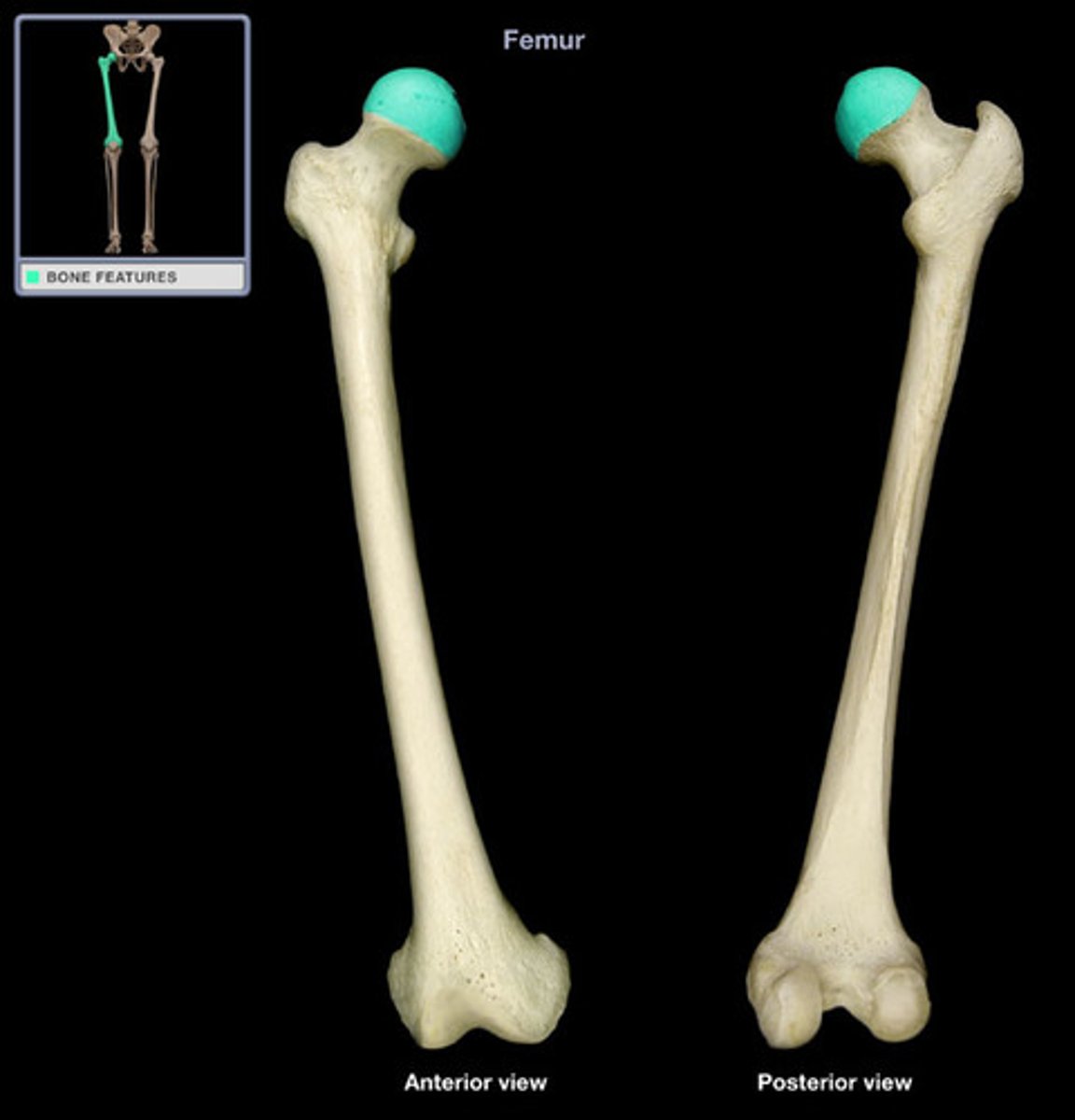
surfaces that form joints
head, facet, condyle, ramus
head
body expansion carried on a narrow neck
facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
condyle
rounded articular projection, often articulates with a corresponding fossa
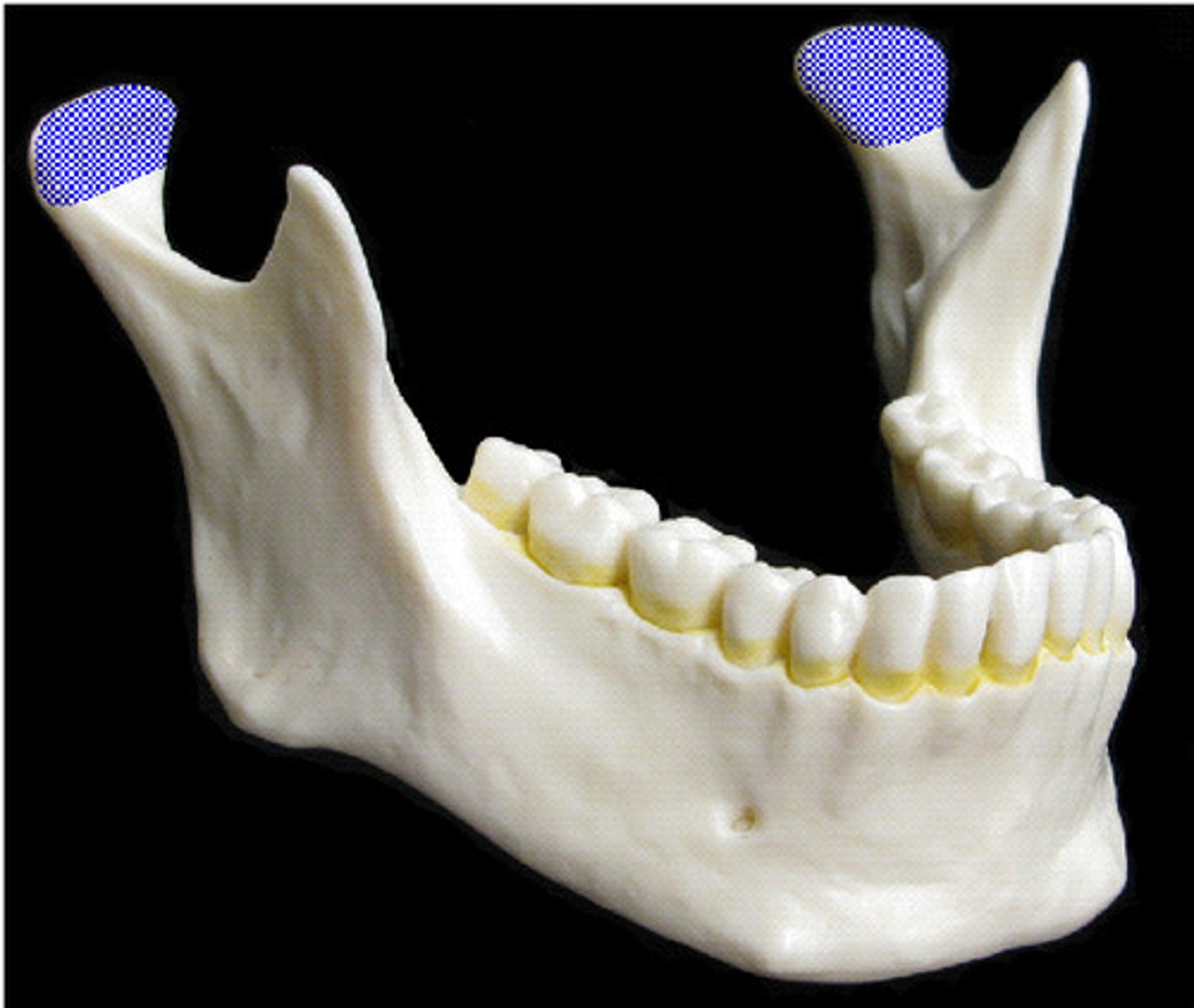
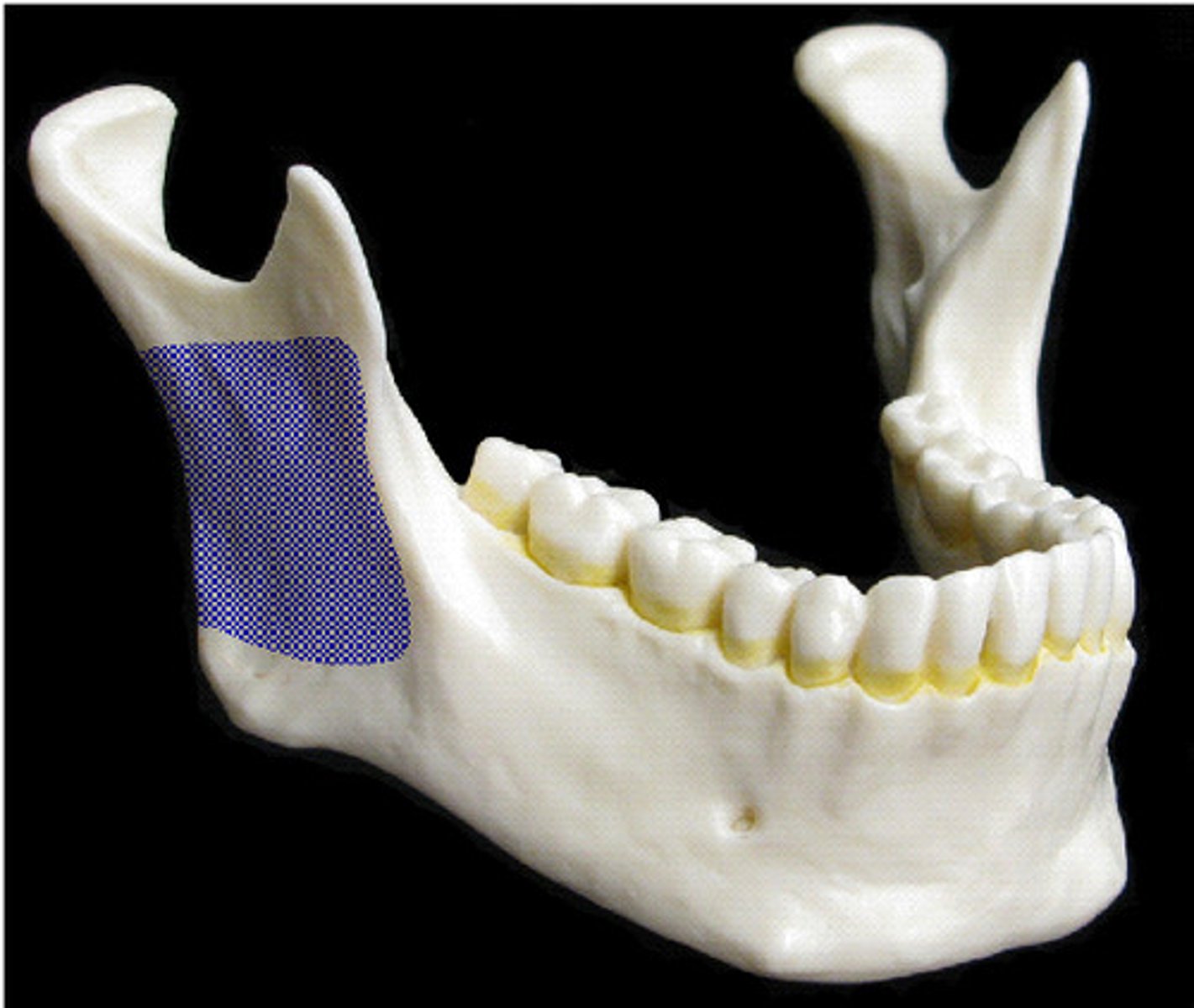
ramus
arm-like bar of bone
depressions and openings
foramen, groove, fissure, notch, fossa, meatus, sinus
foramen
round or oval opening through a bone
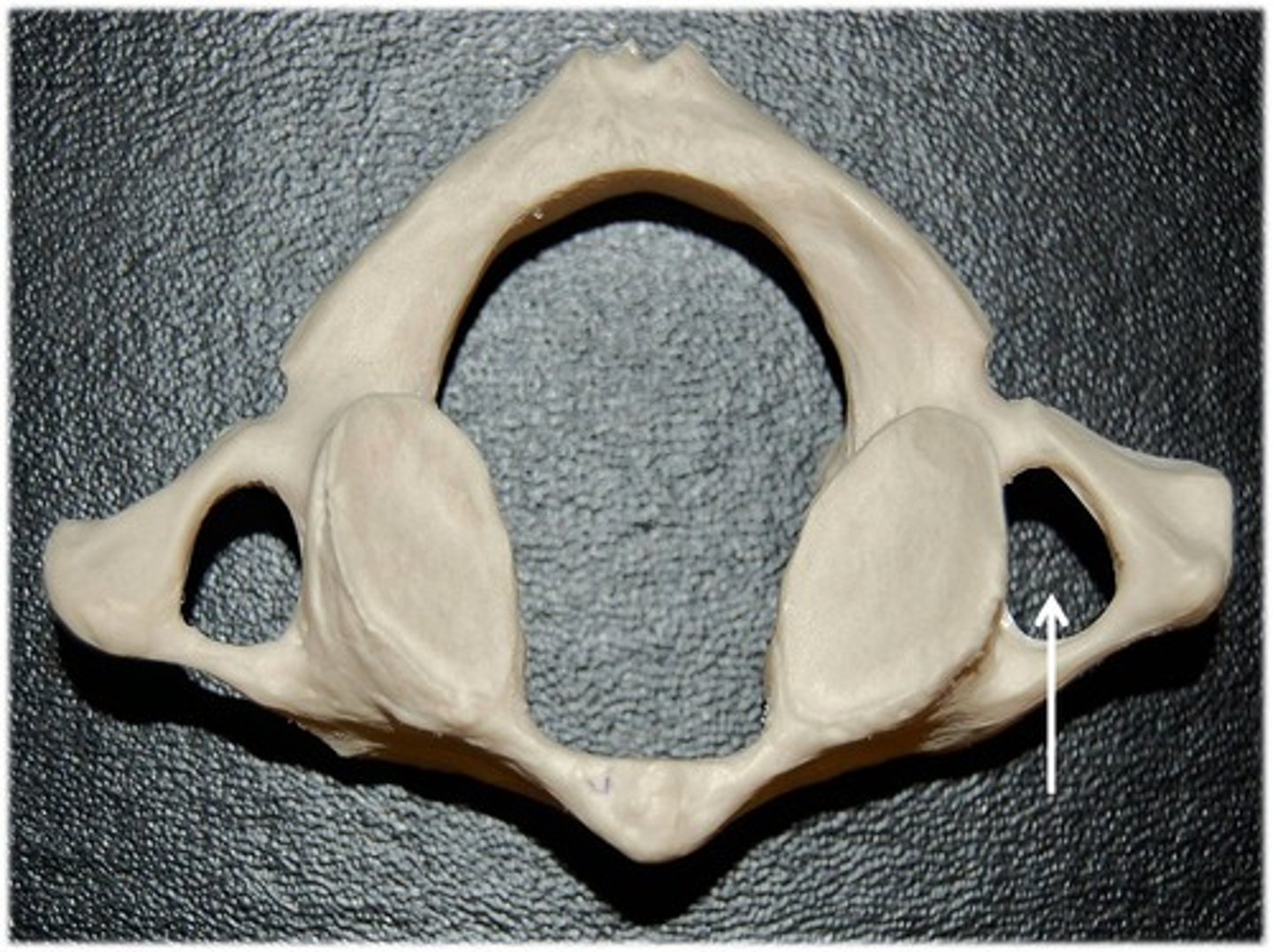
groove
furrow
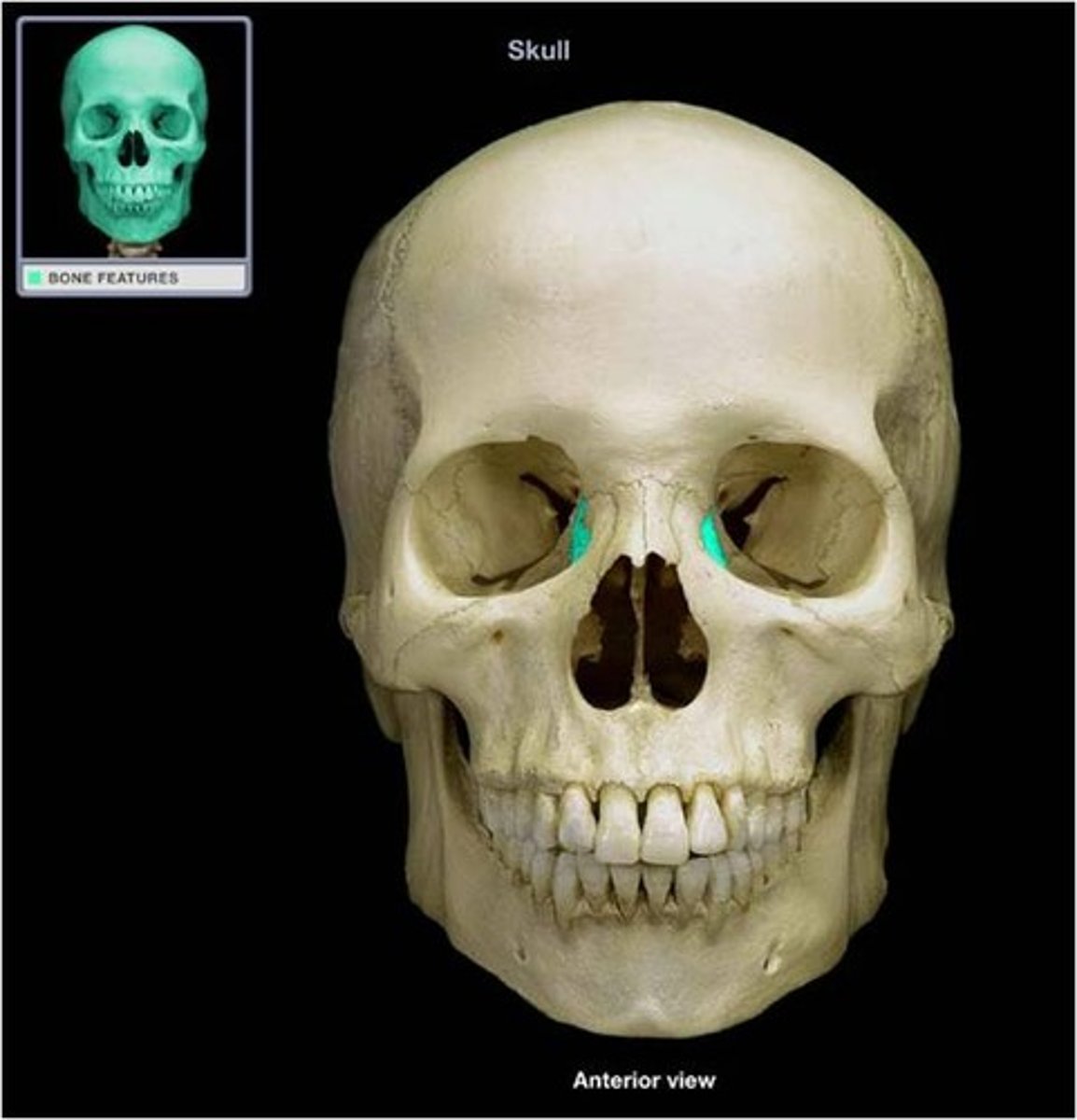
fissure
narrow, slit-like opening
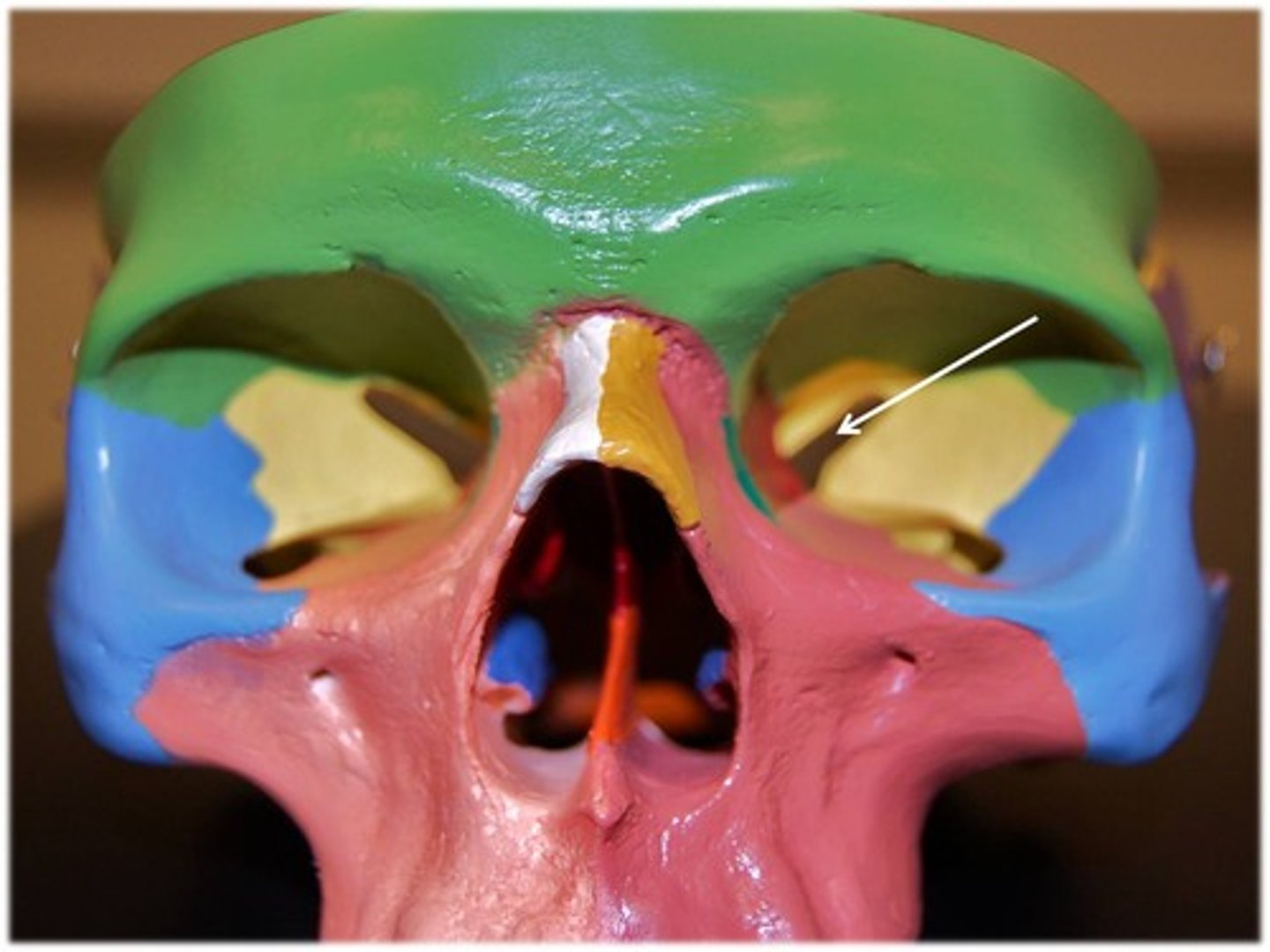
notch
indentation at the end of a structure
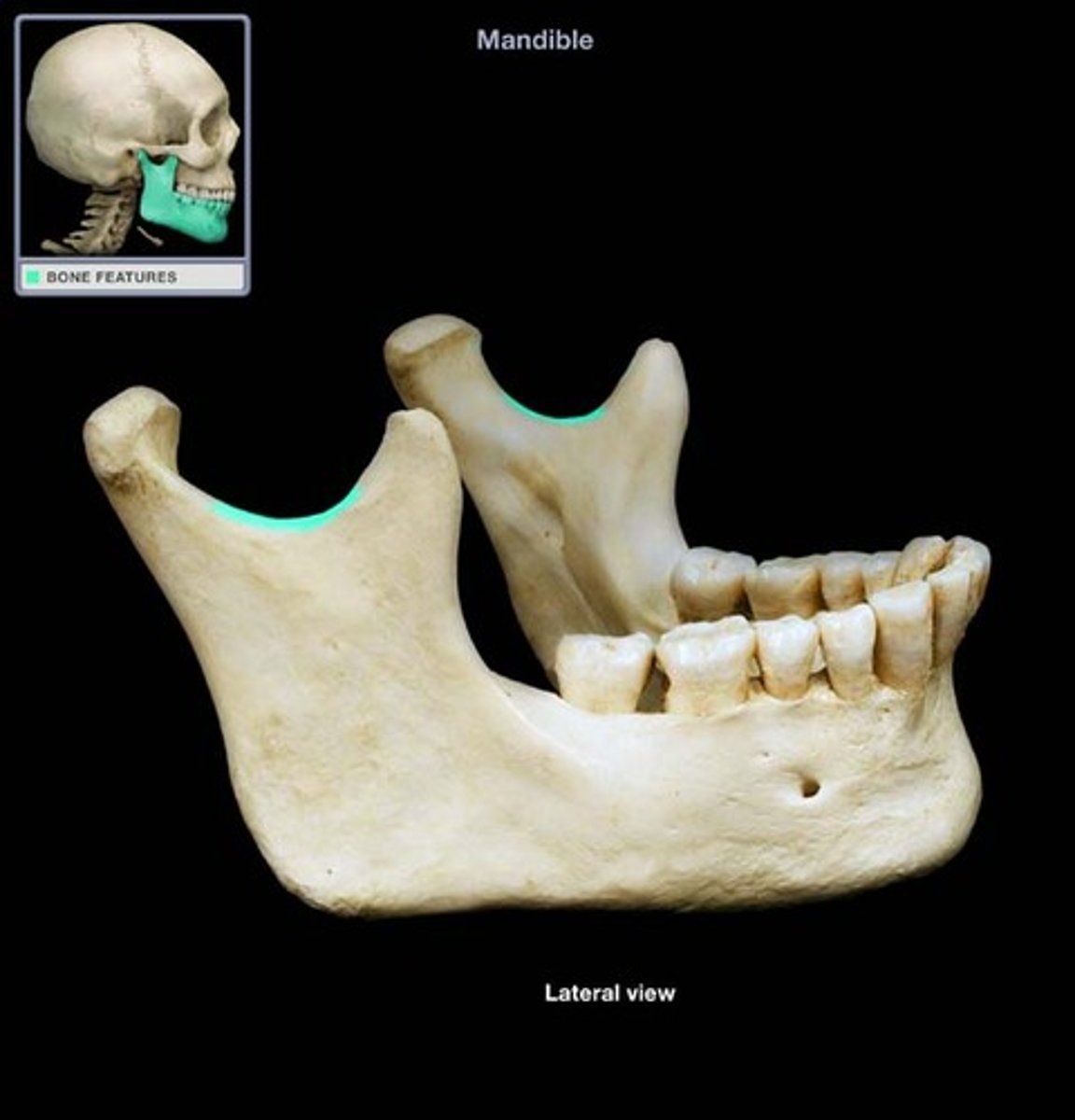
fossa
shallow, basin-like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
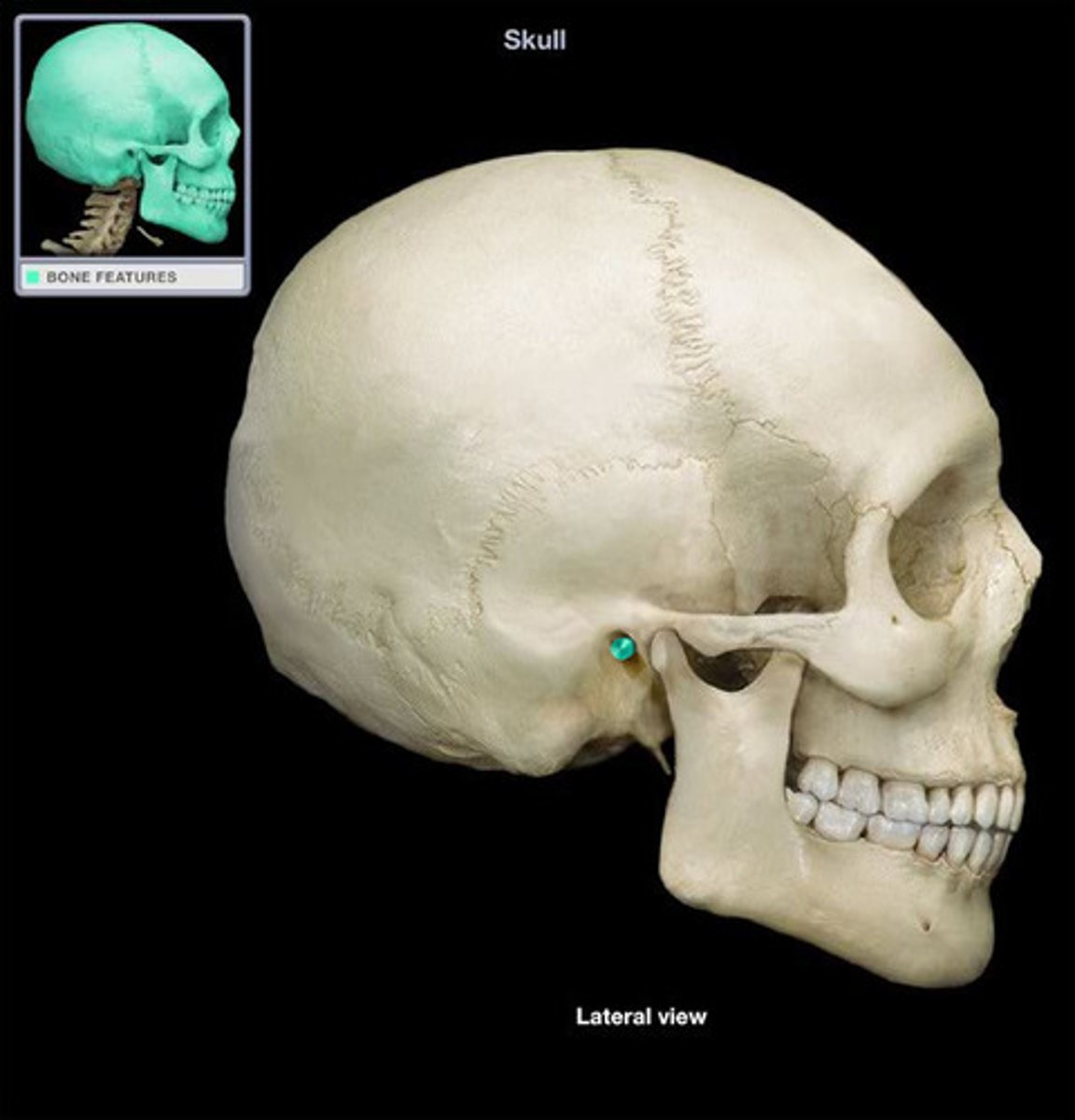
