ap human geography | thinking geographically
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
physical geography
the study of spatial characteristics of various elements of the physical environment
landforms, bodies of water, climate, ecosystems, and erosion
human geography
the study of spatial characteristic of humans and human activities
population, culture, politics, urban areas, and economics
reference maps
designed for people to refer to for general information about places
political maps
show and label human-created boundaries and designations, such as countries, states, cities, and capitals
physical maps
show and label natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts
road maps
show and label highways, streets, and alleys
plat maps
show and label property lines and details of land ownership
thematic maps
show spatial aspects of information or of a phenomenon
cloropleth maps
use various colors, shades, or patterns to the show the location and distribution of spatial data
dot distribution maps
used to show the specific location and distribution across a map
each dot represents a specified quantity
graduated symbol maps
use symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something
isoline maps
also called isometric maps
use lines that connect points of equal value to depict variations in data across space
when lines are further, phenomenon is relatively the same
when lines are close together, the map depicts rapid change
topographic maps
a type of isoline map that connects points of equal elevation
cartogram
the sizes of countries (or other area sizes) are shown according to some specific statistic
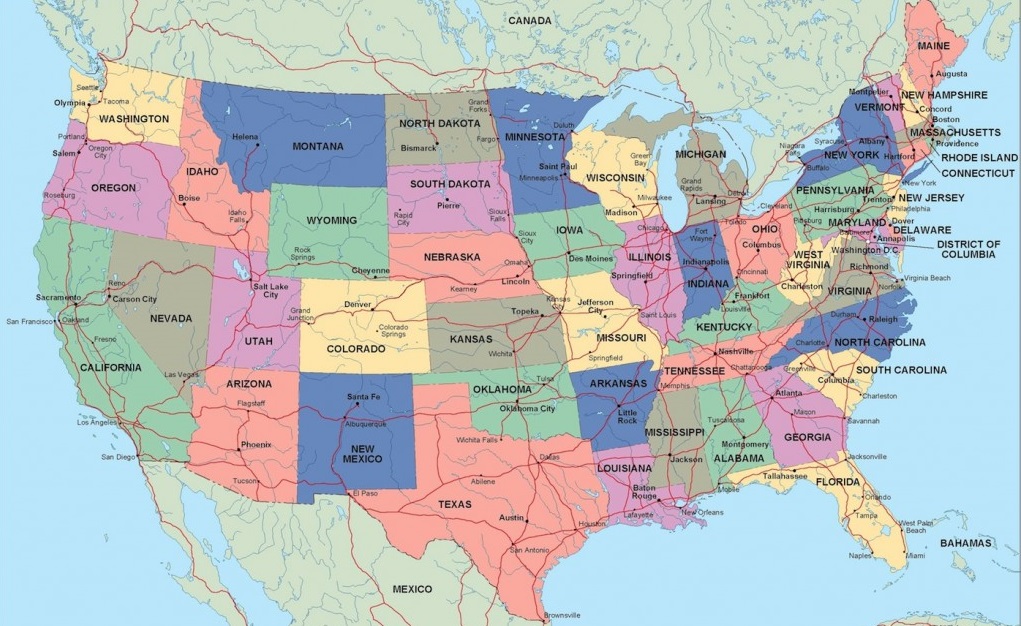
what kind of map is this?
