2.1 ATI Principles in Community and Public Health Nursing
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Community health nursing
Nursing care that focuses on the overall health of the community, including individuals, families, and groups.
Public health nursing
Nursing care that is population-focused and strives to prevent disease, extend life, promote health, and increase efficiency through a coordinated community effort.
Community
A group of people who share or have common beliefs and have a common purpose.
Advocacy
Pleading and supporting a cause, idea, or policy for clients, communities, systems, family, and profession.
Nursing advocacy
Supporting clients' rights to make their own decisions about their health.
Six client rights
self-determination, confidentiality, access to health care, choice, information, and redress
Examples of self-determination
The right to informed consent
The right to take part in clinical decisions and treatment alternatives
Examples of confidentiality
The right to information privacy
The right to access one’s own medical record
Examples of access to health care
The right to benefit from medical treatment
The right to obtain timely, safe, and high quality of care
Examples of choice
The right to choose a health care provider
The right to a second opinion
Examples of information
The right to information about one’s health
The right to information about health care providers
The right to information about rights and entitlements
Examples of redress
The right to dispute and oppose
The right to compensation
Four stages of the advocacy process
Evaluate the client’s needs
Identify the client’s goals working with the client to create goals
Develop a plan to meet the goals
Evaluate the results of the advocacy steps
Health literacy
The degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information needed to make appropriate health decisions.
Characteristics of a Healthy Community
Educational opportunities
Economic opportunity
Infrastructure that includes recreational activities and essential services (sanitation, transportation, utilities)
Safe environment
Opportunities for health care
Diversity in leadership and decision-making
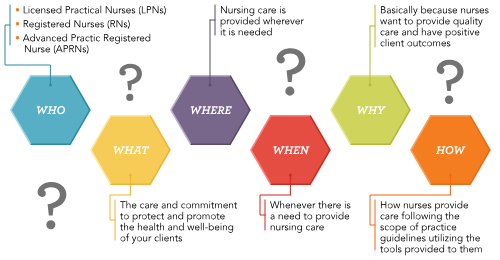
Scope of nursing practice key questions (ANA)
First six standards of practice
Assessment: Relevant data and information is collected.
Analysis: The data is analyzed, and actual or potential diagnoses are formed.
Outcomes Identification: Expected outcomes/goals are determined.
Planning: The plan of care is developed.
Implementation: Interventions are implemented.
Evaluation: The progress of care is evaluated, goals and outcomes met or not.
Remaining standards of practice
Ethics
Advocacy
Respectful and equitable practice
Communication
Collaboration
Leadership
Education
Scholarly inquiry
Quality of practice
Professional practice evaluation
Resource stewardship
Environmental health
Eight practice domains community/public health nursing competencies
Assessment and analytic skills
Policy development/program planning skills
Communication skills
Cultural competency skills
Community dimensions of practice skills
Public health sciences skills
Financial planning, evaluation, and management skills
Leadership and systems thinking skills
Types of cases brought to the board of nursing
practice-related, drug-related, boundary violations, sexual misconduct, abuse, fraud, positive criminal background check
Values
A person’s principles or standards of behavior; one’s judgment of what is important in life.
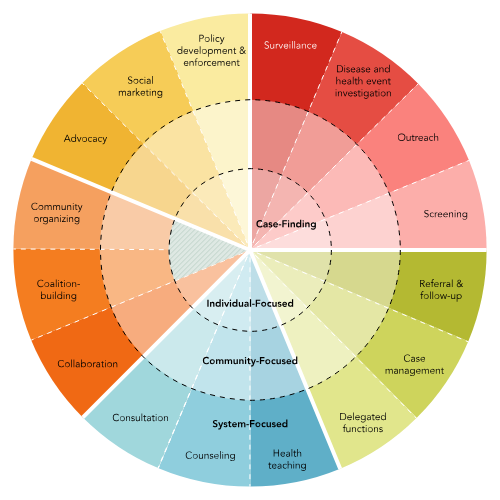
Minnesota Model for Public Health Nursing Practice
Four principles of nursing ethics
Autonomy - the ability to explain one’s actions and make informed decisions independently.
Beneficence - actively promote all good benefits, protecting one from harm by taking positive action helping others.
Nonmaleficence - the practice of “do no harm” by balancing the risks and benefits of care.
Justice - the principle of fairness, commitment to provide fair treatment on the basis of equality and equity.
Social justice
Equal rights and equitable opportunities for all.
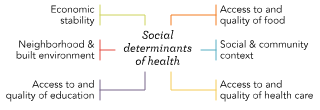
Social determinants of health (SDOH)
Conditions that are formed by social, economic, and political forces where people are born, grow, live, work, and age.
Inequities
Instances of injustice or unfairness.
16 Elements of the social contract
Professional Societal Expectations of Nursing
Caring service
Privacy of the patient
Knowledge, skill, and competence
Hazardous service
Responsibility and accountability
Progress and development
Ethical practice
Collaboration
Promotion of the health of the public
Nursing’s Expectations of Society
Autonomy of practice
Self-governance
Title and practice protection
Respectful and just remuneration
Freedom to practice
Workforce sustainability
Protection in hazardous service
Five ways public policy can influence health