meatus
canal-like passageway
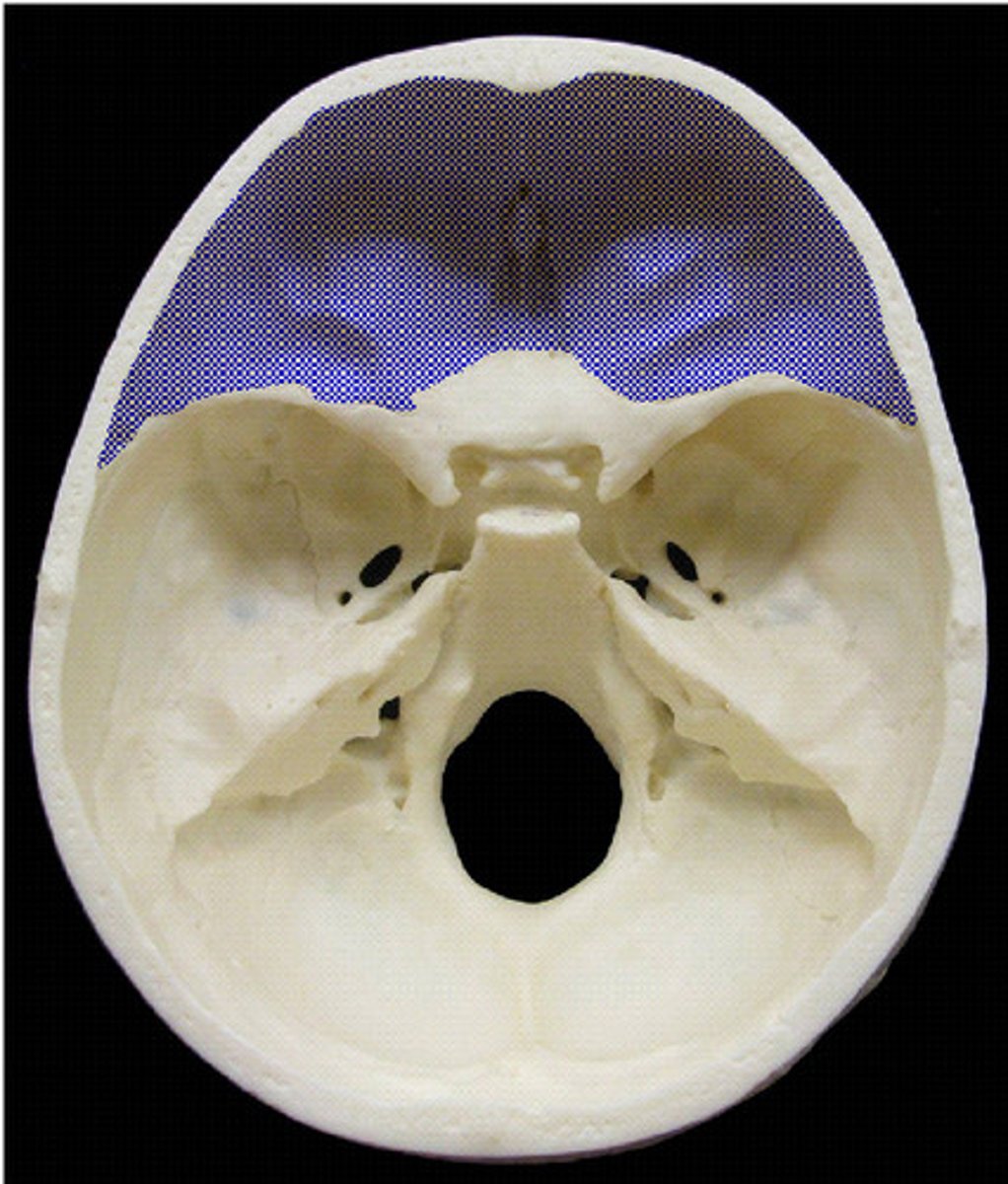
sinus
bone cavity, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
5 types of vertebrae
cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral, and coccygeal
unfused vertebrae
cervical, thoracic, and lumbar
cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)
- less confined articulations, allows for a wide range of motion in the head and neck
- have bifid spinous process and transverse foramen
- transverse foramina transmit the vertebral arteries which form the basilar artery and deliver blood to the brain
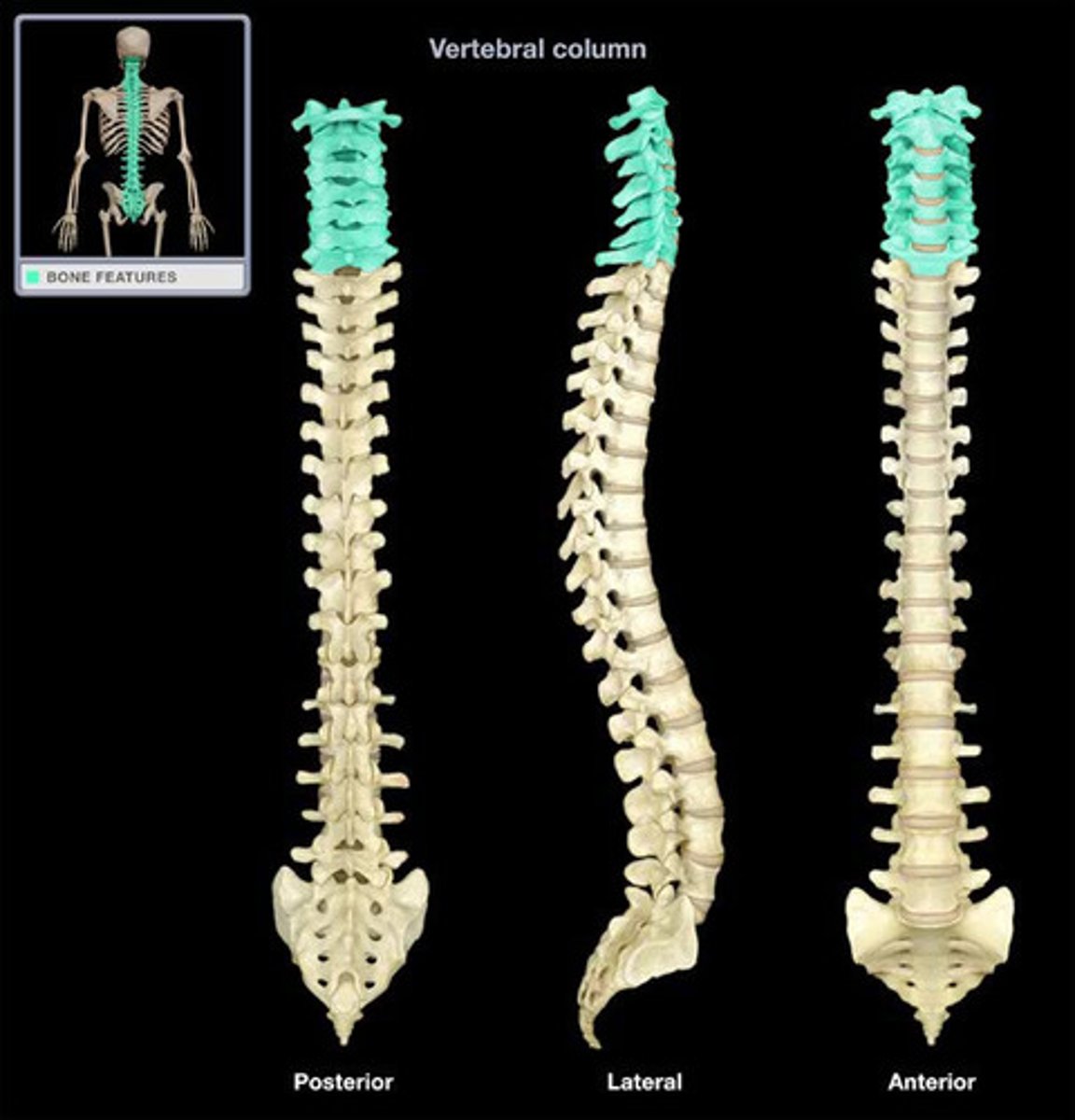
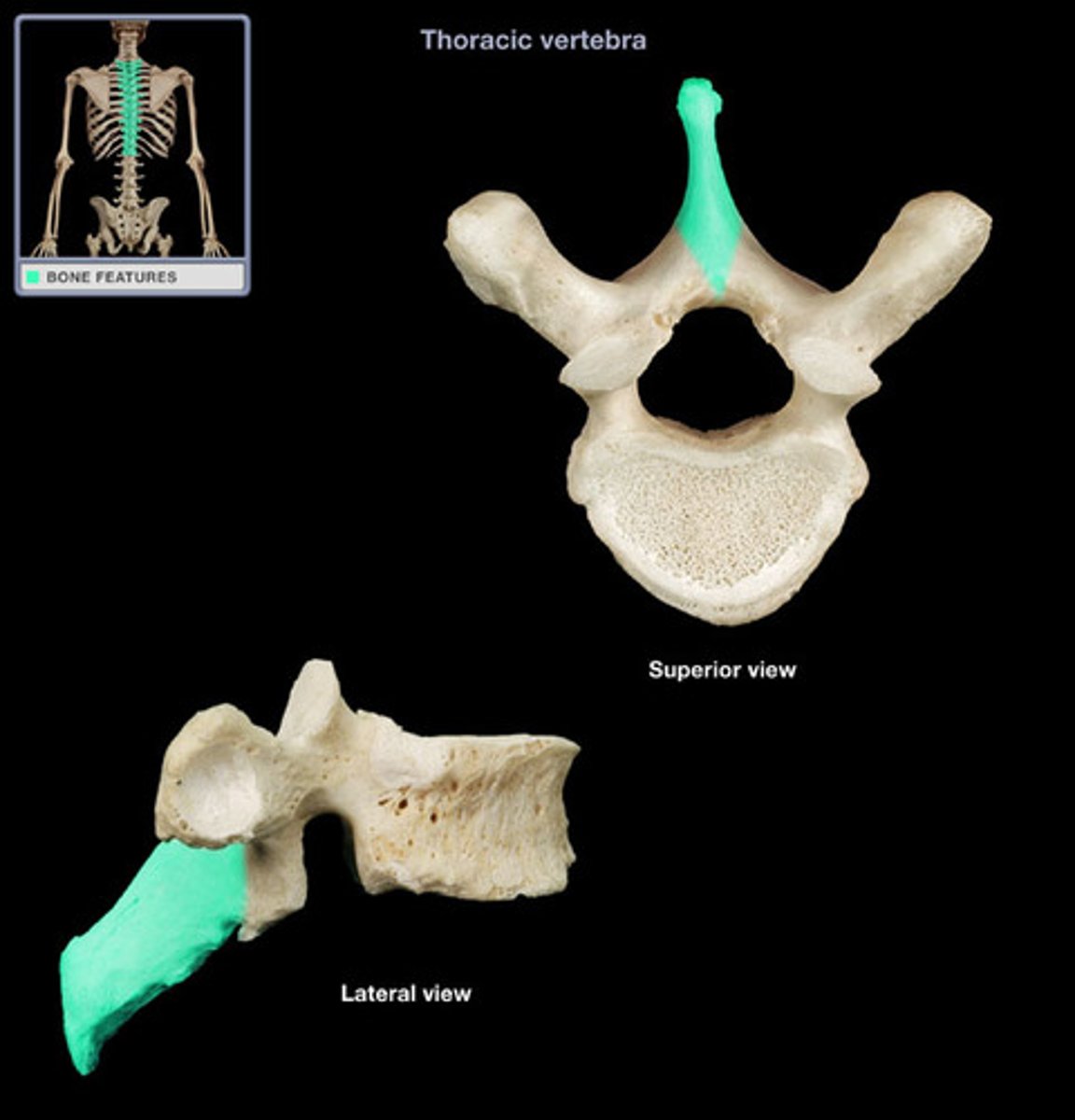
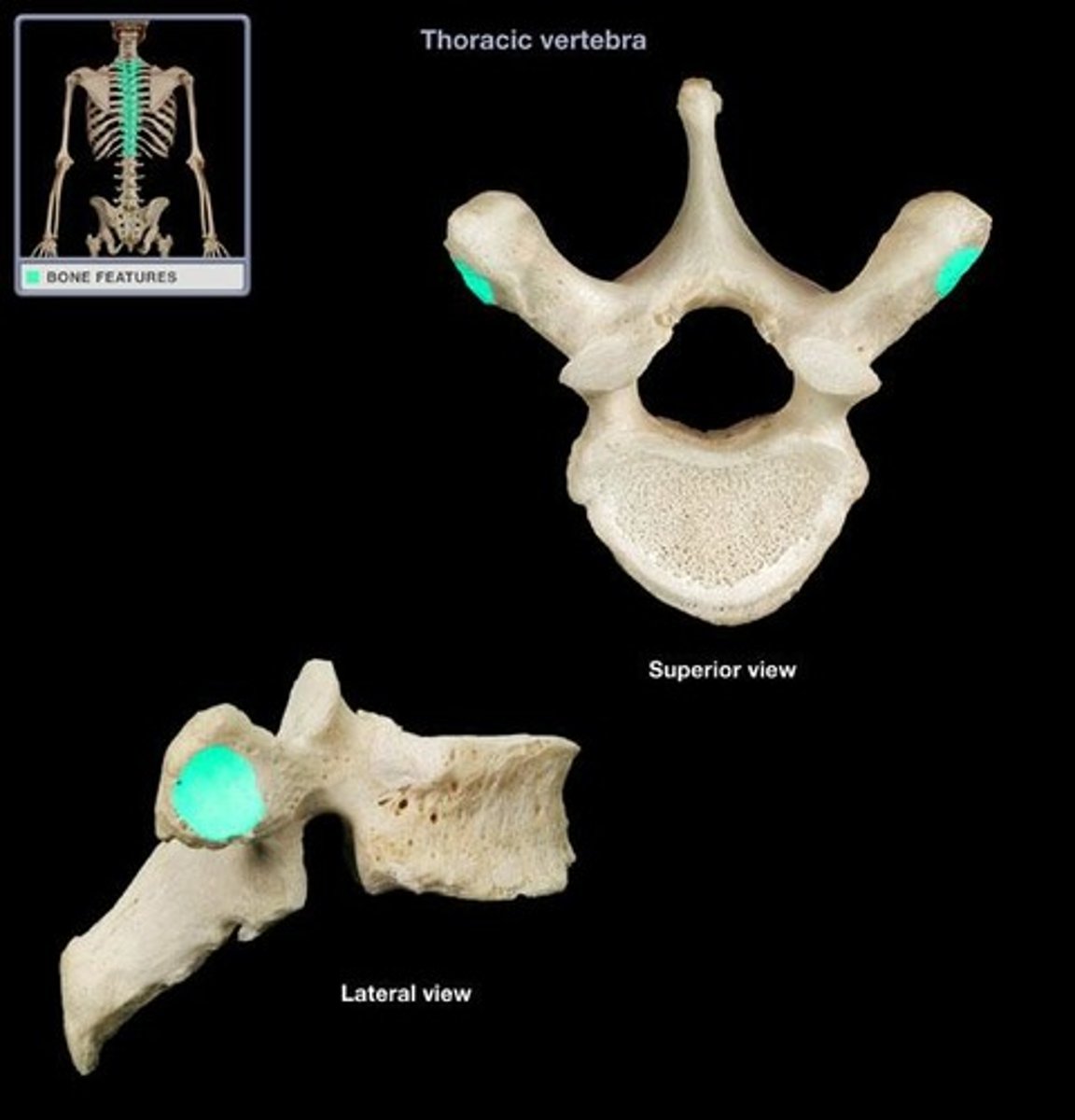
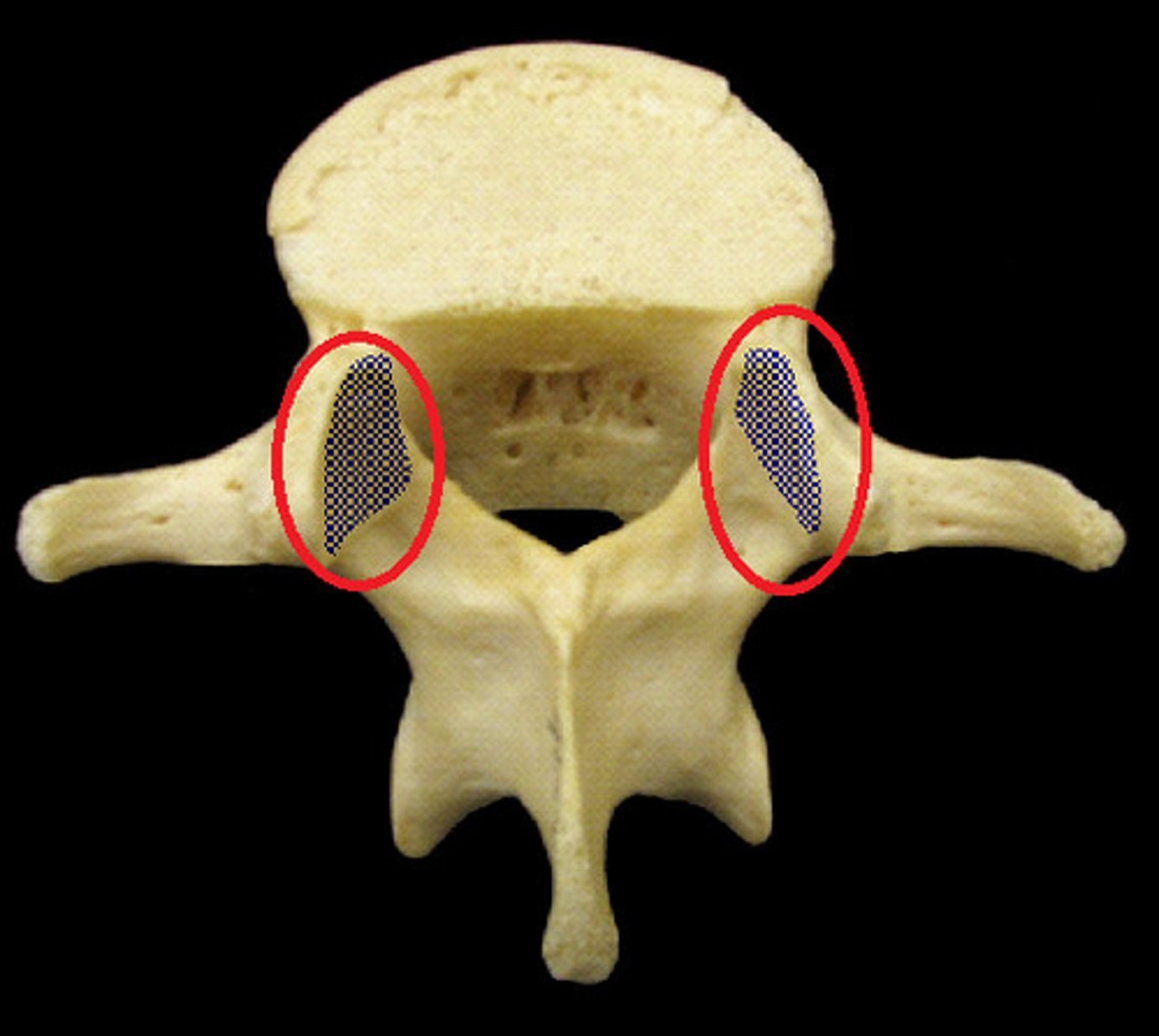
thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12)
- articulate with the ribs, which limits flexion in the thorax
