PHAR2210 exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:10 AM on 6/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
drug absorption
The movement of the drug from its site of administration to the systemic circulation.
2
New cards
paracellular and transcellular
what are the two ways for drugs to cross the lipid membrane from one compartment to another
3
New cards
it has a high affinity for calcium, and so accumulates in bones and teeth. can affect bone growth or lead to birth defects.
why are tetracyclines not used in pregnant people or young children?
4
New cards
describe the feature of thiopental which makes it appropriate for inducing anaesthesia, but not maintaining anaesthesia.
it is very lipophilic. due to blood flow, after administration it is first distributed into well perfused areas (liver and brain) and then slowly distributed into fat and muscle. if the drug is continuously infused, the drug will slowly accumulate in body fat but due to distribution being reversible, after it has stopped being administered, it will slowly return to systemic circulation. this could lead to hangover effects if it was used to maintain anaesthesia.
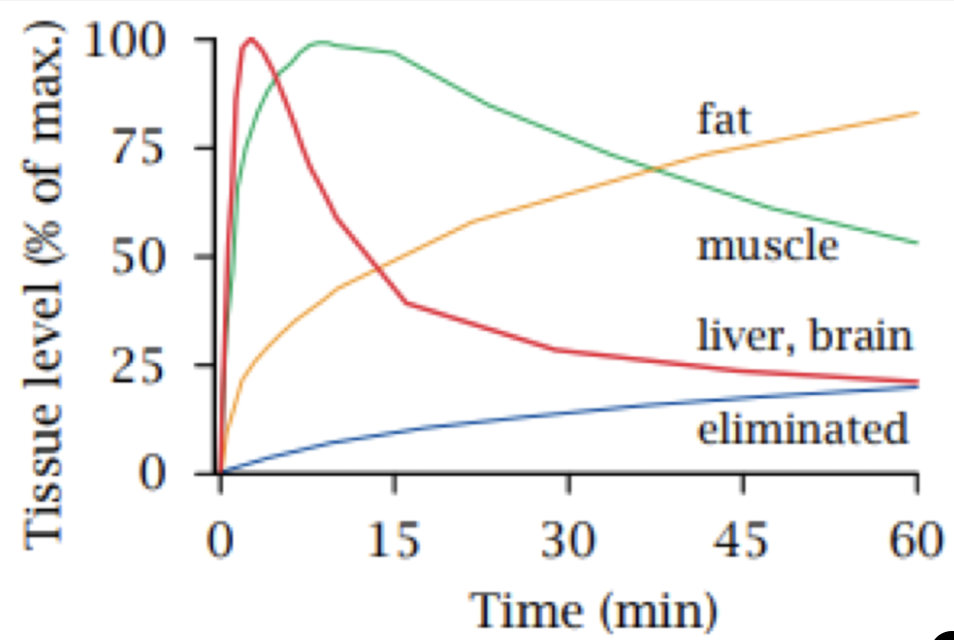
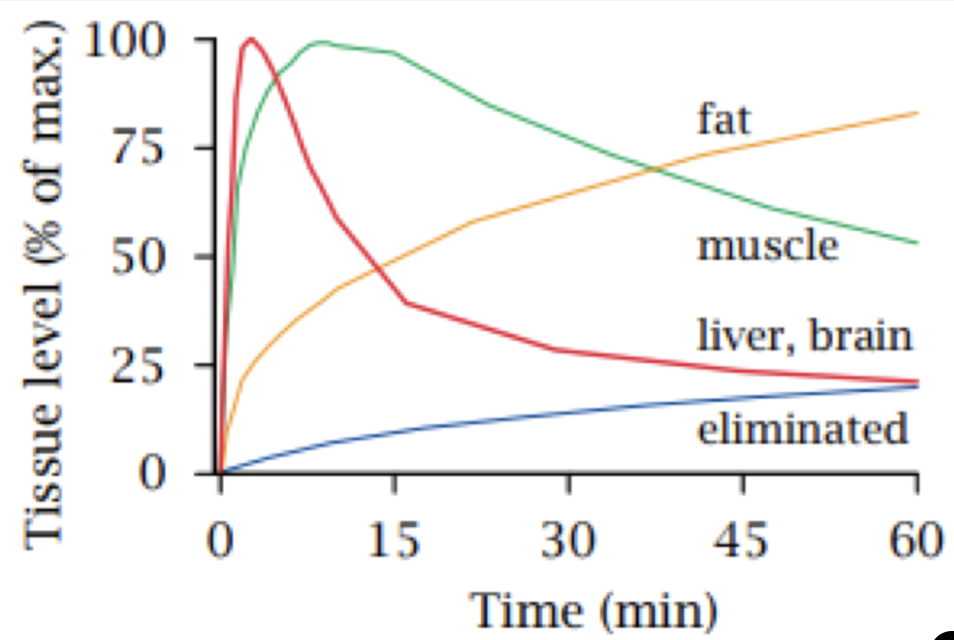
5
New cards
distribution
what pharmacokinetic process is responsible for the trends in this graph?