political map
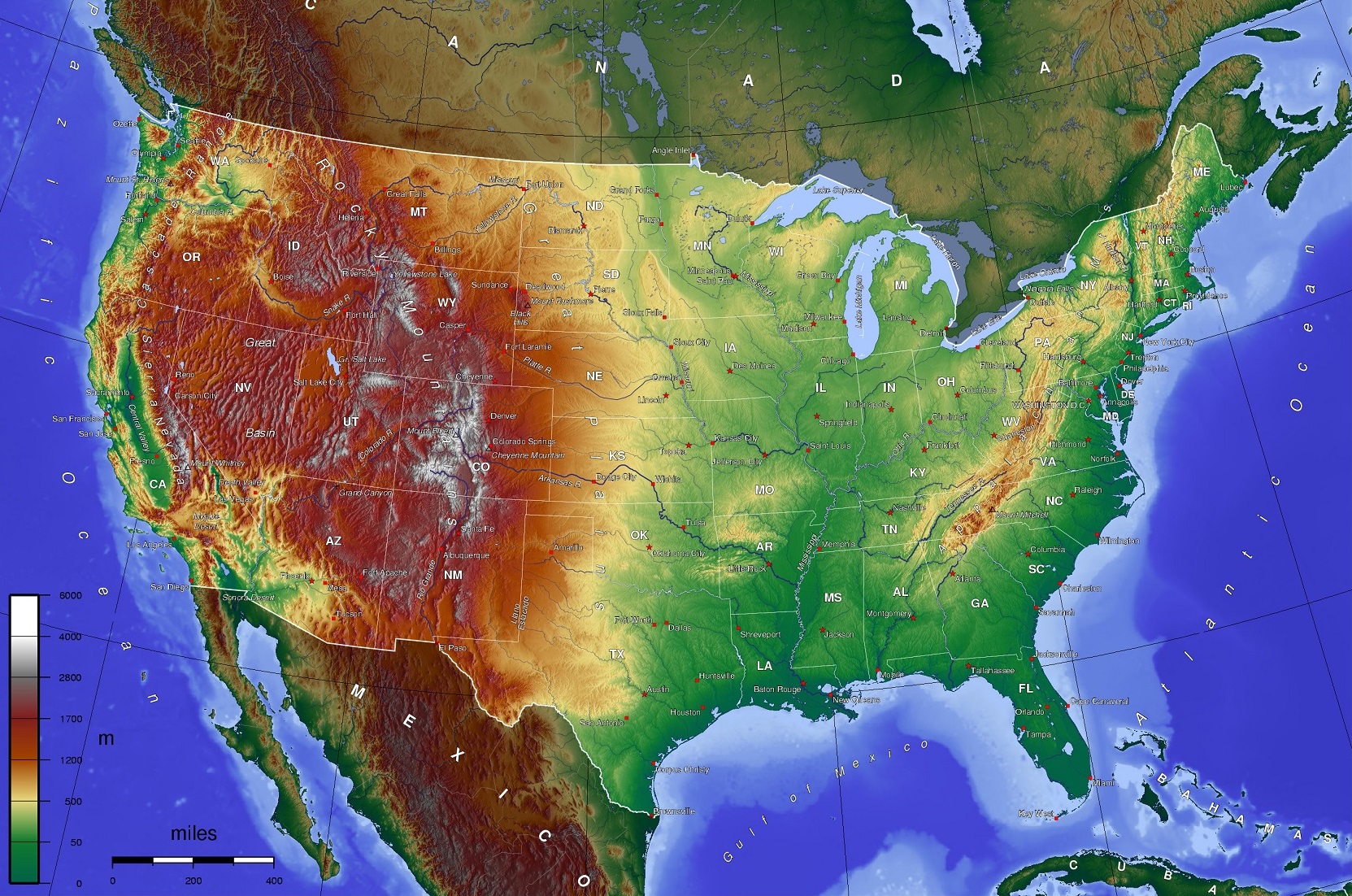
what kind of map is this?
