Chapter 9 BIO: Cell to Cell Communication
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
cell signaling canoccur in abiotic and biotic conditions
True
signal transduction pathway
1. signal received from outside of cell
2. activates a series of response
3. evokes a cellular response
ancestral signaling ----- from prokaryotes
evolved
sensory cell
receive external signal and then secrets ligand
target cell
has receptor and receives signal
nuclear receptors
located in nucleus, regulates gene expression
cytoplasmic recptor
can accept ligands that cross membrane (hydrophobic)
transmembrane receptors
spans cell membrane
quorum sensing
method used by bacteria to sense population density
biofilm
bacteria accumulation on surface (become resistant to the host cells system factor)
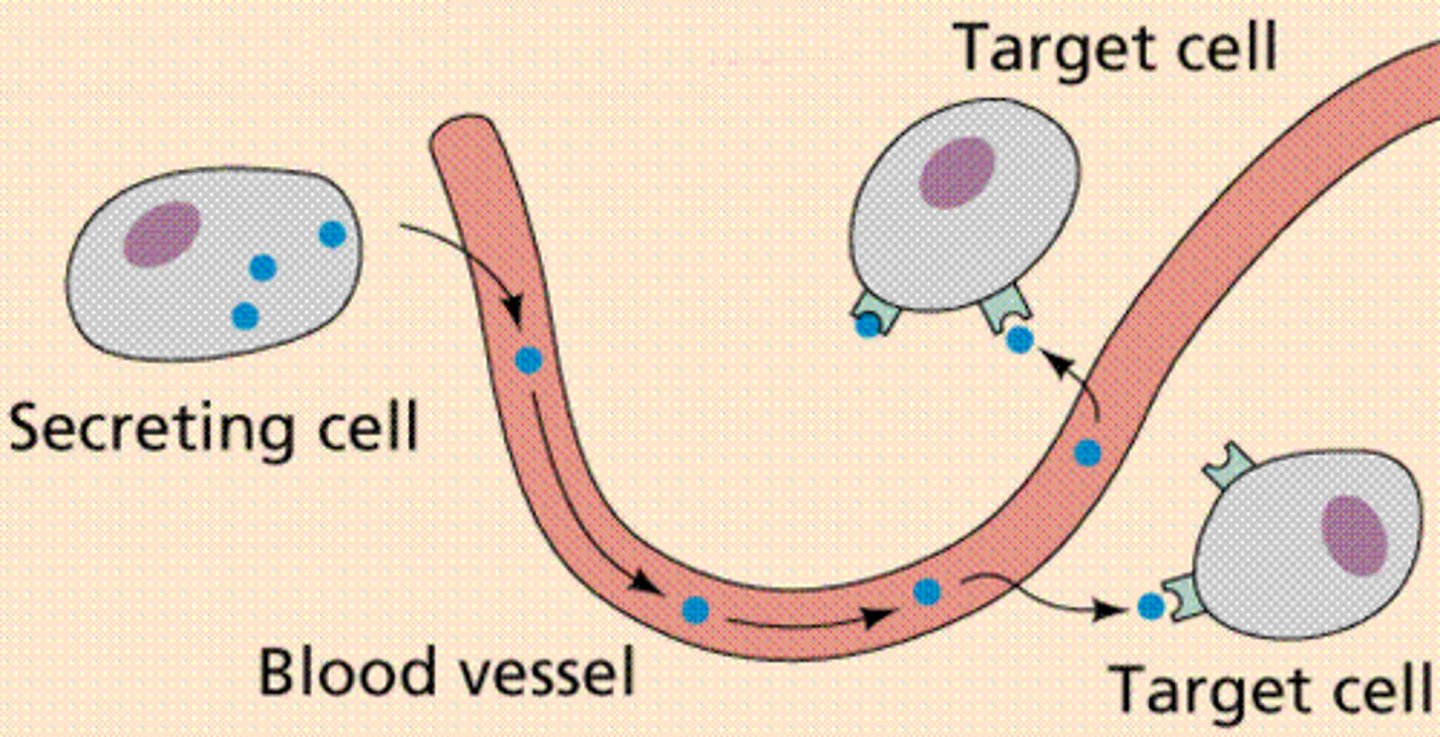
endocrine
hormones secreted into blood stream and travel long distance to reach target cell
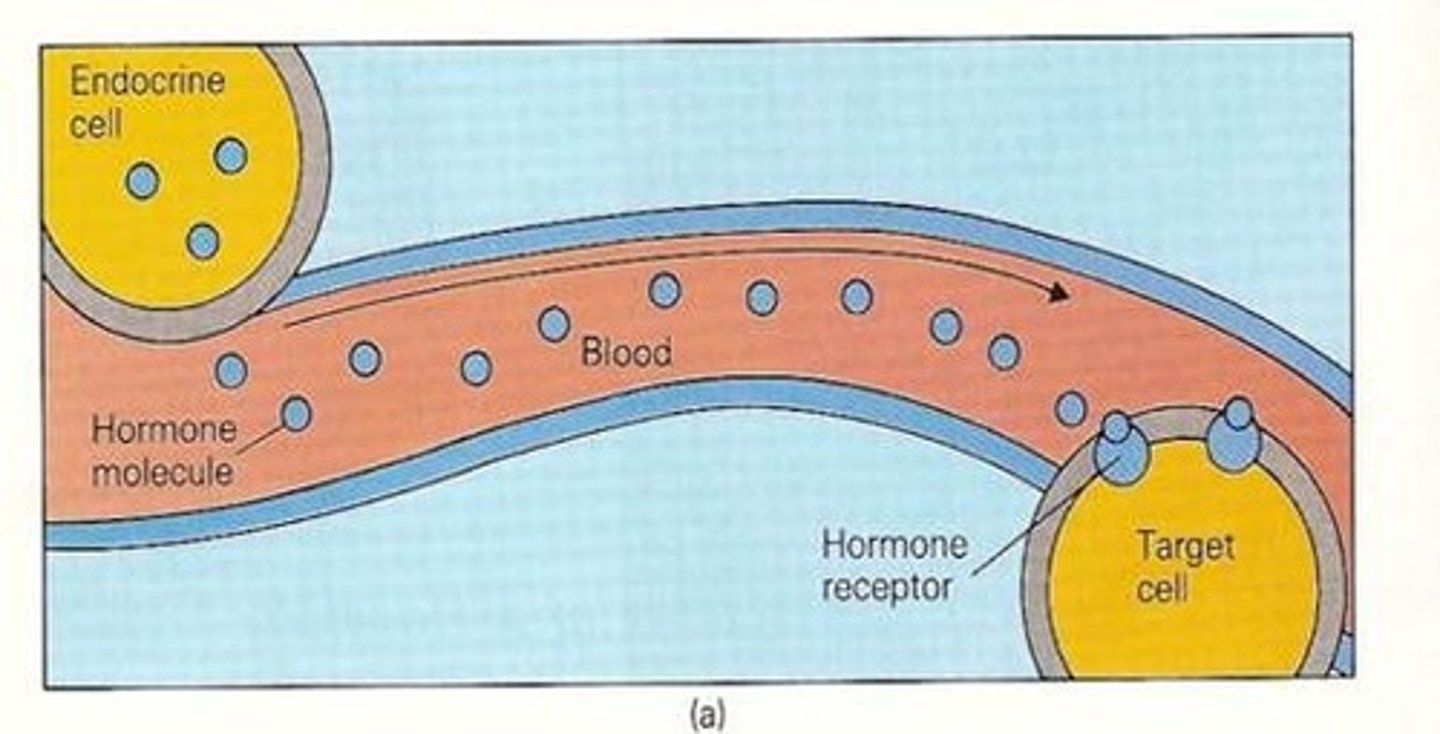
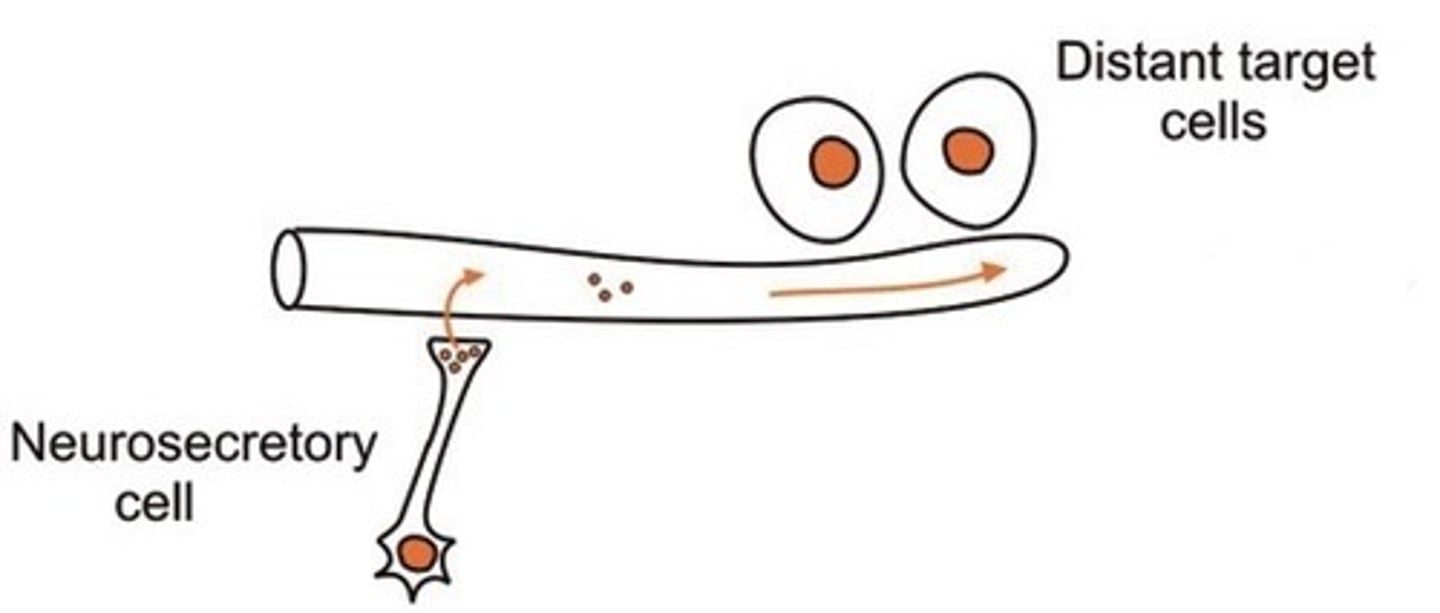
neuroendocrine
same as endocrine, secreting cell us a neuron (releases hormones)
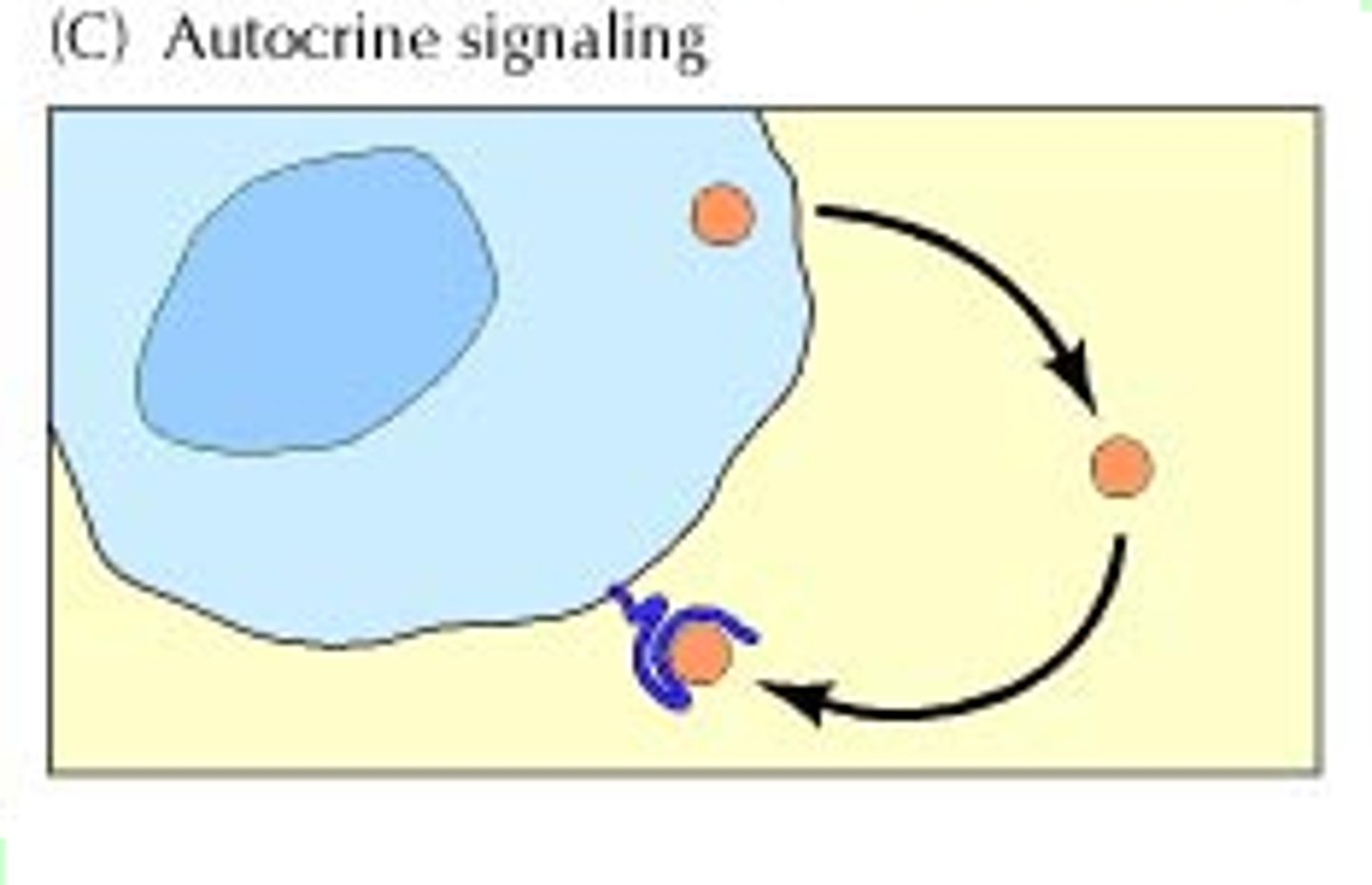
autocrine
in immune system, cell release a factor that is going to bind to its own receptors and then activate them further
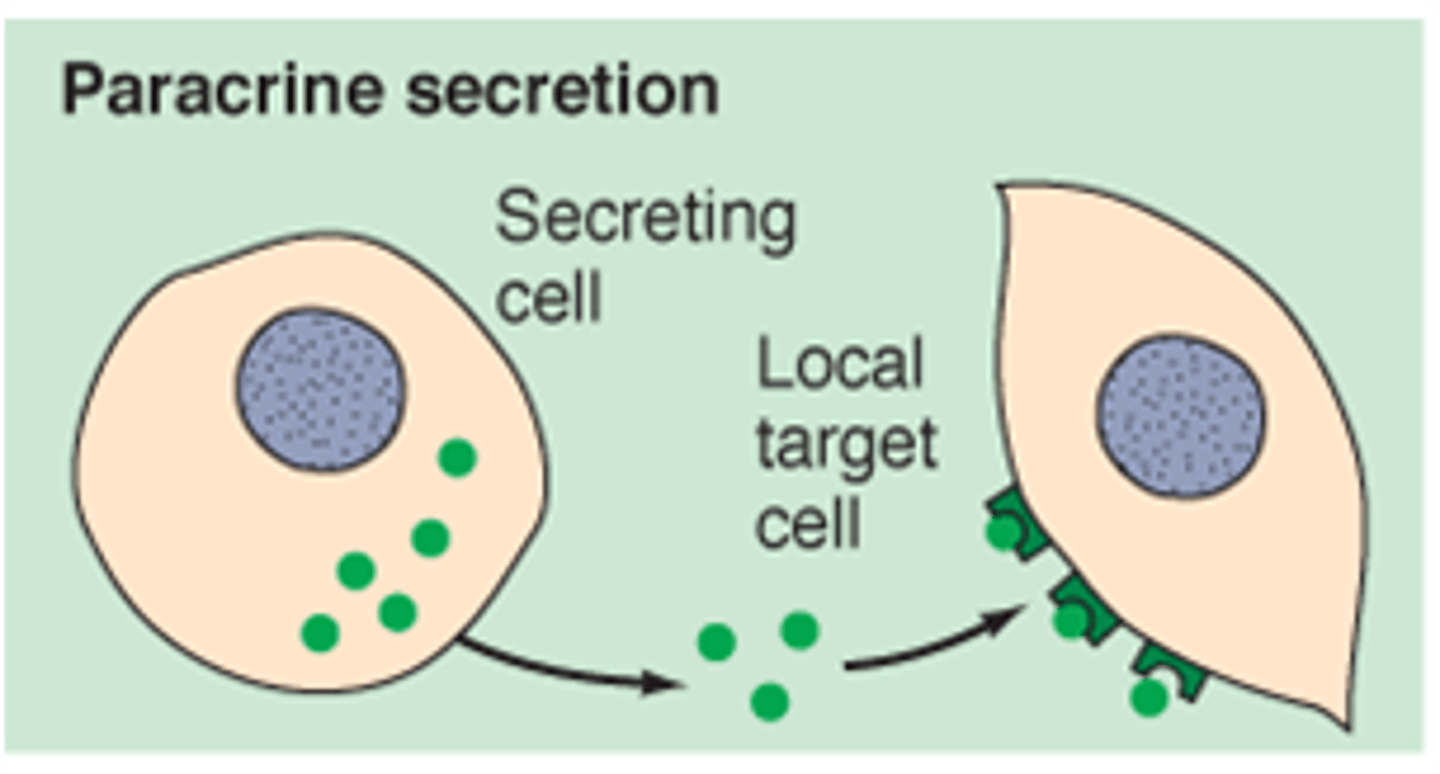
paracrine
signal is released by one cell and diffusing through interstitial fluid to get to other near by cells
synaptic
