Topic 1.2: River Environments
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
How does precipitation affect a river regime?
More precipitation = more water in the drainage basin
More water in drainage basin means higher water table
This make the area more likely too flood
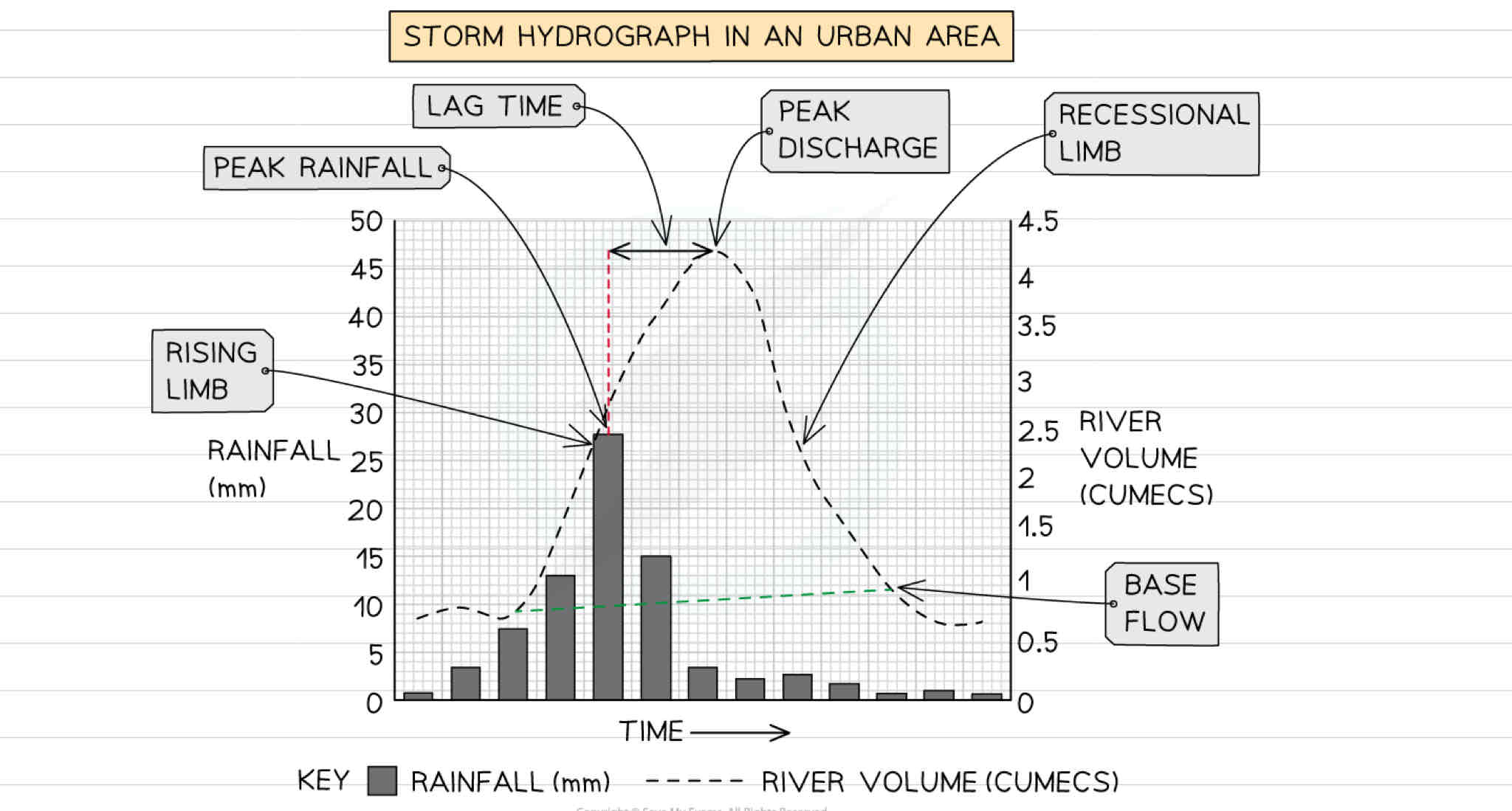
What can a storm hydrograph show?
What does a hydrograph show?
A storm hydrograph shows the change in river discharge after a storm event
How does vegetation affect a rivers regime?
Vegetation increases interception and infiltration leading to reduced surface runoff and so lower river discharge
(Deciduous trees lose their leaves in winter decreasing interception, increasing overland flow and river discharge)
How is a river regime affected by land use?
Concrete and tarmac in urban areas and built environments are impermeable leading to high overland flow - this is rapidly taken by drainage systems to the rivers/streams, increasing river discharge
How is a river regime affected by dams?
Dams control the flow of water, so can both increase and decrease river discharge
Reservoirs experience higher levels of evaporation which can decrease river discharge
How much of a rivers energy is used to overcome friction?
95%
4 types of erosion
Hydraulic Action
Abrasion
Attrition
Solution
Definition of Hydraulic Action
The force of water which removes material from the bed and banks of the river
Definition of Abrasion
Material carried by the river scrapes and erodes the bed and banks
Definition of Attrition
Material in the river hits each other and the pieces become rounder and smaller
Solution definition
When rocks are dissolved by the slightly acidic water
What are the two main types of mass movement present in river valleys?
