Anatomy of the Brain
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
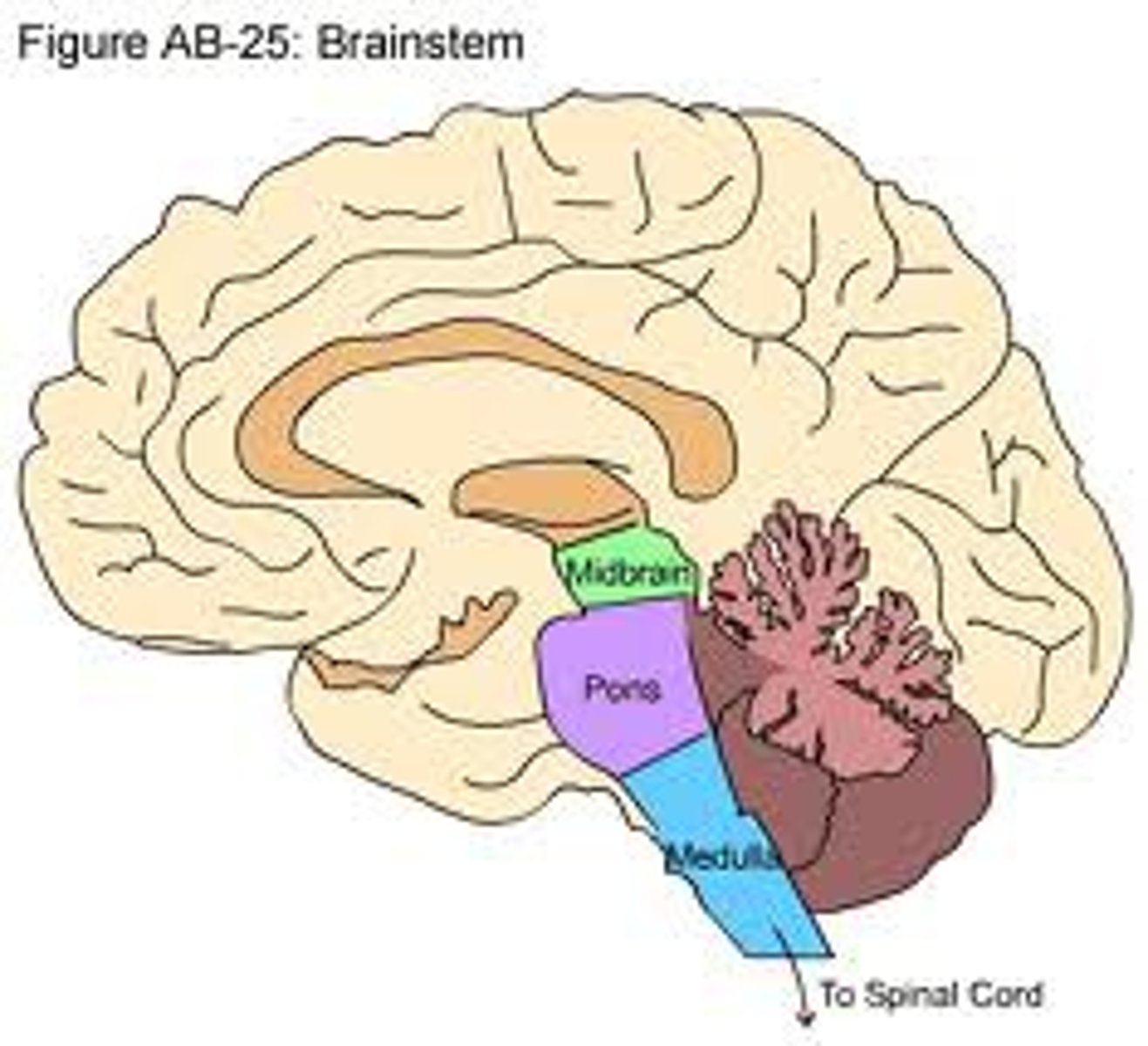
Brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Meninges
Three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater
dura mater
Thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
Middle layer of the meninges named for the spider-web-like trabeculae that extend between it and the pia mater
pia mater
Thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges.