physical map
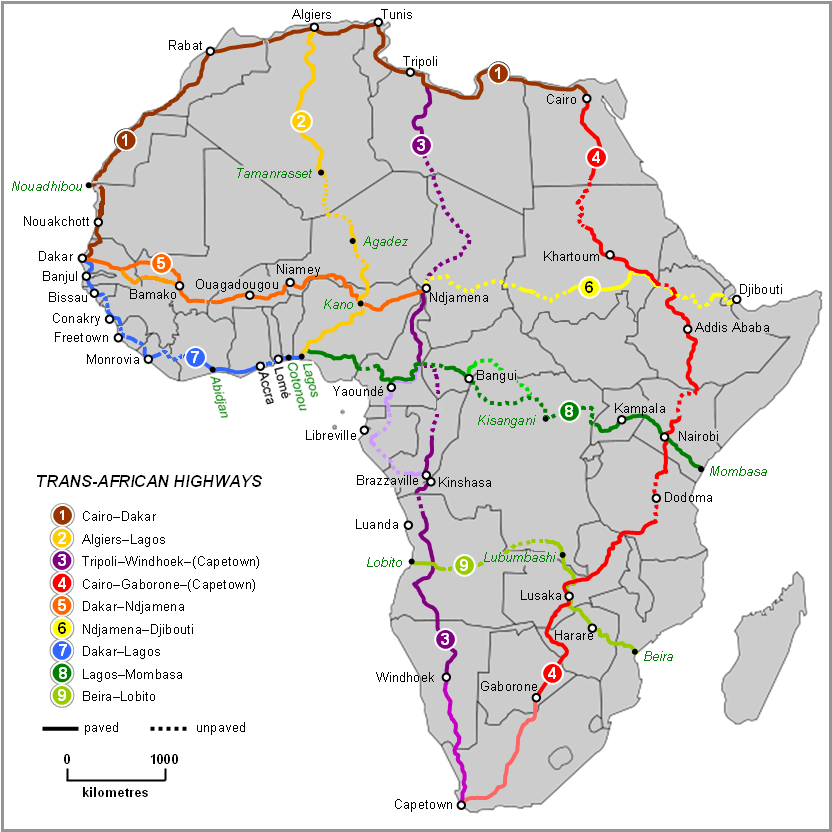
what kind of map is this?
road map
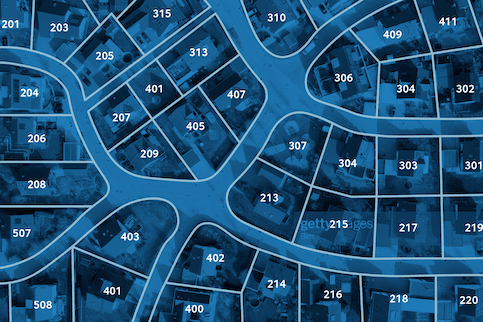
what kind of map is this?
plat map
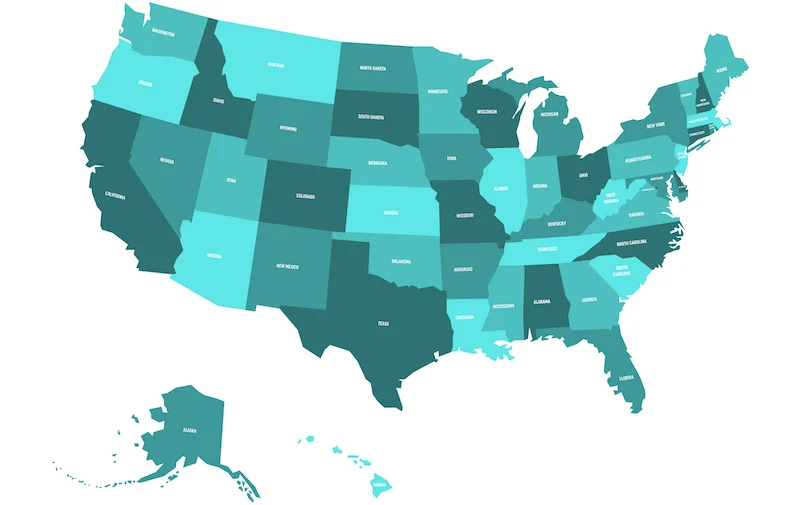
what kind of map is this?
choropleth map
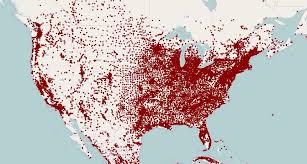
what kind of map is this?
