U2 Vocab – AP Macro
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2 AP Macro Carney
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
business cycle (components)
(+ disinflation is when it slows rate of increasing)
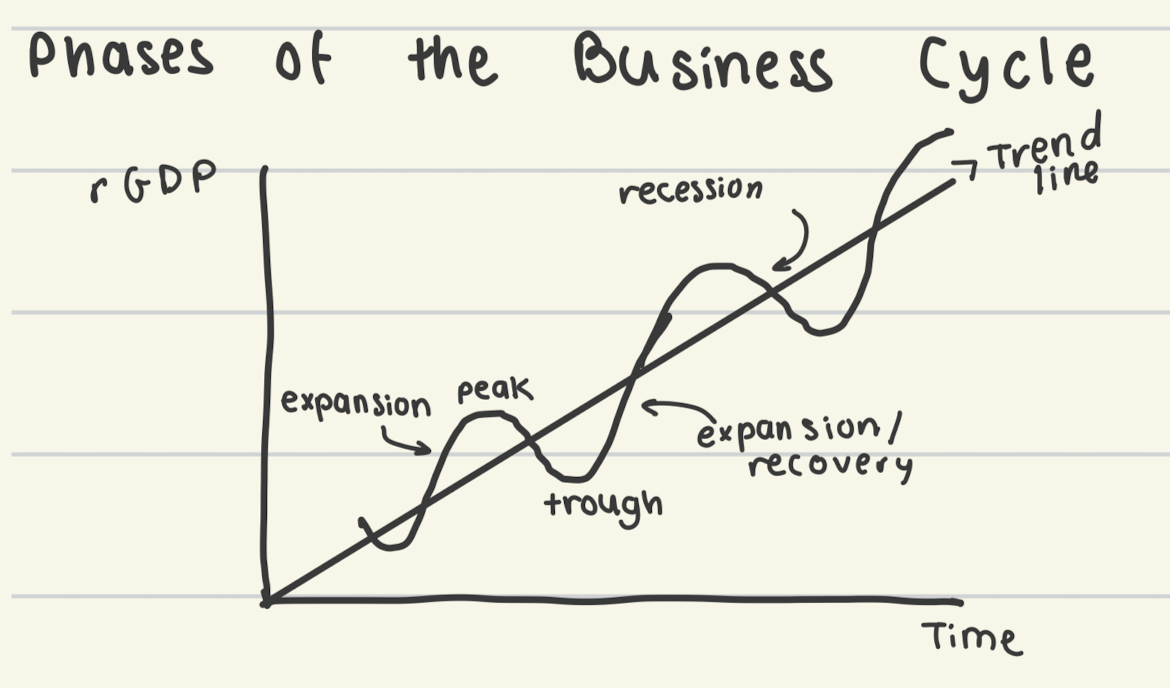
recession
periods of economic downturns when output and employment falling
economic depression
very deep and prolonged economic downturn
economic growth
an increase in the maximum possible economy output (leads to bring able to afford more material goods)
gross domestic product
measures total value of final goods/services created/provided by an economy over a year
intermediate goods
brought from firm by firm to be inputs for product of final goods/services (one person’s intermediate could be someone else’s final! selling lettuce at store vs using for a taco truck)
final goods
goods sold to the final / end user; end product
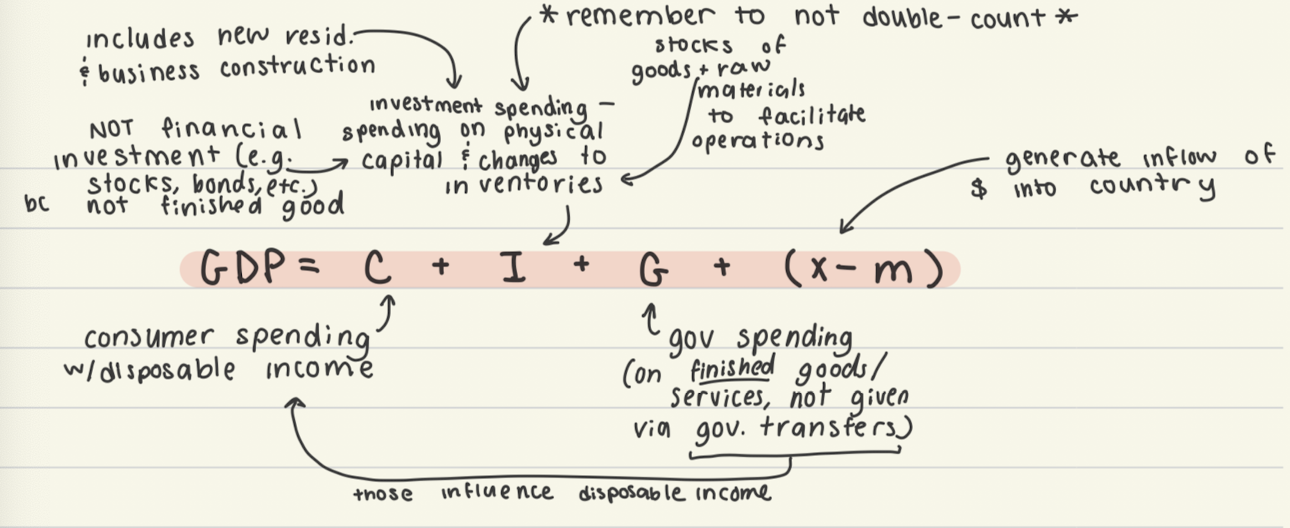
expenditure approach
GDP = C + I + G + (x-m)
C = Consumer spending
I = Investment spending
G = Goverment spending
(x-m) or Xn = net exports
does not count purchase of secondhand goods, stocks/bonds, or illegal items not in legal market because they do not represent new production
income approach
addition of wages, interest, rent, profit
does not include income / profits earned by US citizens abroad, transfer payments (e.g. Social Security, interest payments)
value-added approach
how much value was added at each step of the process of production for the final good (addition of value added [price sold for; don’t double-count] of each good)
nonmarket transactions
transactions that do not occur in a (legal) market; do not count towards GDP
government purchases
counts for the G in the expenditure equation
