Chapter 3: Two-Dimensional Kinematics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
1
New cards
position vector
A natural way to describe the position of an object in more than one dimension is to define a _______ that points from the origin to the location of the object.
2
New cards
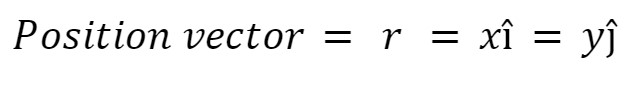
Position Vector Definiton
3
New cards
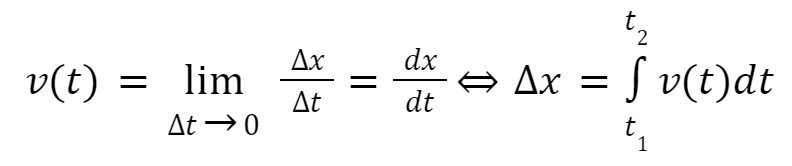
**Instantaneous velocity (2D Kinematics)**
4
New cards
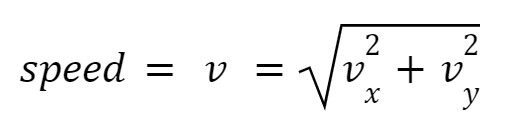
**Instantaneous speed (2D Kinematics)**
5
New cards
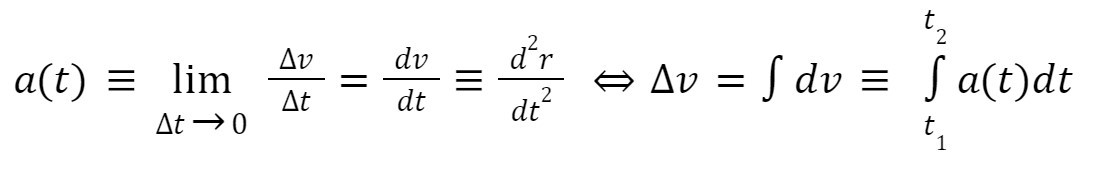
**Instantaneous acceleration (2D Kinematics)**
6
New cards
**two-dimensional vector equations**
The definitions of velocity and acceleration are **____________**, each of which is equivalent to a set of two one-dimensional equations.
7
New cards
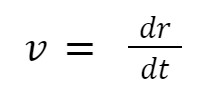
definition of velocity
8
New cards
**instantaneous velocity**
For the **______________ vector**, the magnitude is the speed (a scalar), and its direction is in the direction of motion (tangent to the path of the object).
9
New cards
**inertial reference frames**
For most problems that you will have to deal with, the two reference frames will be **_____________**, which means that they move with a constant velocity with respect to each other.
10
New cards
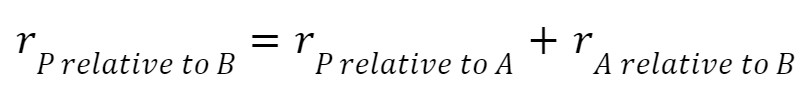
Vector addition relates the position of an object relative to two different frames of reference
11
New cards
**Tangential Acceleration (a∥)**
Affects only the magnitude of the velocity vector.
12
New cards
**Radial Acceleration (a⊥)**
Affects only the direction of the velocity vector.
13
New cards
**ω**
determines the sense of rotation
14
New cards
**magnitude of ω**
determines how quickly the r(t) vector rotates.
15
New cards
**Phase shift angle** (ϕ)
A parameter that determines the initial angle and thus the initial position.
16
New cards
**Nonuniform circular motion**
Refers to motion in a circular path with nonconstant velocity.