- articular process is directed anterior and posterior, decreasing flexion and extension in the thorax
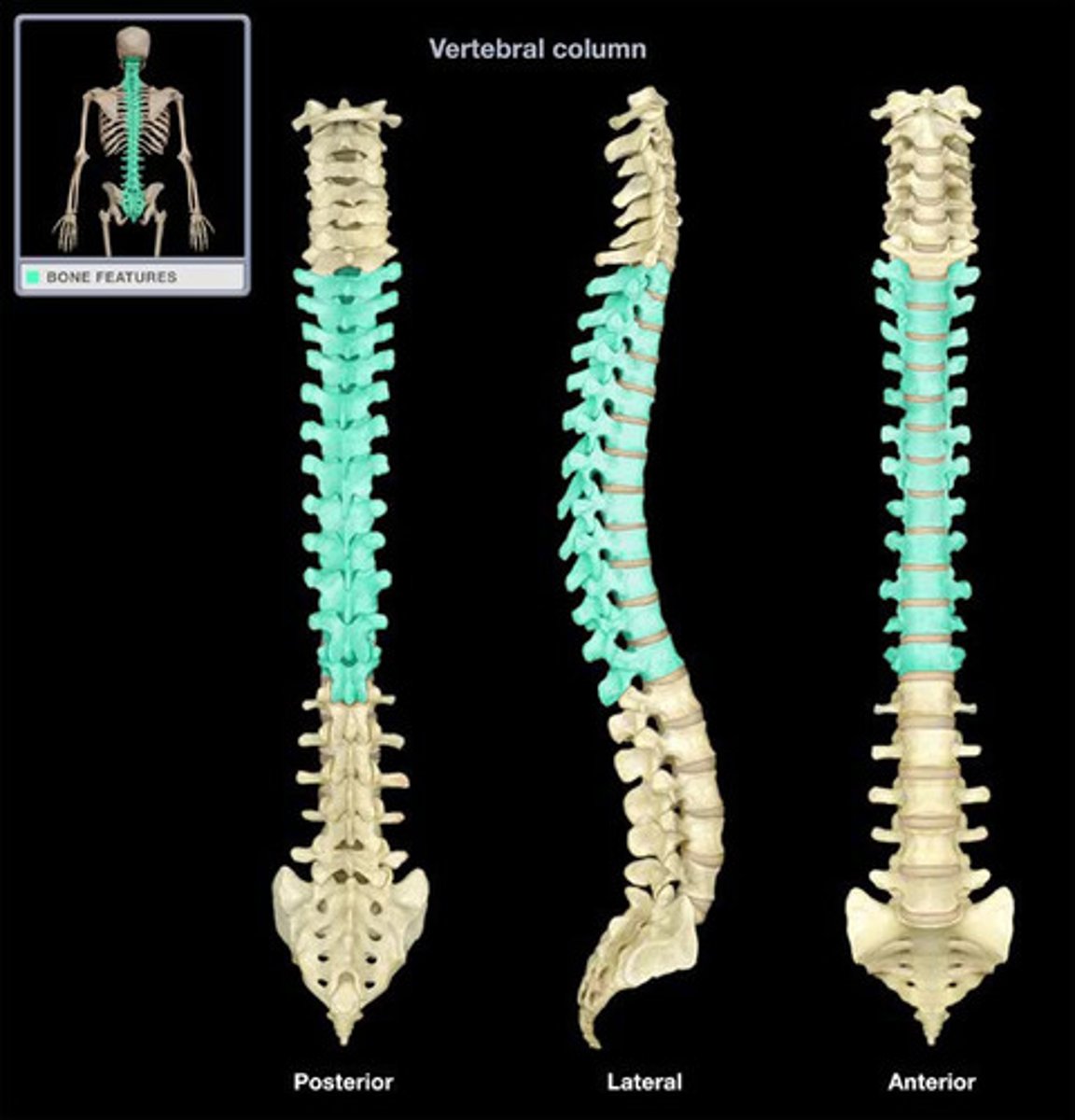
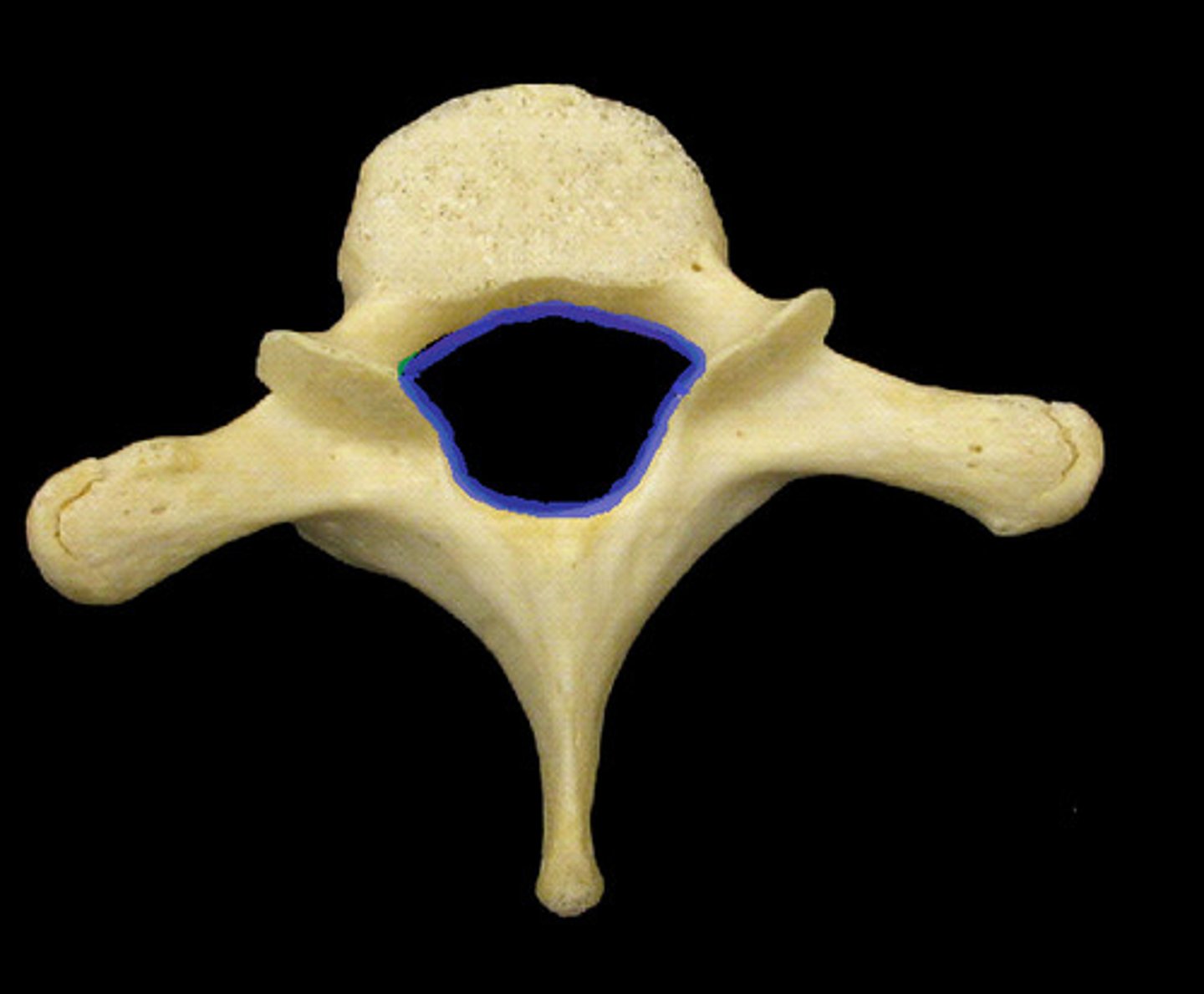
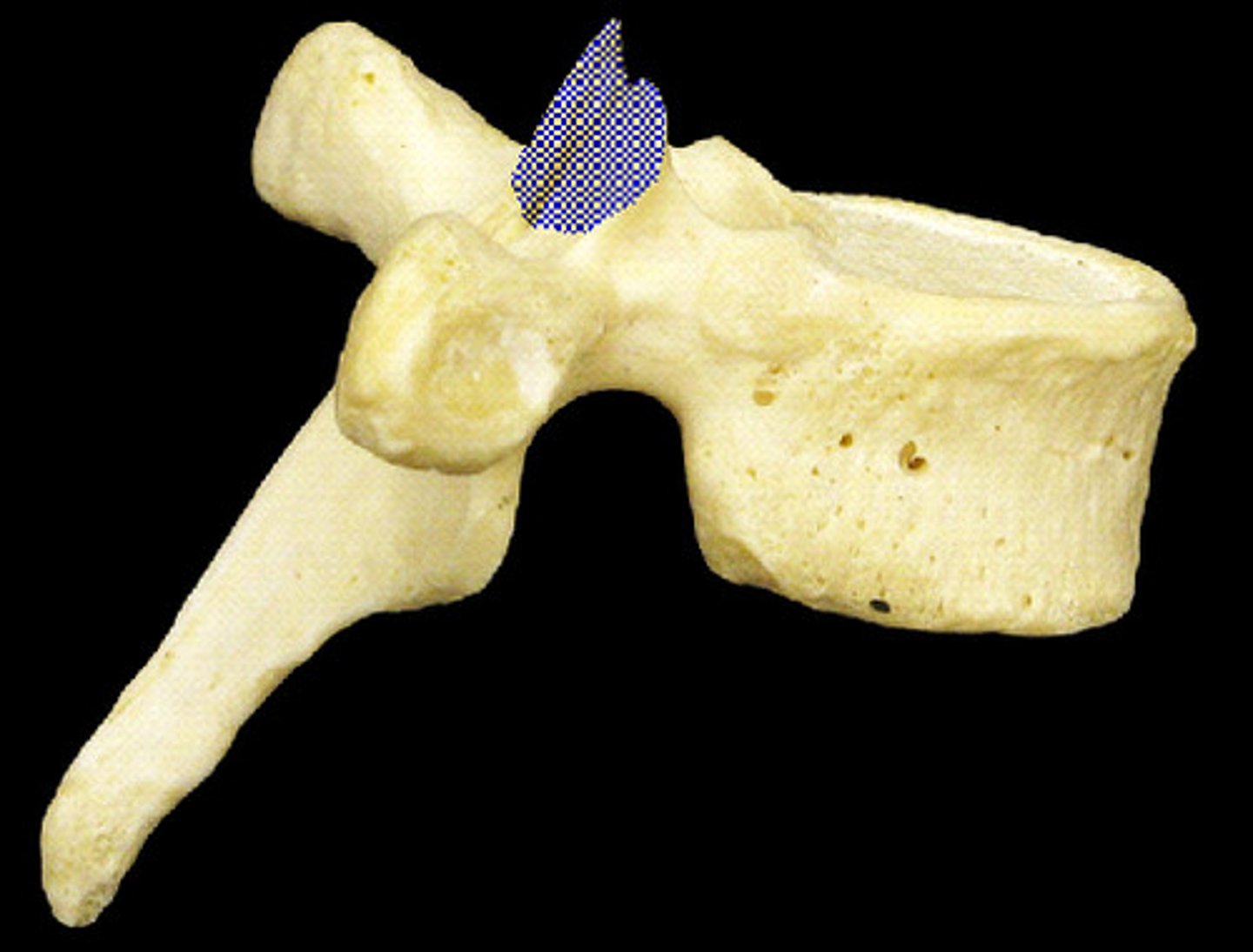
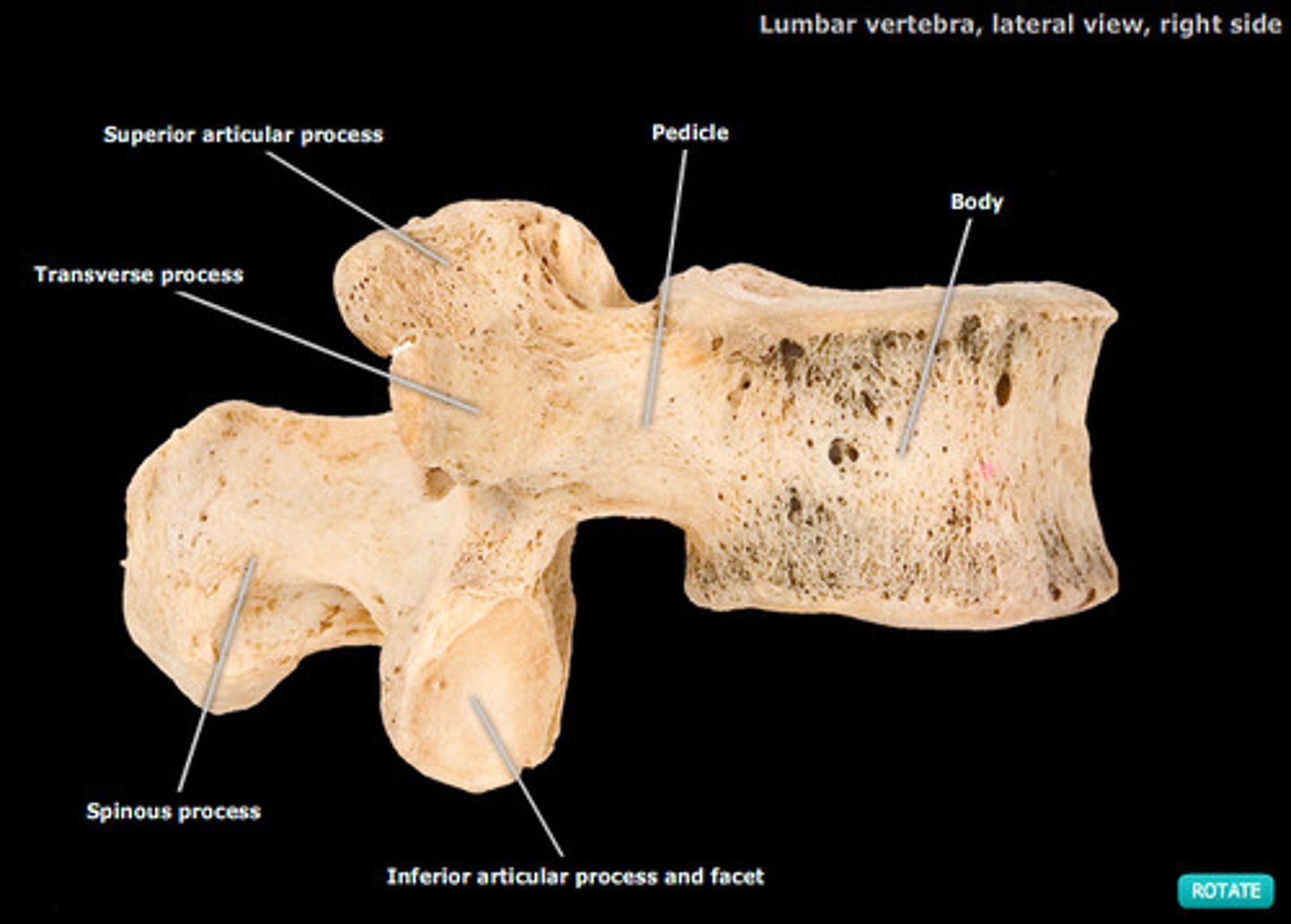
lumbar vertebrae (L1-L5)
- directed medially and laterally, limiting rotation in lower spine
- spinal cord proper stops here
- spinal taps are done in this area to avoid hitting spinal cord
- largest vertebrae in the human body
cauda equina
the spot at L1 where the spinal cord proper stops and becomes hanging "roots"
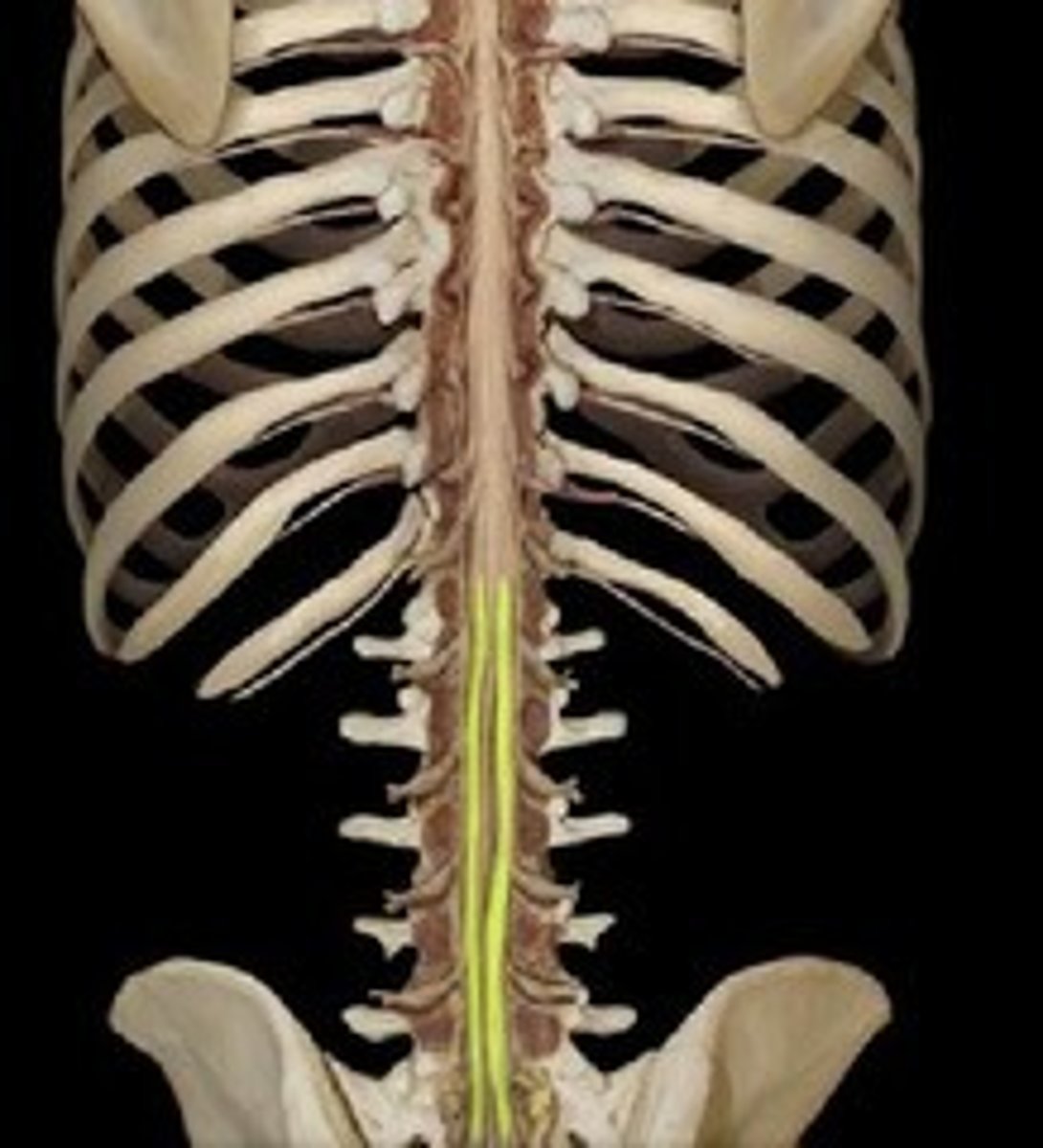
between L3 and L4
where a spinal tap is performed in order to avoid hitting the spinal cord
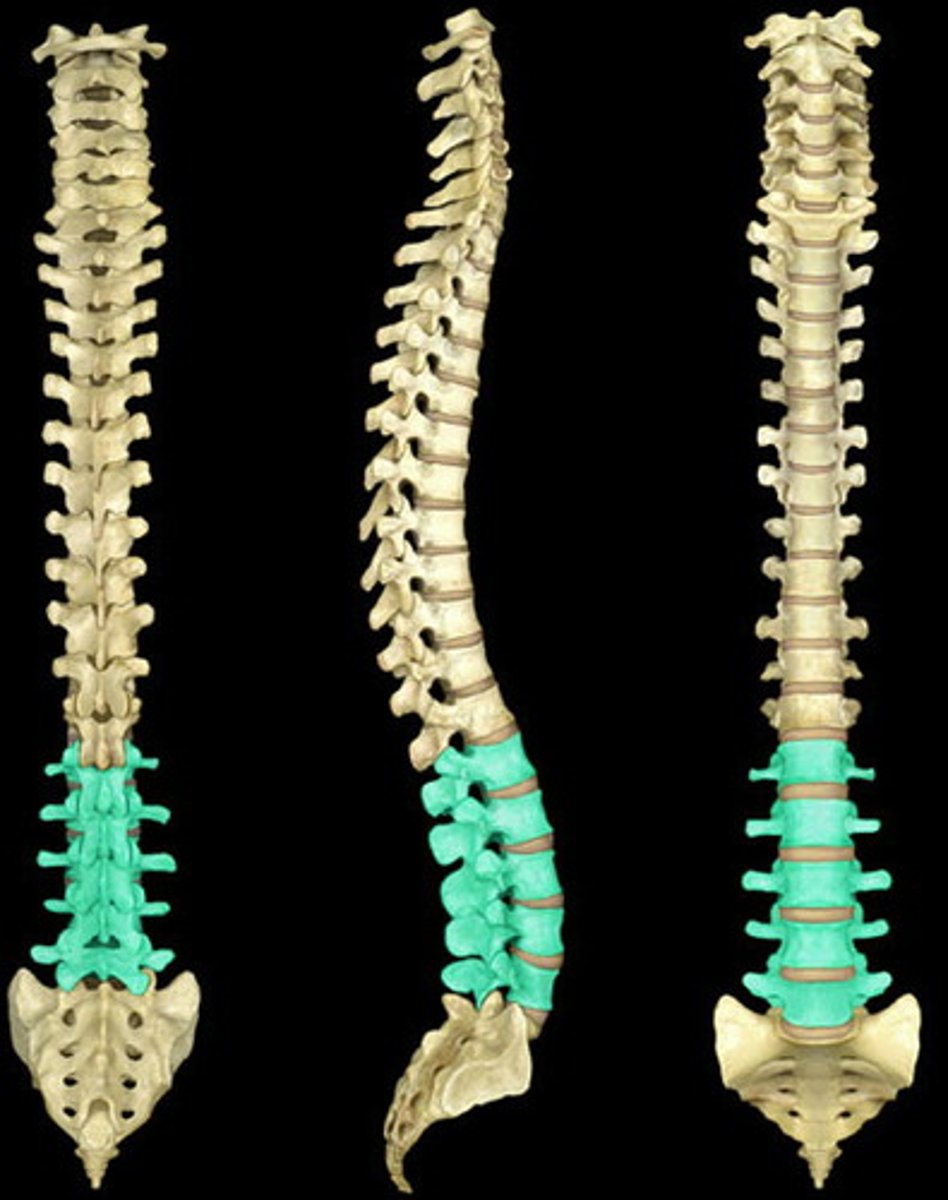
sacrum
- made up of 5 fused vertebrae
- foramina transmit blood vessels and spinal nerves to the lower body