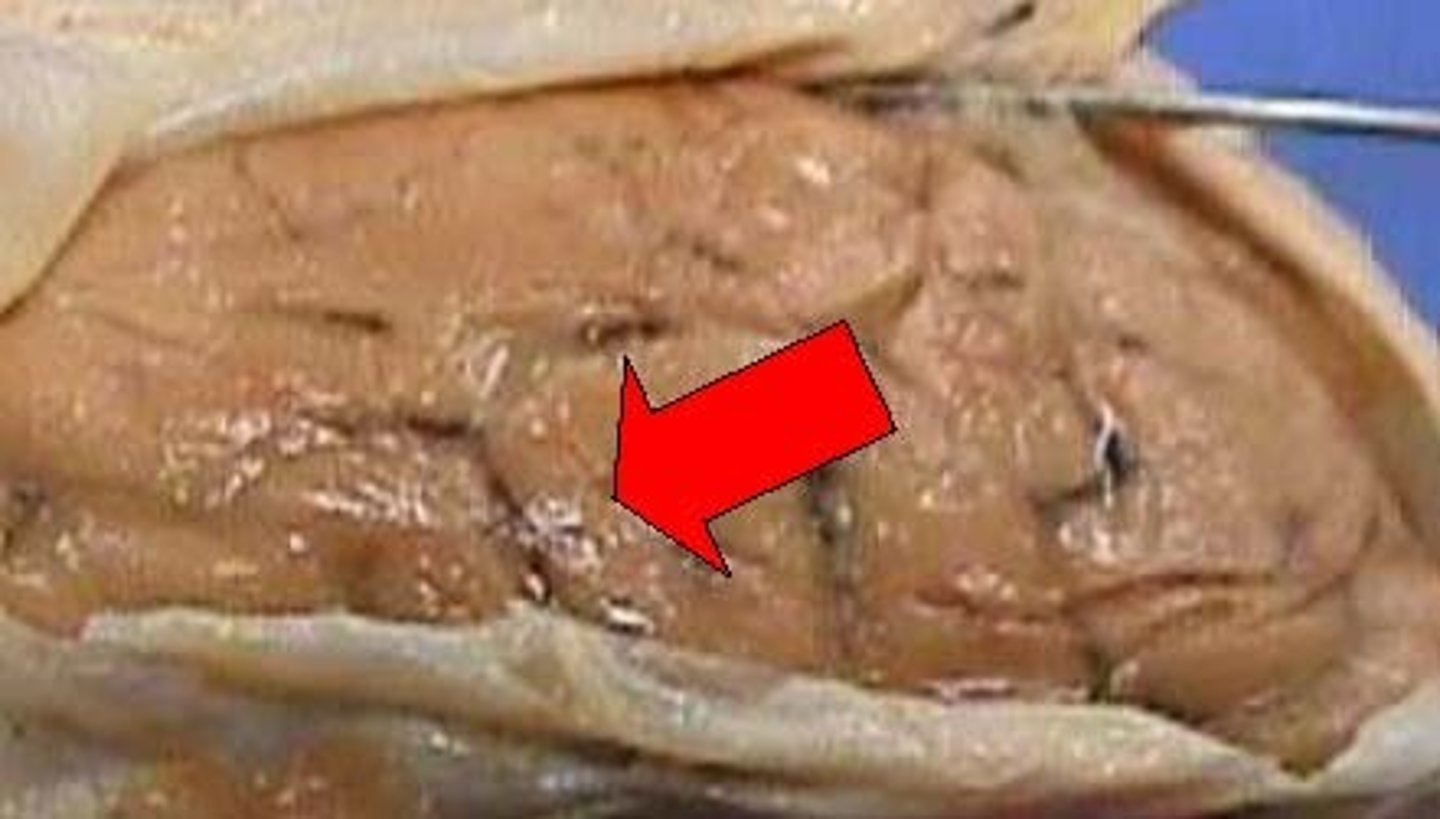
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
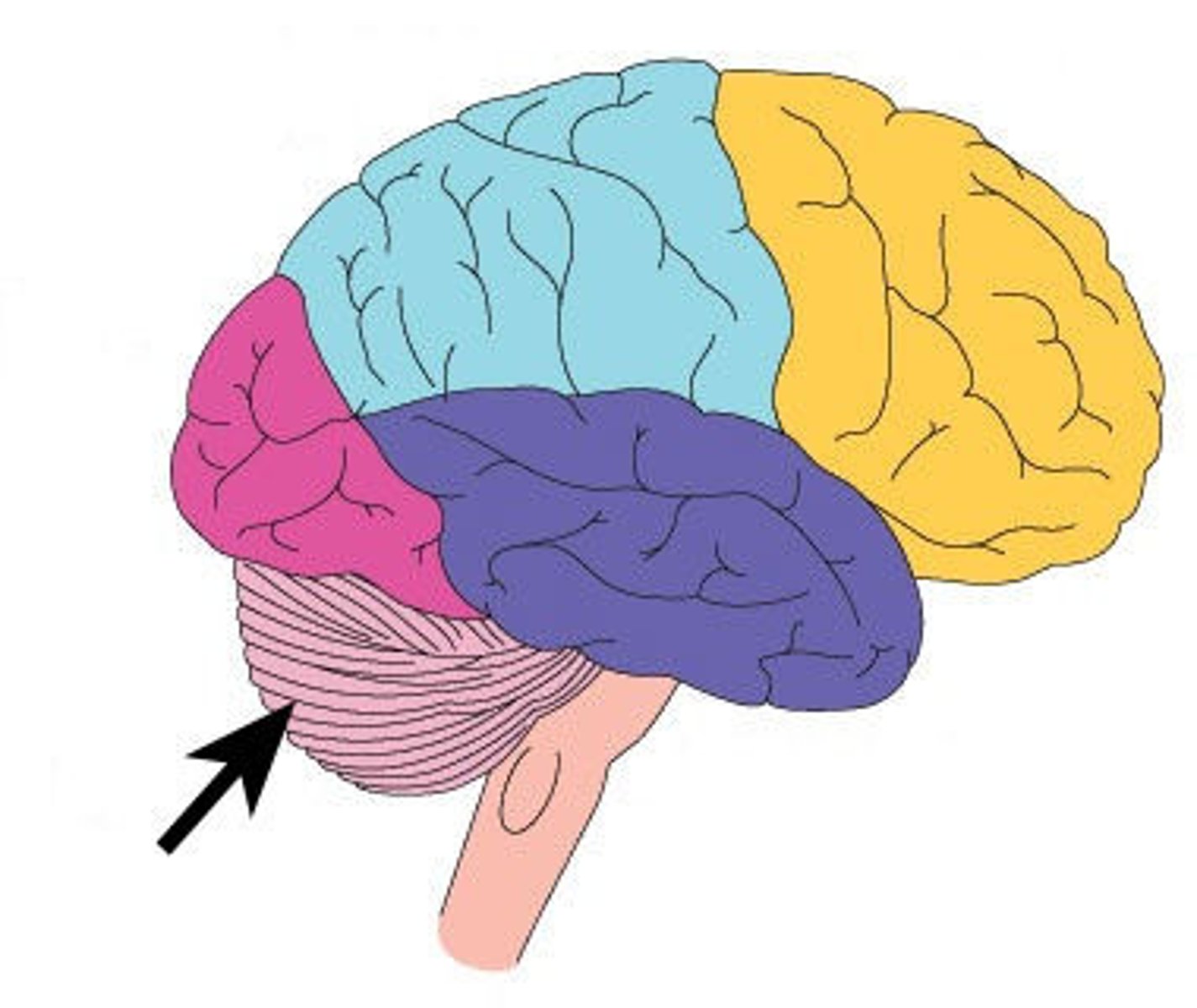
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills such as balance and coordination
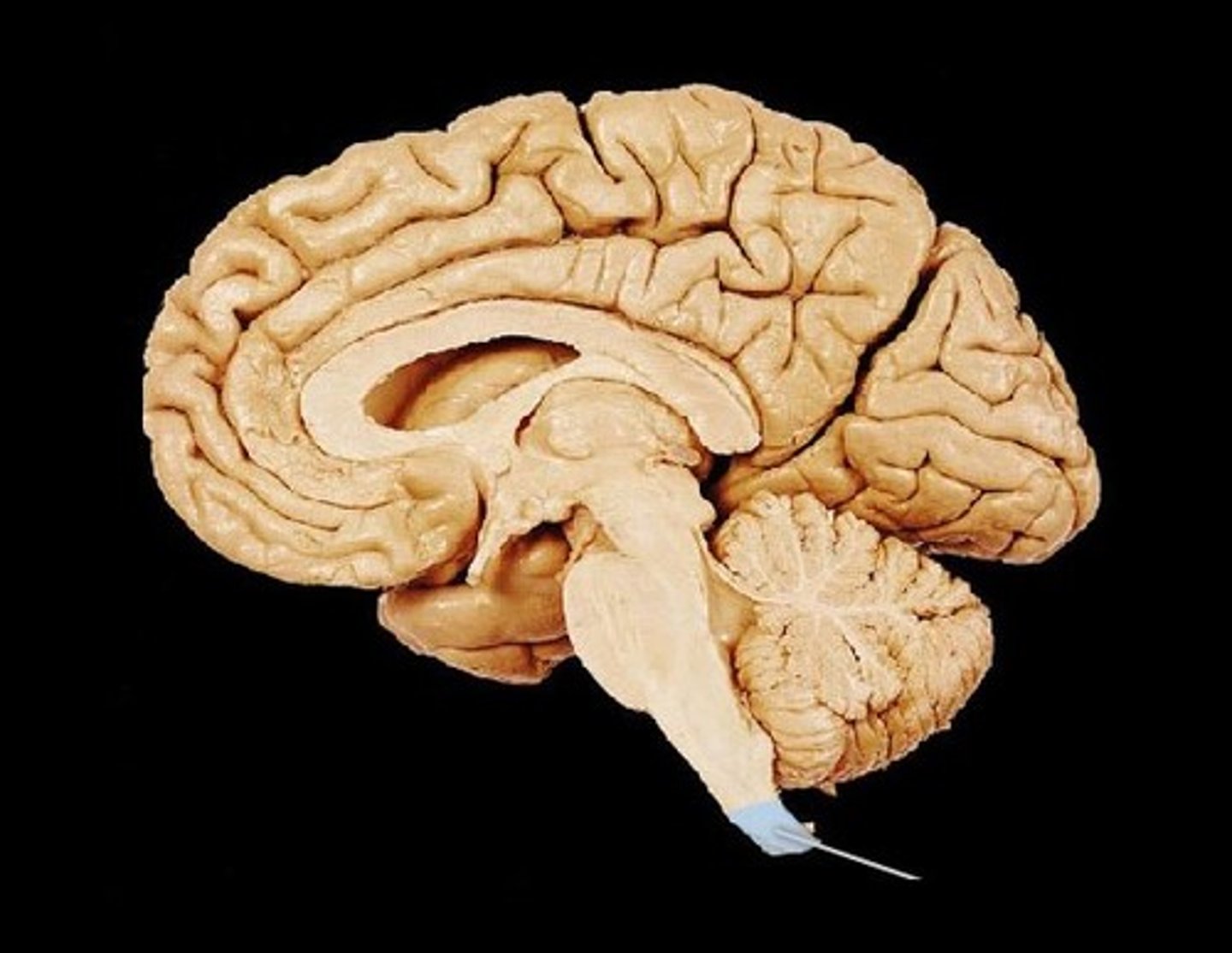
spinal cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
