Different wave types and what influences them
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Factors of wave formation
Strength +direction of wind
strong , swash aligned waves are the largest and most damaging
Duration of the wind
as time passes wave increase in height and power
Water depth
The deeper the water the less frictional drag
As a wave approaches the shore the depth decreases and slows it down, causing the wavelength to become shorter and and increases its height
Wave fetch
The distance of open the sea the wind blows
The longer the fetch, the greater the potential for destructive waves
E.g. Cornwall with 4000km waves from Florida
Features of constructive waves
distant weather systems generate them
Low, surging waves
Long wavelength
Strong swash, weak backwash
Beach profile goes from gentle to steep over time
6-8 waves per minute
Features of destructive waves
local storms are responsible
High, plunging waves
Short wavelength
Weak swash, strong backwash
Goes from steeper to flatter overtime
13-15 waves per minute
Seasonal variation
Summer
steeper (more constructive waves)
Strong swash so berms form due to deposition
Sediment is organised in size order (small sediment at backshore)
Winter
destructive waves lower angle of the beach
Shingle beaches
Sediment randomly dispersed
Daily variation
storm events change profile in a few hours
Calm, anticyclonic conditions in winter produces constructive waves that rebuild the beach profile pre storm
Destructive waves go to constructive when the wind drops
Storm beaches are high at the backshore due to high energy deposition of very course sediment
How are tides formed and what do they do
formed by the gravitational pull of the mon acting on the earth
The can also influence but the moon has 2.2x more gravitational influence
This pulls the water towards them causing high and low tides 2x a day
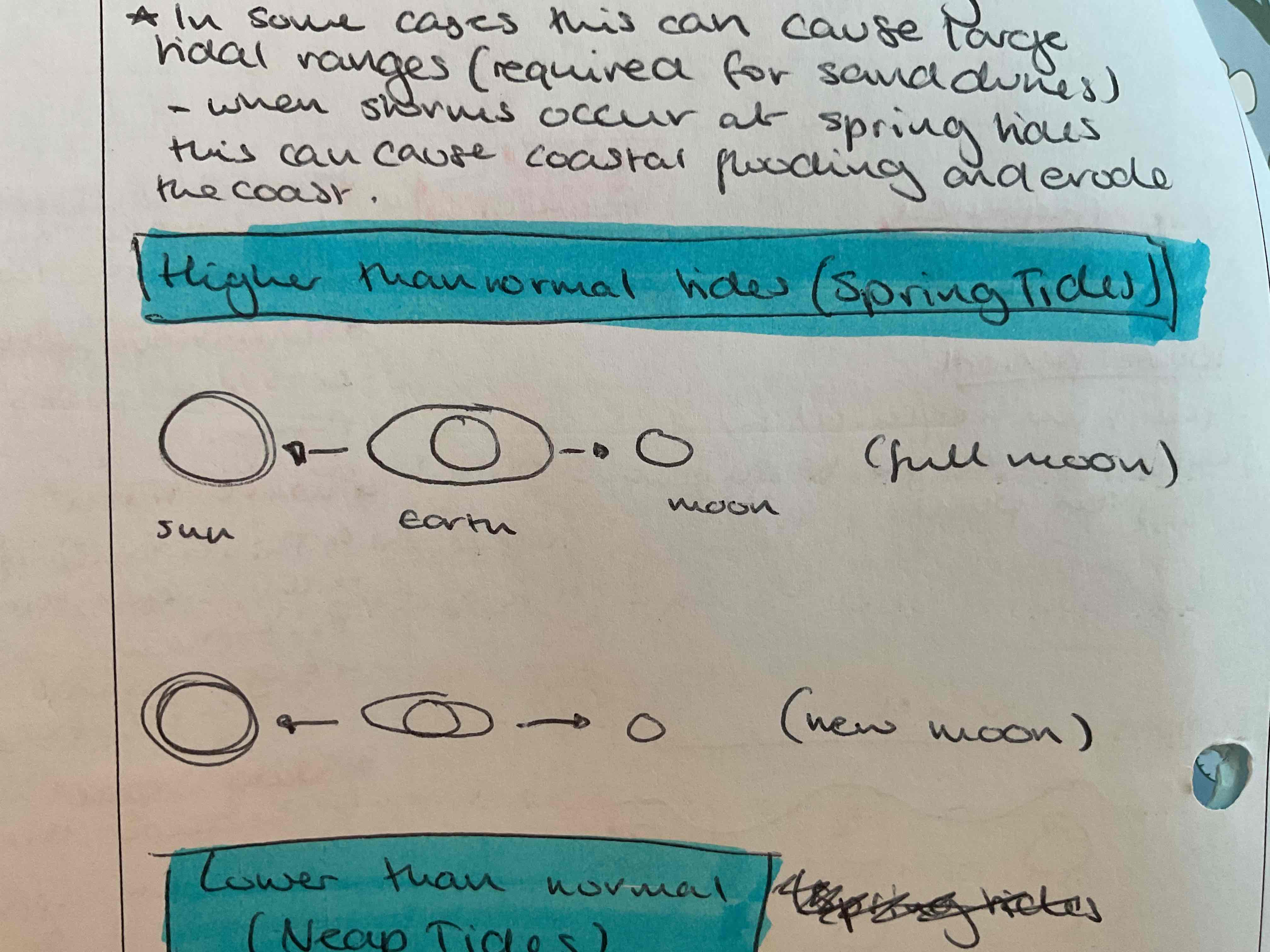
This can cause large tidal ranges (sand dunes)
When storms occur at spring (high) tide this can cause coastal flooding and erode the coast
when do spring sides occur?