Slumping and Soil Creep
What is slumping?
Where the slope is eroded by the river. This undercuts the slope causing large-scale movement of material down the slope.
What is soil creep?
The influence of gravity causes weathered materials to slowly move down the slope towards the river
Vertical erosion definition
Dominant in upper course of rivers, it increases the depth of the river and valley as river erodes downwards
Lateral erosion definition
Dominant in middle and lower course of rivers. It increases the width of river and valley as it erodes sideways
What are the 4 processes of transportation and deposition?
Traction, saltation, suspension and solution
Traction def
Larger rocks and materials are rolled along the river bed
Saltation def
Smaller rocks bounces along the river bed
Suspension
Lighter material carried within the river flow
Solution
When materials are dissolve in river water
Deposition
When a river lacks the energy to carry materials so deposits them
What are causes of reduced energy in a river?
Decreased gradient
Slower flow on inside of a meander
Reduced discharge due to lack of precipitation or abstraction upstream
How does climate impact river processes?
Heavy rainfall and/or low temperatures lead to higher discharge which increases erosion and transportation; below average rainfall and/or high temperatures lead to lower discharge and decreased erosion and transportation
How does altitude affect river processes?
Melting snow and ice increase discharge and therefore there is more erosion and transportation
How does aspect affect river processes?
South-facing slopes have higher rates of evaporation and transpiration which decreases discharge
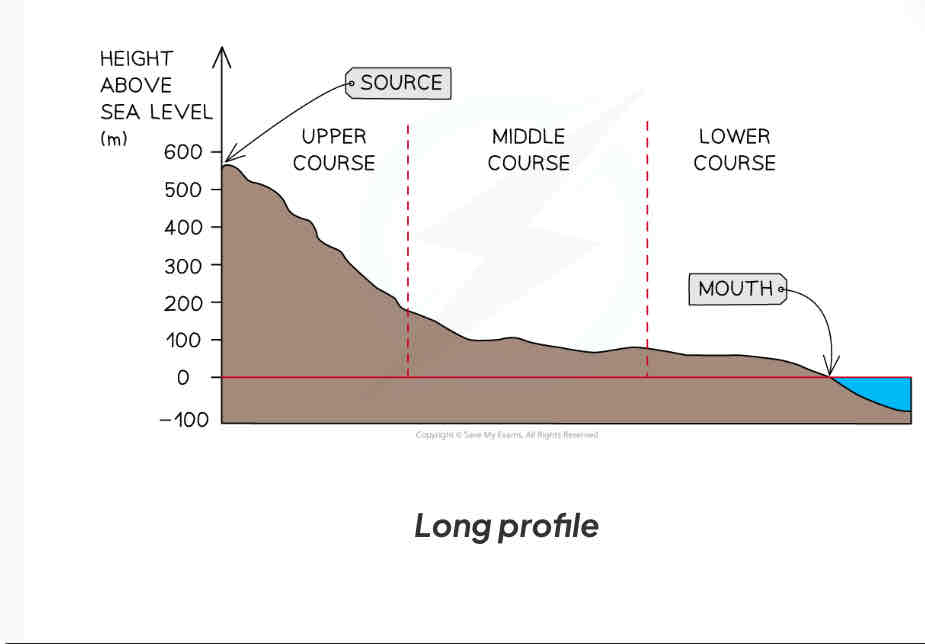
What do long profiles show?
Changes in river gradient from source to mouth
Most long profiles have which similar characteristics?
Upper course- steep and uneven surfaces
Middle course - gradient decrease
Lower course - gradient decreases to sea level
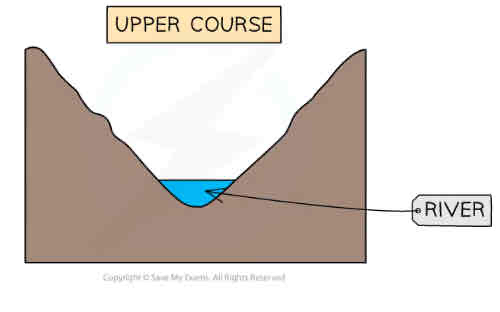
What are cross profiles?
