clinical introduction to endocrine system
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is a hormone?
chemical messengers secreted directly into the bloodstream
Key characteristics of hormones
- travel via circulatory system to target organs
- bind to specific receptors on target cells
- trigger cellular responses through signal transduction
- subject to feedback control mechanisms
Types of Hormonal Signalling:
endocrine - Distance signalling via bloodstream
Paracrine - Local cell-to-cell communication
Autocrine - Self-signalling
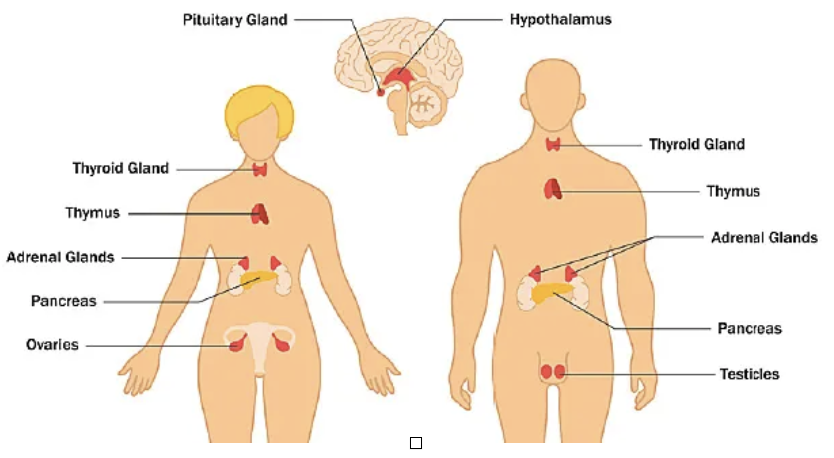
What are the major endocrine glands?
• Hypothalamus - Master regulator
• Pituitary gland - Master gland
• Thyroid gland - Metabolism control
• Parathyroid glands - Calcium homeostasis
• Adrenal glands - Stress response
• Pancreas - Glucose regulation
• Gonads (ovaries/testes) - Reproduction
Key functions of the endocrine system
• Control of growth and differentiation
• Maintenance of homeostasis
• Regulation of reproduction
• Metabolism regulation
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
- produces releasing and inhibiting hormones
- links nervous and endocrine systems
- controls pituitary gland function
where in the body the endocrine glands are
yes
what re the key hormones in the hypothalamus
CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone)
TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone)
GnRH (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone)
GHRH (Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone)
Somatostatin, Dopamine
what are the key hormones in the pituitary gland
Anterior: TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, GH, Prolactin
Posterior: ADH, Oxytocin
What are the 3 classifications of hormones?
pepide, steroid, monoamine
Structure, examples and characteristics of peptide hormones
- structure: modified amino acids, peptide/protein chains
- examples: insulin, glucagon, growth hormone
- characteristics: water soluble, cannot cross cell membrane
Structure, examples and characteristics of steroid hormones
- structure: derived from cholesterol
- examples: cortisol, testosterone, estrogen
- characteristics: lipid soluble, cross cell membrane easily
Structure, examples and characteristics of monoamine hormones
- structure: derived from aromatic amino acids
- examples: thyroid hormones, epinephrine
- characteristics: variable solubility
What is the hormone signalling mechanism of a water soluble hormone?
- bind to cell surface receptors
- activate second messenger systems
- rapid response (secs to mins)
What is the hormone signalling mechanism of a lipid soluble hormone?
- cross cell membrane freely
- bind to intracellular receptors
- slower response (hours to days)
What are the two feedback loop mechanisms?
- negative feedback: product inhibits its own production, maintains homeostasis
- positive feedback: product stimulates its own production, creates amplification
what is the pathway and mechanism for the hypothamic-pituatry-adrenal axis
hormal response that controls cortisol release linking the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and adrenal cortex
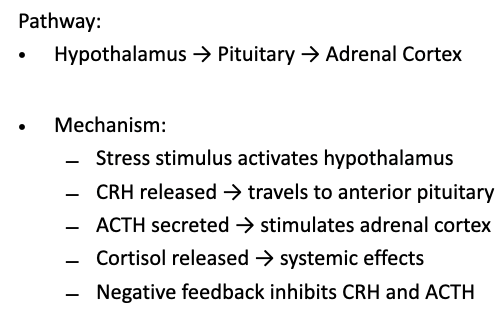
what is the function of cortisol
Increases blood glucose (gluconeogenesis)
Anti-inflammatory effects
Immune system suppression
Stress response coordination
Circadian rhythm (peak morning levels)
what are the implication of corticosteroid therapy
HPA axis suppression and dental implications
HPA axis suppression:
Long-term steroids suppress CRH/ACTH
Adrenal cortex atrophy
Reduced stress response capability
Risk of crisis
dental implication
Delayed healing
Increased infection risk
Poor stress tolerance
Need for steroid cover in surgery
what is the pathway Mechanism of hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis
hormonal control system that regulates thyroid hormone release by linking hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid gland
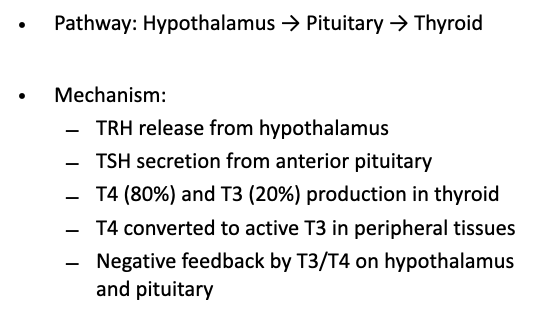
what is the function of thyroid hormone
Metabolic rate regulation
Growth and development
Protein synthesis
CNS development
Cardiovascular function
summary of pancreatic endocrine functions
Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans):
Cell Types:
α-cells (20%) → Glucagon production
β-cells (75%) → Insulin production
δ-cells (4%) → Somatostatin production
PP cells (1%) → Pancreatic polypeptide
Glucagon Functions:
Stimulates hepatic glycogenolysis
Promotes gluconeogenesis
Activates lipolysis
Response to low blood glucose
Insulin Functions:
Facilitates glucose uptake by cells
Promotes glycogen synthesis
Stimulates protein and fat synthesis
Response to high blood glucose
what are the two responses to glucose homeostasis mechanisms
Hypoglycaemia Response
Pancreatic α-cells detect low glucose
Glucagon release increases
Liver glycogen → glucose
Amino acids → glucose
Blood glucose rises
Hyperglycaemia Response
Pancreatic β-cells detect high glucose
Insulin release increases
Enhanced glucose uptake
Glucose → glycogen storage
Blood glucose decreases
what are the dental relevance of diabetes, oral manifestations and management
patients can have oral manifestations:
Oral candidiasis (thrush)
Xerostomia (dry mouth)
Increased dental caries risk
Aggressive periodontal disease
Delayed wound healing
Increased infection risk
Sialosis (salivary gland enlargement)
management considerations:
Early morning appointments
Ensure normal meals/medications
Monitor for hypoglycemia
Optimise oral hygiene
what are the 2 treatment in endocrinology
hormone replacement
Replace deficient hormones
Examples: Insulin (diabetes), levothyroxine (hypothyroid)
Physiologic dosing preferred
Monitor response and side effects
hormone suppression
Block excess hormone production/action
Examples: Antithyroid drugs, GH antagonists
Balance efficacy vs. side effects
how do we manage patients with endocrine problems
pre-operative assessments:
Identify endocrine disorders
Assess disease control
Review medications
Consider stress dosing needs
perioperative care
Maintain medication schedules
Monitor glucose levels
Provide steroid cover if needed
Watch for complications
what are the dental implications of endocrine disorders
manifestations:
Diabetes: Candidiasis, xerostomia, periodontal disease
Thyroid: Delayed eruption (hypo), accelerated caries (hyper)
Parathyroid: Enamel defects, bone changes
Adrenal: Pigmentation changes, delayed healing
clinical approach
Comprehensive medical history
Recognise oral signs of systemic disease
Coordinate with medical colleagues
Modify treatment plans appropriately
what is the future of endocrinology
Personalised medicine approaches
Novel therapeutic targets
Improved diagnostic methods
Better understanding of hormone resistance
Integration of technology in care
Continuous glucose monitoring
Closed-loop insulin delivery systems
summary