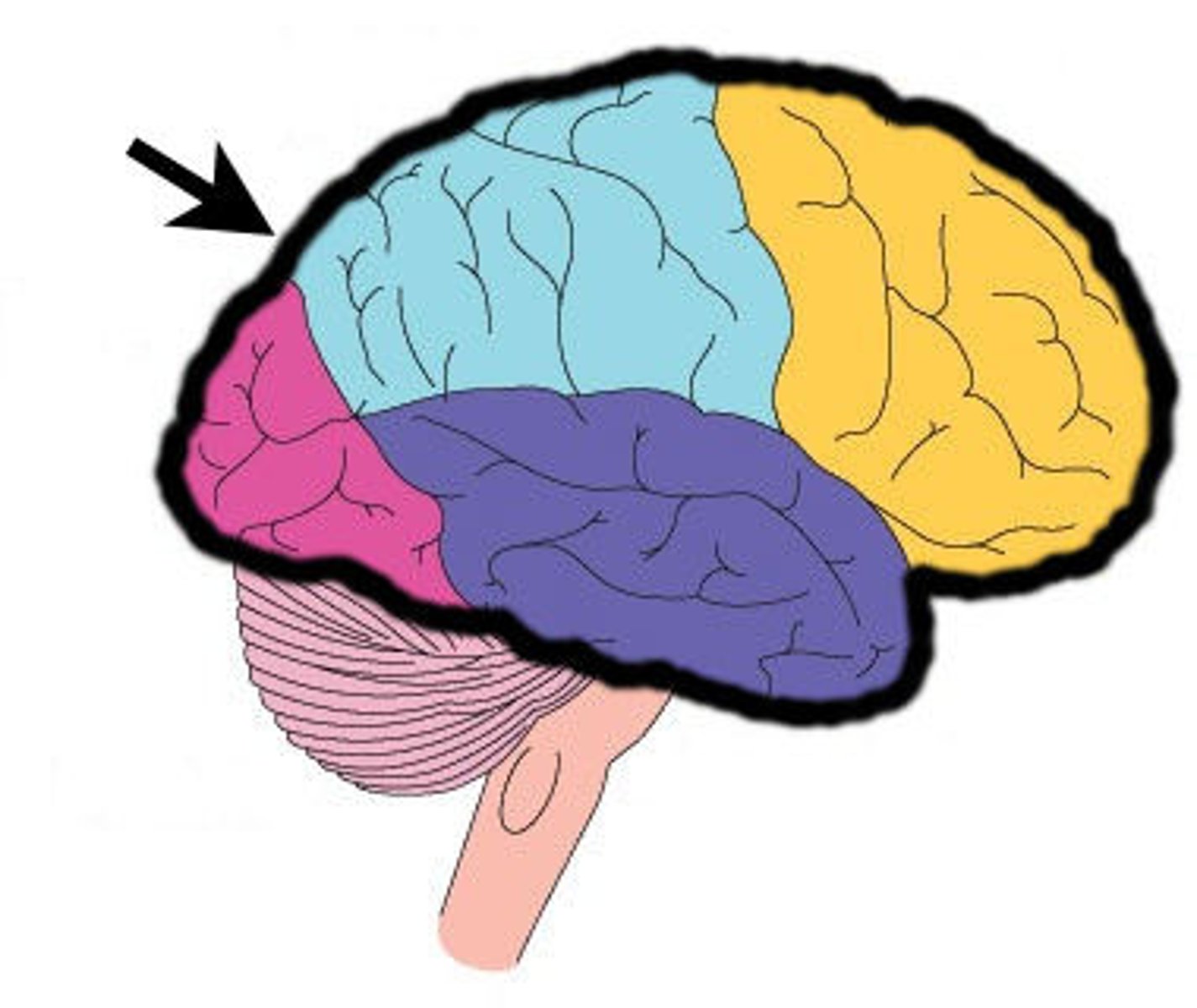
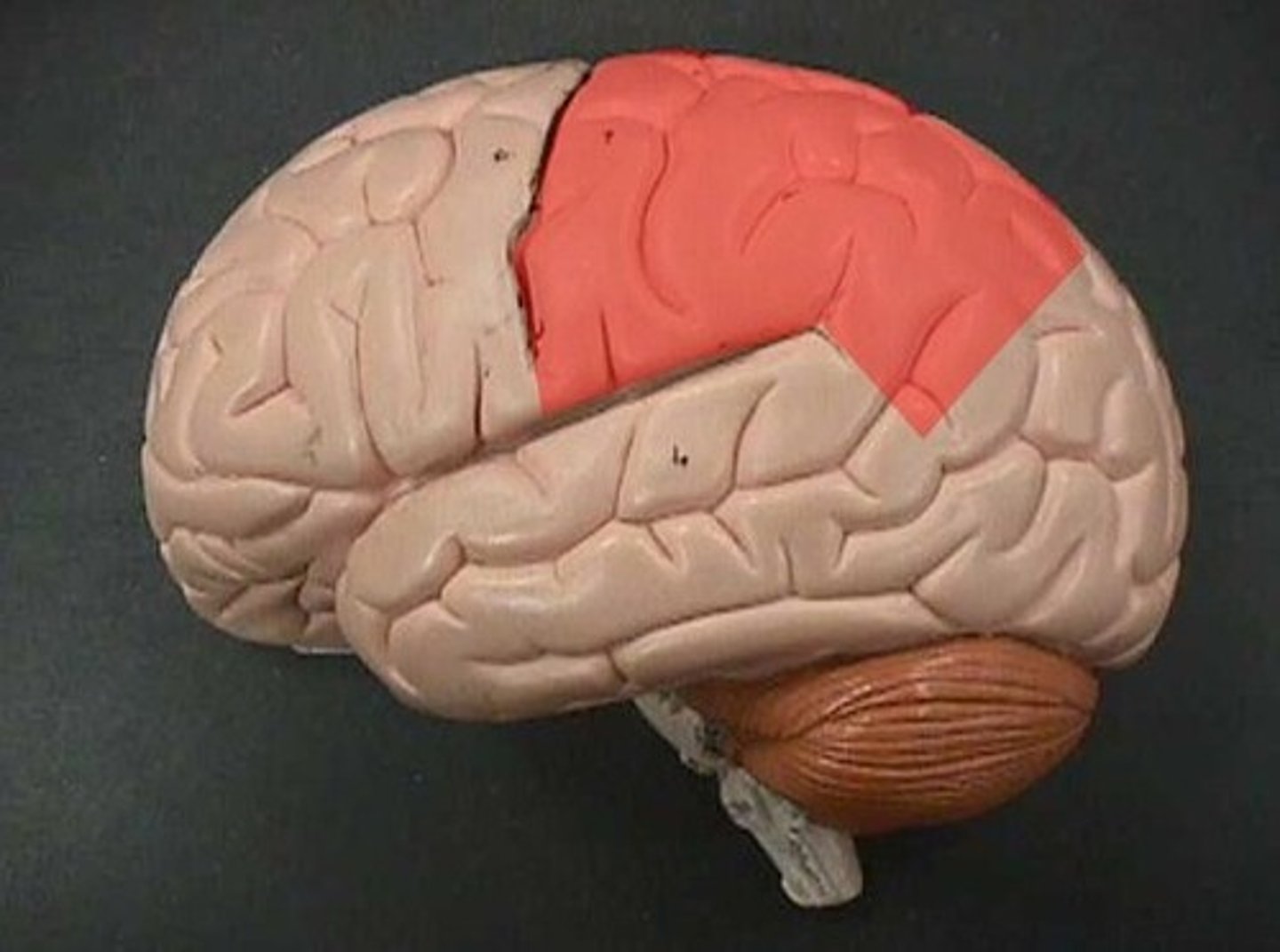
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
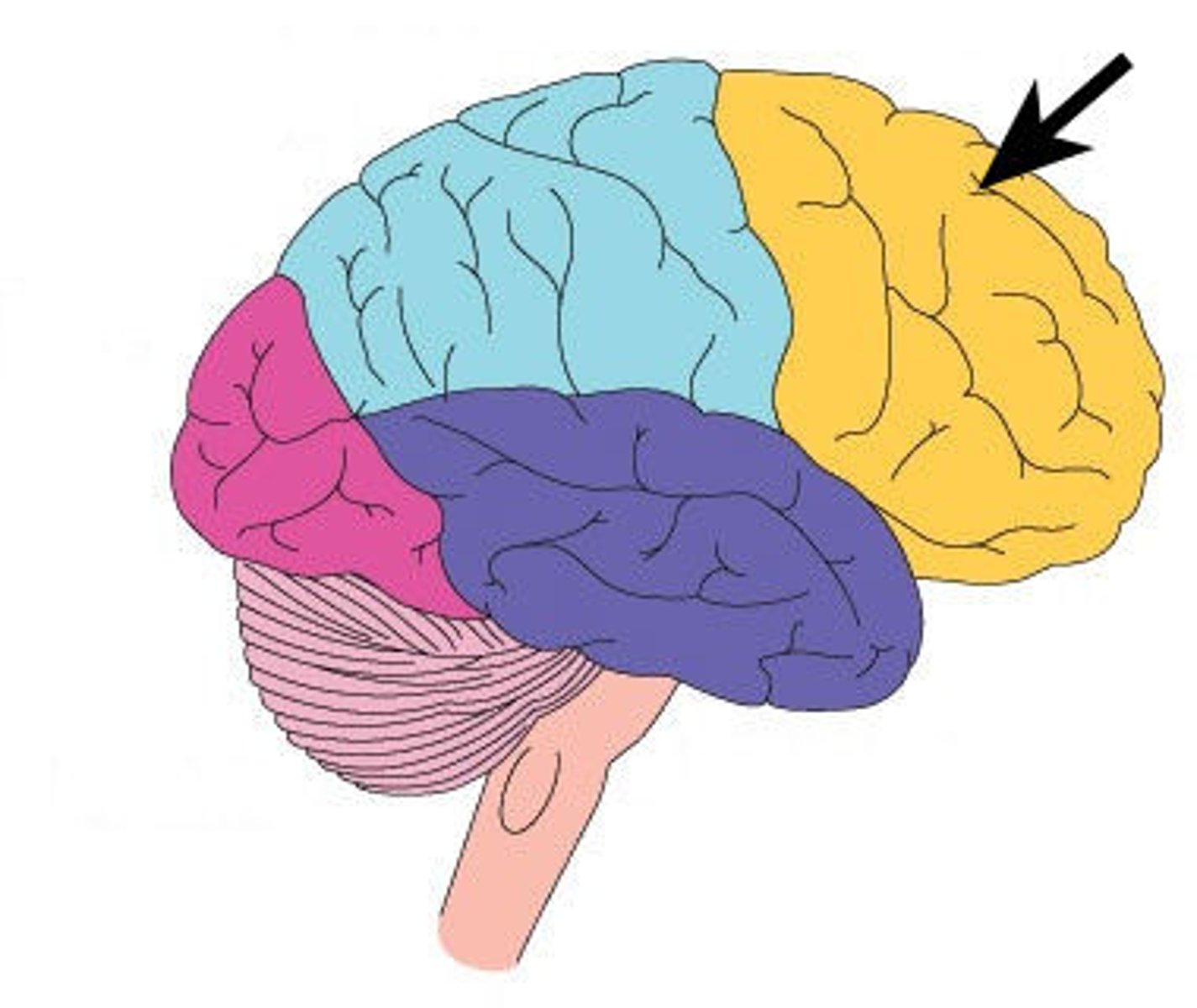
