Ap psych 2.1, 2.2, and 2.8
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Sensation
Involves receiving information from the environment, converting the into a neural message (transaction) and sending to the brain to be evaluated.
Perception
Involves the organizing an interpreting of sensory information.
Bottom up processing
Relies on external sensory information. it’s information processing of basic elements or features to build a perception.
Top down processing
Relies on internal prior expectations. It is information processing that involves experience, expectations and motives to fill gaps and complete a perception.
What are internal factors that filter perceptions of the world?
Schema and perceptual sets
Schema
mental framework for organizing and understanding our world they help to guide our perception and are the basis of top down processing. Through experience, we form these in order to help interpret and organize new information And help guide our perception.
Perceptual set
The readiness to perceive something in a particular way or having an expectation for a stimulus, we see what we expect to see. (Goes with top down)
What are the external factors that filter perceptions of the world?
Context and culture
Gestalt principles
Perceptual principles proposed by gestalt psychology helped explain how humans organize their perceptual world. A gestalt is an organized whole
What are the 4 gestalt principles?
Closure, figure And ground, proximity, similarity
Closure
The principle of making a whole or completed object by filling in the gaps
Figure and ground
The principle in which the figure is the object and the ground is the surroundings
Proximity
The principle that items close together, a group, more easily than items far apart
Similarity
The principle that items more like (e.g. similar color size shape, orientation or texture) group more easily than items that are different.
Attention
An interaction of sensation and perception that is affected by internal and external processes.
Selective attention
Focused awareness of certain stimuli in the environment we pay attention to what we deem, important and filter, irrelevant or extraneous information. Attention is limited, this helps us not be bombarded with too much info at once
Cocktail party effect
Where people attend to mentions of their names or specific topics in loud or distracting environments (things grab your attention in busy places)
Inattentional blindness
Occurs when attention is focused on one part of the visual field and as a result, you may ignore or miss other parts.
Change blindness
A specific type of intentional blindness which occurs when differences or changes in a visual field are not perceived due to inattention or a brief interruption
Binocular depth cues
Depth cues that use two eyes
Retinal disparity
Is determining depth based on the difference between what each eye sees. The eye sees more differences in things that are closer than things that are further. This is a type of binocular depth cue
Convergence
Is determining depth based on how much both eyes rotate inwards. Things that are closer require the eyes to rotate more. This is a type of binocular depth cue
Monocular cues
Use one eye to give the illusion of depth on flat or two dimensional surfaces.
What are the five monocular depth cues?
Relative clarity, relative size, texture gradient, linear perspective, interposition (placement of an object)
Visual perception constancies
Maintain the perception of an object, even when the images of the objects In the visual field change. This includes color constancy, brightness constancy, shape constancy, and size constancy
Apparent movement
Makes it seem like something’s moving, even though it’s stationary. Includes phi phenomenon (lights flashing, think of those signs with word that look like the words are moving on/off screen) and stroboscopic movement (the use of still images to make it seem like something is moving, think of animation)
Concept
Mental groupings based on shared features and come from experience. For example, fruit, automobiles, and dogs. Concepts are usually Organized in three level hierarchy, rankings going from broad to specific (ex fruit → apple → granny smith). Concepts can be concrete or abstract and are used to help organize things
Prototypes
The ideal example of any given concept, these are typically developed from your own experience. An example of this is like if I’m asked to think of a tree my brain is gonna go like palm tree or something because I grew up here in the Middle East. I wouldn’t immediately think of an apple tree or oak tree cause that’s not my experience
Assimilation
Taking a new information, but not changing the schema in light of it. It often places new information into an existing schema. Past experiences influence what and how we think about new experiences.
Accommodation
Taking a new information and changing the schema to incorporate the new information of creating a new schema
Algorithm
Addresses problems by attempting all possible solutions until the correct one is found. Think of math formulas, flowcharts, etc
Heuristic
Addresses problems by using mental shortcuts or a rule of thumb to make judgments. Like determining, who’s the oldest by seeing who is the tallest or determining the best brand by figuring out which one’s the most expensive
Representative heuristics
Can lead to an error in judgement when discussions are made based on prior expectations or stereotypes
Availability heuristic
Can lead to an error in judgement when decisions are made by recalling the first or most vivid example that comes to mind
Mental set
The tendency to approach new problems or games in a way that has previously worked.
Framing
Circumstances surrounding a decision
Gamblers fallacy
A false belief that you can predict a chance of event based on past chance events
Sunk cost fallacy
A bad decision based on money time or effort that had already been spent
Executive functions
Cognitive processes that allow individuals to generate, organize, plan, and carry out goal directed behaviors and critical thinking. Linked to prefrontal cortex
Divergent thinking
Coming up with many ideas
Convergent thinking
Narrows down ideas to a single best solution
Functional fixedness
Failing to solve a problem because you are stuck on the objects common use
Multiple intelligences
Intelligence is based on unrelated domains (street smart, book smart, etc)
Two factor theory
The theory that general intelligence (g) underlies specific mental abilities (s), suggesting that intelligence can be understood as a combination of a general factor and specific factors.
Two types of g
Cattell proposed two types of general intelligence: Fluid Intelligence (Gf), which involves the ability to reason and solve novel problems independent of acquired knowledge, and Crystallized Intelligence (Gc), which involves the use of learned knowledge and experience.
Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
Proposed by Robert Sternberg, this theory distinguishes three types of intelligence: analytical (problem-solving), creative (innovation), and practical (real-world application).
Reciprocal determinism
A concept developed by Albert Bandura that explains how personal factors, behavior, and the environment interact and influence each other mutually.
Individualistic
Values freedom and individuality, success and intelligence are based on what you alone can achieve
Collectivistic
Values connection and harmony, success and intelligence are based on what you can achieve with others
Stereotype threat
The unconscious process of one’s performance being reduced to match what society believes
Stereotype Lift
The unconscious process of one’s performance being improved to match what society believes
An intelligence test must have what 3 traits?
Standardization, reliability, and validity
Construct validity
The extent to which a test accurately measures the theoretical construct it is intended to measure.
Criterion validity
Do results from the test match the results from other tests that measure the same thing
Content validity
What content is present on the test
Predictive validity
Does the test result gathered at a certain time match what actually happens in the future
The Flynn effect
The phenomena that describes the finding that intelligence scores increased over several decades
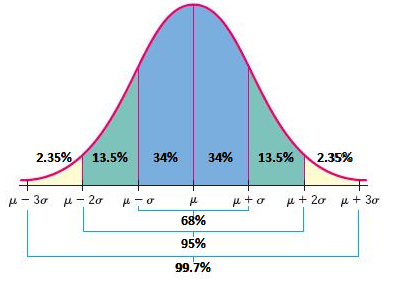
Standard deviation percentages
(If you score the mean then it’s 50%)
Reliability vs validity
Reliability refers to the consistency of a test's results over time, while validity measures how well a test actually assesses what it claims to measure.