Unit 2: Cognition
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit Two of AP Psychology; Cognition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Bottom-Up Processing
an analysis of the stimulus begins with the sense receptors and works up to the level of the brain and mind
Top-Down Processing
information guided by higher-level mental processes as we construct perceptions, drawing on our experience and expectations
Cocktail Party Effect
your ability to attend to only one voice while also being able to hear your name from across the room
Gestalt Psychology
theory of perception that emphasizes the processing of entire patterns and configurations, and not merely individual components
Figure-Ground
organization of visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings
Grouping
perceptual tendency to organize into meaningful groups (continuity, closure, proximity, etc)
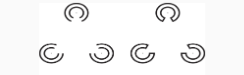
Closure
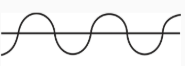
Continuity
Proximity
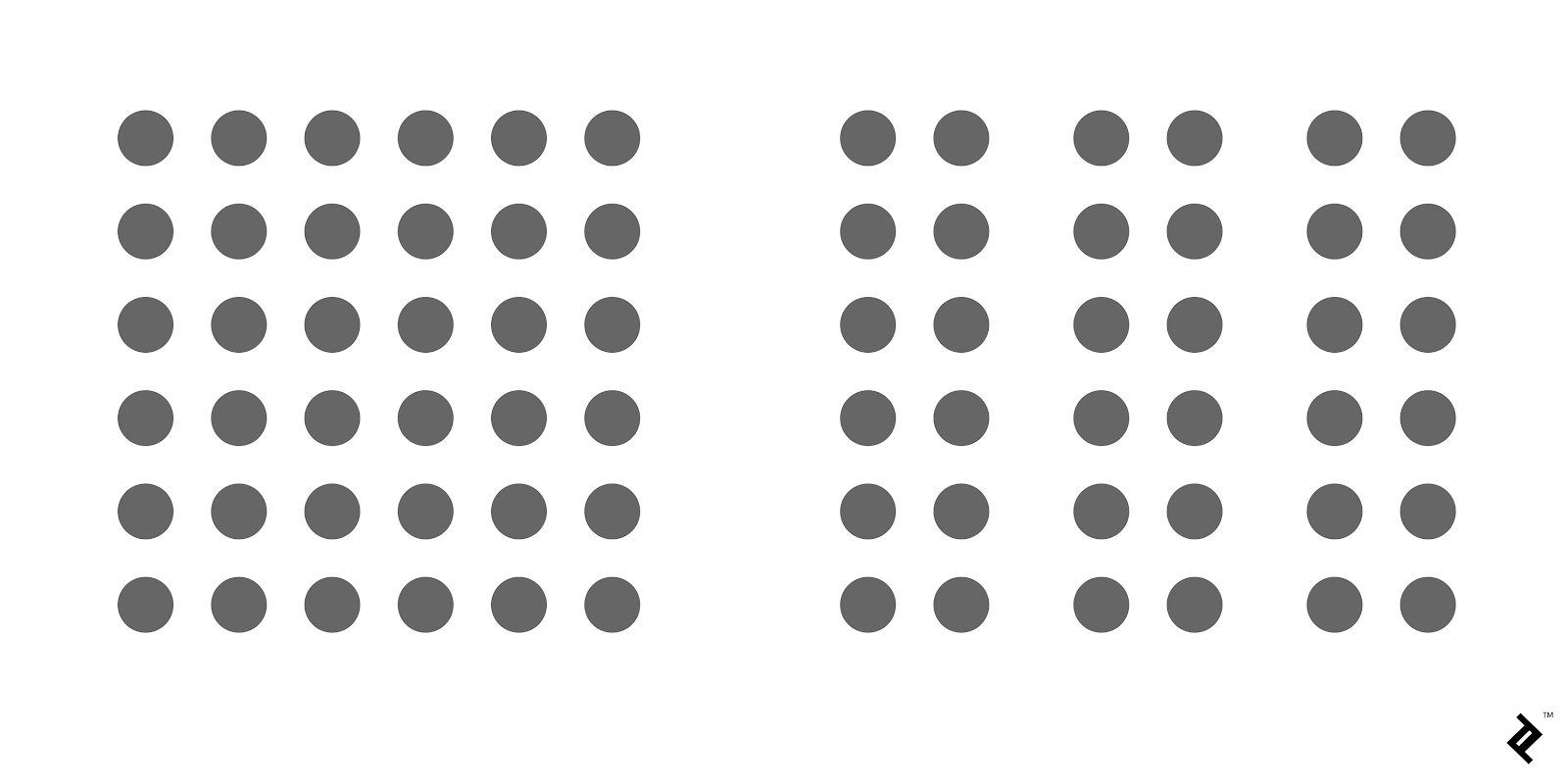
Binocular Cues
two eyes help perception of depth
Retinal Disparity
binocular cue for depth perception; brain calculates image by comparing images from both sets of eyes
Monocular Cues
linear perspective; relative size, motion and height
Color Constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even if changing illumination alters the wavelengths reflected by the object
Size Constancy
perception of objects as having constant size when distant from them varies
Perceptual Adaptation
ability to adjust to an artificially displace or even inverted visual field
Phi Phenonmenon
illusion of movement that arises when stationary objects are placed side by side and illuminated rapidly one after another
Motion Parallax
objects moving at a constant speed across frame will appear to move a greater amount if they are closer to an observer/camera than they would at a greater distance
schema
cognitive framework or concept that helps organize and interpret information
concept
a mental representation of objects and categories
formal concept
concept with characteristics defined by clear rules
natural concept
a concept without clearly defined characteristics
prototype
a mental image or “best example” of a concept; has all the most typical features of an item within an overarching concept
assimilate
the process of integrating new information, experiences, or ideas into an individual’s existing cognitive structure or schemas (ex: child fits pug and corgi into the same category: dogs)
accommodate
the process of adjusting existing mental structures, or schemas, to fit new information or experiences
algorithm
methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem; a step-by-step procedure
heuristic
simple thinking strategy that often allow us to make judgments and solve problems quick and efficiently
representativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent or match, particular prototypes or past experiences
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory
convergent thinking
type of thinking in which the number of possible solutions is narrowed down to the single best solution (ex: pros and cons)
divergent thinking
type of thinking in which the number of possible solutions is expanded to include multiple feasible solutions (ex: game strategy)
perceptual set
a tendency to view things only in a certain way; people tend to see things the way we expect them to be
fixation
inability to see a problem from a new perspective; impediment to problem solving
mental set
tendency to approach a problem in a particular way; especially a way that has been successful previously successful
functional fixedness
tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions; an impediment to problem solving
framing
a way an issue/problem is posed; bias undetected in question
sunk-cost fallacy
phenomenon whereby a person is reluctant to abandon a strategy or course of action because they have invested heavily in it, even when it is clear that abandonment would be more beneficial
gambler’s fallacy
an individual erroneously believes that a certain random event is less likely or more likely to happen based on the outcome of a previous event or series of events
encoding
gets information into our brain
storage
retention of information
retrieval
getting the information back out
long-term memory
area of storage for retrieval; infinite capacity
short-term memory
encode information through rehearsal; limited capacity
priming
the activation of particular associations in a memory
iconic memory
a brief sensory of visual stimuli
echoic memory
a brief sensory memory of auditory stimuli
explicit memory
type of memory controlled consciously, intentionally, and flexibly