- provides a stable anchoring point for the bones of the pelvic girdle
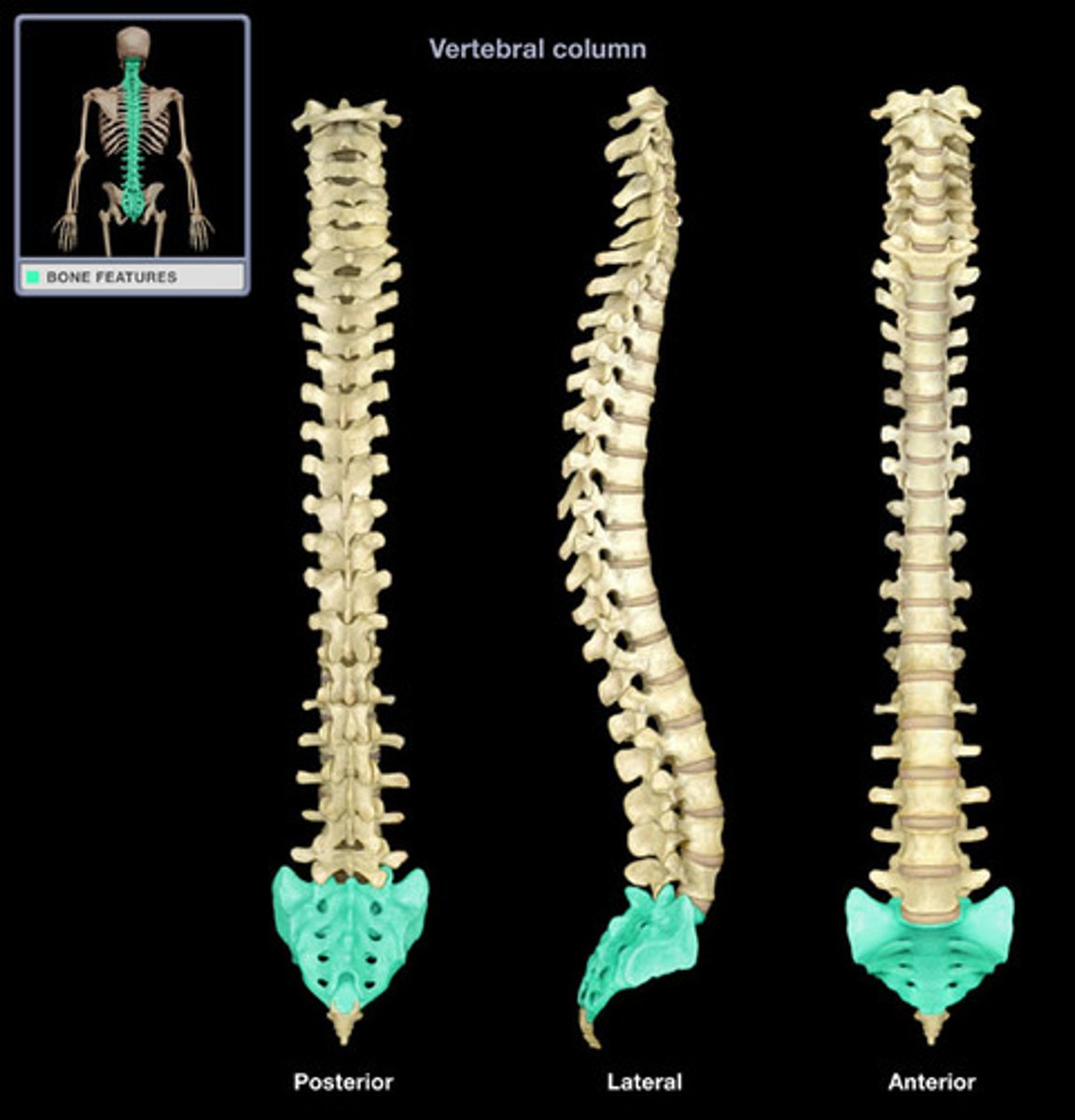
coccyx
- tail bone
- made up of four fused vertebrae
- an attachment point for several ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor
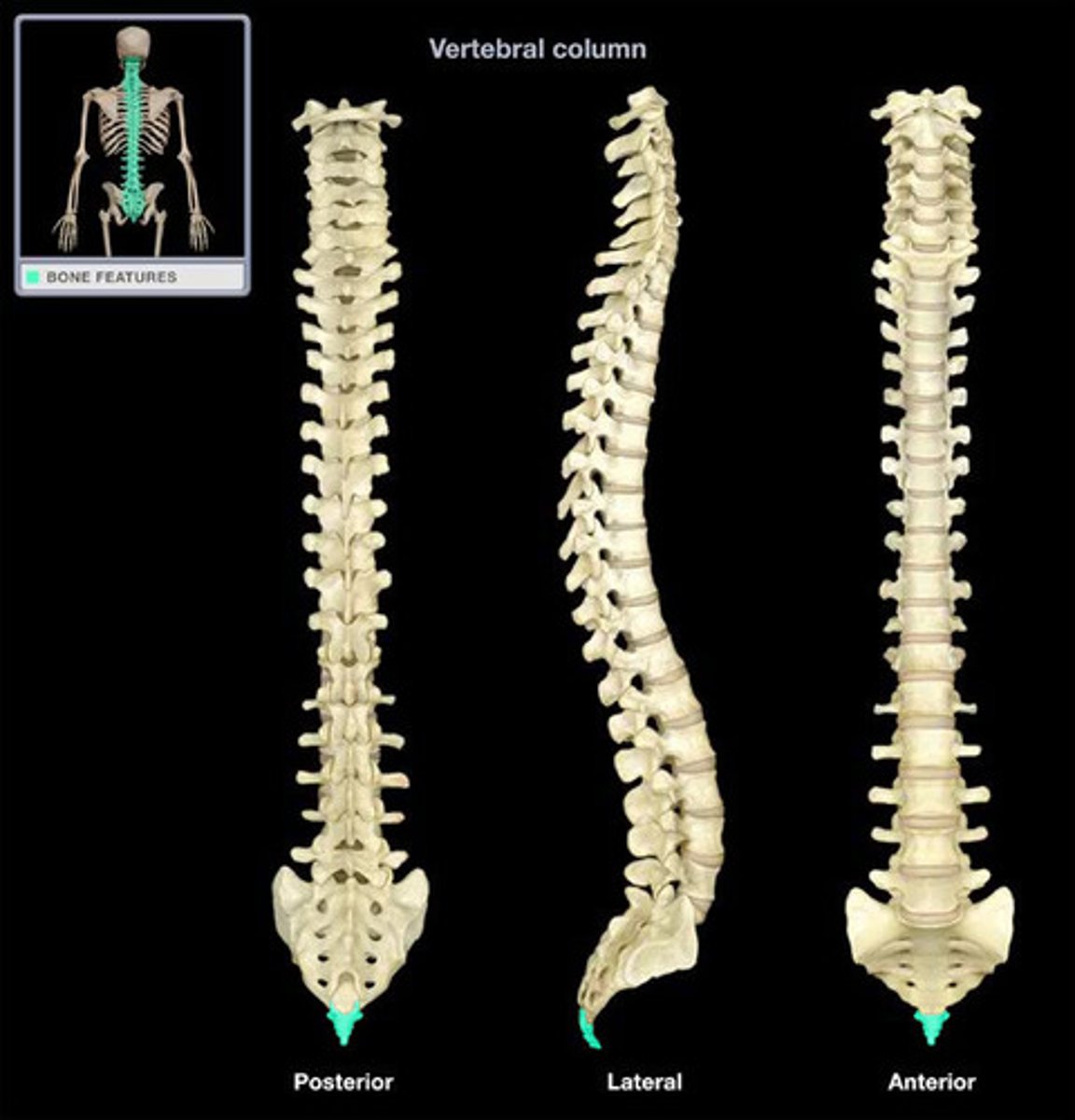
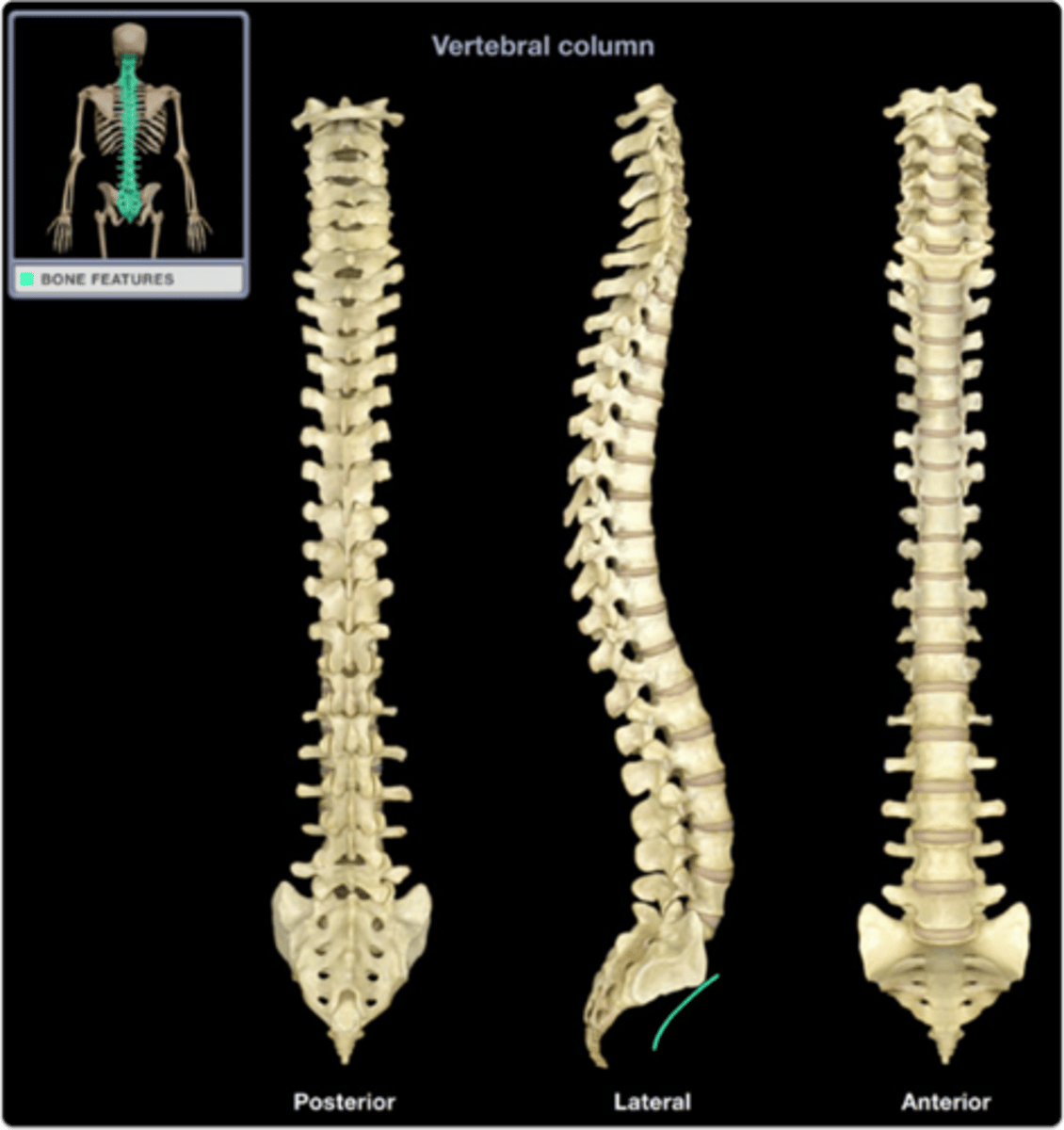
4 natural curvatures of the spinal cord
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
cervical curvature
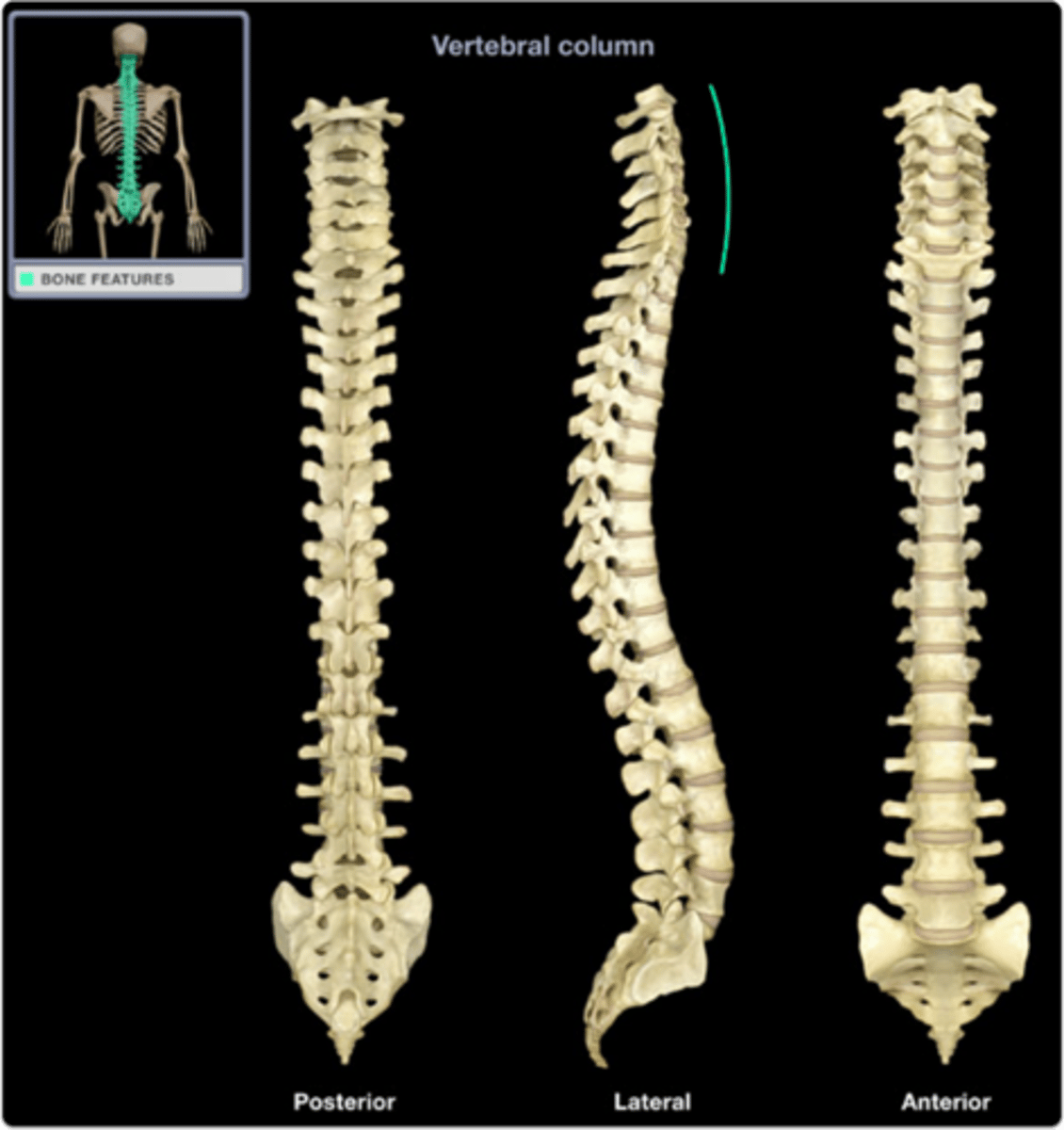
thoracic curvature
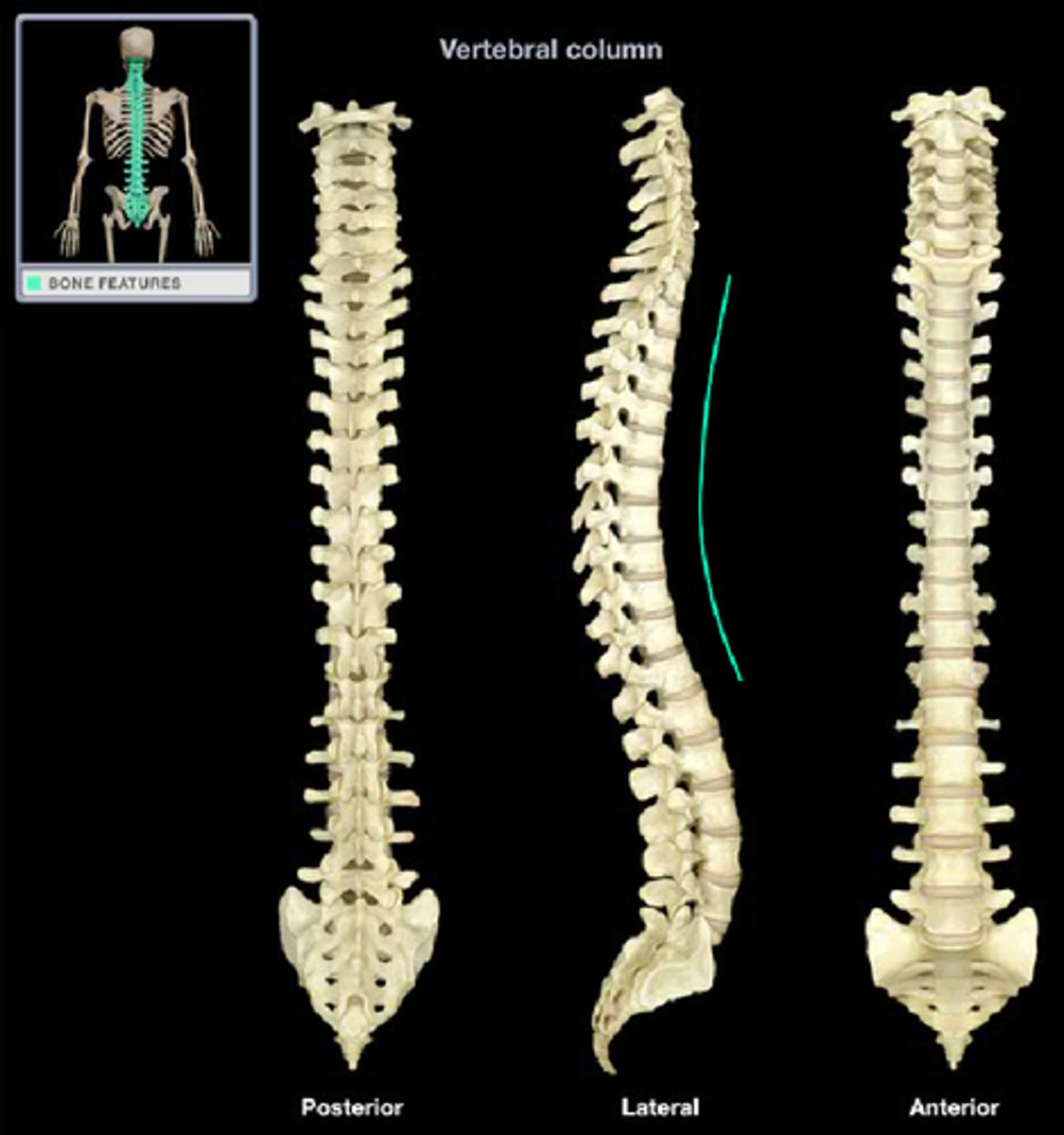
lumbar curvature
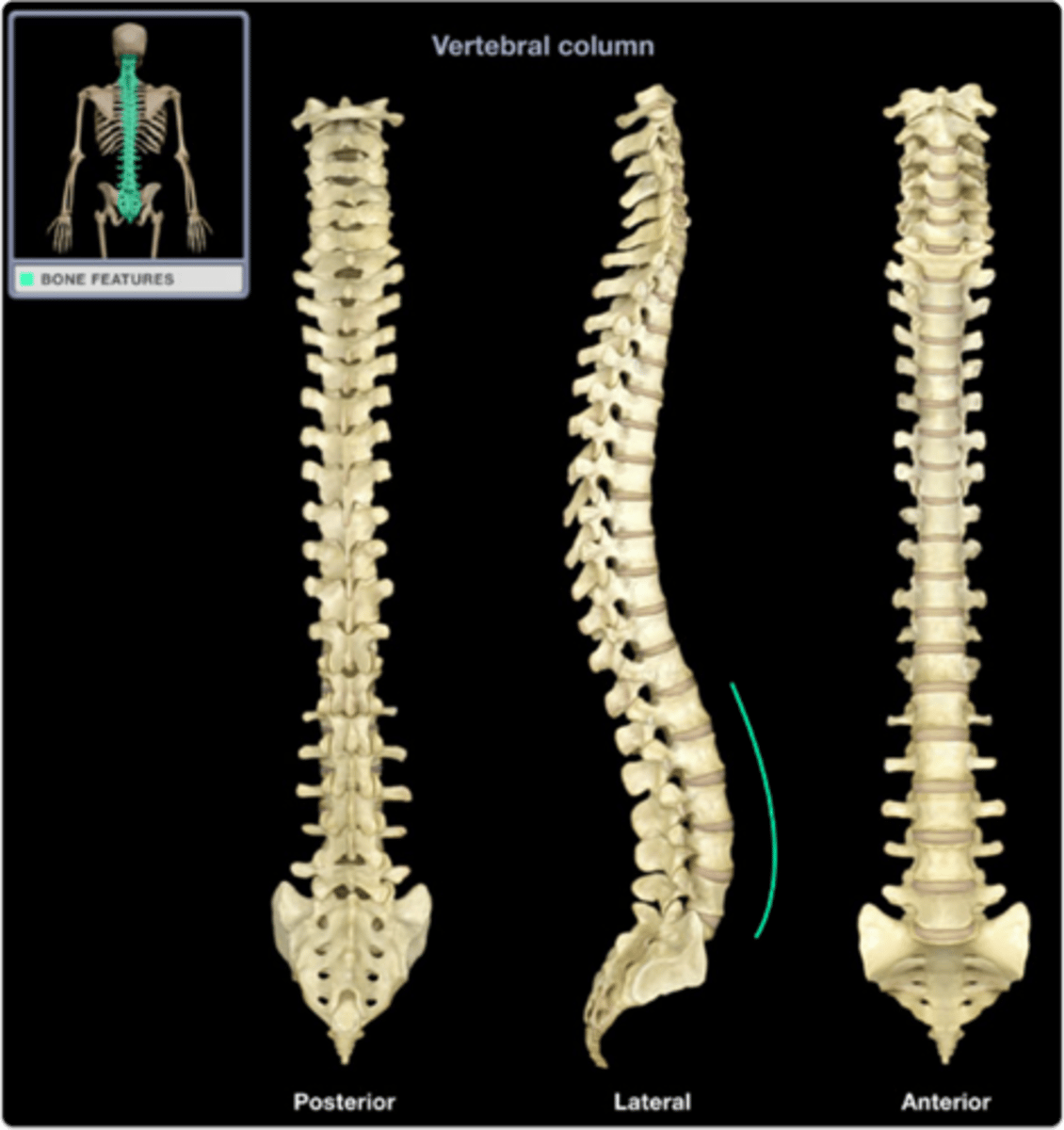
sacral curvature
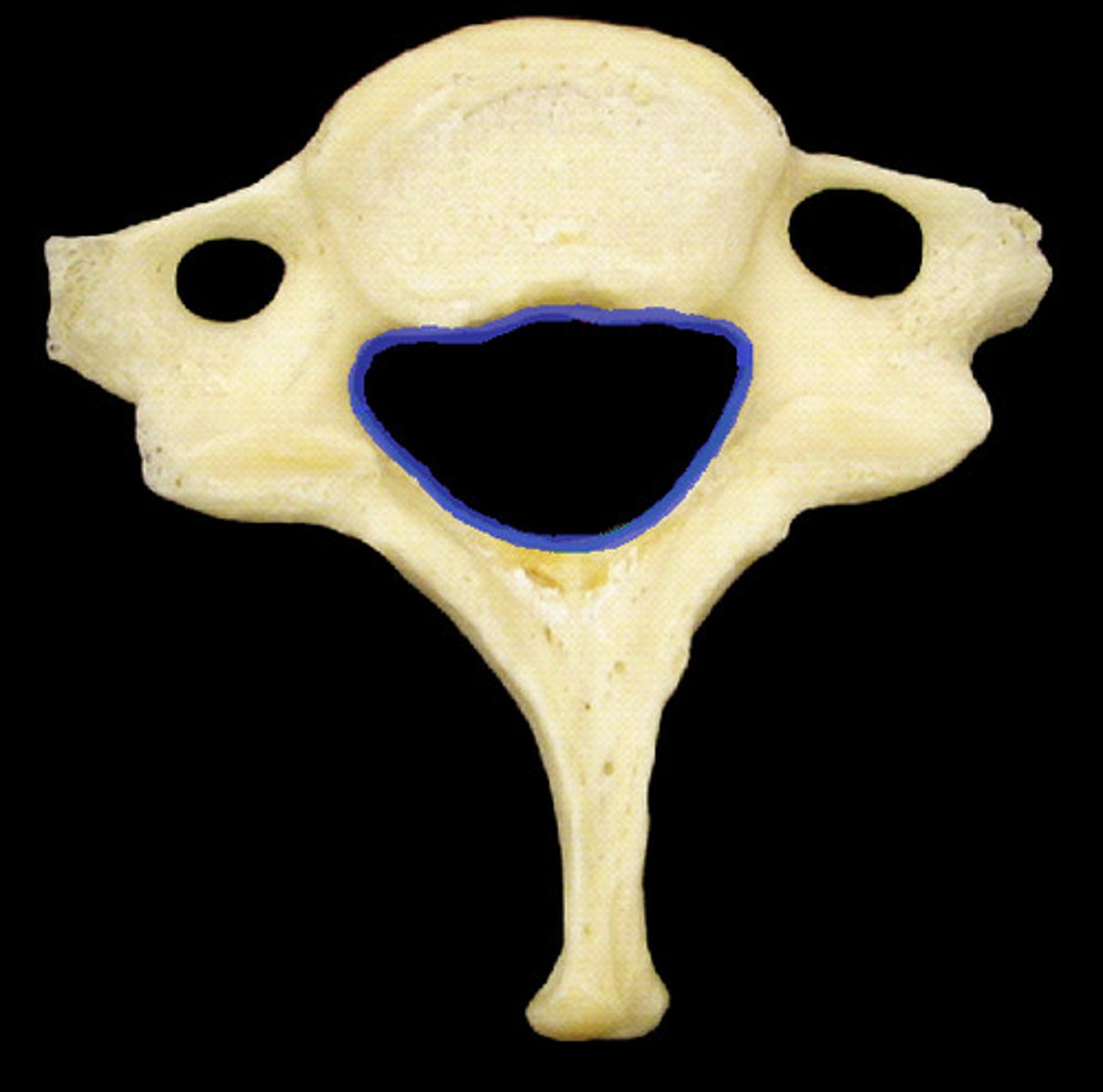
articular process of vertebrae
- inferior articulates with the superior of the vertebrae below it
- when determining which is superior and inferior, it is based on their position on the vertebra (NOT in the joint!)