6
New cards
drug distribution
what does the pH of a body compartment influence
7
New cards
solute carrier transporters (SLC)
______ transport drugs via facilitated diffusion and active transport
8
New cards
facilitated, active
SLC’s transport drugs via ____ diffusion and _____ transport
9
New cards
ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC)
______ transport drugs via active transport
10
New cards
MDR1, BCRP and MRP2
what are the three important efflux transporters that Caco-2 cells express?
11
New cards
apical, basolateral
top membrane is the _____ membrane and the bottom membrane is the _____ membrane
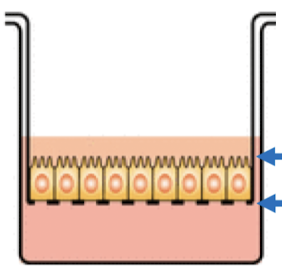
12
New cards
the apical membrane
in Caco-2 cells, the efflux transporters are located on which membrane?
13
New cards
how can you calculate drug efflux using caco-2 cells
By measuring the ratio of drug transported from the apical to basolateral side (B-A) to the drug transported from the basolateral to apical side (A-B). This is known as the efflux ratio (ER). The efflux ratio can be calculated using the following formula: ER = (B-A)/ (A-B).
14
New cards
by comparing the drug uptake and efflux in the knockout cells with the wild-type cells. If the drug uptake or efflux is significantly altered in the knockout cells, it suggests that the knocked-out transporter is involved in the drug transport.
How can you use transporter knockout Caco-2 cell lines to determine which drug transporter is involved with a drug?
15
New cards
which drug transporter is involved in the efflux of a particular drug
what can knocking out one or two of drug transporters in Caco-2 cell lines help to determine?
16
New cards
* as the ER for the WT cells is greater than 2, we can determine that these drugs undergo transporter-mediated efflux
* these two drugs are purely mediated by MDR1, and not BCRP or MRP2
* these two drugs are purely mediated by MDR1, and not BCRP or MRP2
what does this graph tell you about the efflux of the two drugs?
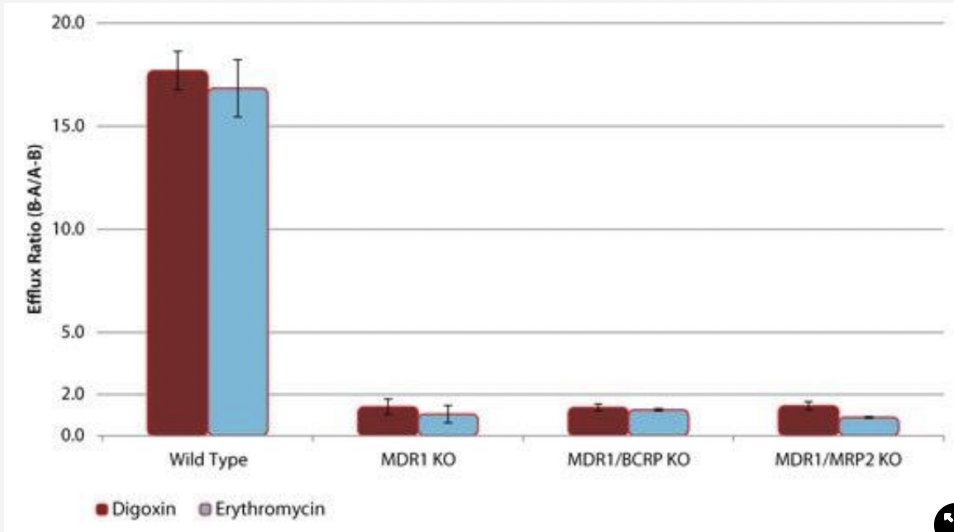
17
New cards
to determine what transporter is responsible for efflux of a drug
what is the purpose of transfecting cells with a transporter of interest
18
New cards
pH of compartment, blood flow, tissue binding, plasma protein binding, permeability of blood-tissue barrier, expression of transporters
list 4 of the 7 factors that influence drug distribution
19
New cards
basic
does alpha1 acid glycoprotein bind acidic or basic drugs?
