Organic Chemistry (Gr. 12)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Organic Compound
A molecular compound of carbon, not including CO, CO2, and HCN.
Hydrocarbon
A compound containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Saturated Hydrocarbon (Alkane)
A hydrocarbon with only single covalent bonds between its carbon atoms. CnH2n+2
Cyclic Alkane
A hydrocarbon in which the main structure consists of a chain of carbon atoms joined to form a closed ring. CnH2n
Alkyl Group
One or more carbon atoms that form a branch off the main chain of a hydrocarbon.
Substituent Group
An atom or group that replaces a hydrogen atom in an organic compound.
Alkyl Halide (Halogenoalkane)
An alkane in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been substituted with one or more halogen atoms.
Structural Isomer
A compound that has the same molecular formula as another compound, but a different structure.
What is the relationship between the length of a carbon chain, and the BP’s. Explain. What about branches?
The relationship between the length of a carbon chain and boiling points (BP's) is generally that as the chain length increases, the boiling point also increases. This is because longer carbon chains result in a larger surface area, which enhances the LDF forces, meaning more engery to overcome thus a higher BP. Additionally, when considering branches, branched hydrocarbons typically have a lower boiling point than their straight-chain counterparts. This is due to the fact that branching decreases the surface area, which in turn reduces the strength of the LDF between the molecules.
What are the main uses of relatively short carbon chains (alkanes)? (3)
→fuels(natural gas)
→butane (for lighters)
→ jet fuel
What are the main uses of alkane chains between 20 and 50 carbons? (4)
→ home heating oil
→ diesel fuel, ship fuel
→ lubricating oils (engine oil), thick oils
→ waxes
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
an organic compound, contain carbon and hydrogen, w/ one or more double or triple bonds between carbon atoms, resulting in fewer hydrogen atoms compared to saturated hydrocarbons. (include alkenes and alkynes, which are more reactive due to these multiple bonds)
Alkene
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon-carbon double bond. (CnH2n)
Alkyne
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon characterized by at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. CnH2n-2
Functional group (R group)
a single atom or a group of atoms which determine the chemical reactivity of an organic molecule under a given set of conditions.
Steroisomer (geometric isomer)
molecules that have the same chemical formula and structural backbonem but w/ a different arraangement of atoms in space
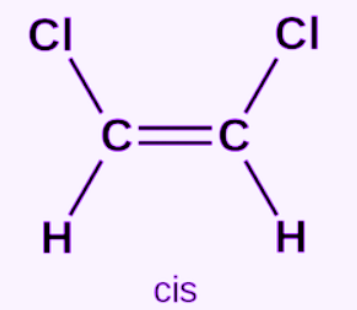
Cis-isomer
A type of geometric isomer in which groups of interest are located on the same side of the double bond
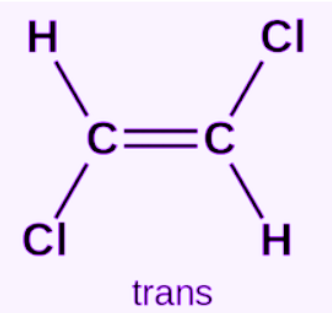
Trans-isomer
A geometric isomer in which groups of interest are located on opposite sides of a double bond.
What is Markovnikov’s Rule?
Rich get richer! The hydrogen atom is added to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms in an alkene reaction, resulting in the halogen getting added to the atom with less hydrogen atoms. This forms the major product of the reaction. (Occurs in hydration and hydrohalogenation)
Addition Reaction
a reaction in which the atoms from one molecule are added to another molecule to form a single molecule
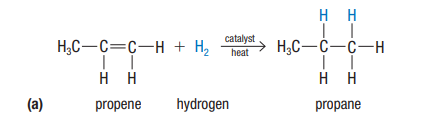
Hydrogenation
alkene + H2 → alkane
adding hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon, (w/ catalyst/heat), resulting in the formation of a saturated compound.
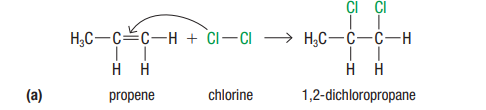
Halogenation
alkene + halogen → halogenoalkane
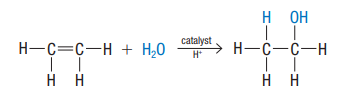
Hydration
alkene + water → alcohol
has major and minor products
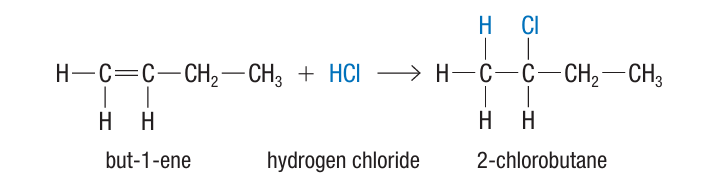
Hydrohalogenation
alkene + H(halogen) → halogenoalkane
HBr, HCl etc, has a major and minor product
Organic Class/Family
organic compounds that are characterized by the same functional group (Eg. ketones are classified with a interior carboxyl functional group)