superior view of cervical vertebrae
lateral view of cervical vertebrae
superior view of thoracic vertebrae
lateral view of thoracic vertebrae
superior view of lumbar vertebrae
lateral view of lumbar vertebrae
cervical vertebrae
- kidney bean shaped body
- spinous process is horizontal with a bifid spine in 3-6
- hyoid bone does not actually articulate with them
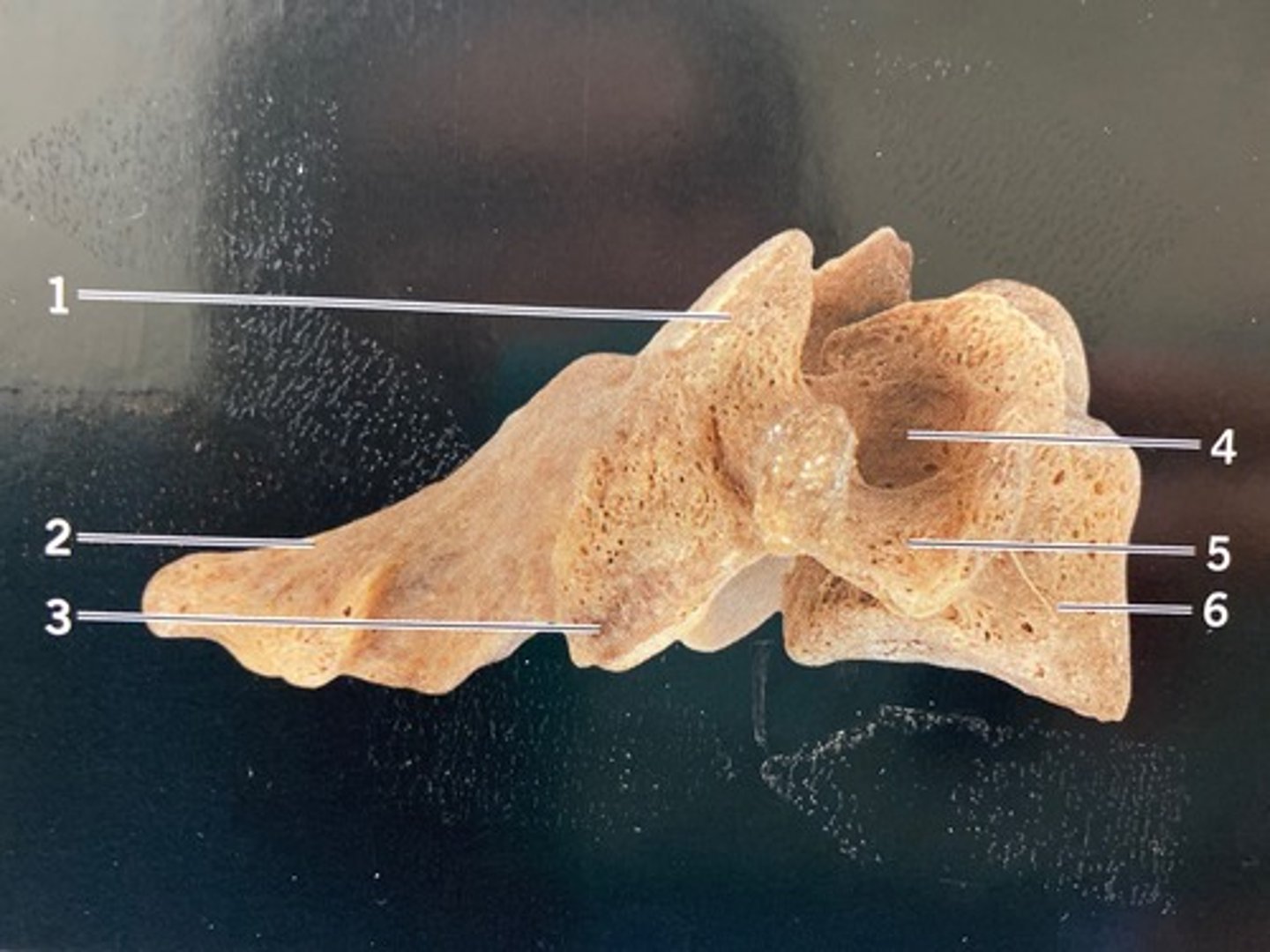
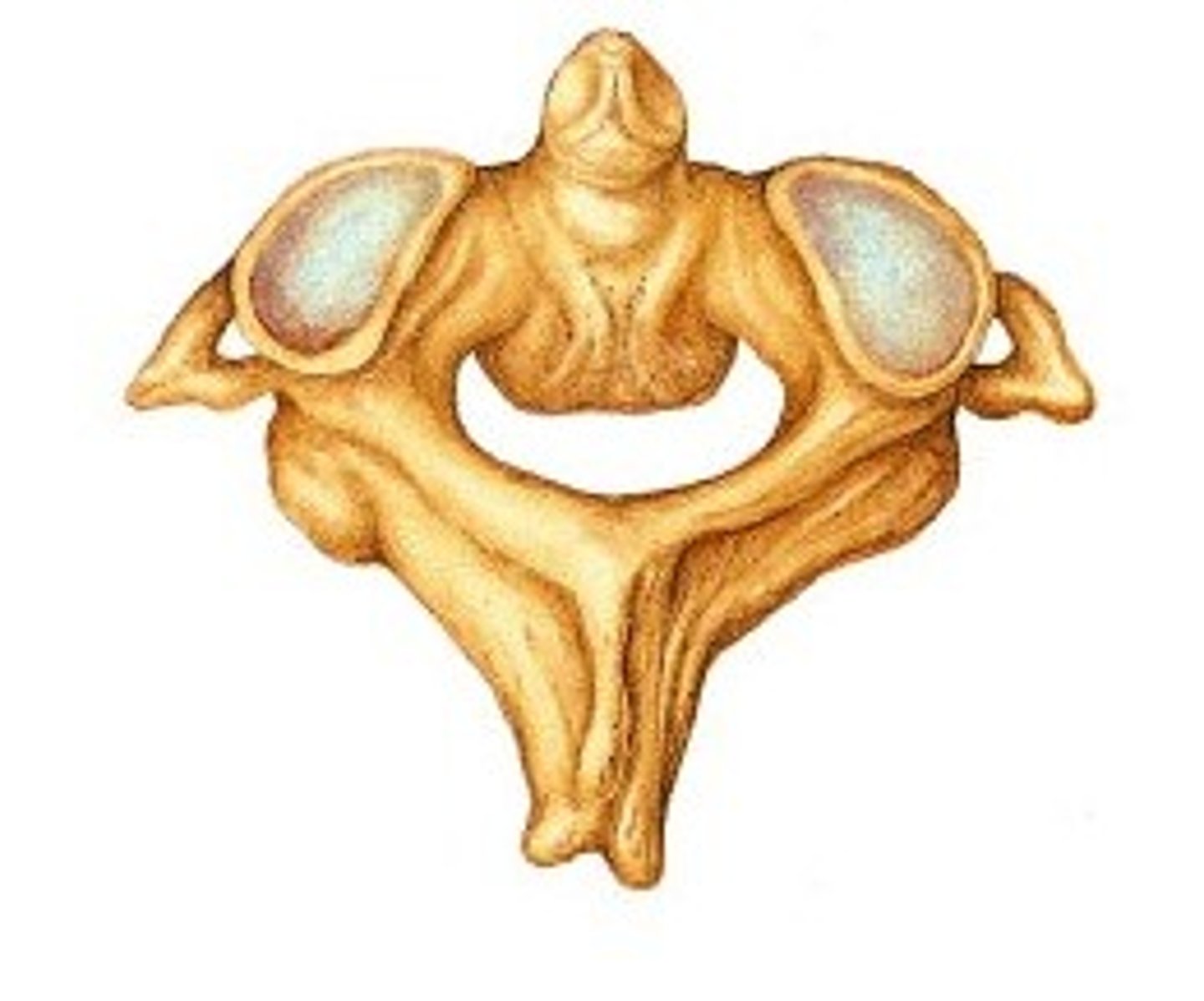
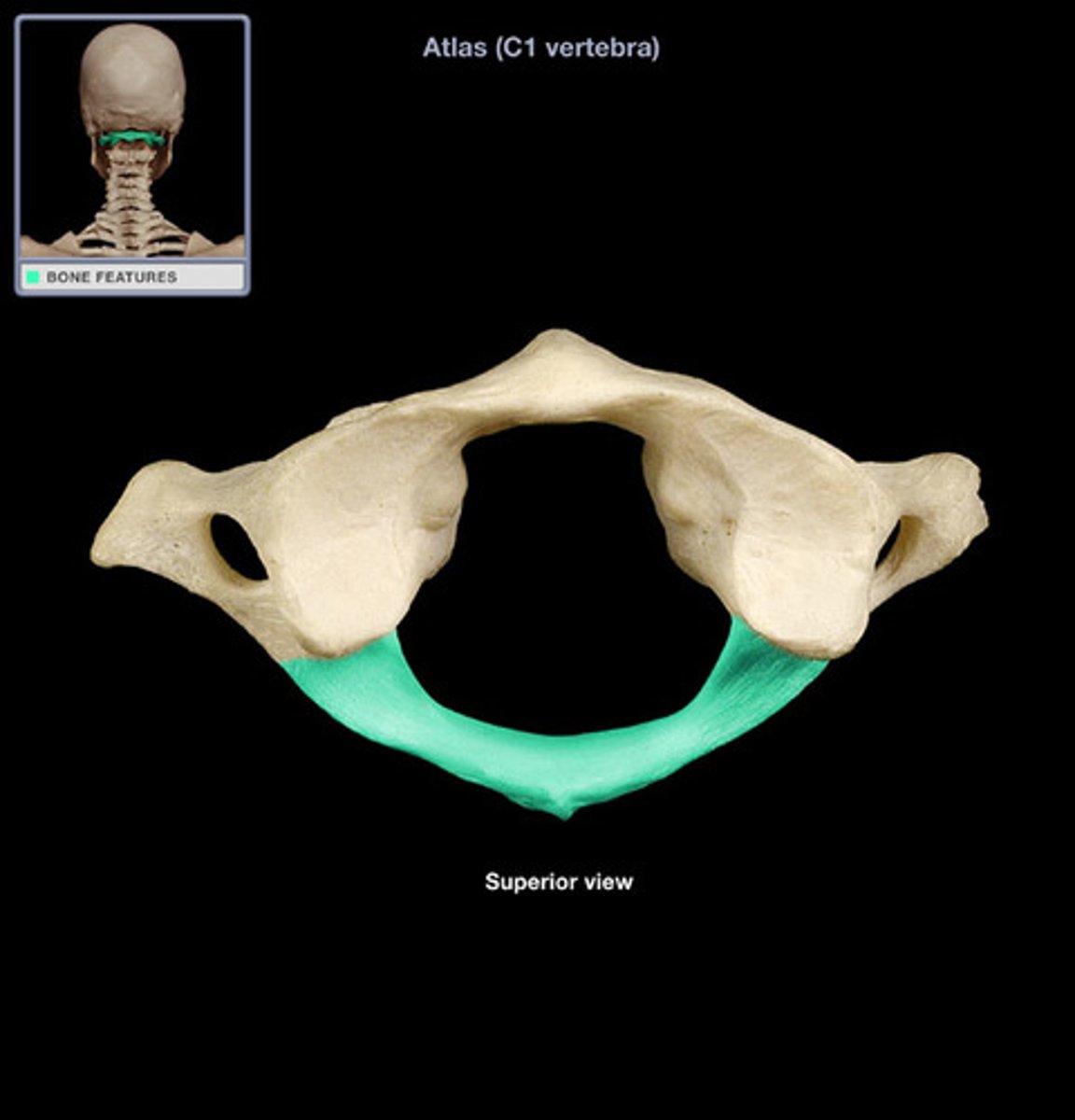
atlas
- first cervical vertebra (C1)
- no body
- large vertebral foramen
- articulates with the skull
- has no spinous process
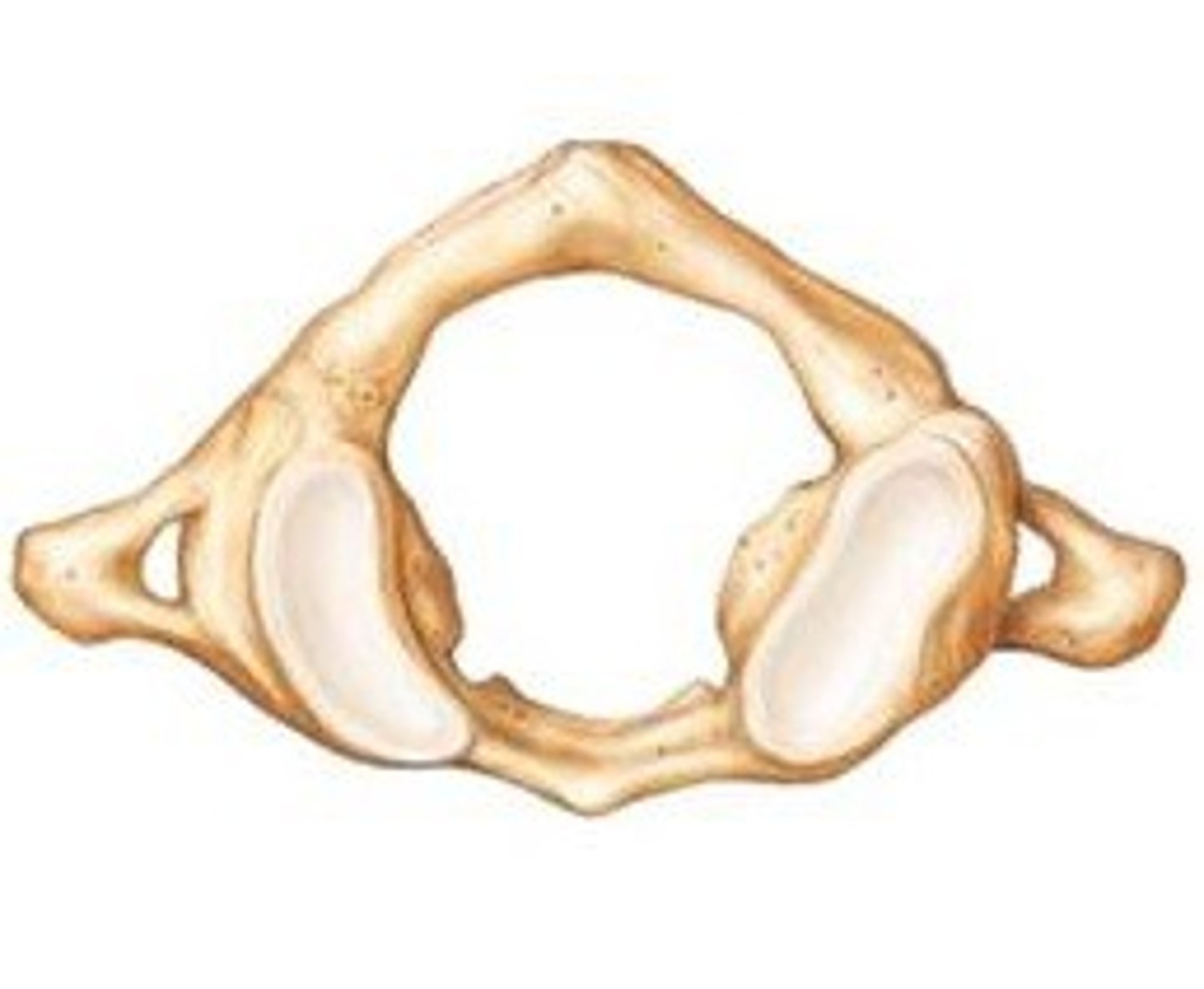
axis