government spending on finished goods and services; does not include money given to citizens via government transfers (social security, unemployment, etc. becomes part of consumer spending as disposable income)
disposable personal income
counts for the C in the expenditure equation
the amount of money that a person/household has to spend after taxes are deducted
labor force
LF = E + U
the amount of people in an economy aged 16+ who are either employed (including subsection of underemployed) or unemployed
unemployment rate
UR = U/LF * 100%
the percent of the labor force that is unemployed
labor force participation rate
LFPR = LF/[total population] * 100%
please note that the labor force only includes employed people and those currently looking for a job (unemployed)
frictional unemployment
people who are temporarily between jobs
me terms – these people are choosing unemployment in order for better opportunities (due to individual choices; e.g. looking for better pay than minimum wage)
structural unemployment
involves mismatches between job seekers and job openings; applicant skills don’t fit needed workers / the industry has changed to have different needs (e.g. automation means people to sew certain clothing is not needed)
me terms – more so up to individual businesses/industries; typically not an economy-wide issue
cyclical unemployment
people not working because firms do not need labor due to lack of demand / economic downturn; due to the business cycle
me terms – think recession, depression, downturn in sales
discouraged workers
people who have given up looking for a job due to poor state of the job market but would otherwise (in different job market conditions) be working
not considered in labor force therefore a part of why unemployment rate may understate true rate
underemployed workers