dot distribution map
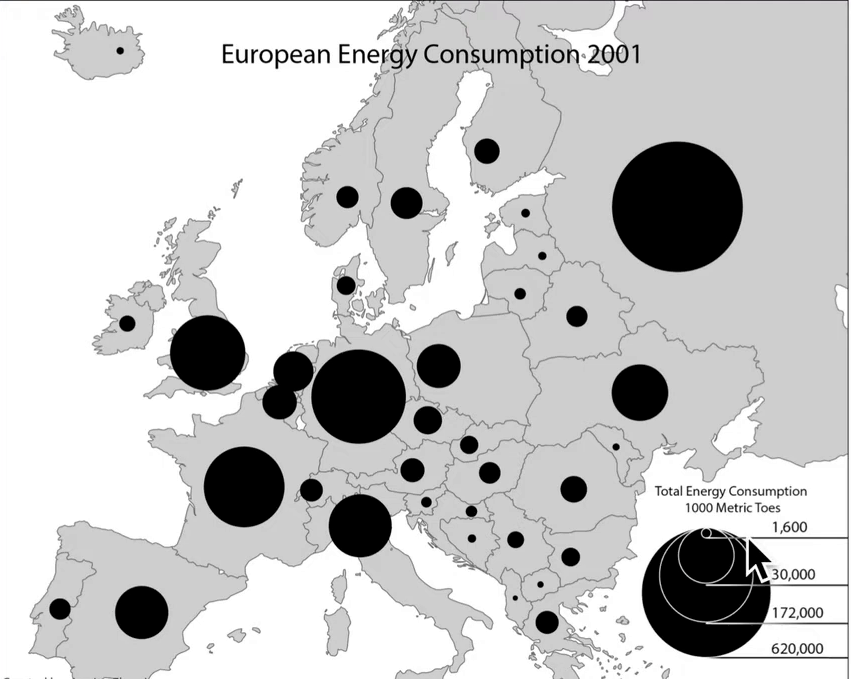
what kind of map is this?
graduated symbol map
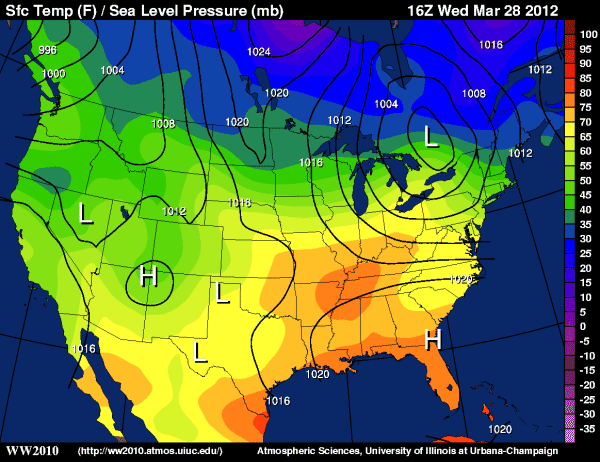
what kind of map is this?
isoline map
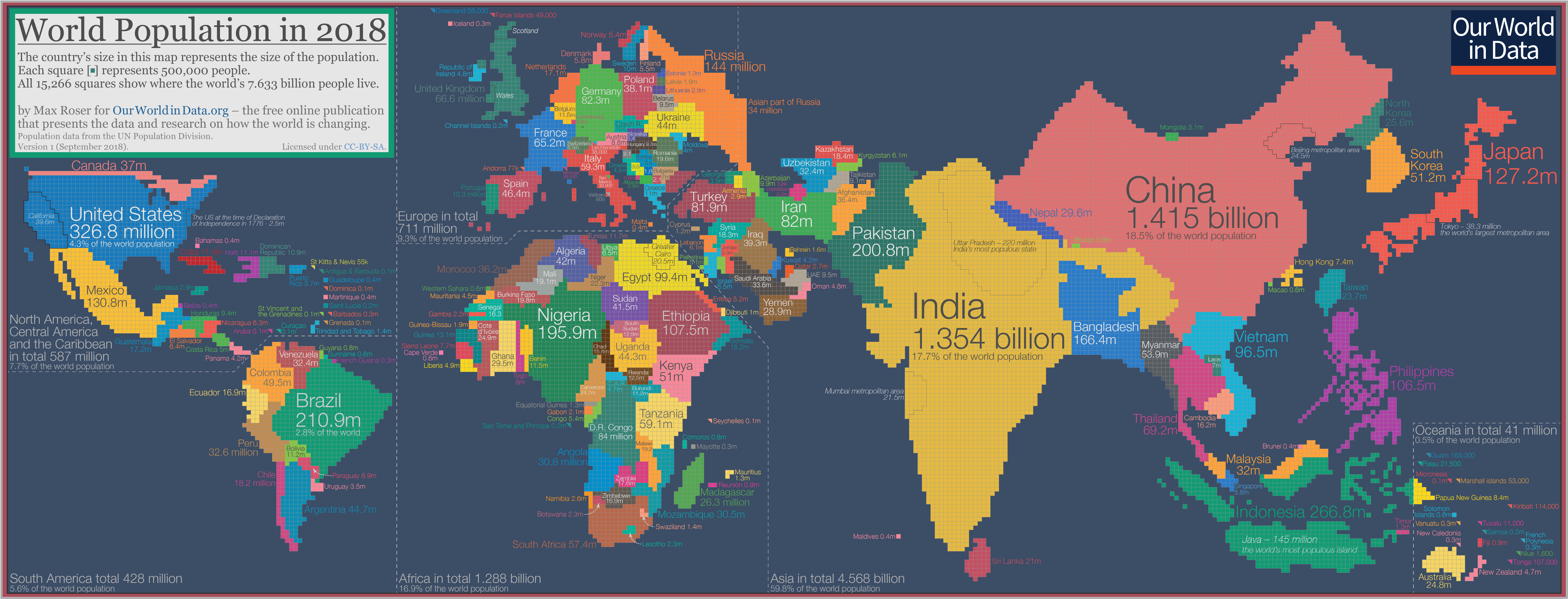
what kind of map is this?
cartogram
cloropleth, dot distribution, graduated symbol, isoline maps, and cartograms are all examples of what kind of map?
thematic
cartographic scale
the way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents
small-scale maps
show a larger amount of area with less detail
large scale maps
show a smaller amount of area with greater amounts for detail
absolute location
precise spot or where something is according to a system
example ; longitude + latitude
latittude
horizontal lines
the distance north or south of the equator
longtitude
vertical lines
distance east or west of the prime meridian
international date line
the line extending between the north and south poles that is the boundary between one calendar day and the next
equator
an imaginary line that circles the earth at 0 degrees latitude
(horizontal)
prime meridian
an imaginary line that circles the earth at 0 degrees longitude
(vertical)
relative location
a description of where something is in relation to other things
connectivity
how well two locations are tied together by roads or other links
accessibility
how quickly and easily people in one location can interact with people in another location
relative location is often described in terms of
connectivity and accessibility
direction
is used in order to describe where thing are in relation to each other
north, east, south, west or intermediate directions are cardinal directions
absolute distance
measured in terms of feet, miles, meters, etc.
relative distance
indicates the degree of nearness based on time
example ; 25 minute walk, 10 minute drive, etc.