special type of paracrine signaling, only applicable when you have neuron releasing a signal to a near by cell
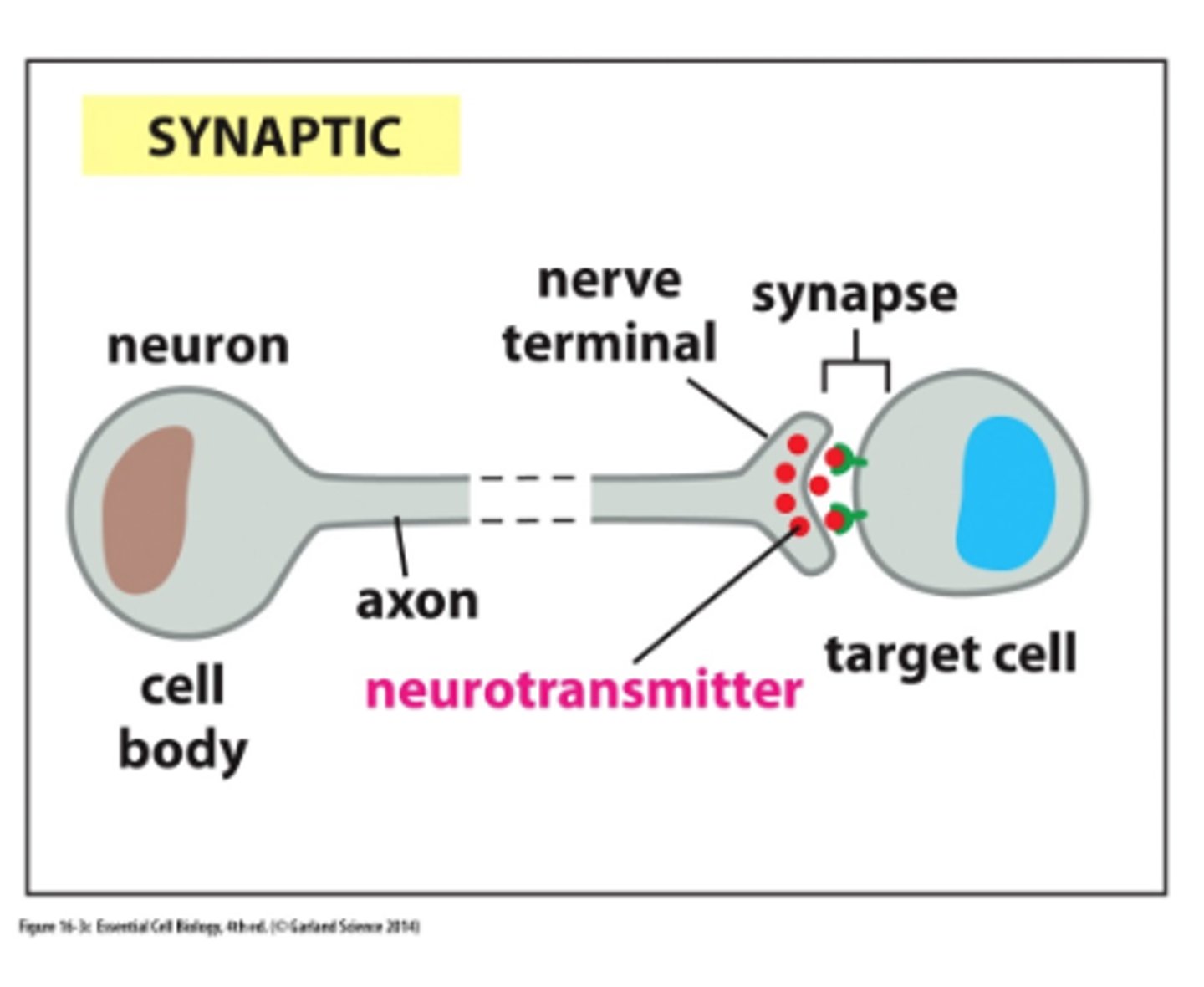
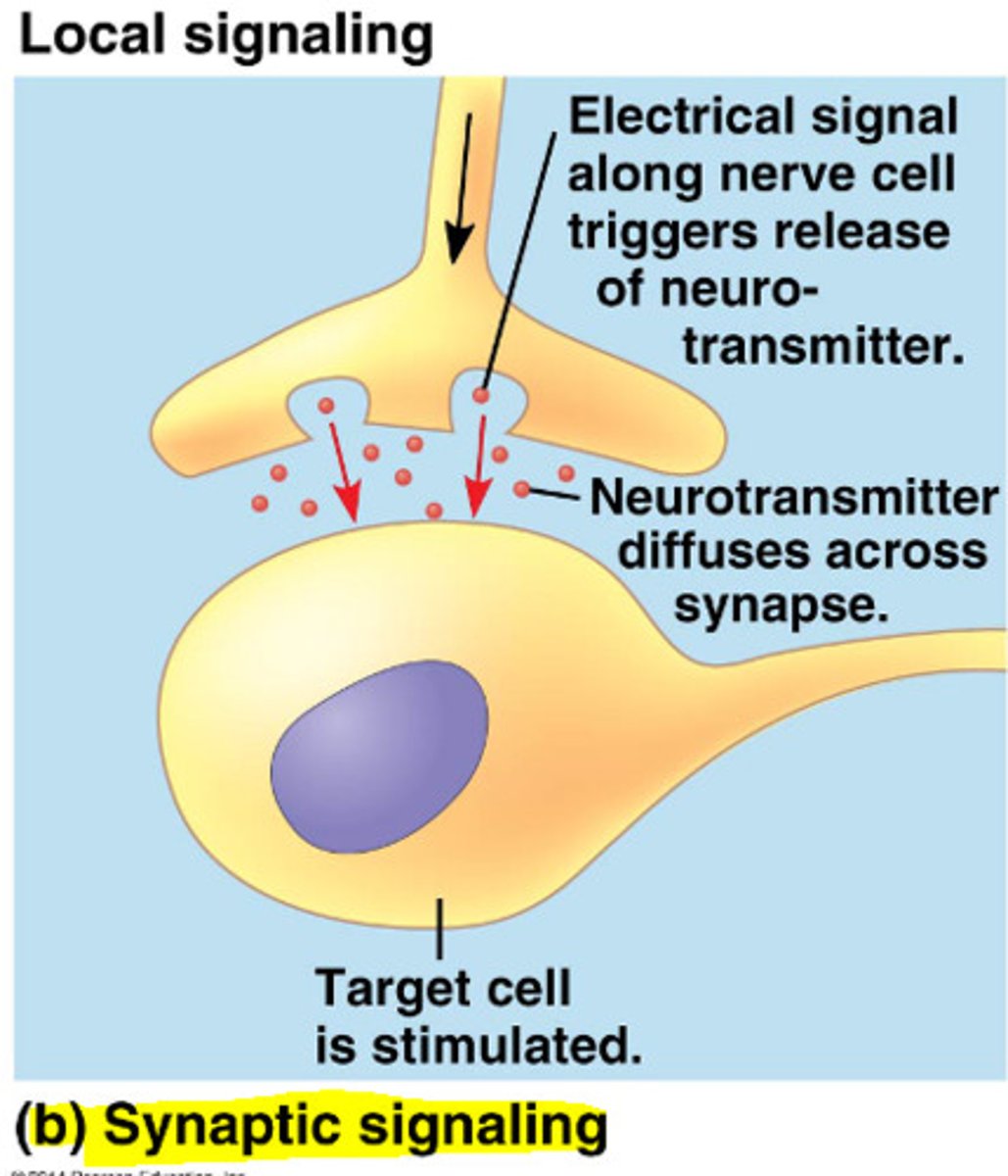
chemical synaptic
neurotransmitter is released by one neuro\n going to another neuron or muscle
direct contact
signal molecule is not released, this cell has to touch the other cell for this signaling molecule to attach to the receptor on the other cell
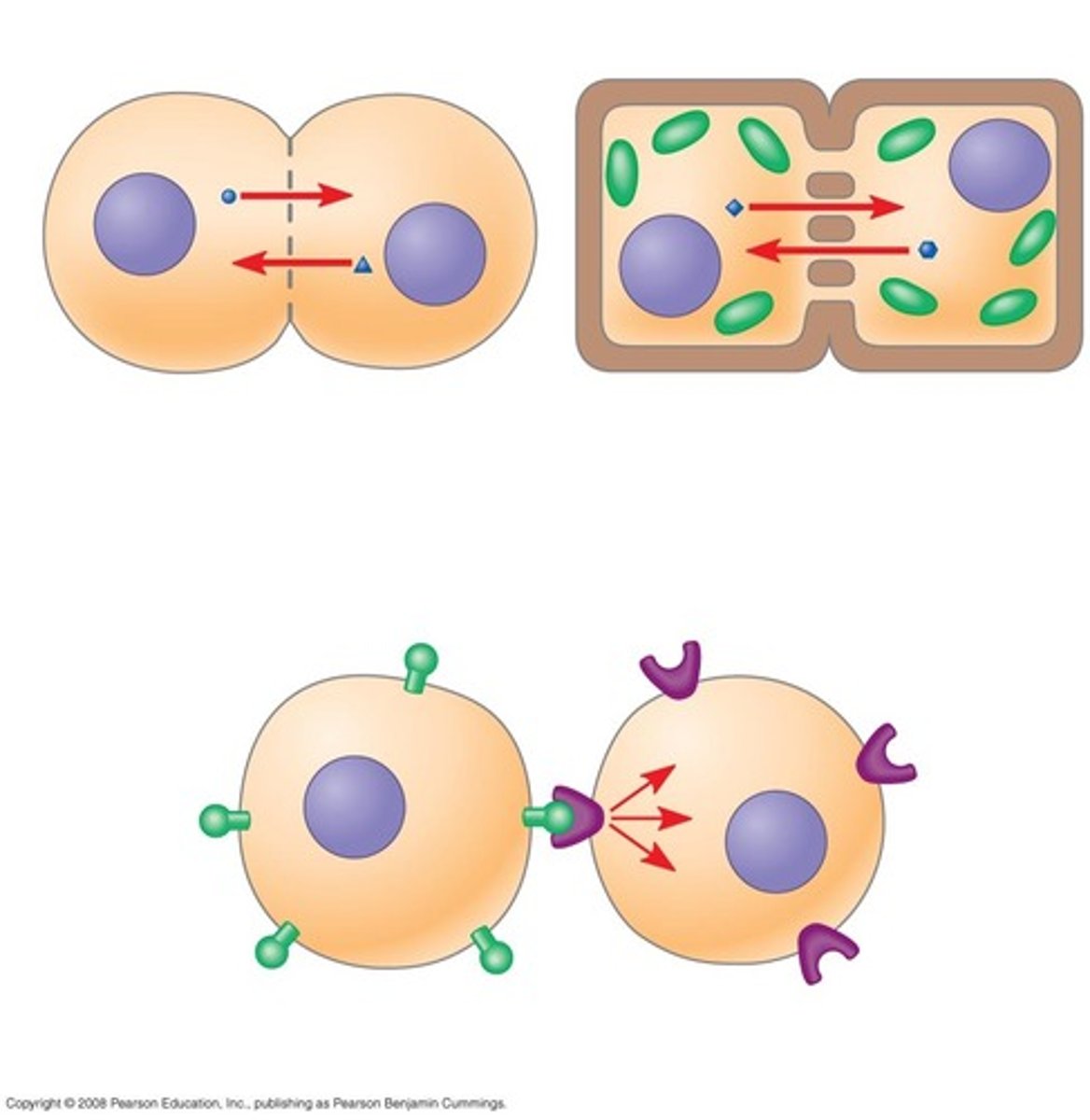
gap junctions
in animal cells, and will link 2 cells together, allows for the movment of ions, nutrients, and water between cells, allows for direct communication
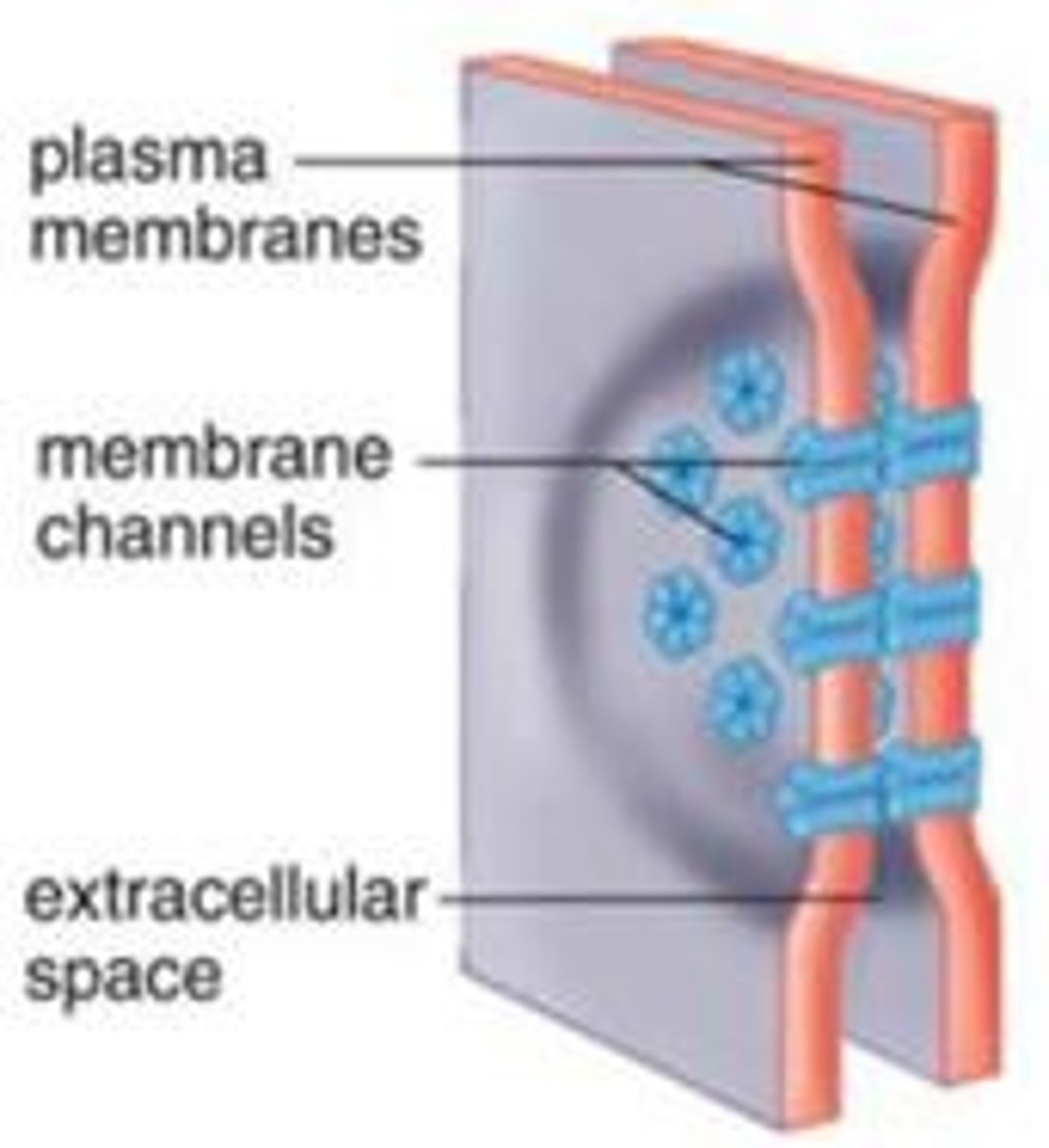
gap junctions have connexons that are made up of ----- -------