Cross section from one bank to the other
What does the cross profile of the upper course look like?
shallow channel
Steep valley sides
Narrow channel
vertical erosion
Middle course characteristics
Deeper than upper course channel
Smoother channel bed
Lateral erosion
Lower Course characteristic
flat floodplains
greatest velocity
lowest friction
deposition is dominant

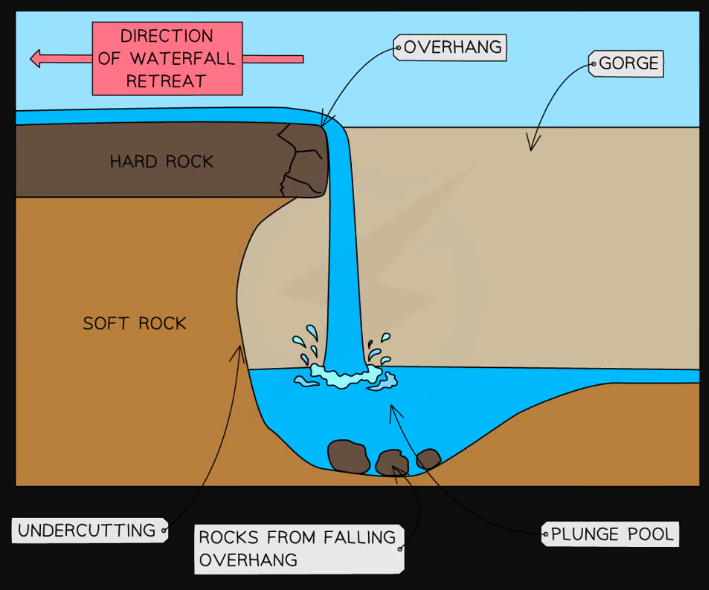
explain the formation of a waterfall
waterfalls occur where there is a step in the landscape often where hard rock meets soft rock
soft rock erodes due to hydraulic action at a faster rate than the hard rock this leads to undercutting and the formation of a plunge pool
leaves an overhang of hardrock which eventually collapses due to gravity
the process is then repeated causing the waterfall to retreat upstream leaving a steep sided gorge
how is a v shaped valley formed
Vertical erosion is dominant in the upper course of the river
This cuts down into the river bed and deepens the river channel
Weathering and mass movement leads to material from the valley sides collapsing into the river forming a steep v-shaped valley
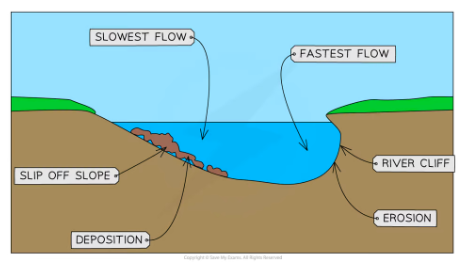
Explain the formation of meanders
obstacle falls in the river, this diverts the thalweg which bounces from bank to bank
thalweg hits outside bank this causes high energy erosions by hydraulic action and abrasion this causes undercutting and a river cliff
on the inside bank energy decreases due to friction with shallow bed leads to deposition forming slip off slope
over time erosion on the outer bank and deposition on the inside bank leads to lateral erosion and the meandr to become more sinuous eventually leading to meander migration and oxbow lakes
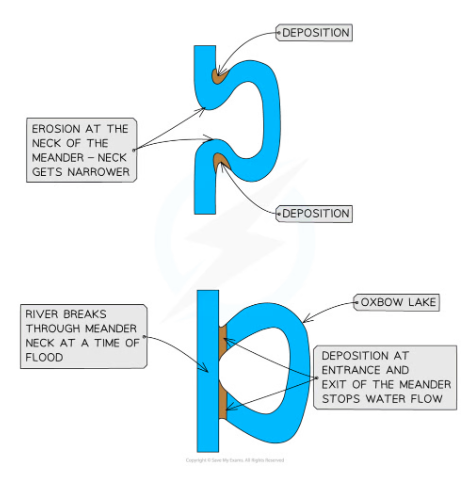
formation of oxbow lakes
with distance downstream the size of the meander increase
the erosion on outside bend can eventually lead to the formation fo a meander neck
(at time of flood, the river may cut through the neck of the meander forming a straighter course for the water)
flow of water at entry and exit from the meander will be slower leading to deposition
the meander becomes cut off from main river channel forming an oxbow lake
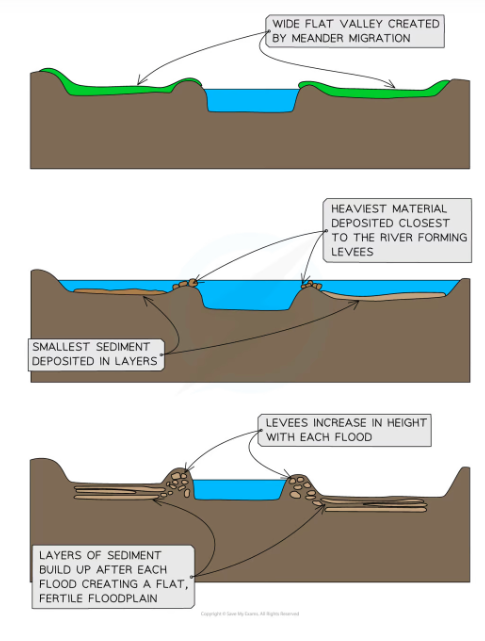
Floodplains and levees
Floodplains are flat expanses of land on either side of the river
The migration of meanders leads to the formation of the floodplain
High discharge may cause the river to overflow the banks
More of the water is in contact with the land surface as the water spreads across the floodplain
Increased friction reduces velocity and material is deposited across the floodplain gradually increasing the floodplain height
The heaviest material is deposited first nearest to the river channel forming natural embankments called levees