full moon
New moon
Causes high tide
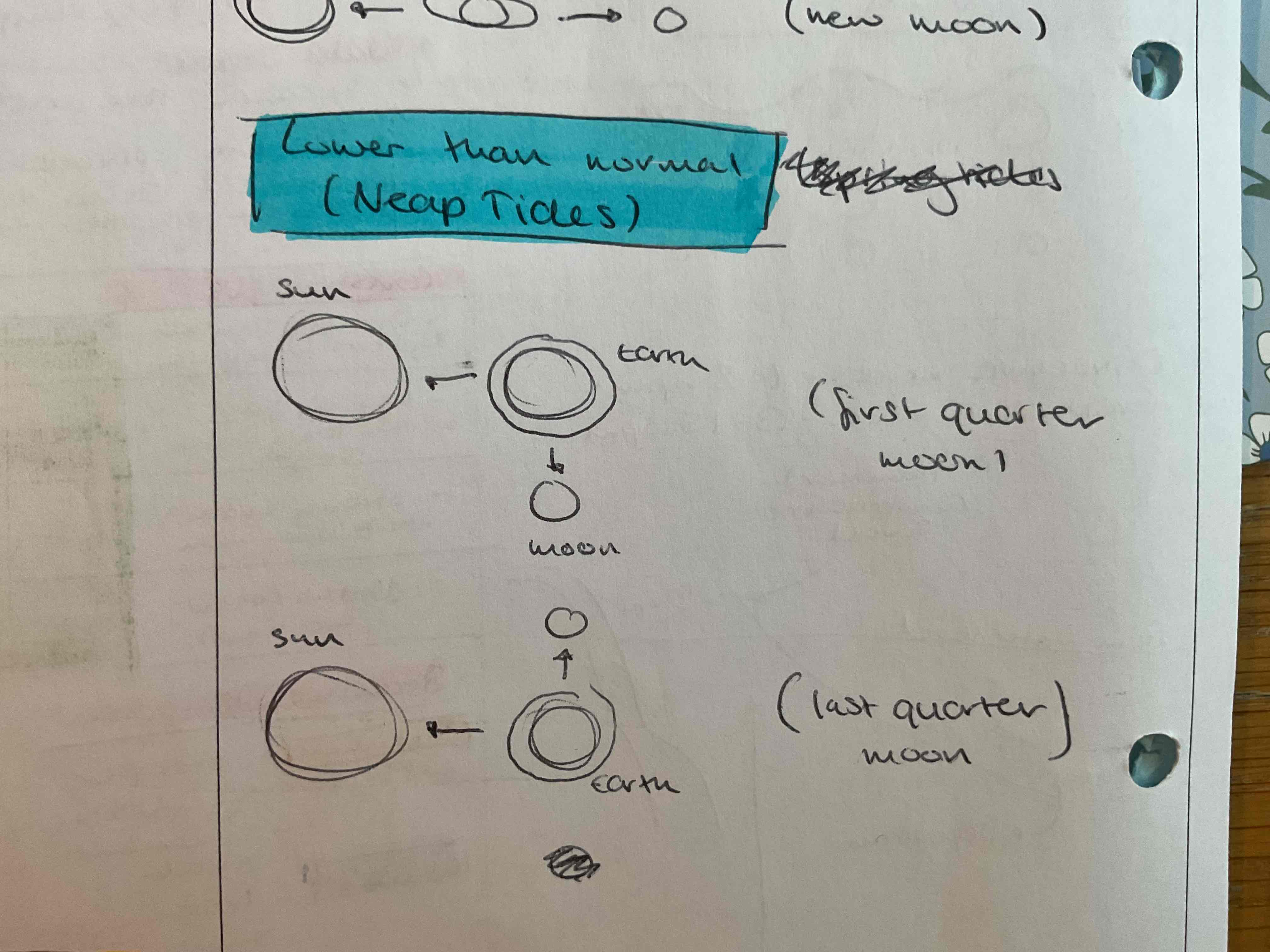
When do neap tides occur ?
first quarter moon
Last quarter moon
Low tide
How do rides influence beach morphology?
high tides create berms
Spring tides aes associated with the formation of storm beaches
A high tidal range is required to form sand dunes