Anaerobic Respiration
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Obligate Anaerobes
Cannot survive in oxygen
Most are prokaryotes
Facultative Anaerobes
Use aerobic resp. when in oxygen, but use anaerobic resp. when no oxygen available
E.g. yeast
Obligate Aerobes
Only synthesise ATP w. O2 present
Individual cells can cope for a little while without
E.g. mammals
What doesn’t anaerobic respiration go thru like aerobic does?
Link reaction, Krebs cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation
Fermentation
The process by which complex organic compounds are broken down into simpler inorganic compounds without the use of oxygen or the involvement of an ETC
What are the 2 processes of anaerobic resp. known as and what do they differ by?
Lactate Fermentation
Alcoholic Fermentation
Differ in which organisms they occur in and what happens to the pyruvate.
What organisms use which anaerobic pathway?
Yeast and some plant root cells use ethanol fermentation
Mammalian muscle cells and other microorganisms use lactate fermentation
How are small amount of ATP produced during anaerobic resp.?
Some cells oxidise red. NAD produced during glycolysis so it can be used for further H transport
Glycolysis continues, producing small amount of ATP
Synthesised by substrate-level phosphorylation only
NOTE: Glucose is not fully broken down, hence the less ATP
Lactate Fermentation
NAD accepts H+ in glycolysis
Pyruvate accepts H+ from red. NAD, forming lactate + NAD
Pyruvate reduced to lactate
Catalysed by lactate dehydrogenase
NAD regenerates to be used again in glycolysis
What happens once lactate is produced?
Converts to lactic acid
Transported to liver in bloodstream
Liver uses oxygen to convert lactic acid into pyruvate, then glucose
Can be converted into glycogen tho
Why can’t lactate fermentation occur indefinitely?
Only 2 ATP made; isn’t enough to maintain vital processes for a long time
Accumulation of lactic acid decreases pH, protein structures/ enzymes denature, & cease to function
Why do we breathe deeper and faster after exercise?
Oxidation of lactate to pyruvate requires extra oxygen
Referred to as an ‘oxygen debt’
Lactate fermentation image

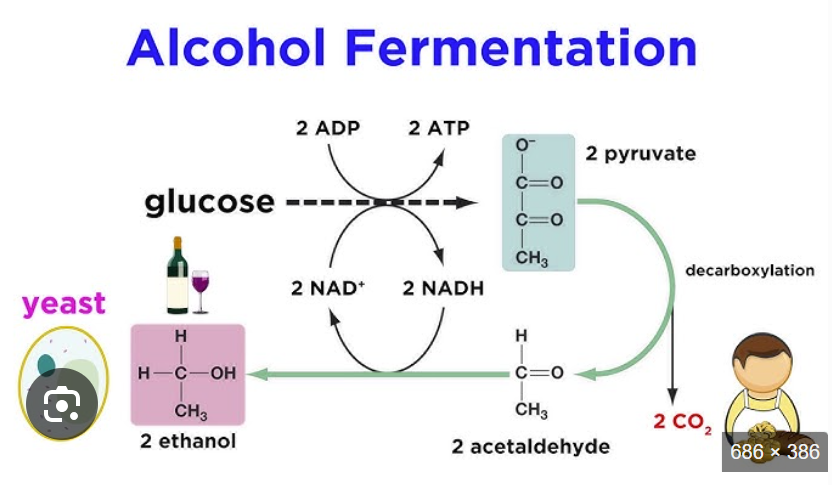
Alcoholic fermentation
Pyruvate converted to ethanal, catalysed by pyruvate decarboxylase
Ethanal accepts H+ from red. NAD, to make ethanol
Ethanol is final product, builds up to 15% before killing yeast
NAD regenerates, continues to act as coenzyme, glycolysis continues
Difference in time anaerobic processes last
Alcoholic fermentation is NOT short-term and an continue indefinitely in the absence of oxygen
Lactate fermentation is short-term and CANNOT continue indefinitely in the absence of oxygen
Alcohol Fermentation image
Benefit of anaerobic respiration
Used when oxygen cannot be supplied fast enough to respiring cells
It is a temporary emergency measure to keep vital processes functioning
Experiment with yeast
Check textbook, and sme