elevation
the distance of features above sea level
distribution
the way a phenomenon is spread out over an area
clustered or agglomerated pattern distribution
arranged in a group or concentration area
linear pattern distribution
arranged in a straight line
dispersed pattern distribution
spread out over a large area
circular pattern distribution
equally spaced from a central point, forming a circle
geometric pattern distribution
in a regular arrangement such as squares
random pattern distribution
have no order in their position
mercator map projection
purpose ; navigation
advantages ; direction, latitude + longitude
distortion ; distance + land masses near the poles appear large
peters map projection
purpose ; spatial distributions related to area
advantages ; sizes of land masses are accurate
distortion ; shapes are inaccurate, especially near the poles
conic map projection
purpose ; general use in midlatittude countries
advantages ; lines of longitude converge, lines of latitude are curved, size + shape are both close to reality
distortion ; direction is not constant, not accurate on other parts of world
robinson map projection
purpose ; general use
advantages ; no major distortion, oval shape
distortion ; area, shape, size, and direction are all slightly distorted
landscape analysis
the task of defining and describing landscapes
field observation
the act of physically visiting a location, place, or region and recording, firsthand, information there
spatial data
all information that can be tied to specific locations
remote sensing
gathering information from satellites or other craft above the atmosphere
aerial photography
professional images captured from planes within he atmosphere
fieldwork
observing and recording information on location
geovisualizations
geographic data converted into 2d or 3d interactive maps
gps
global positioning system
uses multiple satellites to determine + record a receiver’s exact location
remote sensing
the use of cameras or other sensors mounted on aircraft or satellites to college images or video of the earth’s surface
geographic information systems (gis)
computer system that can store, analyze, and display information from multiple digital maps or geospatial data sets
smartphone and computer applications
location-aware apps that gather, store, and use locational data from computers or other personal devices
community-based solutions increase the likelihood of success because
they create buy-in from local residents and are more likely to be culturally accepted
spatial approach
considers the arrangement of the phenomena being studied across the surface of the earth
looks at elements such as ;
location, distance, direction, orientation, flow, pattern, interconnection
space
the area between two or more phenomena or things
location
identifies where specific phenomena are located either on a grid system or relative to another location
place
the specific human + physical characteristics of a location
region
a group of places in the same area that share a characteristic
site
the characteristics at the immediate location
situation
location of a place relative to its surroundings and its connectivity to other places
sense of place
the way humans tend to perceive the characteristics of place in different ways based on their personal beliefs
placelessness
if a place inspires no strong emotional ties in people or lacks uniqueness
aka no sense of place
toponyms
place names
time-space compression
shrinking the “time-distance” between locations due to improved methods of transportation and communication
spatial interaction
the contact, movement, and flow of things between locations
flow
patterns and movement of ideas, people, products, and other phenomena
friction of distance
when things are farther apart, they tend to be less connected
distance decay
the inverse relationship between distance and connection
as distance increases, interaction decreases
distribution
the phenomenon is spread out or arranged over and area
spatial association
matching patterns of distribution
indicates that two phenomena may be related or associated
human-environmental interaction
the connection and exchange between humans and the natural world
natural resource
items that occur in the natural environment that people use
renewable natural resources
theoretically are unlimited and will not be depleted based on use by people
examples ; air, water, solar, biomass
non-renewable natural resources
limited and can be exhausted by human use
examples ; fossil fuels, minerals, soil, underground freshwater
sustainability
trying to use resources now in ways that allow their use in the future while minimizing negative impacts on the environment
land use
the study of how land is utilized, modified, and organized by people
built environment
physical artifacts that humans have created and that form parts of the landscape
cultural ecology
the study of how humans adapt to the environment
environmental determinism
the belief that landforms and climate are the biggest influences on human behavior and societal developement
possibilism
a view that acknowledges limits on the effects of the natural environment
humans have more power and influences over their circumstances than the environment
geographic scale/relative scale
the area of the world being studied
aggregation
when geographers organize data into different scales such as by census tract, city, county, or country
formal regions
aka uniform regions or homogenous regions
united by one or more traits
functional regions
aka nodal regions
regions organized around a focal point, often a node
node
a central or focal point within a functional region
perceptual regions
aka vernacular regions
defined by the informal sense of place that people ascribe to them
subregions
divisions of regions
share some characteristics with the region, but is distinctive in some ways
what map projection is this?