workers who are working part-time jobs because they are unable to find full-time jobs (think: Bill (maybe))
not considered in labor force therefore a part of why unemployment rate may understate true rate
full-employment real output
maximum level of economic output that an economy can sustainably produce when all available factors of production (including labor) used efficiently, but not stretched beyond capacity; occurs at natural rate of unemployment
natural rate of unemployment
rate at which inflation typically remains stable, consisting of sum of frictional and structural unemployment (long-run equilibrium that central banks aim for)
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
CPI = (current yr/base yr) * 100%
measure in change of price of goods/services that consumers most often buy
possible criticism that it’s on a fixed bundle and thus doesn’t properly take into account peoples’ switches to substitutes; possibly not representative because city-based
inflation
increase in aggregate price level of goods/services in the economy; expected but can cause issues if different than expected
deflation
decrease in aggregate price level of goods/services in economy
inflation rate
the annual change in percent (%) of aggregate price level
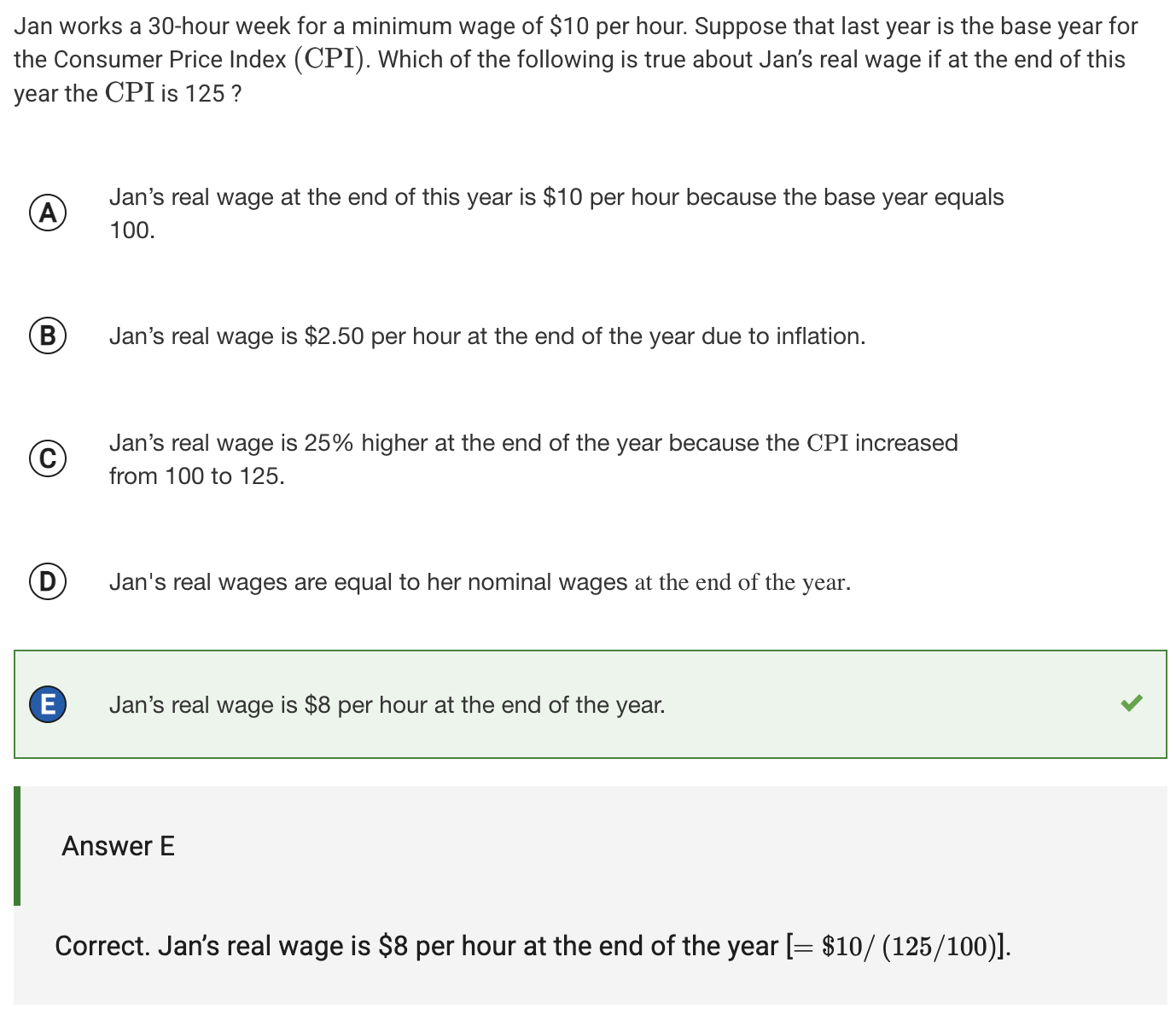
real wages
the purchasing power of one’s wages compared to a base year (use CPI as a comparison)
(APC example in image)
nominal GDP
GDP in current value of currency
real GDP
GDP taking into account price changes (as inflation is expected and nominal GDP includes rises in prices via inflation)
doesn’t address uneven wealth distribution
GDP deflator
GDP deflator = nGDP/rGDP * 100%
measure of the percent change
nGDP = nominal GDP
rGDP = real GDP
percent change equation
(current yr - base yr) / (base yr) * 100%