States of Matter
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to states of matter, including definitions of thermal energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, various states of matter, phase changes, and relevant theories.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

59 Terms
Thermal energy
The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of particles in an object.
Kinetic energy
Energy in motion.
Potential energy
Stored energy.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The theory stating that all matter is made of small particles in constant random motion.
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in an object.
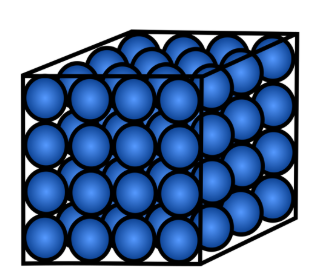
Solid
A state of matter with a fixed volume and fixed shape, where particles are tightly held together.
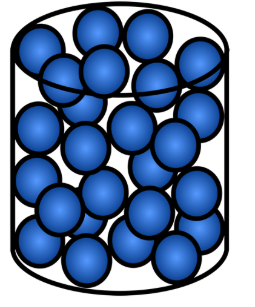
Liquid
A state of matter with a fixed volume but changing shape based on its container.
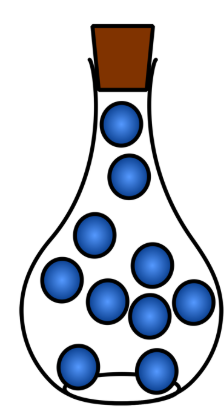
Gas
A state of matter with no fixed volume or shape, where particles can freely move.
Diffusion
The process by which gas particles spread out to fill the container.
Plasma
A state of matter composed of charged particles with high kinetic energy.
Heat of fusion
The amount of energy needed to turn a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
Heat of vaporization
The amount of energy needed to turn a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
Vaporization
The phase/state transition from liquid to gas.
Evaporation
Vaporization that occurs only at the surface of a liquid.
Boiling
Vaporization that occurs throughout the liquid due to a temperature change.
Heating curve
A diagram showing the state transitions a substance undergoes as heat is added to it.
Solid to Liquid
melting
Liquid to Gas
Vaporization
Gas to Solid
Deposition
Solid to gas
Sublimation
Gas to liquid
Condensation
Liquid to Solid
freezing
Solid to liquid adding or removing energy?
Adding
Liquid to solid adding or removing energy?
Removing
Liquid to Gas adding or removing energy?
Adding
Gas to liquid removing or adding energy?
Remving
Gas to solid adding or removing energy?
Removing
Solid to gas adding or removing energy?
Adding
Thermal energy
The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of particles in an object.
Kinetic energy
Energy in motion.
Potential energy
Stored energy.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The theory stating that all matter is made of small particles in constant random motion.
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in an object.
Solid
A state of matter with a fixed volume and fixed shape, where particles are tightly held together.
Liquid
A state of matter with a fixed volume but changing shape based on its container.
Gas
A state of matter with no fixed volume or shape, where particles can freely move.
Diffusion
The process by which gas particles spread out to fill the container.
Plasma
A state of matter composed of charged particles with high kinetic energy.
Heat of fusion
The amount of energy needed to turn a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
Heat of vaporization
The amount of energy needed to turn a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
Vaporization
The phase/state transition from liquid to gas.
Evaporation
Vaporization that occurs only at the surface of a liquid.
Boiling
Vaporization that occurs throughout the liquid due to a temperature change.
Heating curve
A diagram showing the state transitions a substance undergoes as heat is added to it.
Solid to Liquid
melting
Liquid to Gas
Vaporization
Gas to Solid
Deposition
Solid to gas
Sublimation
Gas to liquid
Condensation
Liquid to Solid
freezing
Solid to liquid adding or removing energy?
Adding
Liquid to solid adding or removing energy?
Removing
Liquid to Gas adding or removing energy?
Adding
Gas to liquid removing or adding energy?
Removing
Gas to solid adding or removing energy?
Removing
Solid to gas adding or removing energy?
Adding
Particle arrangement of a solid
Particles are tightly packed in a fixed, regular pattern and vibrate in place.
Particle arrangement of a liquid
Particles are close together but have no regular arrangement, allowing them to flow and slide past each other.
Particle arrangement of a gas
Particles are far apart with no regular arrangement and move rapidly and independently in random motion.