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
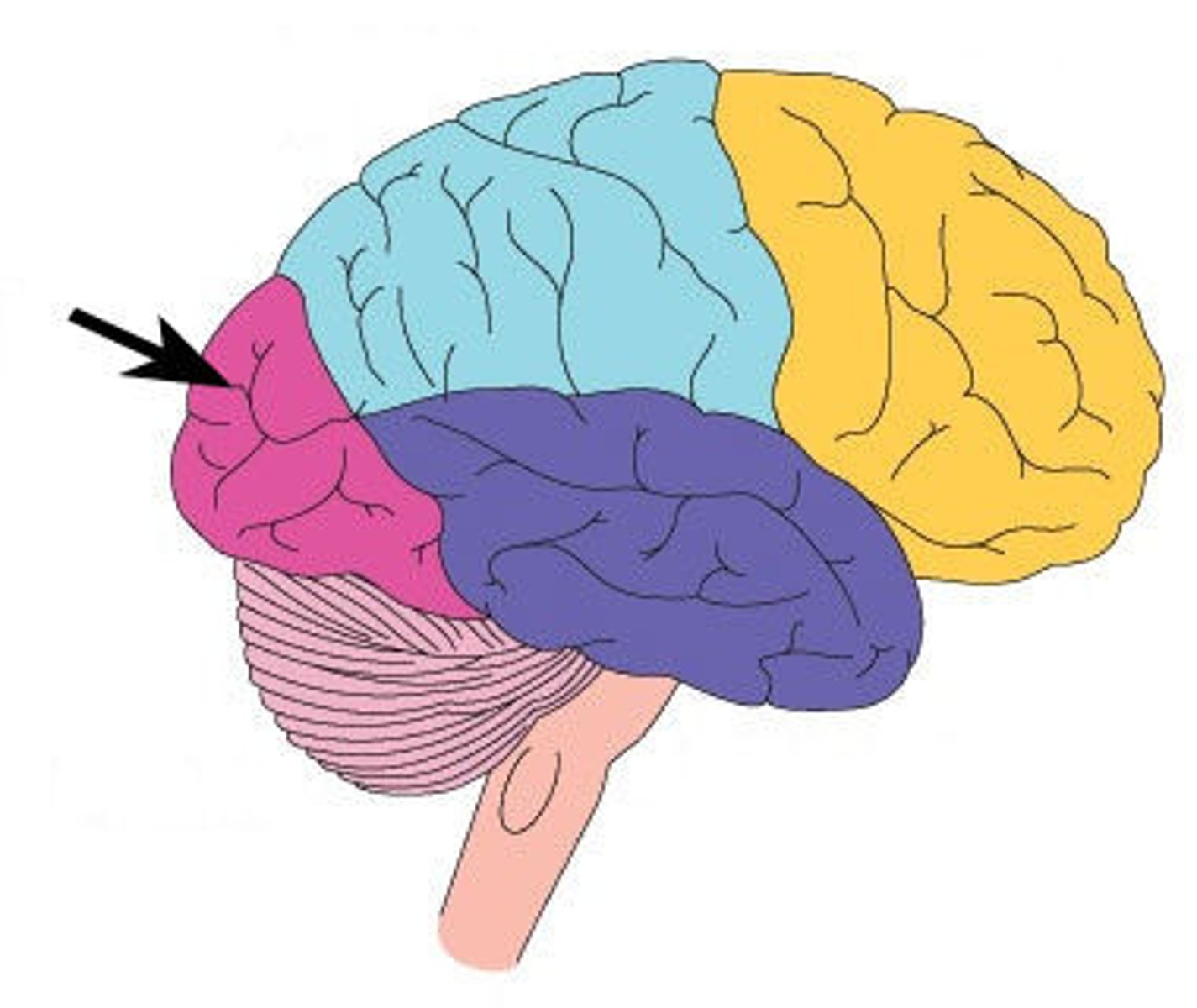
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.

occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; analytical, language, math
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creative, intuitive, spacial
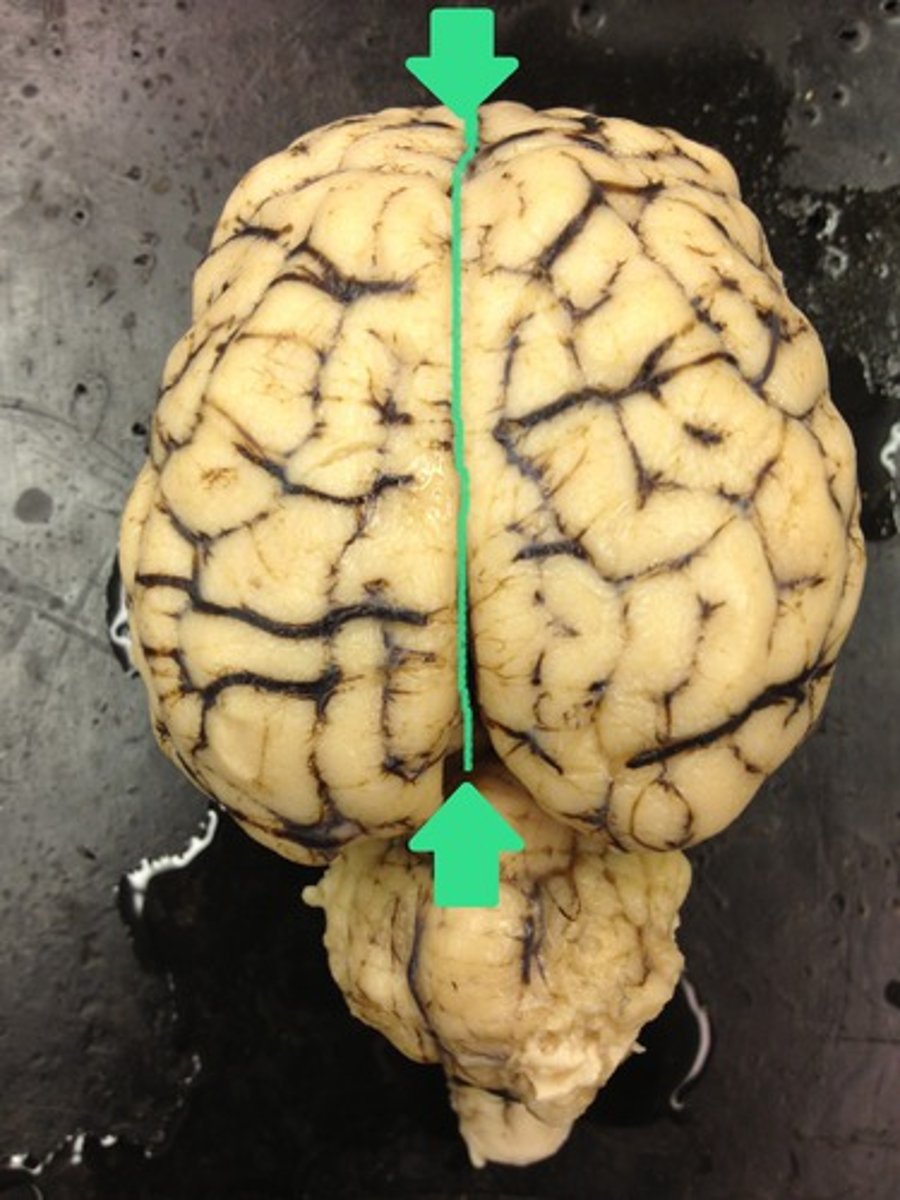
longitudinal fissure
separates left and right hemispheres
medulla oblongata
The posterior part of the brain that