- second cervical vertebra (C2)
- articulates with the atlas
- primary function is to provide the atlas with a pivot point for when the head is turned laterally and medially
anterior arch of atlas
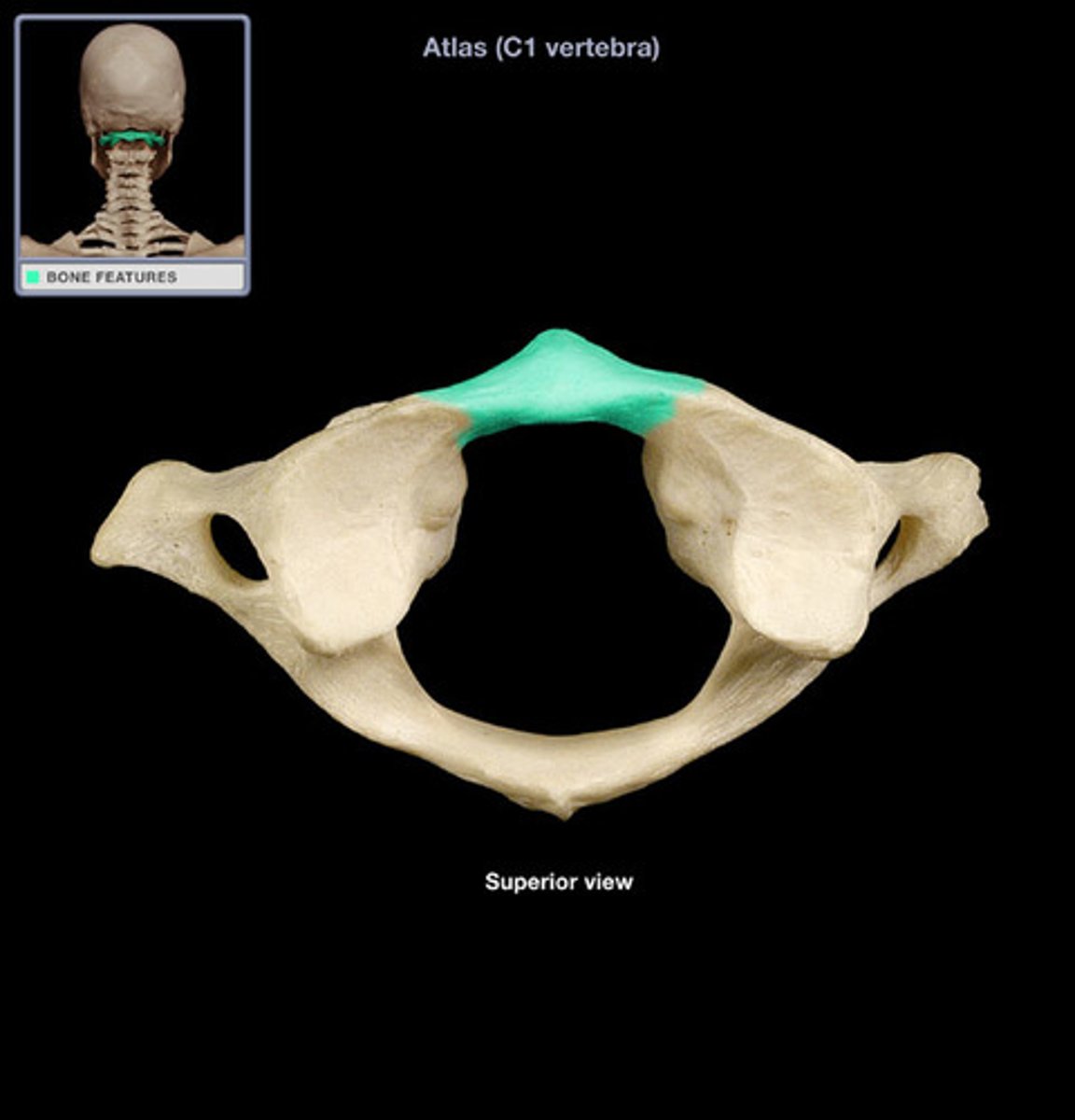
superior articular facet of atlas
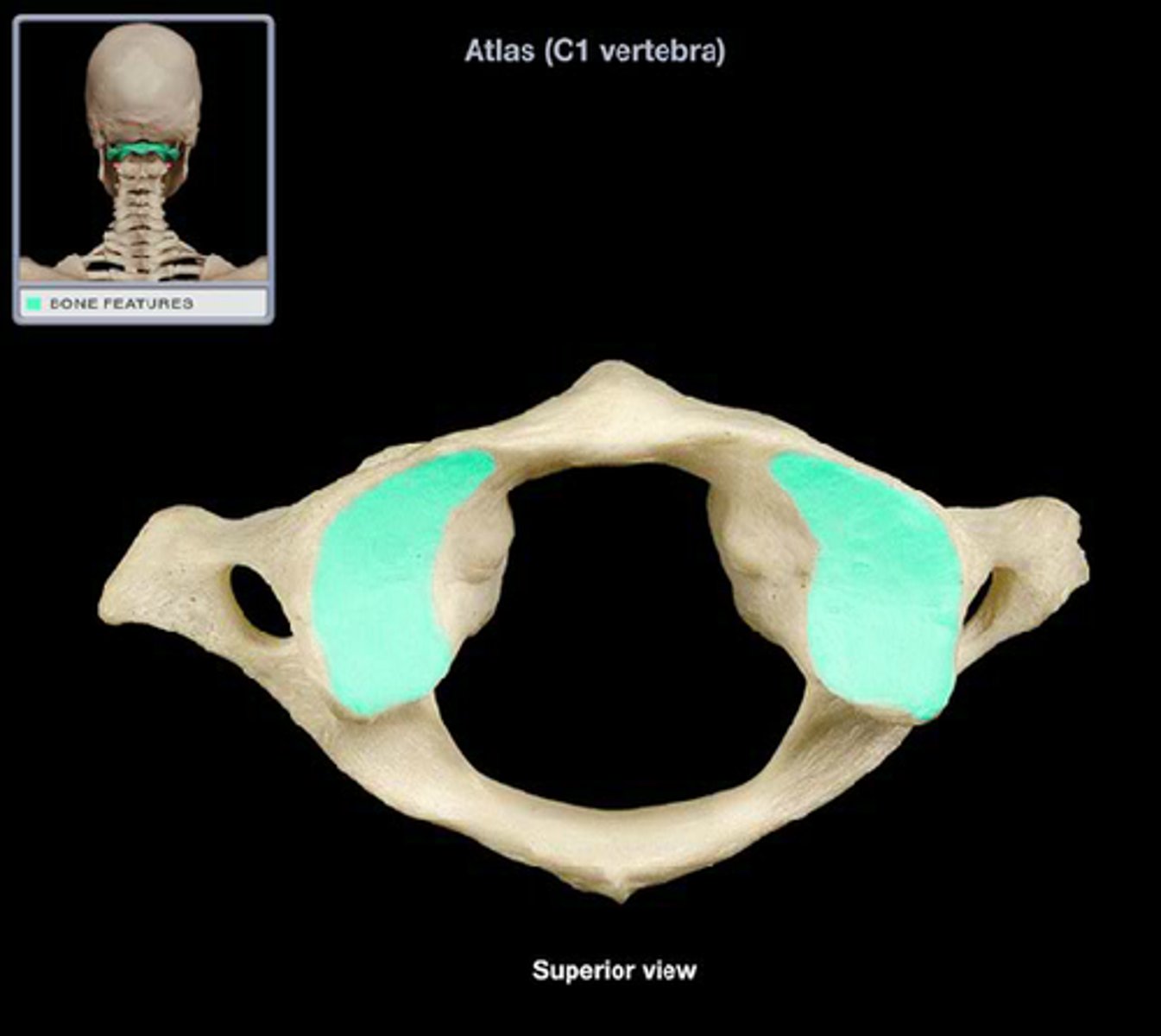
transverse foramen of atlas
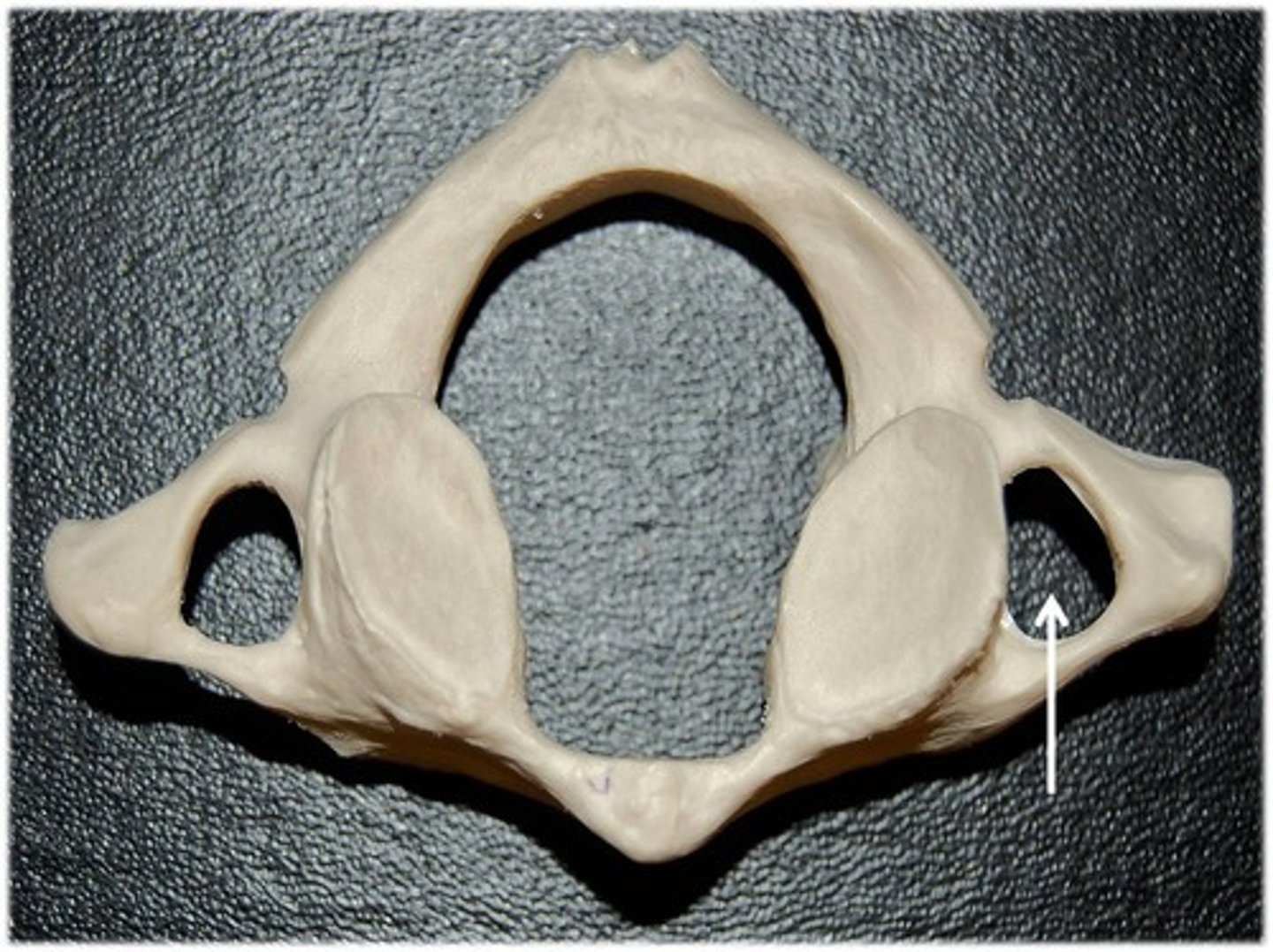
transverse process of atlas
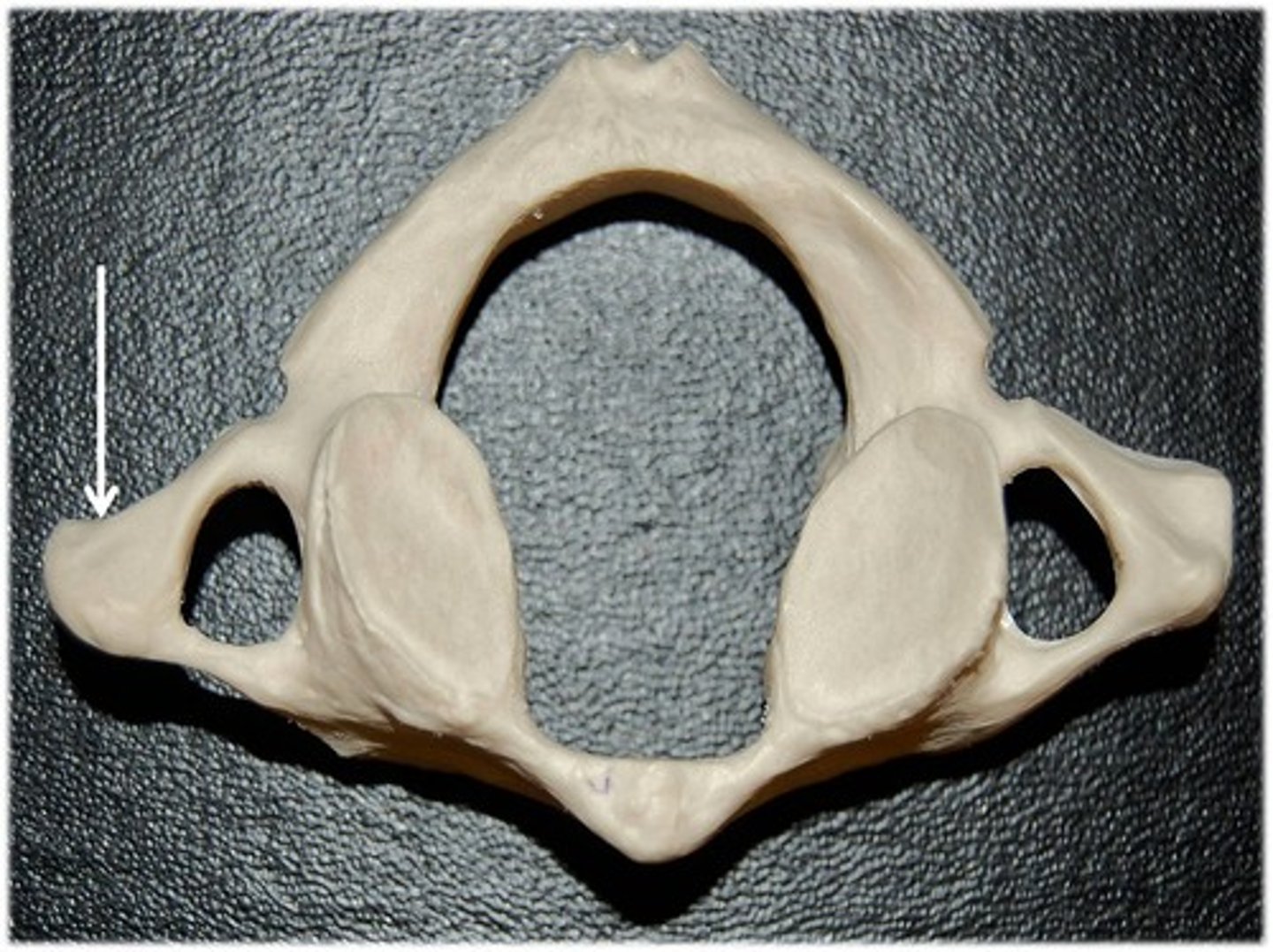
vertebral foramen of atlas
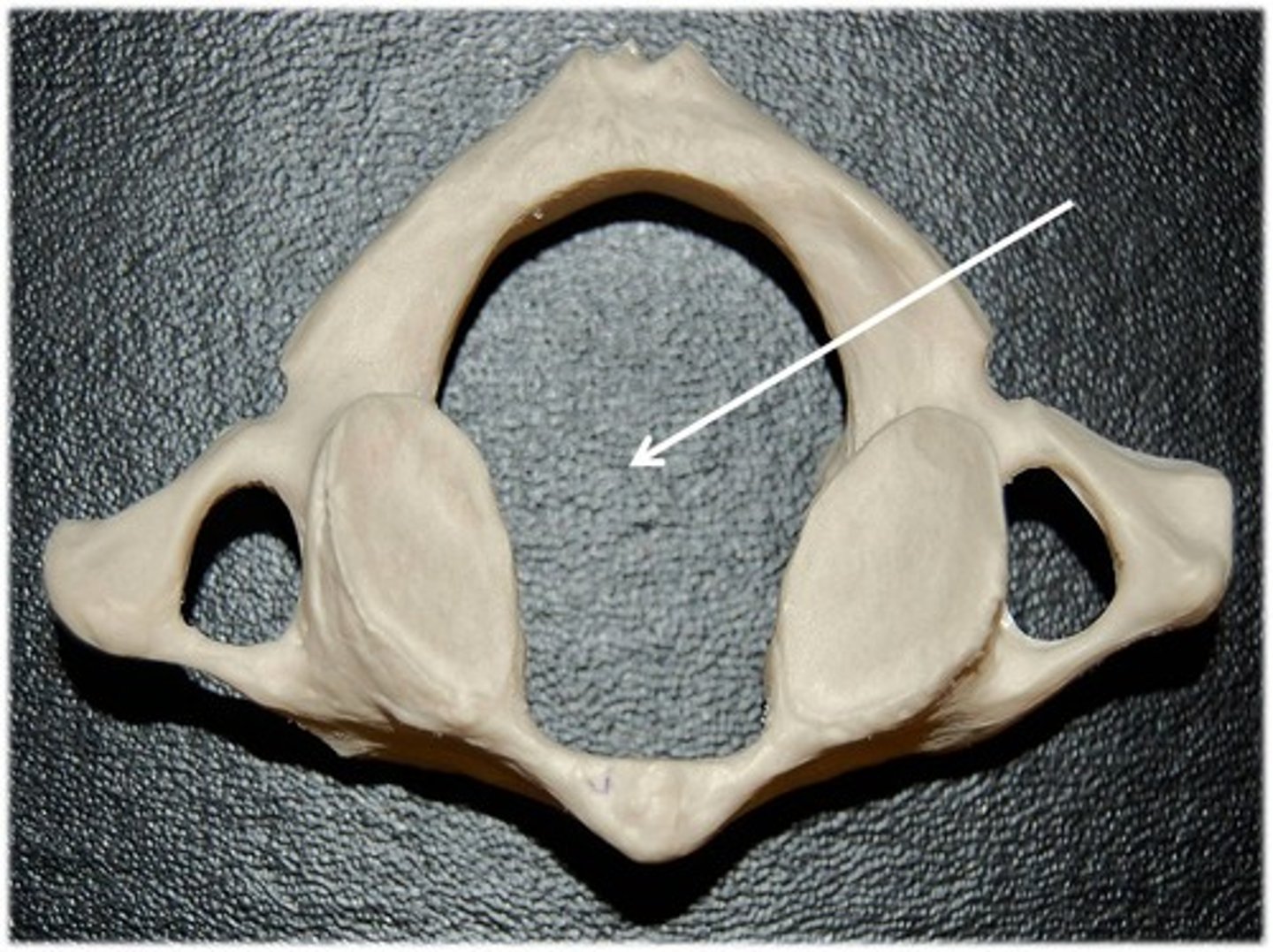
posterior arch of atlas
facet for the dens of C2 on atlas
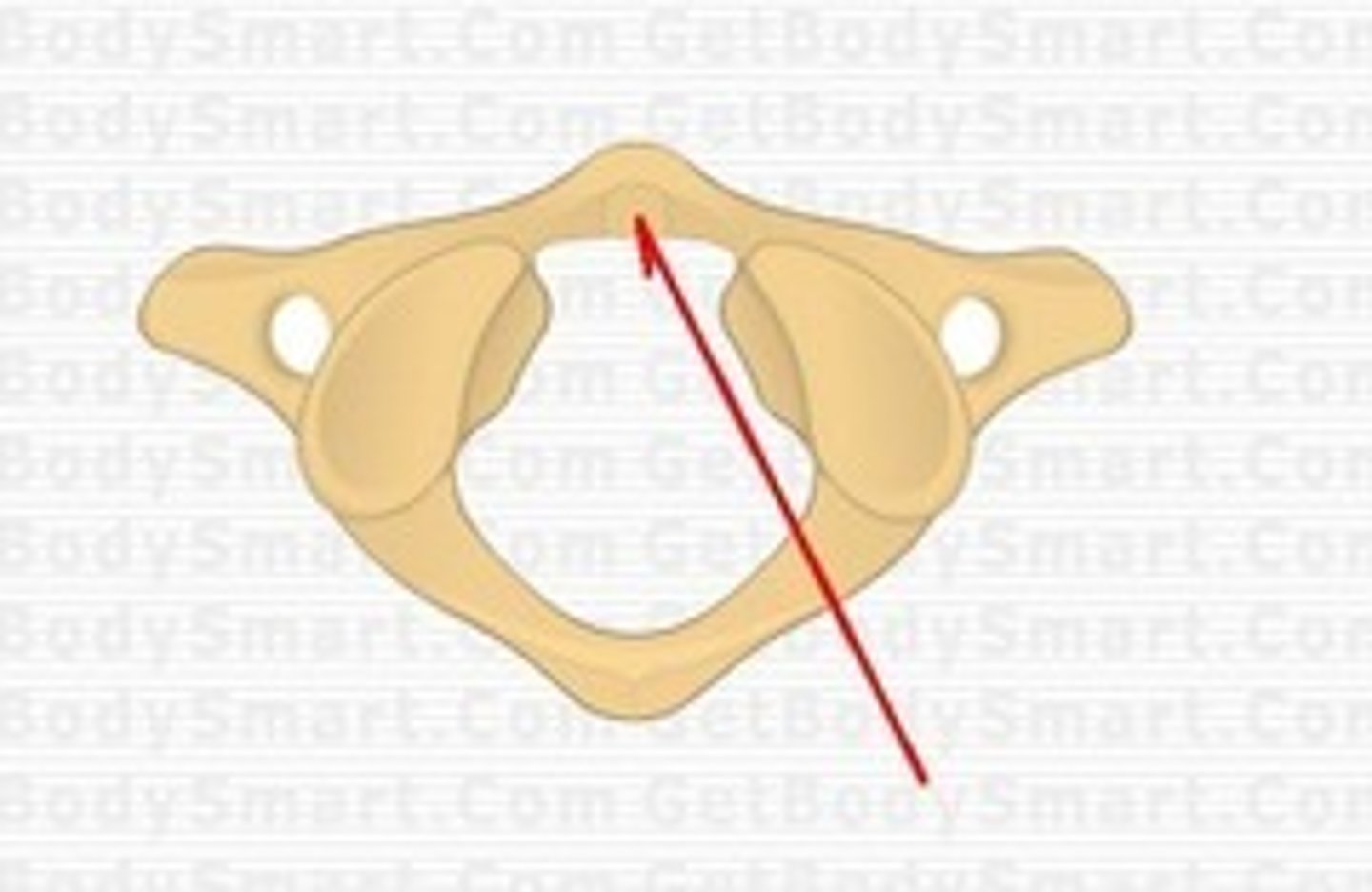
inferior articular facet of atlas