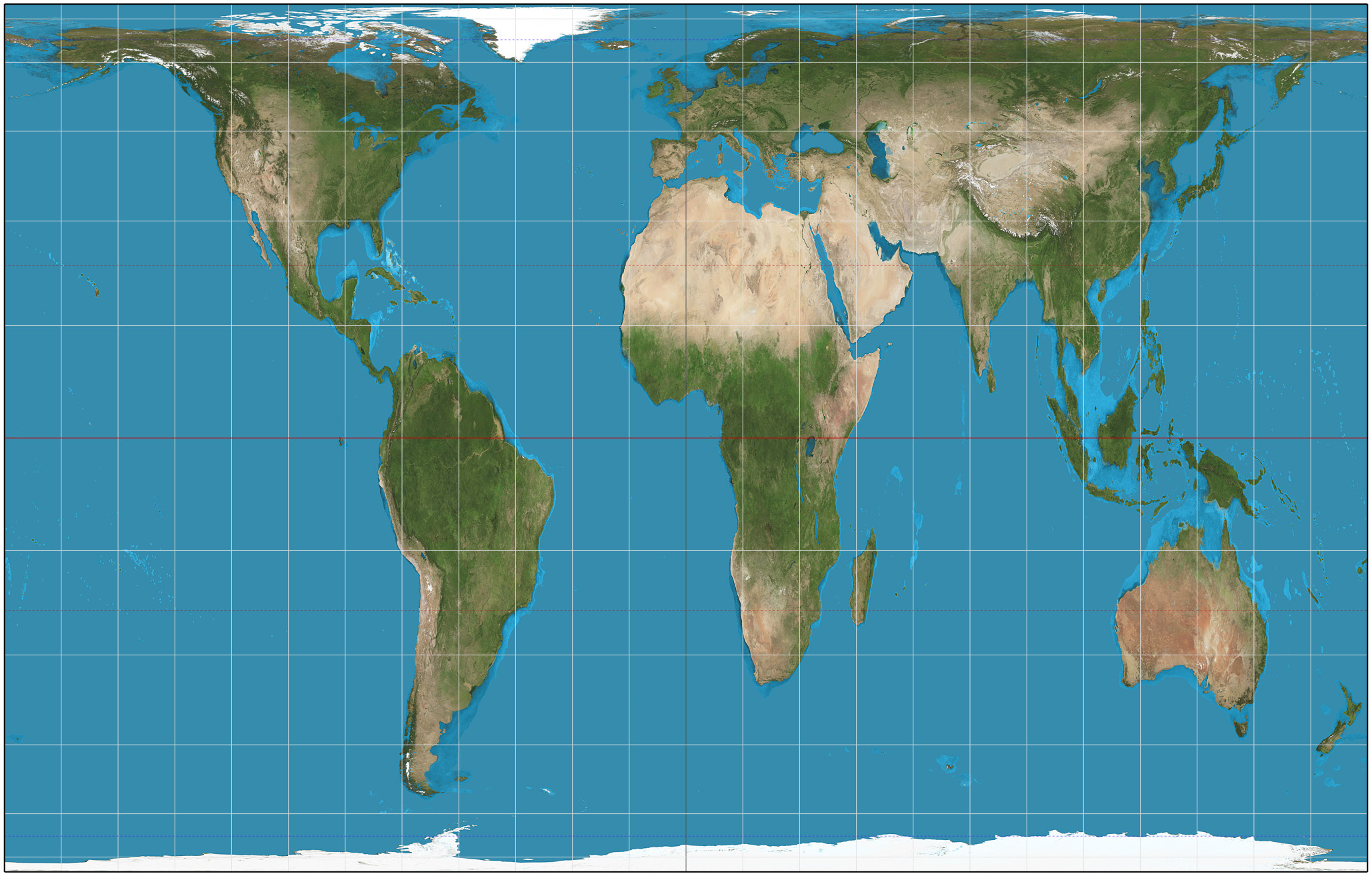
gall-peters map projection
what map projection is this?
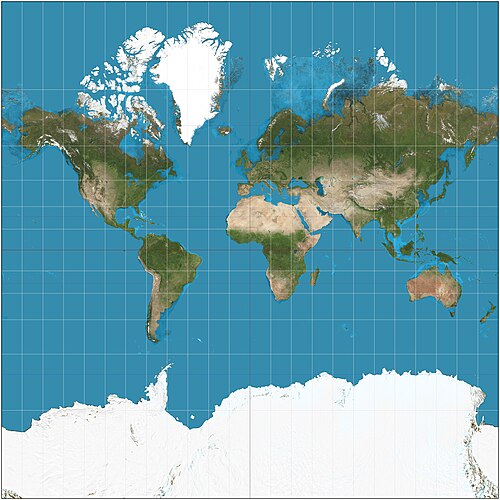
mercator map projection