6 connexins
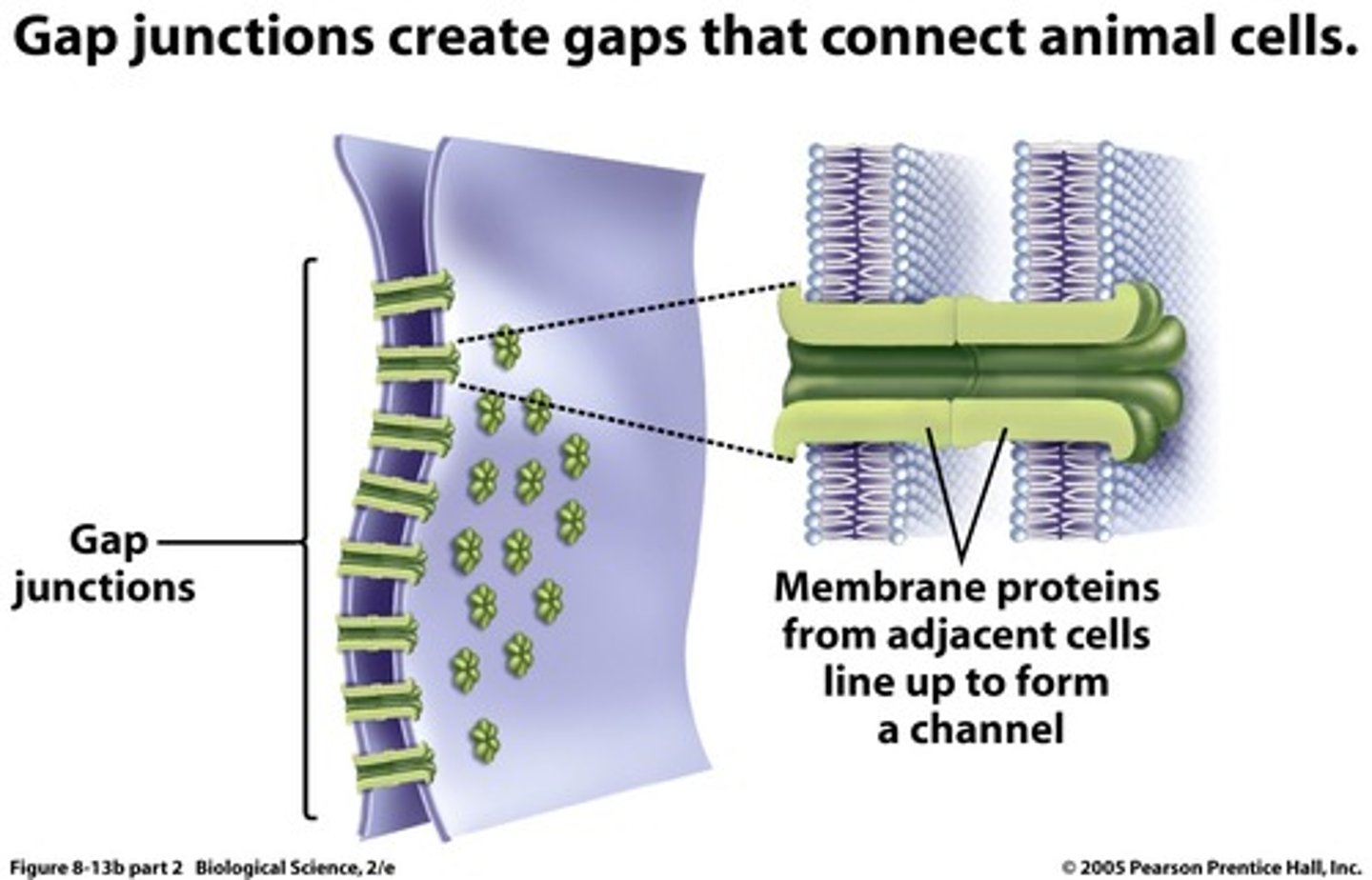
desmotubule
segment that connects ER of one cell to the ER of another cell
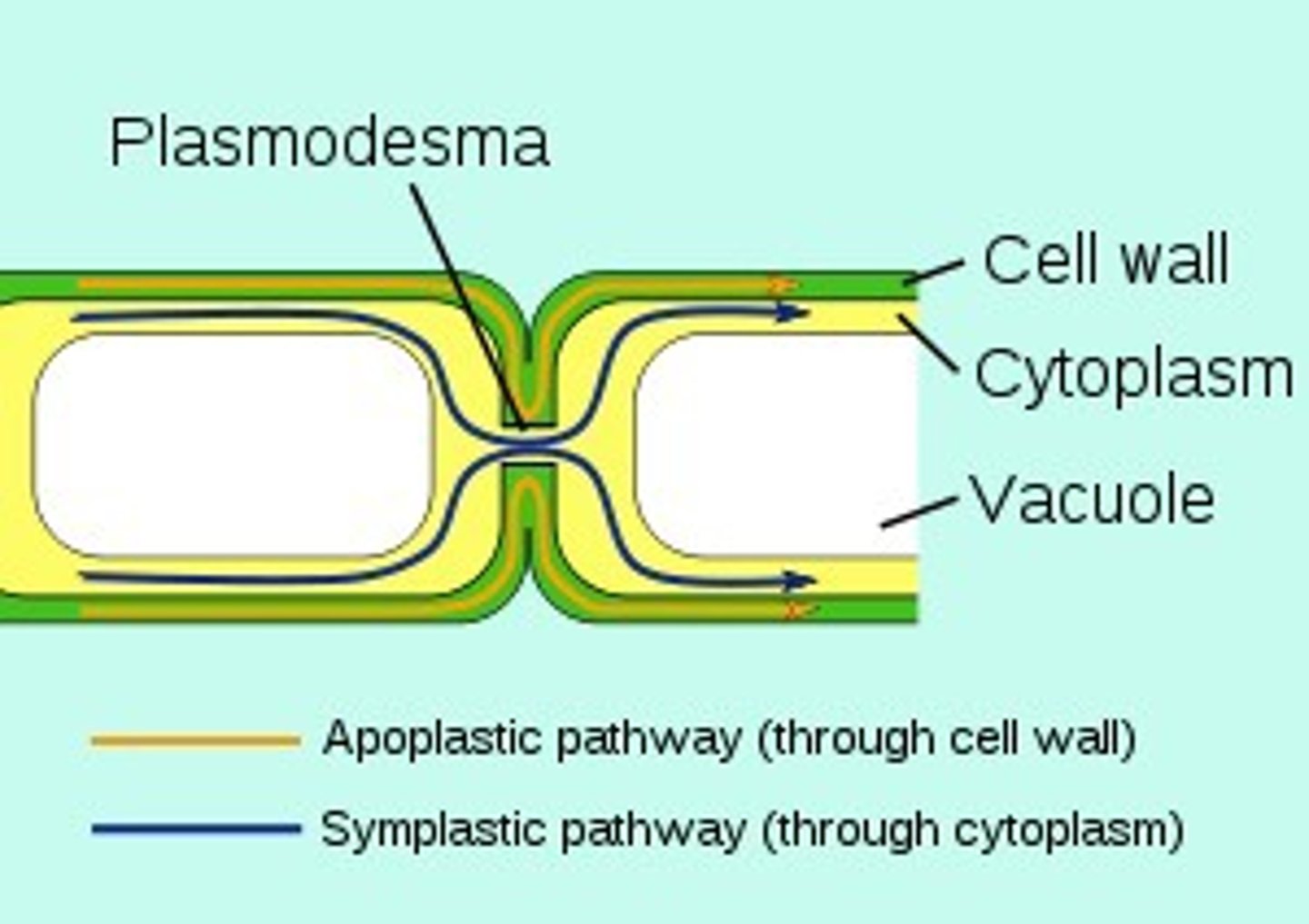
there are size restrictions for what passes through the desmotubule, plasmadesma, and plasma membrane
true
plasmodesma
hannels that connect plant cells, allowing them to communicate with each other and transport cellular contents
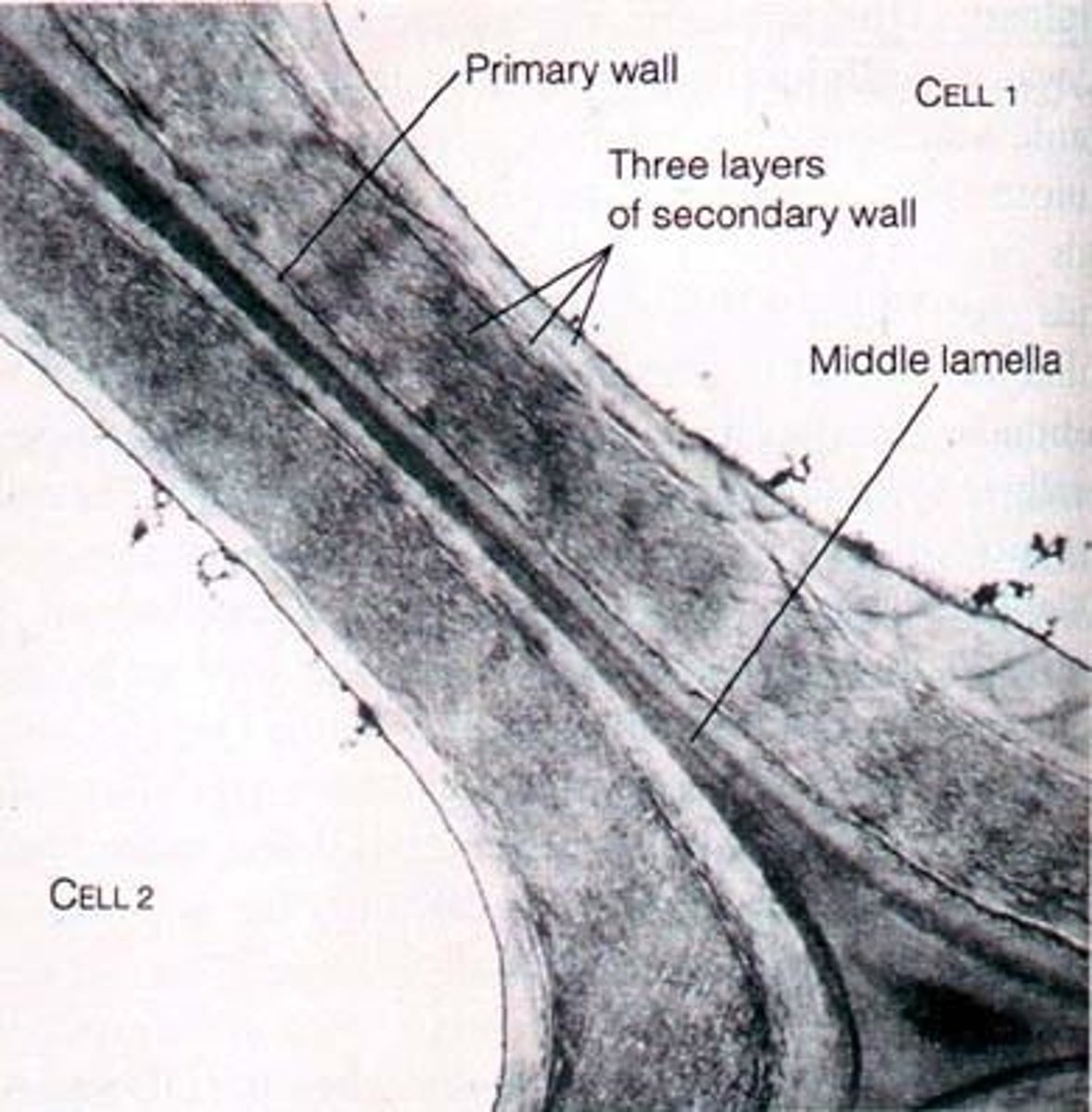
Middle lamella
hold two cell walls together
plants have ----- --- so they cant have gap junctions
cell walls
Ethylene
important hormone in food ripening,
-happens outside individuals can affect nearby plants,
-how can we store tomatoes in the winter?