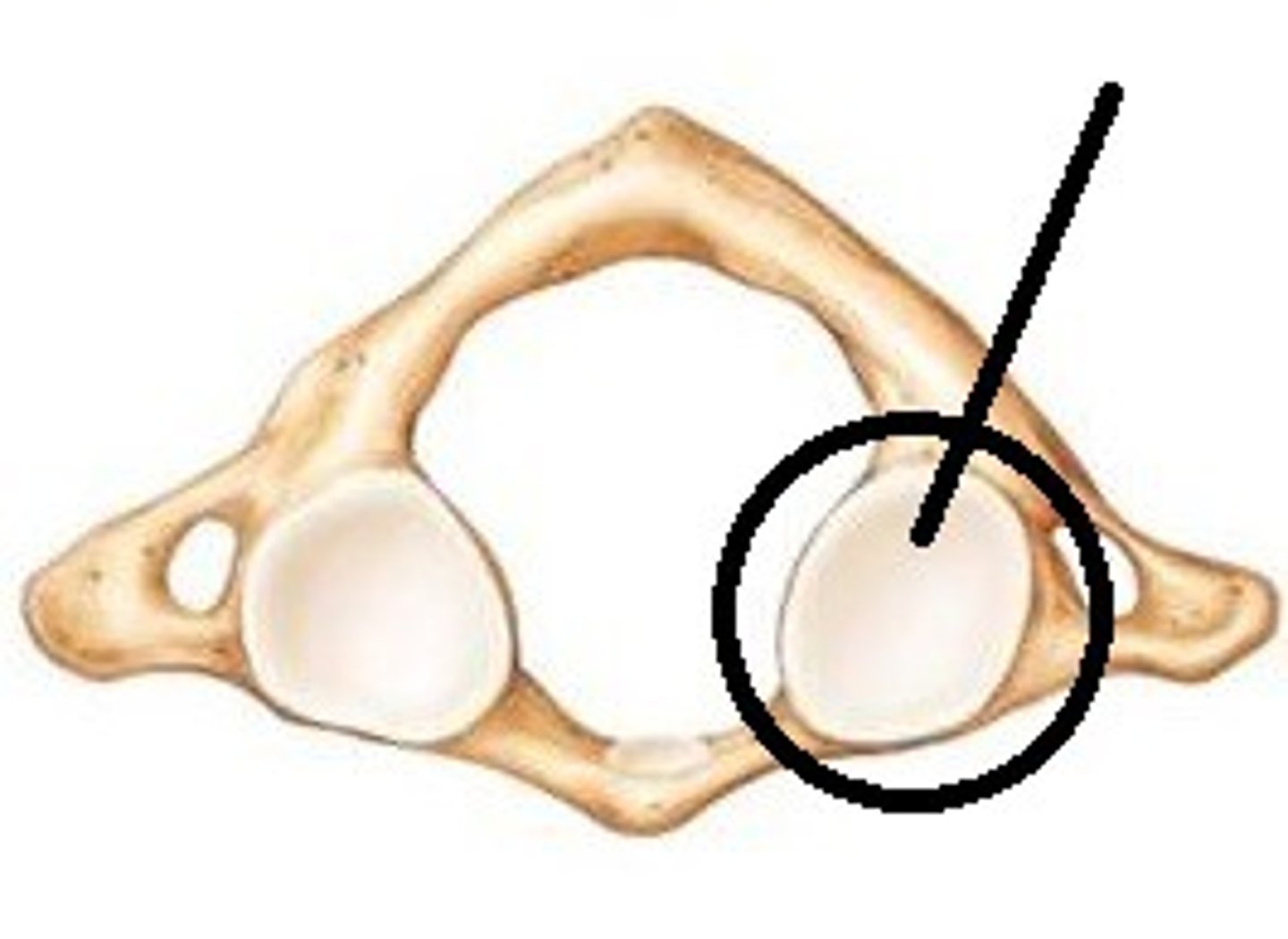
dens of axis
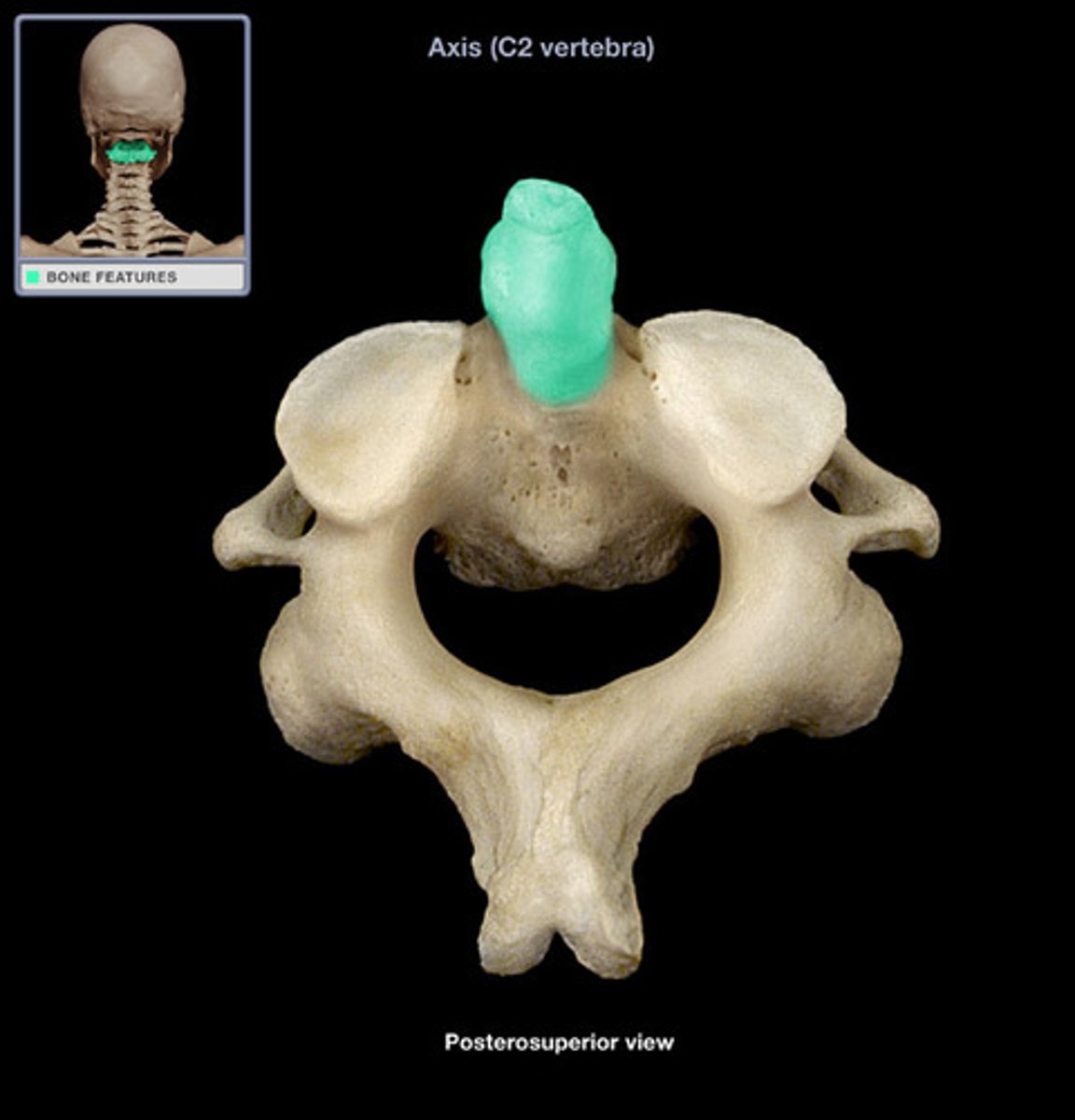
superior articular facet of axis
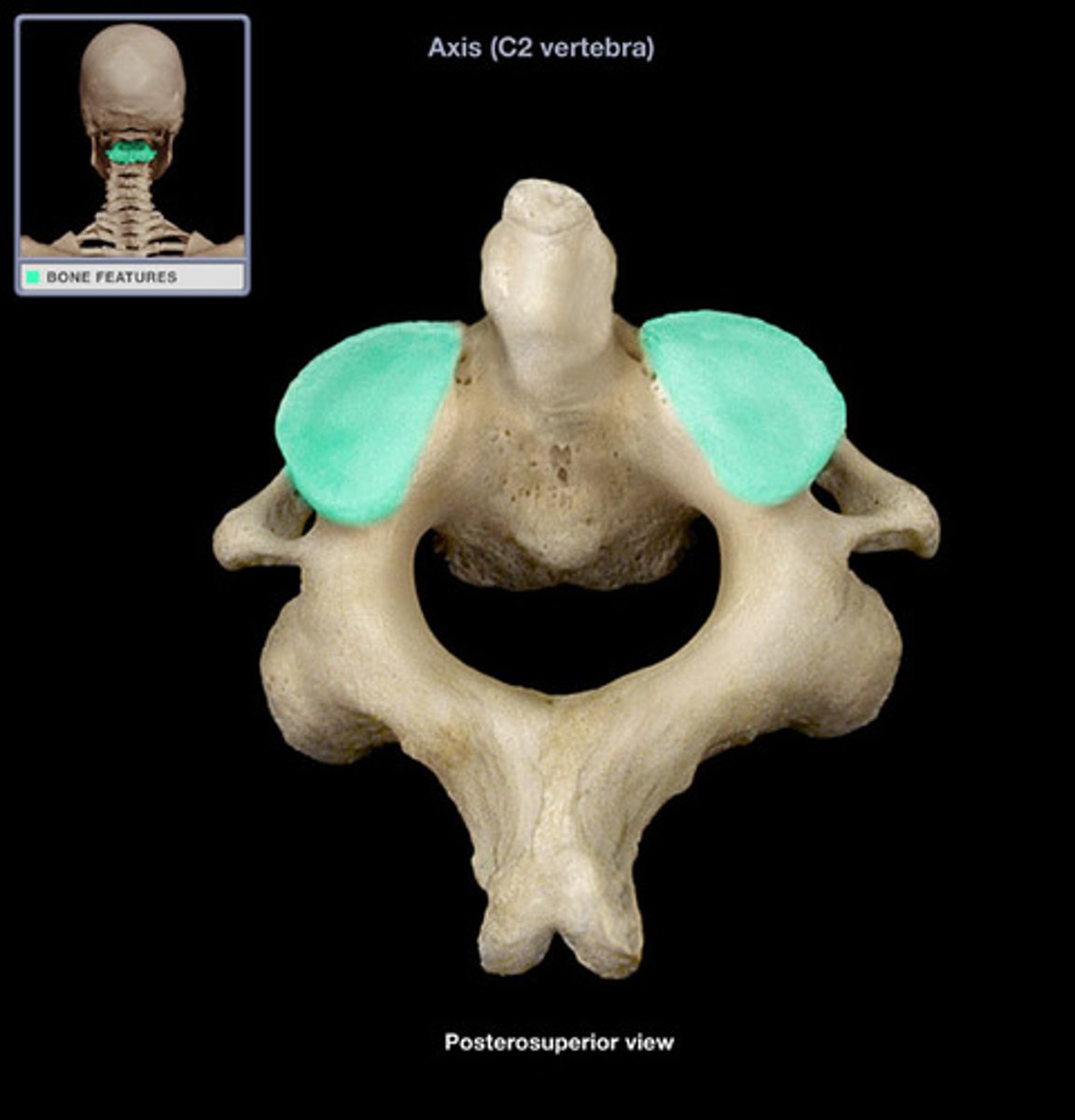
transverse foramen of axis
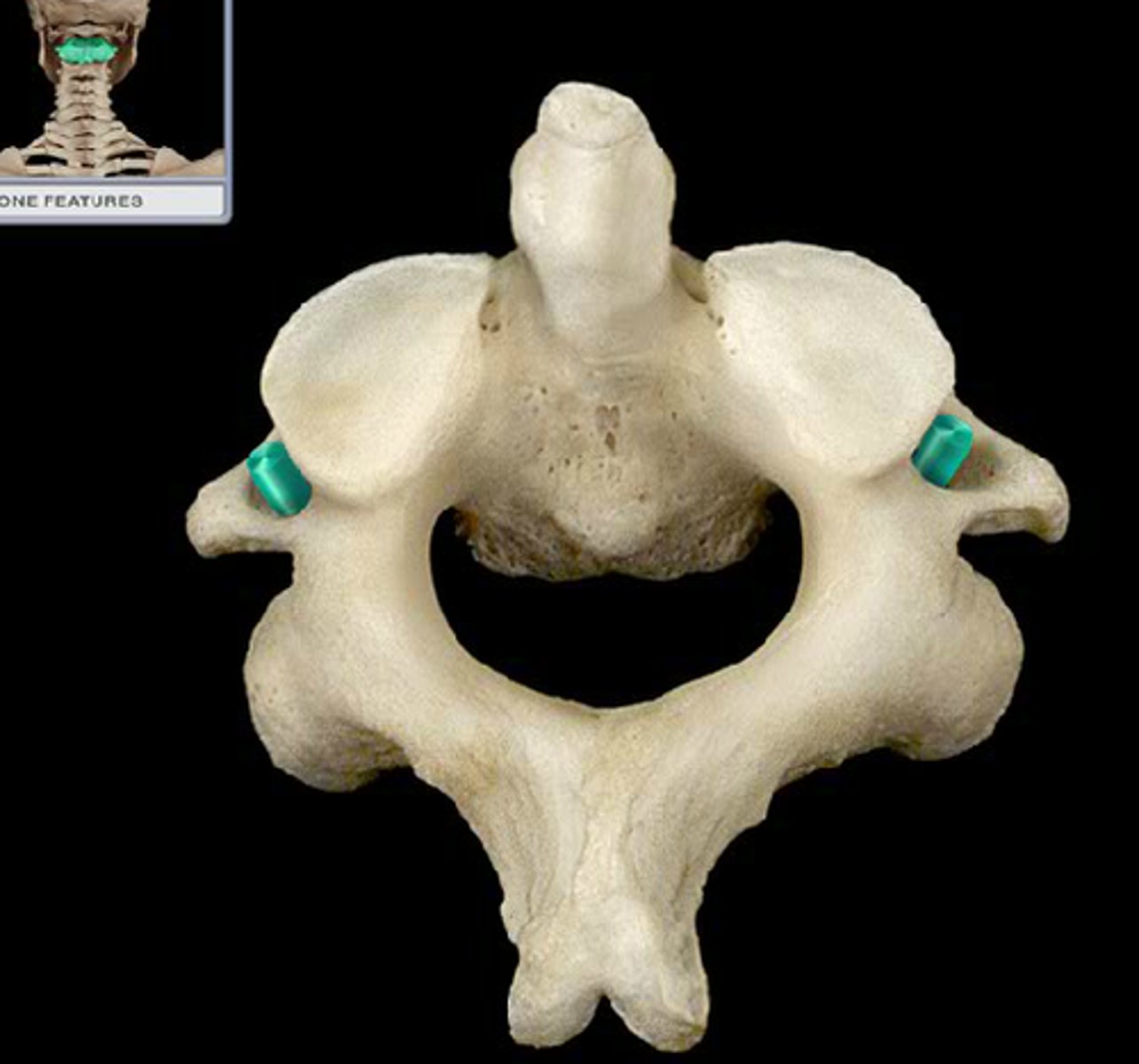
transverse process of axis
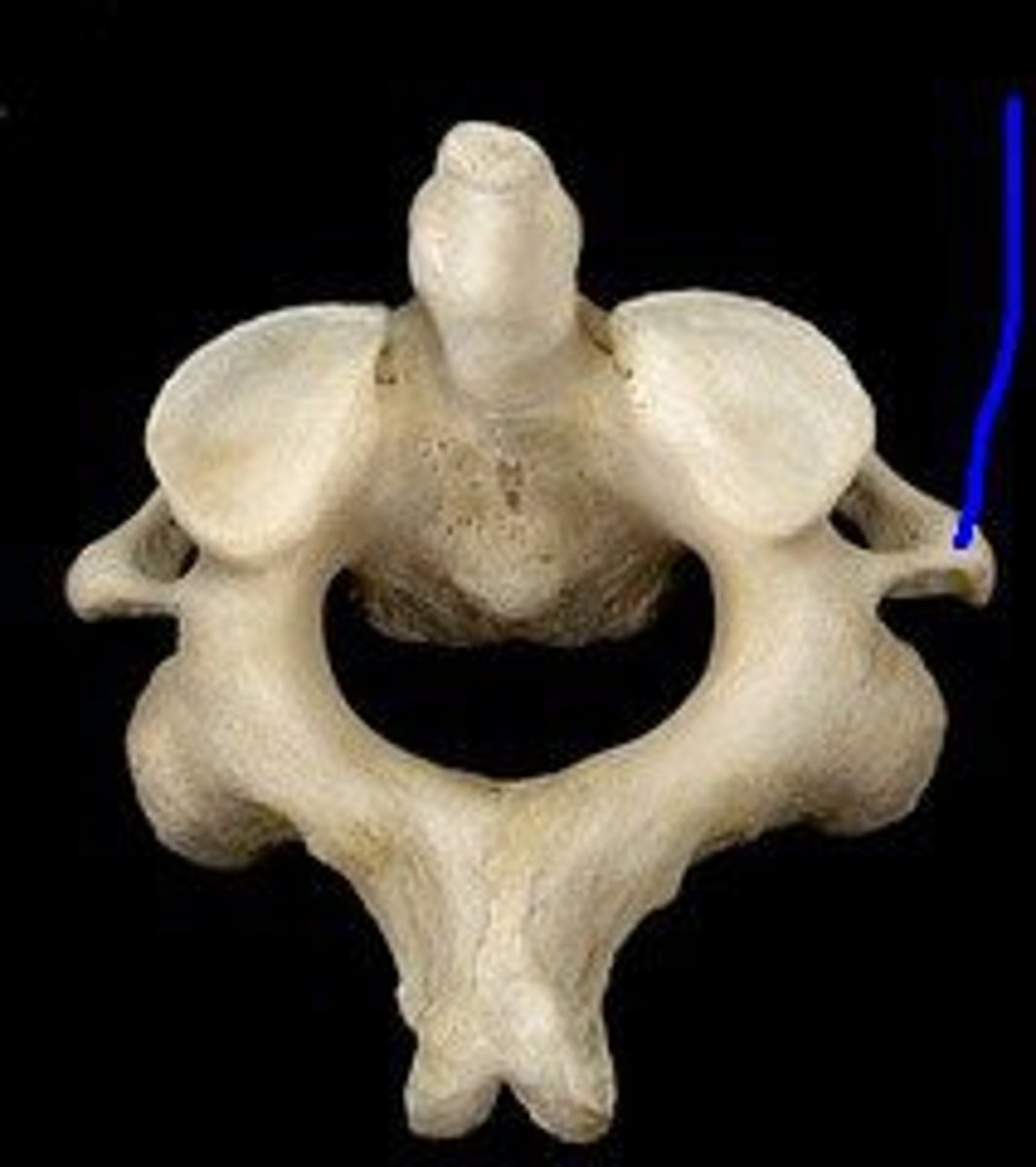
inferior articular process of axis
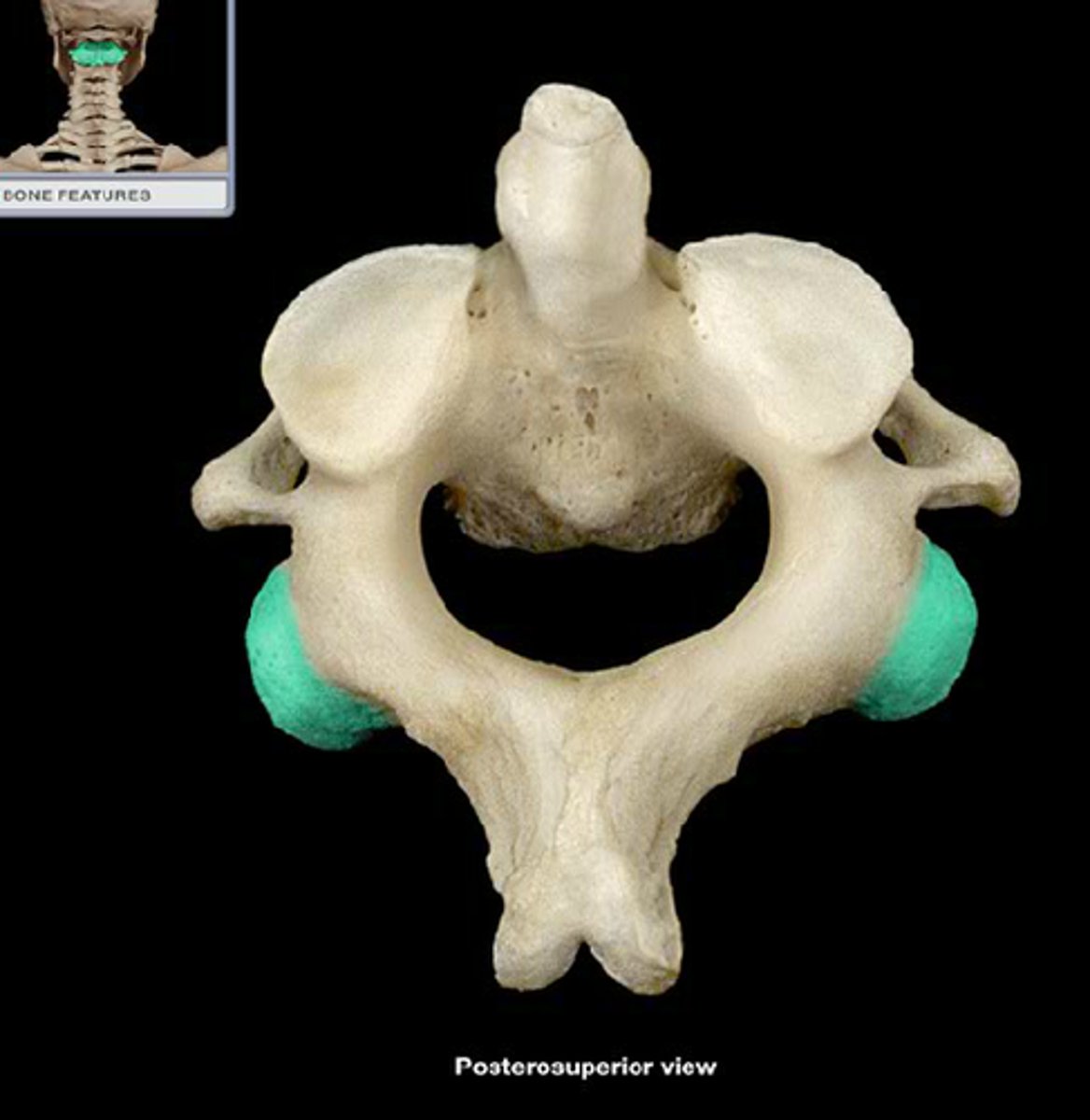
spinous process of axis
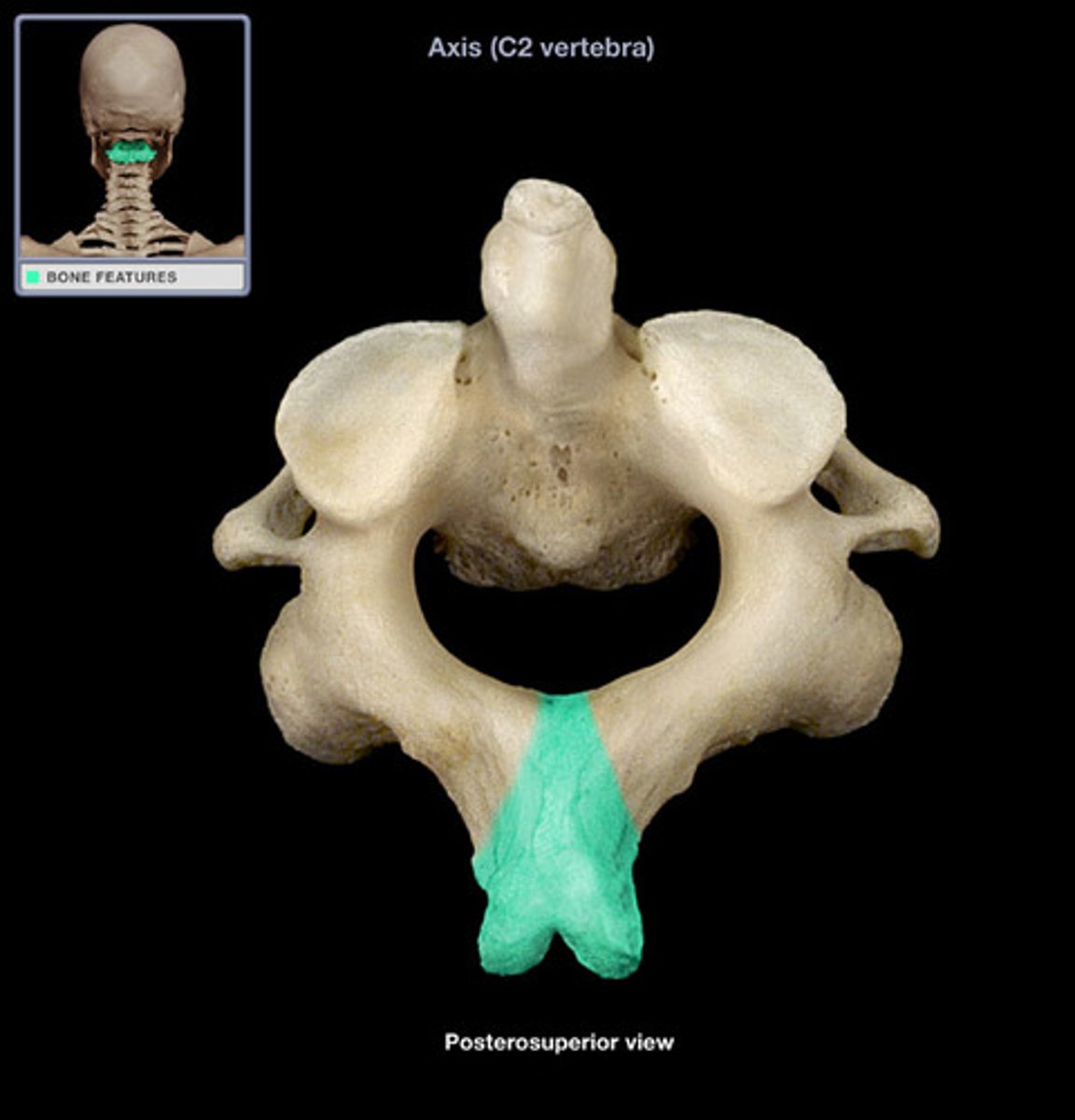
vertebral foramen of axis
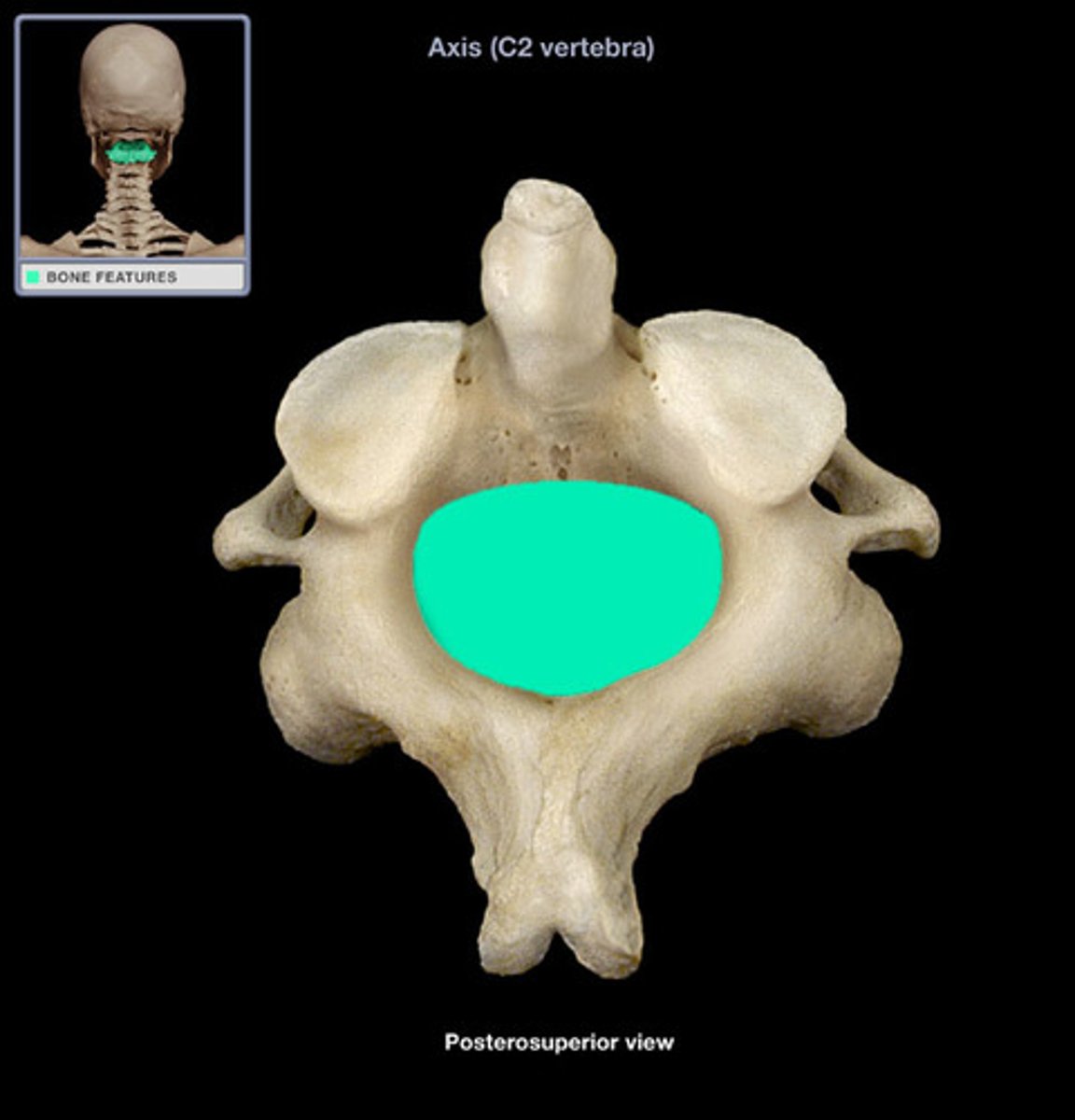
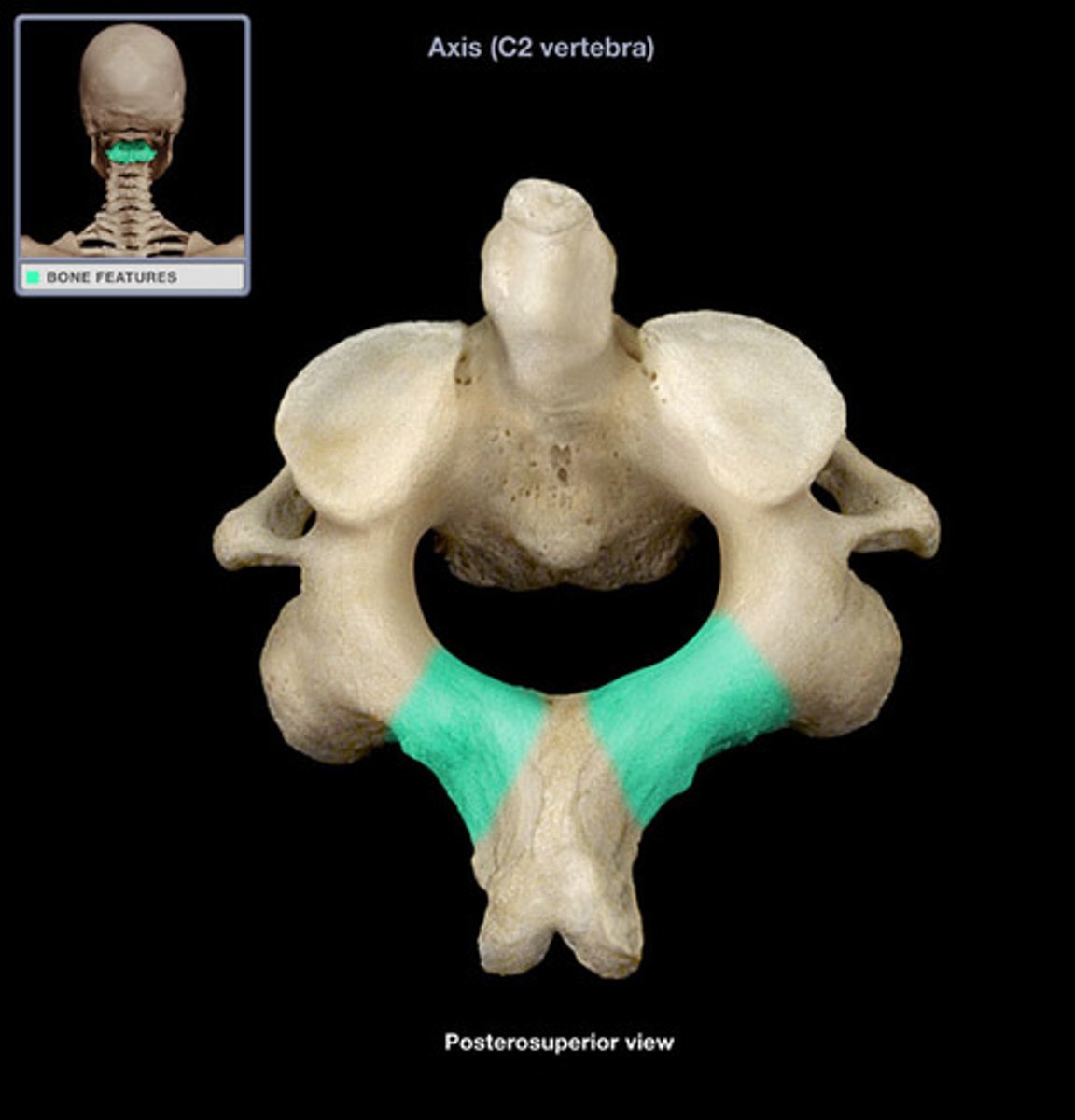
lamina of axis
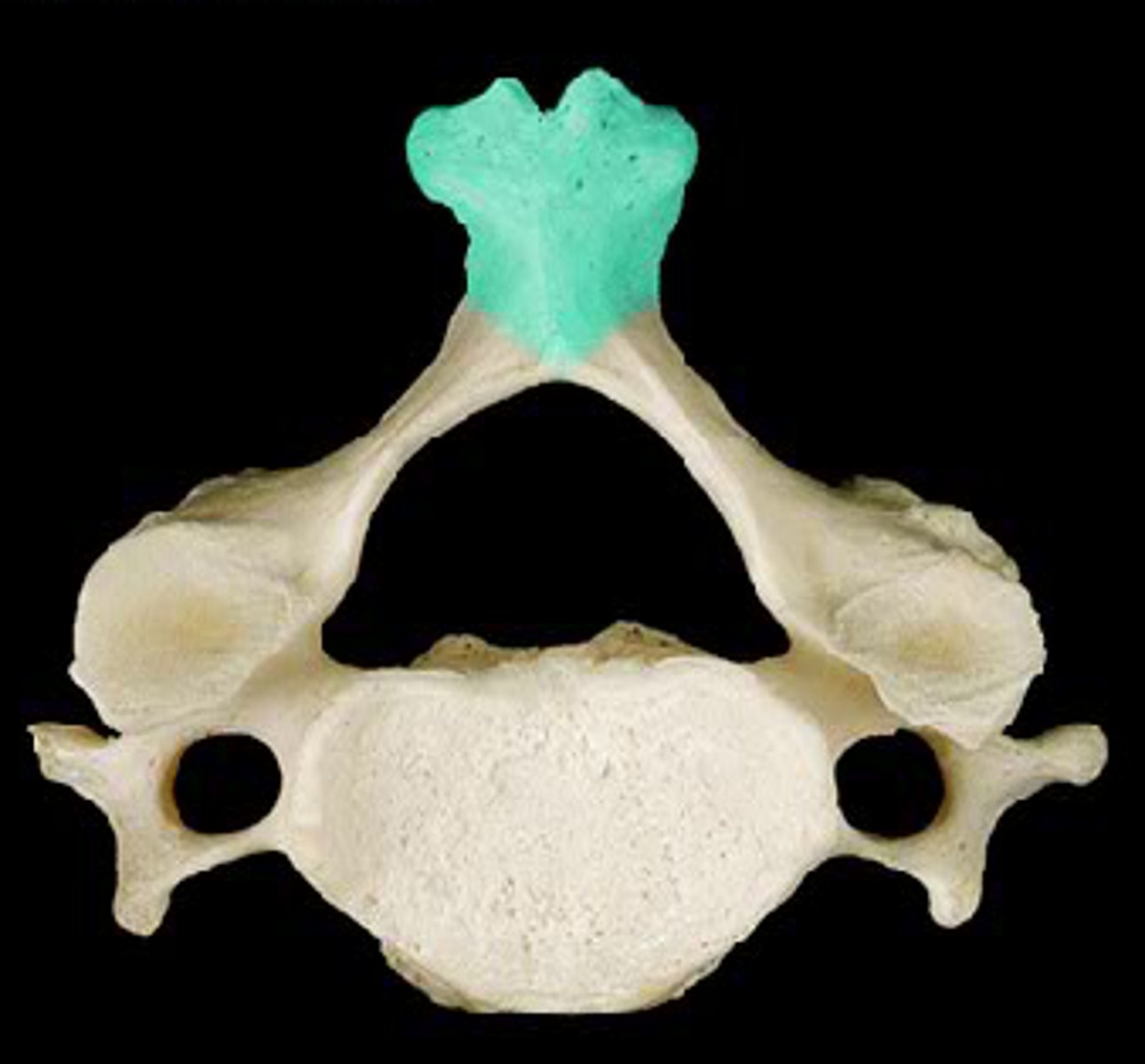
spinous process of cervical vertebrae