20
New cards
acidic
does human serum albumin (HSA) bind acidic or basic drugs?
21
New cards
two
how many drug binding sites does each albumin contain?
22
New cards
fenestrations
what feature of the blood-tissue barrier allows exchange of molecules between the intravascular space and the interstitial fluid
23
New cards
endothelial cell layer and a basal membrane
list two features that the blood-tissue barrier and the blood-brain barrier share
24
New cards
glial cells that are connected by tight junctions
what is the extra protective feature that the blood-brain barrier has
25
New cards
to give more protection from harmful drugs
what is the function of glial cells in the blood-brain barrier
26
New cards
the liver
what is the first point of contact for orally administered drugs
27
New cards
more susceptible to toxicity
what is the side effect of being the first point of contact for orally administered drugs
28
New cards
single nucleotide polymorphism
what is one reason why there is variation in the response to drugs
29
New cards
brain tumour cells over express the same efflux transporters as the blood-brain barrier, so drugs can be returned to systemic circulation without reaching the brain.
why is it difficult for drugs to reach brain tumour cells
30
New cards
MDR1 and BCRP
give the two efflux transporters present at the blood-brain barrier.
31
New cards
\~60%
what percentage of body weight is the total body water.
32
New cards
high
when \[plasma\] is , volume of distribution is low.
33
New cards
oxidation, hydrolysis and dealkylation
what three processes are involved in phase 1 metabolism
34
New cards
phase 1 metabolism
what phase of metabolism: parent drug → metabolite(s)
35
New cards
oxygen atom added to parent drug OR hydrogen removed from a parent drug
describe oxidation in phase 1 metabolism
36
New cards
ethanol
what drug can be oxidised by having the hydrogen removed
37
New cards
codeine to morphine by CPYD2D6
give an example of a drug undergoing demethylation
38
New cards
hydrophilicity
does conjugation increase lipophilicity or hydrophilicity
39
New cards
glucuronidation
by what process is morphine metabolised into two conjugated metabolites, M3G and M6G
40
New cards
SULT transfers sulfonate group from PAPS to a drug or drug metabolite
give an overview of sulfation
41
New cards
morphine to morphine-3-glucuronide
give an example of pharmacologically active parent drug being converted into a pharmacologically inactive metabolite
42
New cards
morphine to morphine-6-glucuronide
give an example of pharmacologically active parent drug being converted into a pharmacologically active metabolite
43
New cards
paracetamol to NAPQI
give an example of pharmacologically active parent drug being converted into a toxic and reactive metabolite
44
New cards
codeine to morphine
give an example of prodrug being converted into a pharmacologically inactive metabolite
45
New cards
increases
drug metabolism _______ the molecular size of a drug
46
New cards
hydrophilic
______ drugs are excreted largely unmetabolised
47
New cards
decreased
how is the half life of a drug affected by drug metabolism
48
New cards
one atom goes to parent drug and the other goes to water molecule
what happens to each atom when O2 is used to metabolise CYPs
49
New cards
NADPH
what is the cofactor of CYPs
50
New cards
CYP2E1
which CYP is responsible for metabolism of paracetamol → NAPQI
51
New cards
UGT transfers glucuronic acid from UDP-glucuronic acid to the metabolite
describe the process of glucuronidation
52
New cards
extensive, metabolites
hepatic clearance drugs undergo ___ metabolism in the liver, and are excreted primarily as drug _______
53
New cards
low
do hepatically cleared drugs have high or low fe
54
New cards
parent, urine
renal clearance drugs are mainly excreted as __ drug in ___
55
New cards
high
do renally cleared drugs have a high or low fe
56
New cards
low
low fu results in ___ renal clearance