(6) Integumentary System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Vitiligo
vitiligo melanocytes are attacked by the immune system & are thus unable to produce melanin which gives pigment to your skin. Vitiligo is not contagious nor life-threatening, but it does often affect the patient's self esteem.
Treatment
Grafting
Topical Creams
PUVA Photochemotherapy
Integument
Largest organ of body
16% of body weight
1.5-2m2 in area
2 parts
cutaneous membrane (skin)
accessory structures (hair & skin)
Functions of integumentary system
Maintains body temp
excretes sweat
protects
synthesizes vitamin D
stores lipids
sensory reception
epidermis
Made of avascular (no blood vessels) stratified squamous epithelium, has either 4 or 6 layers. Thickness of a plastic bag or paper towel.
Where are melanocytes and stem cells?
the stratum basale
melaoncytes
responsible for giving the skin pigment or color, and the melanin they make provides some protection from UV rays
stem cells
continuously dividing, & as the cells age they move up to the superficial surface of the skin. By the time they get to the stratum corneum (the most superficial layer) they are completely dead.
keratin
gives skin strength & a degree of waterproofing. It is found in the epidermis, hair and nails.
fingerprint formation
stratum basale of the epidermis meets the dermis there are papillae which are like ridges
dermis
deep to the epidermis. It contains blood vessels, sweat glands, oil glands, nerves, hair follicles, muscle cells, & lymphatic channels that support & nourish the epidermis. Additionally it has collagen and elastin to give skin strength & flexibility.
hypodermis
not technically part of the integument, but is important in stabilizing skin and separating it from the muscle layer. It contains many fat cells which provide insulation, shock absorption, and an energy reserve.
hair
non-living structure mostly made of keratin projecting from most surfaces of the skin. Not the palms, soles of the feet, or lips.
arrector pili muscle
contract and pull on the follicle, causing the hair to stand up.
Sebaceous gland
exocrine glands that secrete an oil called sebum into hair and skin. It prevents drying out and is antibacterial. There is an increase in puberty.
2 sweat glands
apocrine & eccrine
nails
Keratinzed epidermal cells that protect the tips of the fingers and toes
nerves
found in the dermis and there are various types that sense pressure, temperature, pain, light touch and muscle movement.
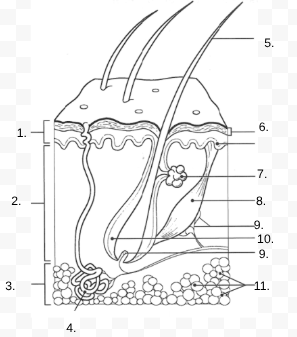
1.
Epidermis
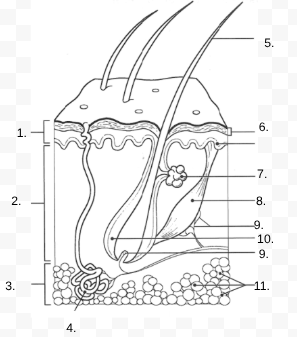
2.
Dermis
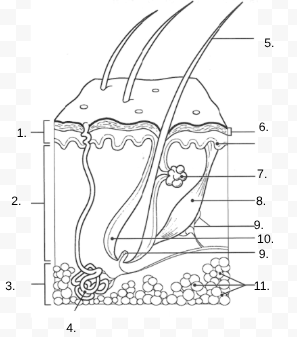
3.
Hypodermis
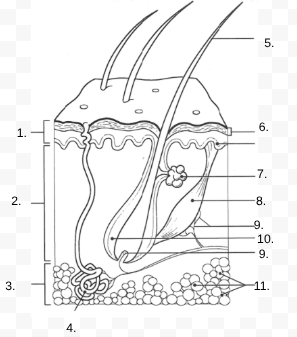
4.
sweat gland
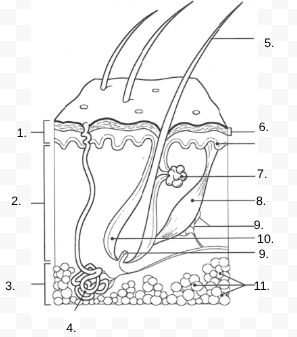
5.
Hair Shaft
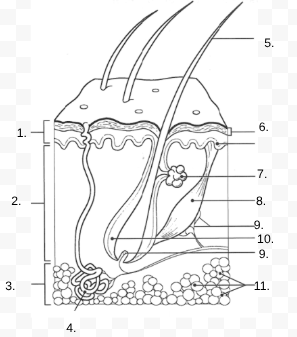
6.
Stratified Squamous Stem Cells
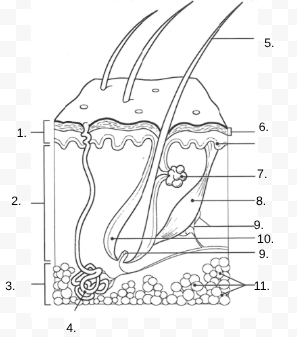
7.
Sebaceous Gland
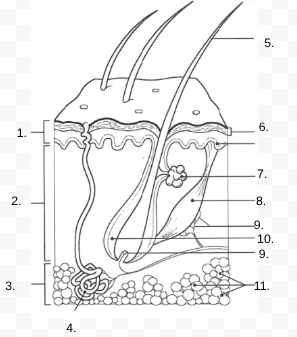
8.
Arrector Pili Muscle
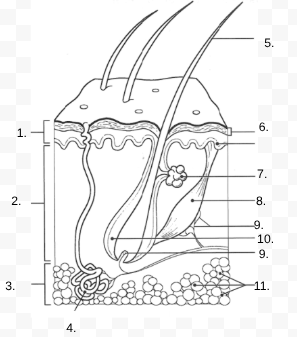
9.
Nerve
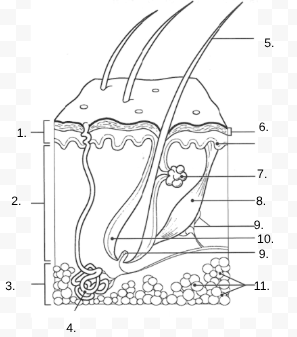
10.
Hair Follicle
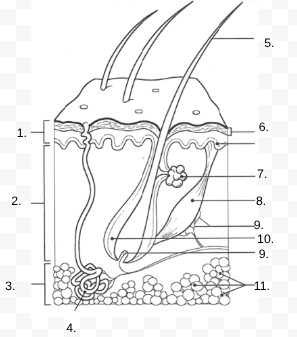
11
Subcutaneous Tissue (Fat Cells)