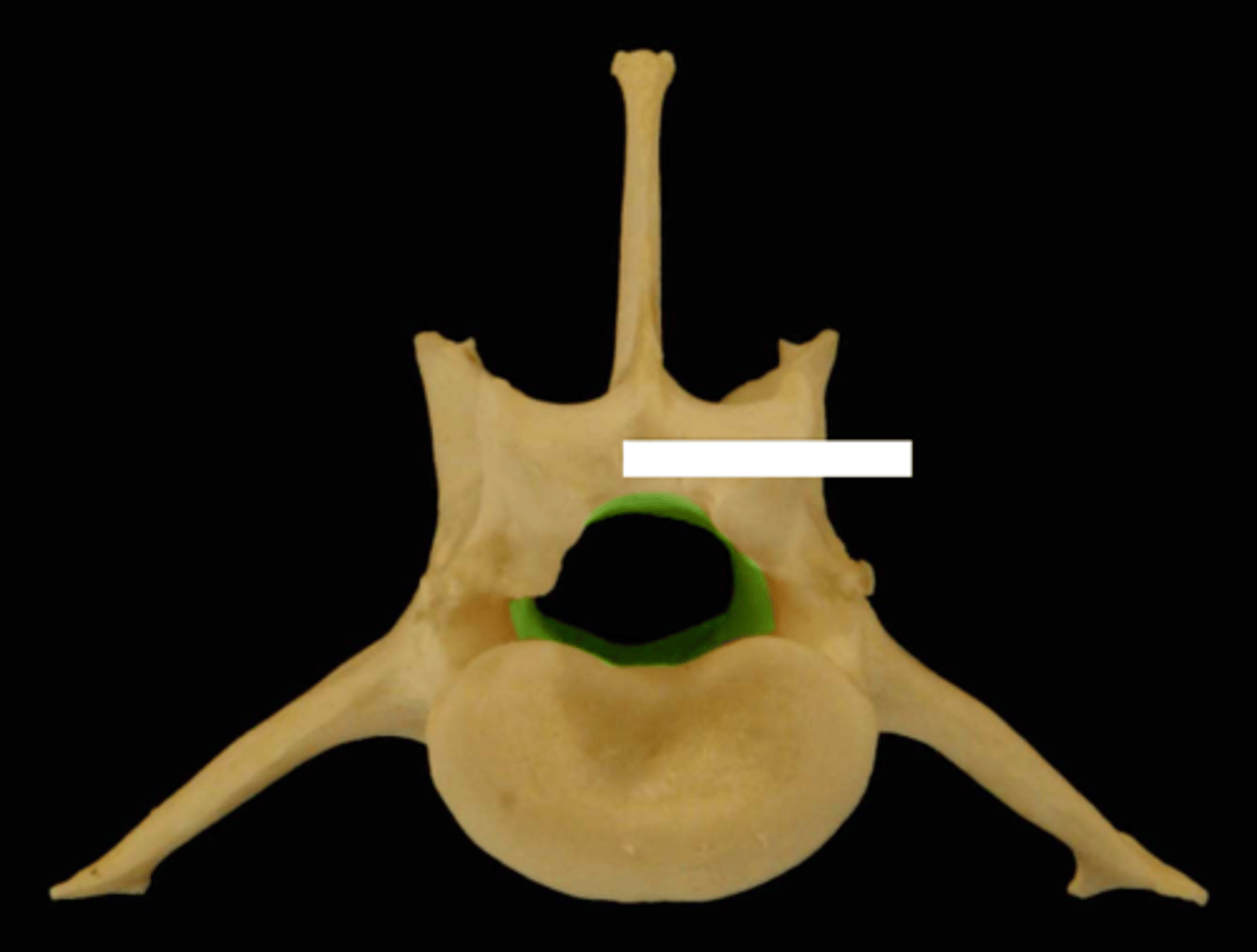
vertebral foramen of cervical vertebrae
lamina of cervical vertebrae
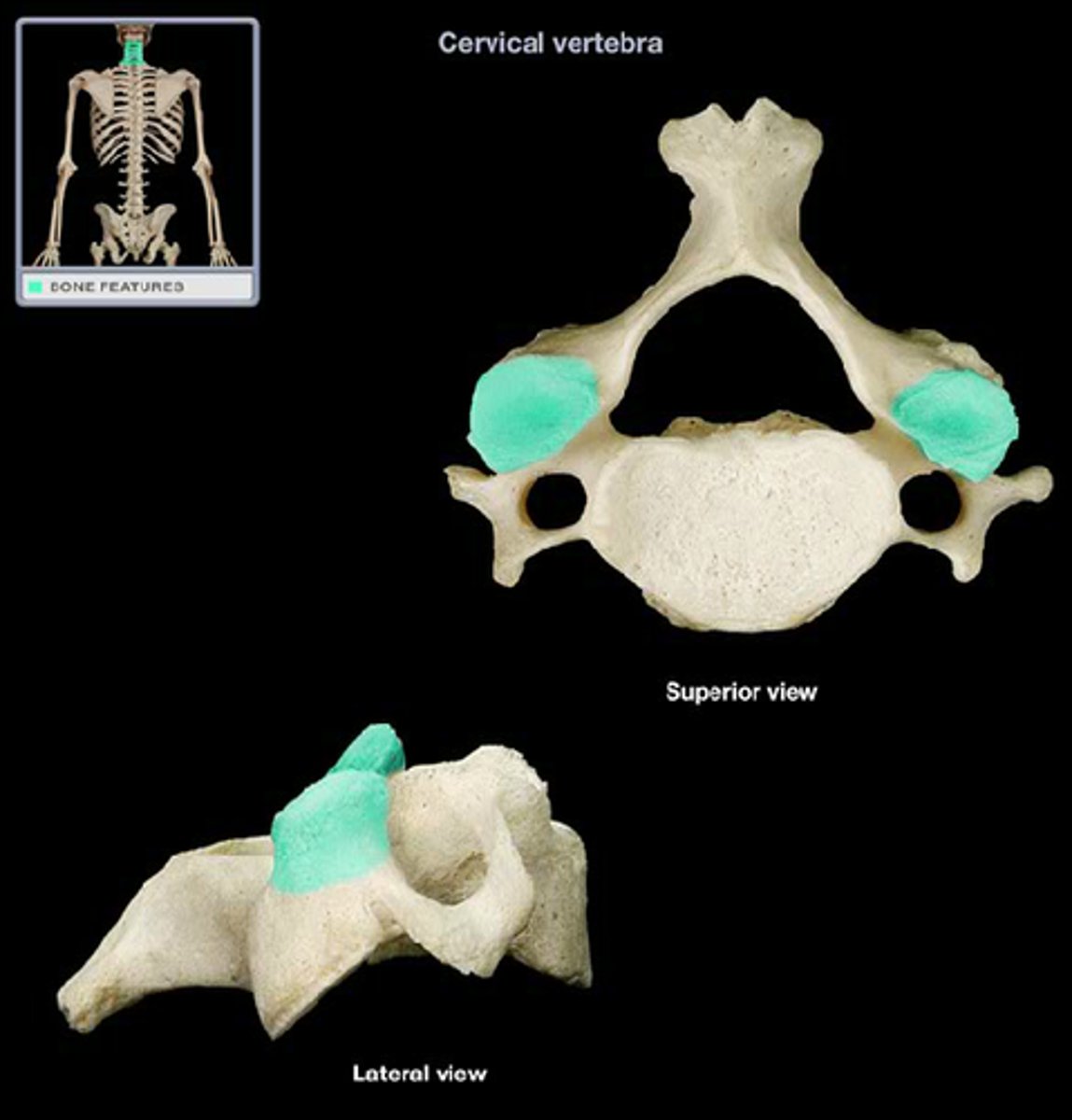
superior articular process of cervical vertebrae
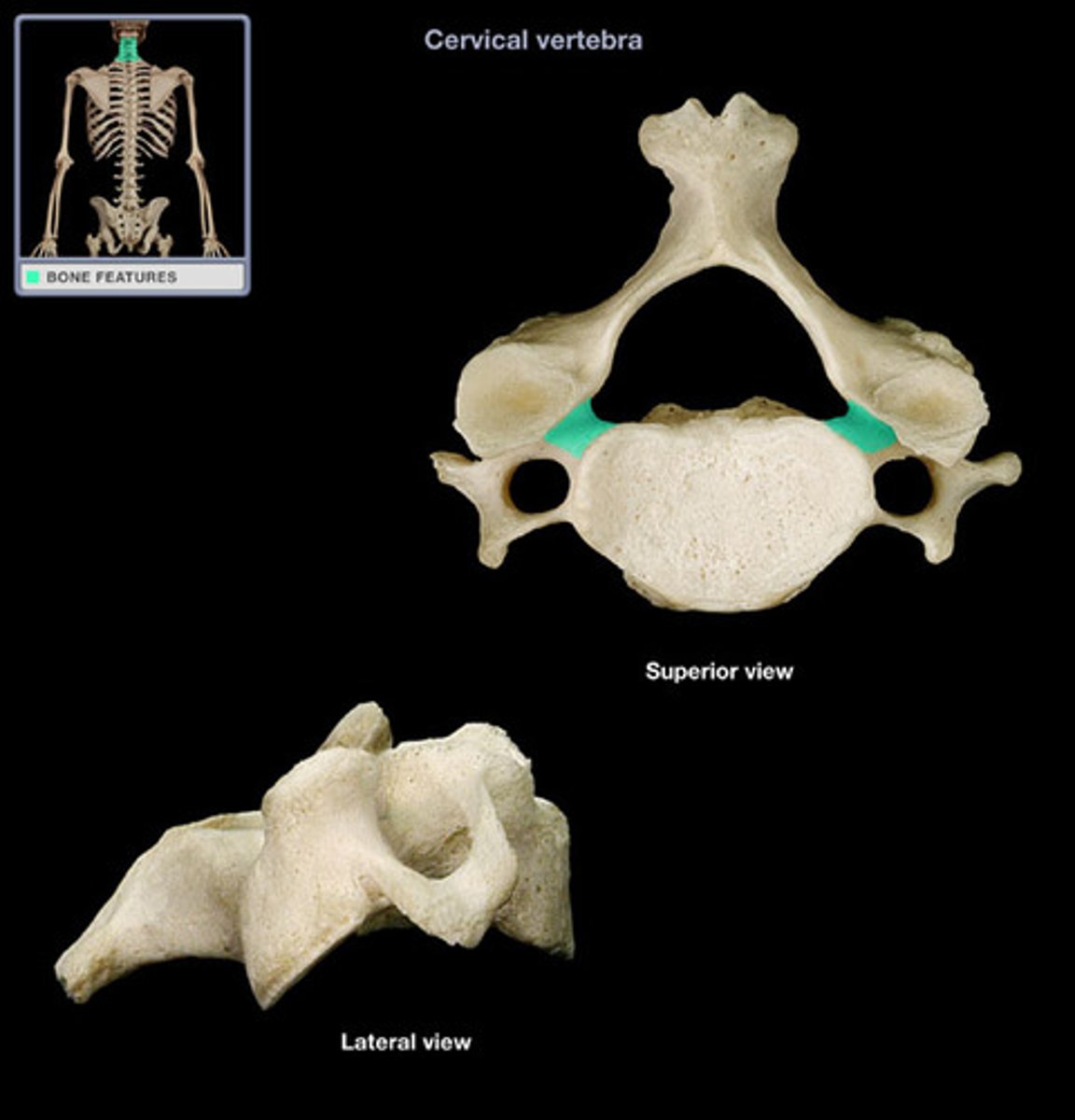
pedicle of cervical vertebrae
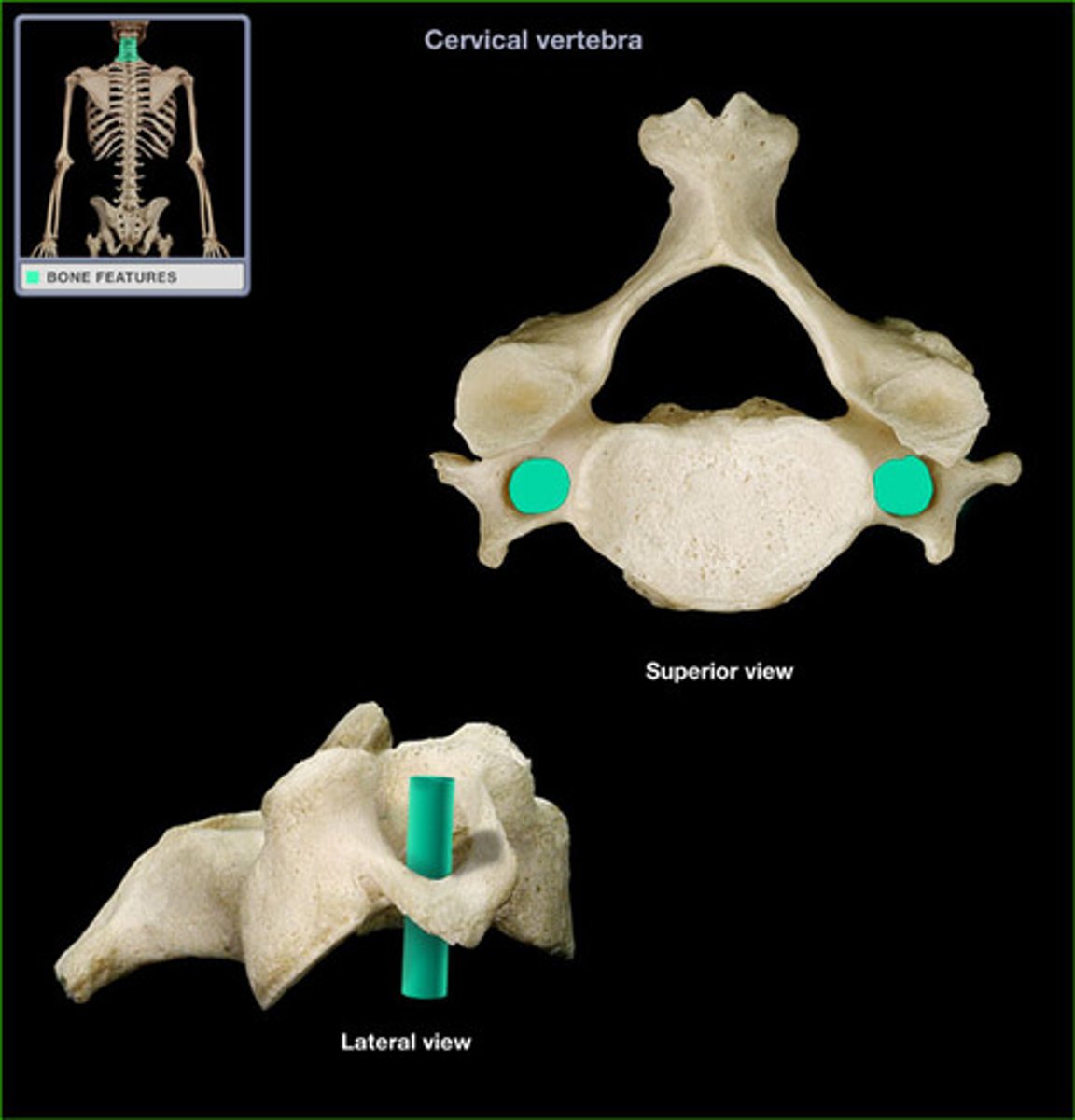
transverse foramen of cervical vertebrae
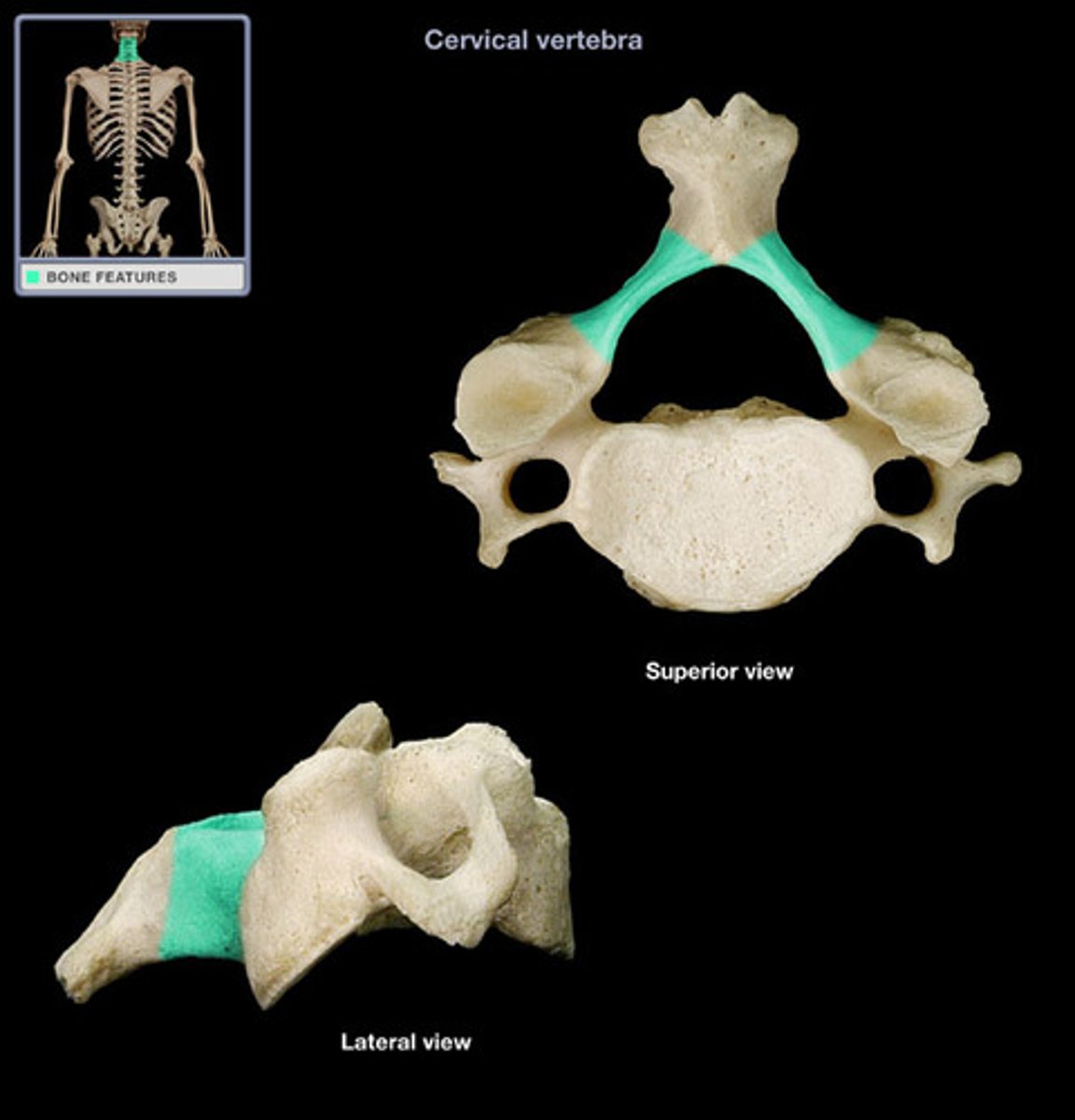
transverse process of cervical vertebrae
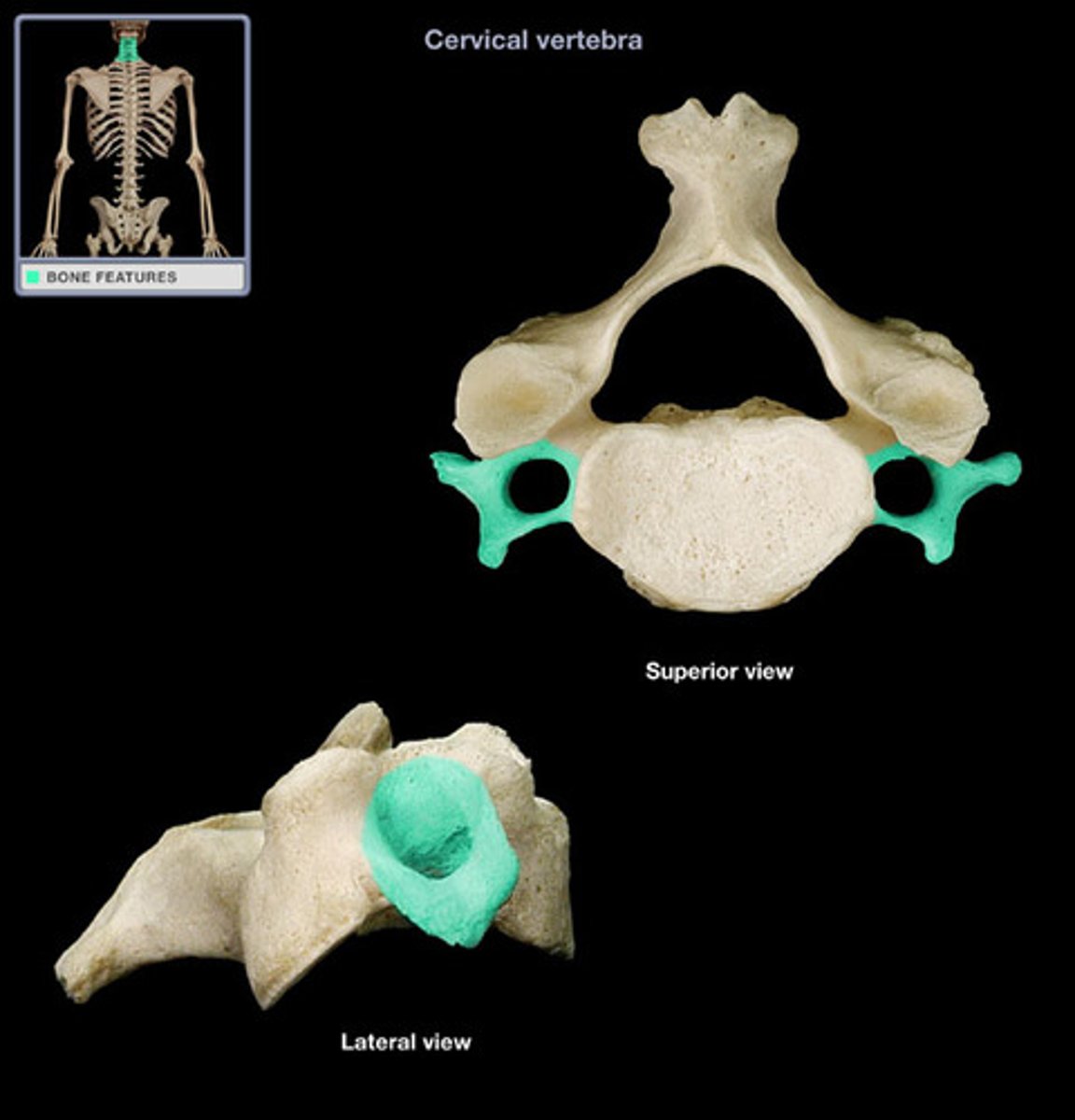
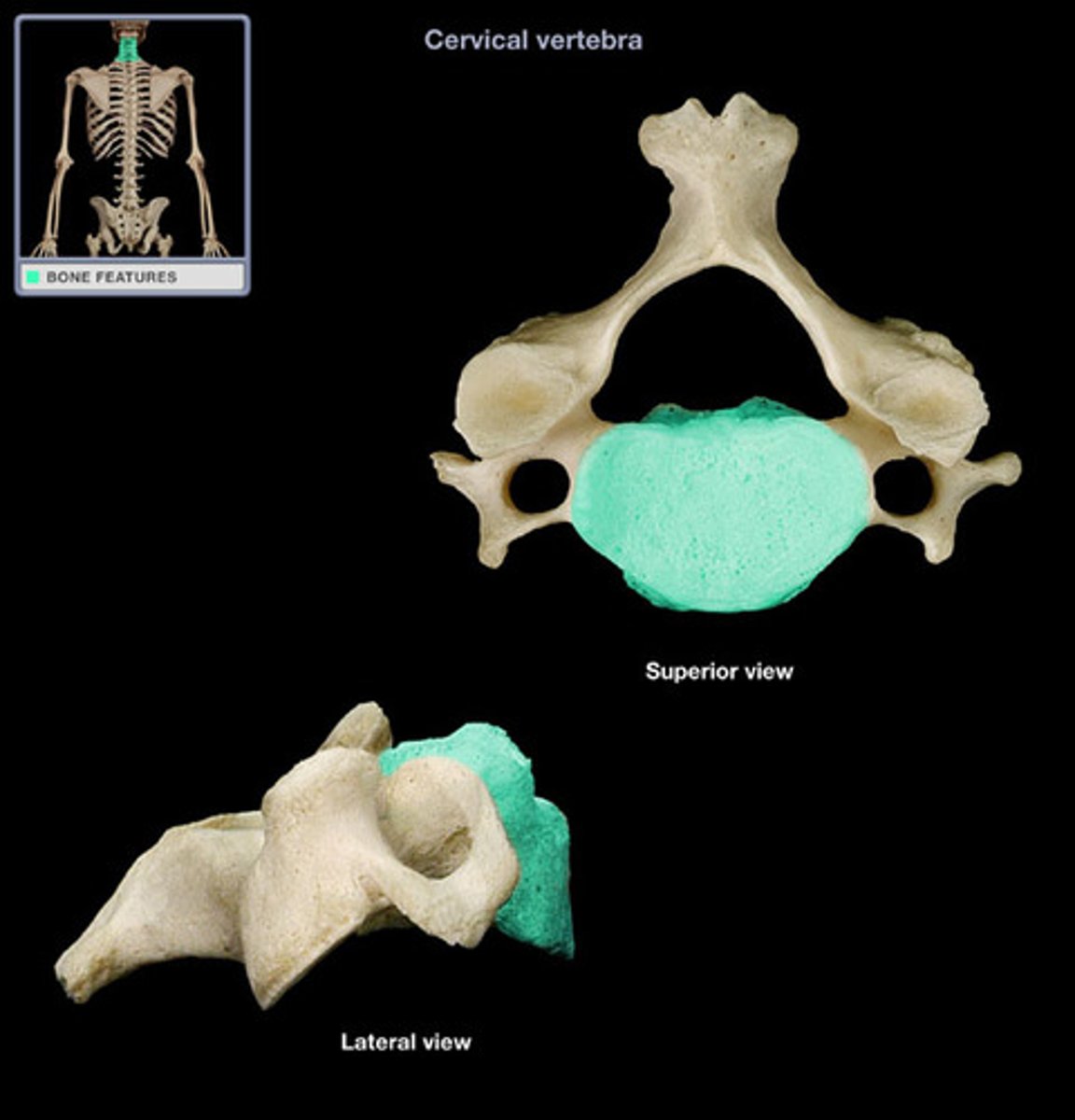
body of cervical vertebrae
inferior articular process of cervical vertebrae
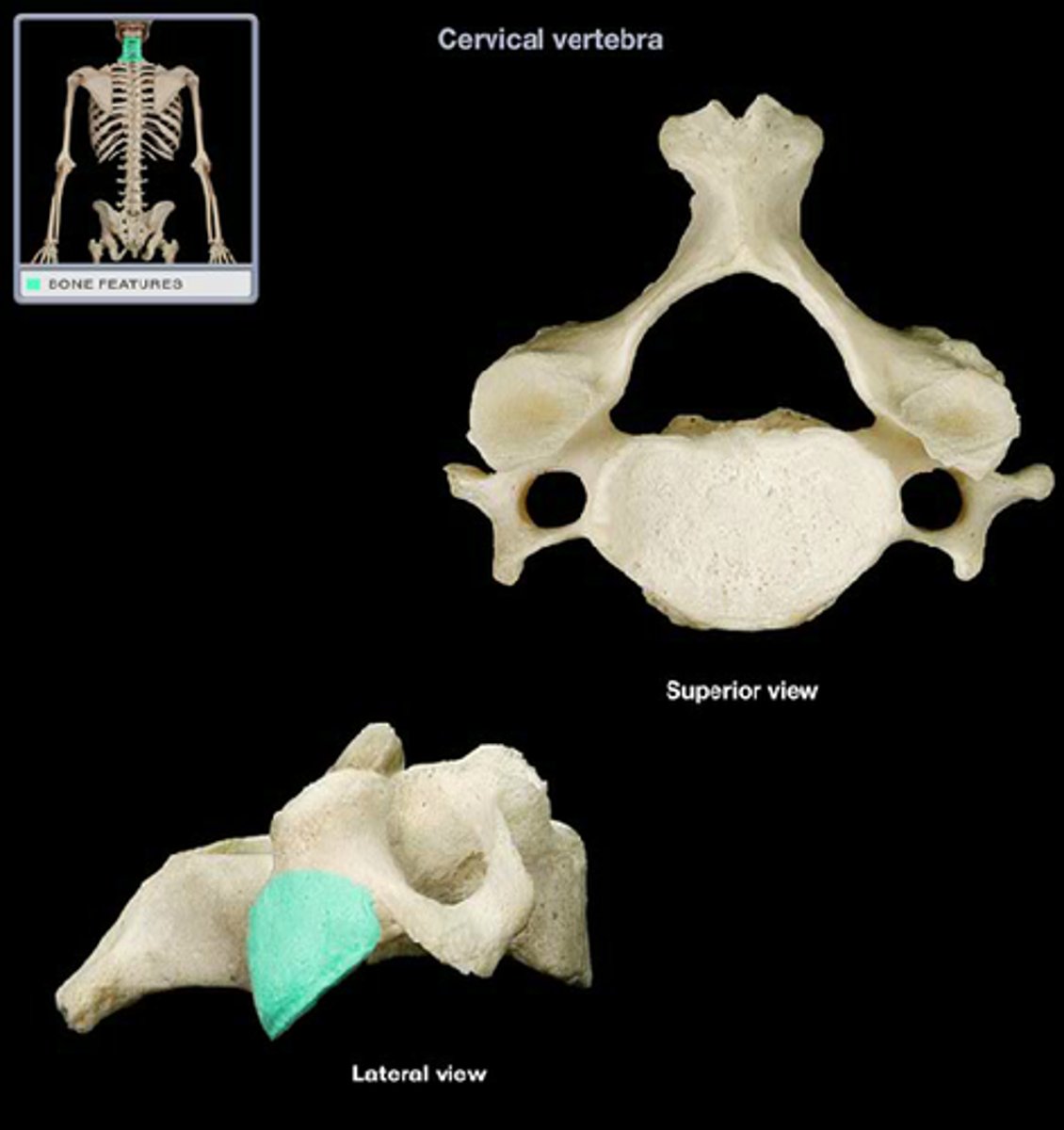
spinous process of thoracic vertebrae