AQA Child Language Acquisition
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA English Language Paper 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the pre-verbal stage and when does it occur?
First stage of language - features include crying and cooing to discover mouth sounds and babbling as infants practice articulating sounds.
Occurs at 0-12 Months
What is the holophrastic stage and when does it occur?
Second stage of language acquisition - single words that convey entire ideas or intentions.
Relying on concrete nouns and non-communication (gestures and pointing)
Occurs at 12-18 months.
What is the two-word stage and when does it occur?
Third stage of language - children are able to use two-word combinations like ‘want milk’
Simple speech begins to show understanding of relationship between words
Occurs at 18-24 months
What is the telegraphic stage and when does it occur?
Fourth stage of language - children begin to use short sentences t produce more complex utterances.
Includes essential words and has grammatical elements required for structural accuracy
Occurs at 24-30 months (2 years)
What is the post-telegraphic stage and when does it occur?
Fifth stage of language - child’s speech becomes increasingly like adult speech
Features include formation of pronouns, auxiliary verbs, deeper understanding of pragmatics (politeness, turn-taking etc)
Occurs at 30+ months
What are Halliday’s 7 functions of initial language (1973) (IRIPRHI)
Instrumental - Fulfilling a need (“up”/”dwink”)
Regulatory - Commanding or persuading (“bed!”/”go away”)
Interactional - Strengthening relations (“love you”/”mama”)
Personal - Developing identity and opinions (“no like it”/”me is good”)
Representational - Giving info and knowledge (“scared”/”help"/”where dada?”)
Heuristic - Gaining knowledge about surroundings (“where it go?”)
Imaginative - Play, imagination and jokes (“abwacadabwa”/”this my baby”)
Chomsky’s approach to language
Nativist approach (1957) - children born with innate ability to learn any language
Biological, not behavioural
Skinner’s approach to language
Behavioural approach (1957) - acquire language through imitation
Positive/negative reinforcement in language
Operant conditioning
Behavioural, not biological
Piaget’s approach to language
The language and thought of a child (1926)
Child cannot articulate concepts they don’t understand
Piaget’s stages (SPCF)
Sensorimotor (0-2y) - Child is egocentric, interacts with environment
Pre-operational (2-6/7y) - uses imagination, remains egocentric, doesn’t understand other’s POV
Concrete operational (6/7-11/12) - No longer egocentric, capable of logical thought
Formal operational (11-16+) - Abstract thinking, logical thoughts
Bruner’s approach to language
Social Interactionist (1983)
Children learn to use language to get what they want
Lang Acquisition Support System (LASS) - Parental support - provides imitation model
Scaffolding - Support for child, enables child to gradually develop speech
Aitchison’s approach to language
Acquisition stages (1987)
Labelling - Link between word and sound used
Packaging - over/under extension leads to understanding range of a word
Network Building - Grasping concepts of words (hyper/hyponms)
Vygotsky’s Scaffolding theory
Doing things for child allows them to develop and for adult to act as ‘more knowledgeable other’
Adult can then direct child to move within zone of proximinal development
Tomasello (2003) language theory
Ability to learn language is social AND cognitive
9-12 = children use pattern forming to learn functions and forms
Able to build generalisations about how words form large syntactic constructions
What is assimilation?
Use sounds that are easier to produce to replace other sounds in a word (s instead of sh in fish) = substitution
What is consonant cluster reduction?
Subconsciously reducing consonant sounds in a word (lipstick becomes liptick)
What is weak syllable deletion?
Removing weak sounds in a word ( Porridge becomes Porge)
What is consonant deletion?
At beginning or end or a word, consonant is removed (fish becomes fis)
What are nasals?
Sounds made by air forced through nasal cavity
(n/m/ng sounds)
What are fricatives?
Sounds made by turbulent air
(z in zebra, f in fish)
What are affricates?
Sound begins as a plosive and ends as fricative
(J in joy, ch in church)
What are approximants?
Consonant that can sound like a vowel
(w in wet, r in right, y in yes)
What is articulatory ease?
Children will naturally choose words and sounds that are easiest to pronounce - shows why ‘dada’ is easier to pronounce than ‘mama’
What are proto words?
Words that a child will use to represent something else
Nana = banana / mama = mum / dada = dad
Types of babbling
Reduplicated - Repeat same syllable (mamama)
Variegated - Combine different syllables (googoobaa)
What is over/under extension?
Over - Uses one word to refer to too many things (ball used to describe dog and squirrel)
Under - Uses one word to refer to too little things (kitty used to describe family cat but not other cats)
What is CDS
Child Directed Speech - Way of caregivers to speak to children, known as baby-talk.
Features:
High pitched/melodic voice
Simpler sentences
Talking in 3rd person about self
tag questions and repeating q/a
Expansion - caregiver expands on child’s comment
Recast - adult agrees with proto word but corrects or repeats it
Multigated imperatives - shall we/ I wonder/ why don’t we
Tabula rasa
Children are born with nothing, learning language from social environment
Behaviourism in data set
Look for caregiver positively/negatively reinforcing child’s language
Interactionalism in data set
caregivers correcting children with children either adopting/rejecting change
Caregivers using LASS or CDS (Bruner)
Nativism in data set
Children resisting/accepting correction then revert back
Mistakes with inflections
Children making virtuous errors
Cognitivism in data set
Children struggling to say something they do not understand
Caregivers explaining something to child
Social Constructivism in data set
Children making virtuous errors
Formulaic expressions (words commonly said in a pattern)
Types of overextension - Rescorla (CAR)
Categorical - Child applies label to all in a category (dog for all animals)
Analogical - Applies label to everything visually similar (tomato for ball)
Relational - Applies label which is in some form related to object (pen for paper)
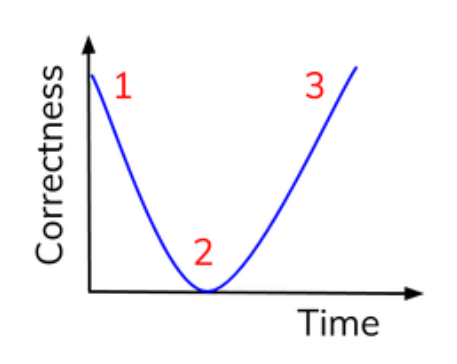
Learning Acquisition curve - Cruttenden
child uses inflection and gets it right
child applies it everywhere and gets it wrong
child learns when to use it correctly
Links to Aitchison