- harvest them unripe, store in cold temp. with high CO2 and low O2 then ship them off, then gas them with ethylene, problem- not as juicy and don't taste as good bc not on vine so didnt get extra minerals and vitamins

green leaf volatiles
-send signals to neighboring plants warning neighbors they are being attacked
- send signals to attract predators of whats attacking them

Sutherlands 3 stages of cell signaling
Reception, Transduction, Response
Reception
when ligand attaches to binding site , will change shape
receptors can be anywhere, for them to reach target they have to cross through the membrane so they have to be
hydrophobic
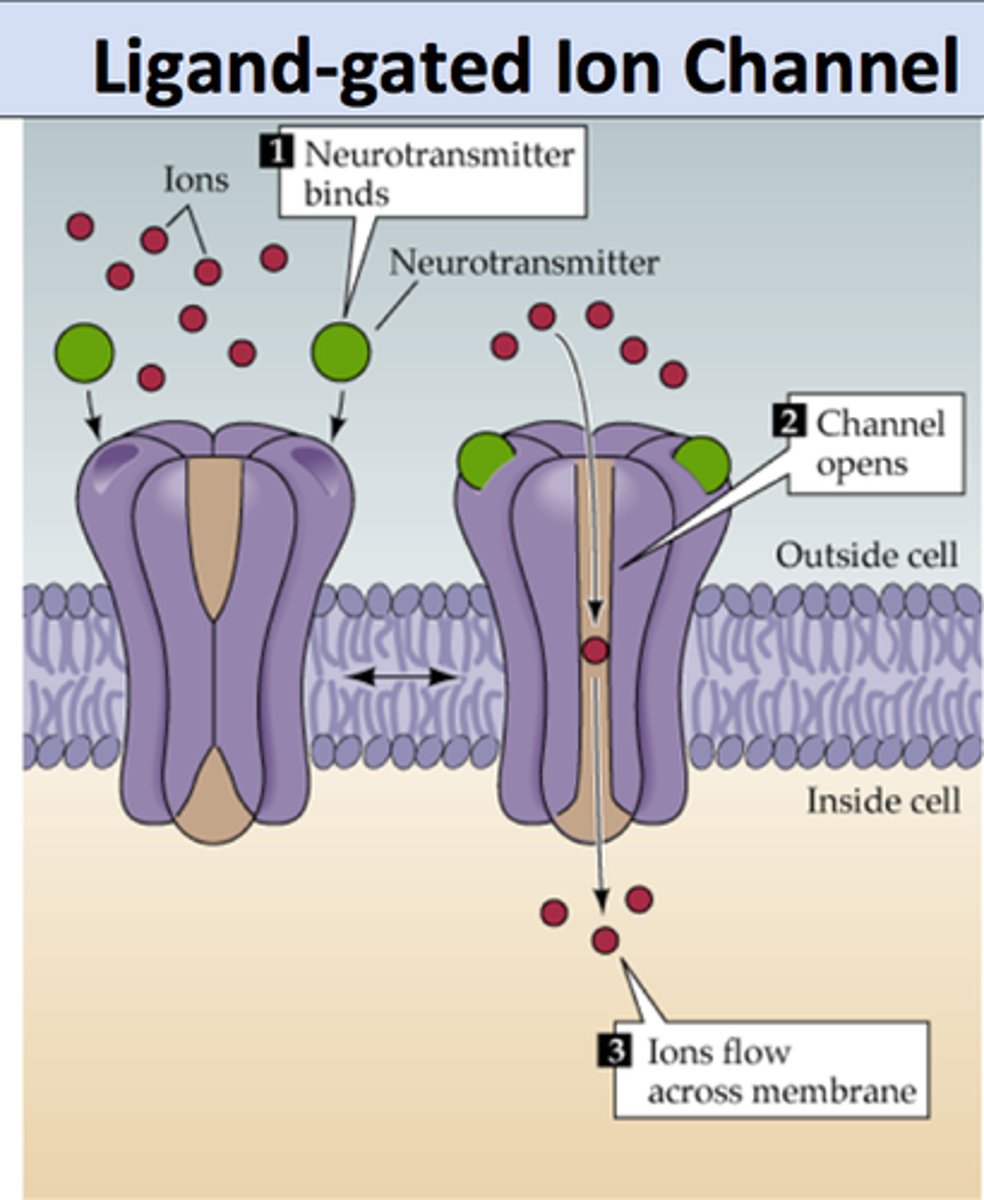
Ligand gated ion channels
-channel closed w/o ligand
-add ligand causes channel to change shape
-ions pass through
-got signal inside cell
recptor tyrosine kinase
- signaling molecule bind to receptor and the recptors dimerize (get close togther)
-bc of this cell is partially activated so it will autophosphorylate
- now it will be fully actiovated after autophorylation and will start a chain reaction to get a cellular response
* if u want to stop u will use phosphotase
g protein coupled receptor
-signaling molecule will attcah to receptor which will cause g protein to release GDP, then GTP will attach causing beta and gama to seperate and do their own thing
-response needs to stop so the alpha subunit is a GTPase so it will hydrolyze itself and release Pi and then turn GTP back to GDP
-alpha will rejoin beta and gamma
secondary messengers
small, nonprotein, usually water soluble molecules or ions \
ex- Ca+, Ip3, DAG, cAMP
regulating Ca 2+
by pumping Ca out of the cell bc we dont want high concentrations in the cell
synthesis of IP3 and DAG
PIP3 is a lipid and it will break down into two seccondary messengers using Phosphlipase C (lithium inhibits this enzyme)
DAG is the fat soluble secondary messenger
IP3 is the water soluble secondary messenger
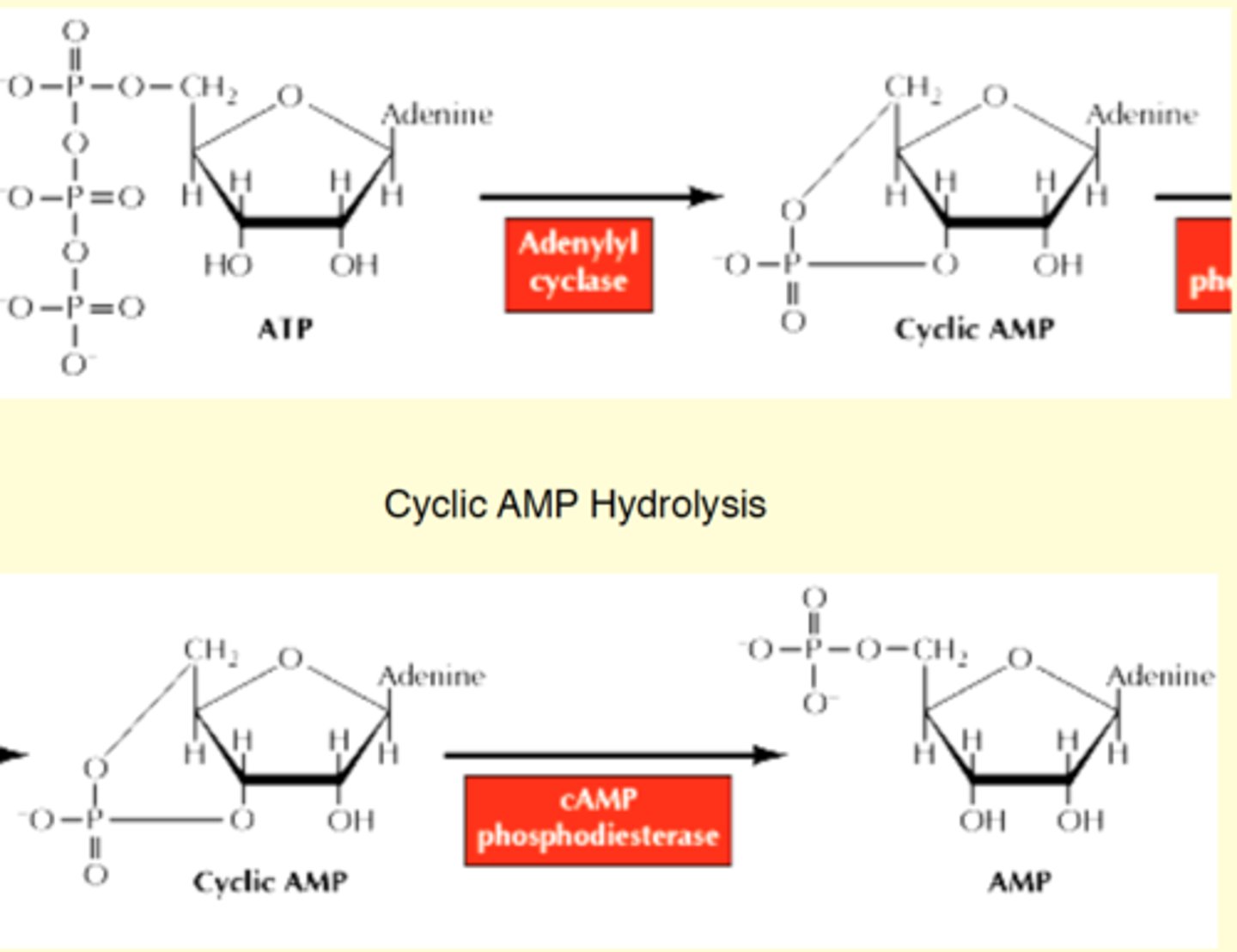
cAMP synthesis
from ATP uses adenylyl cyclase( which will remove 2 phosphate groups), it will attach the other phosphate and form ring
* to break it down- use phosphodieterase and it will turn into AMP (liner form so it wont be active)
to terminate relay proteins
just dephosphprylate it using phosphotase
termination of signal; by
terminating the cell,
G protein Ras
- EGf is the first messenger, it will bind on to receptor and autophosphylate, then it will interact with adaptive proteins to RAS, g protein will activate GTP (enters) and GDP will be rekleased, RAF will get activate and phosphorylate MEK and then ERk will get phosphylated, then it will enter nucleus where it can affect gene transcription--> genes involved in cell divison --> if activated cell division will occur
if Ras is deactived then
cancer will happen, bc unregulated cell division
Pathways can lead to different responses
true