controls the rate of breathing, heartbeat, digestion, sneezing, vomiting, and swallowing. (Regulates respiration/circulation)
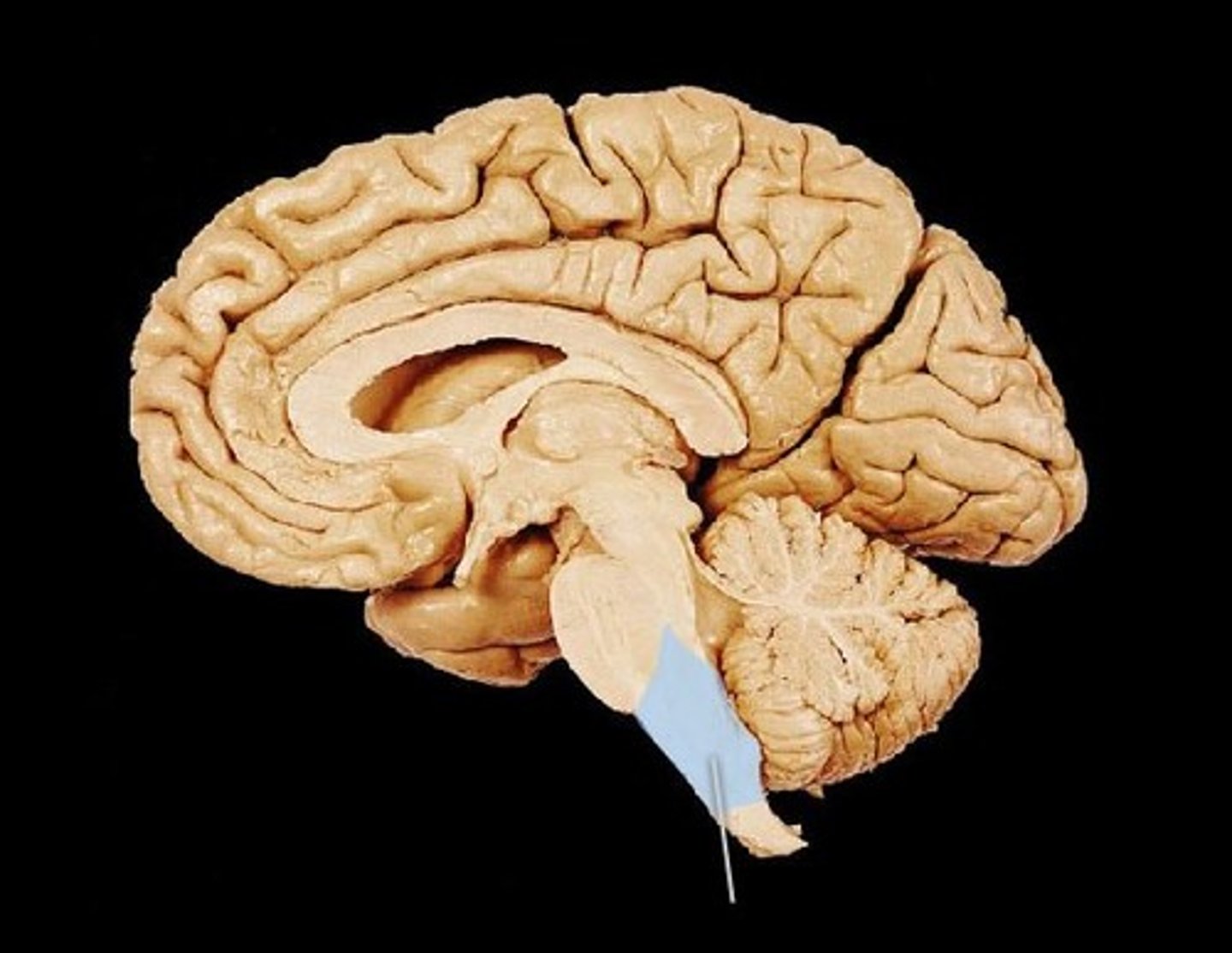
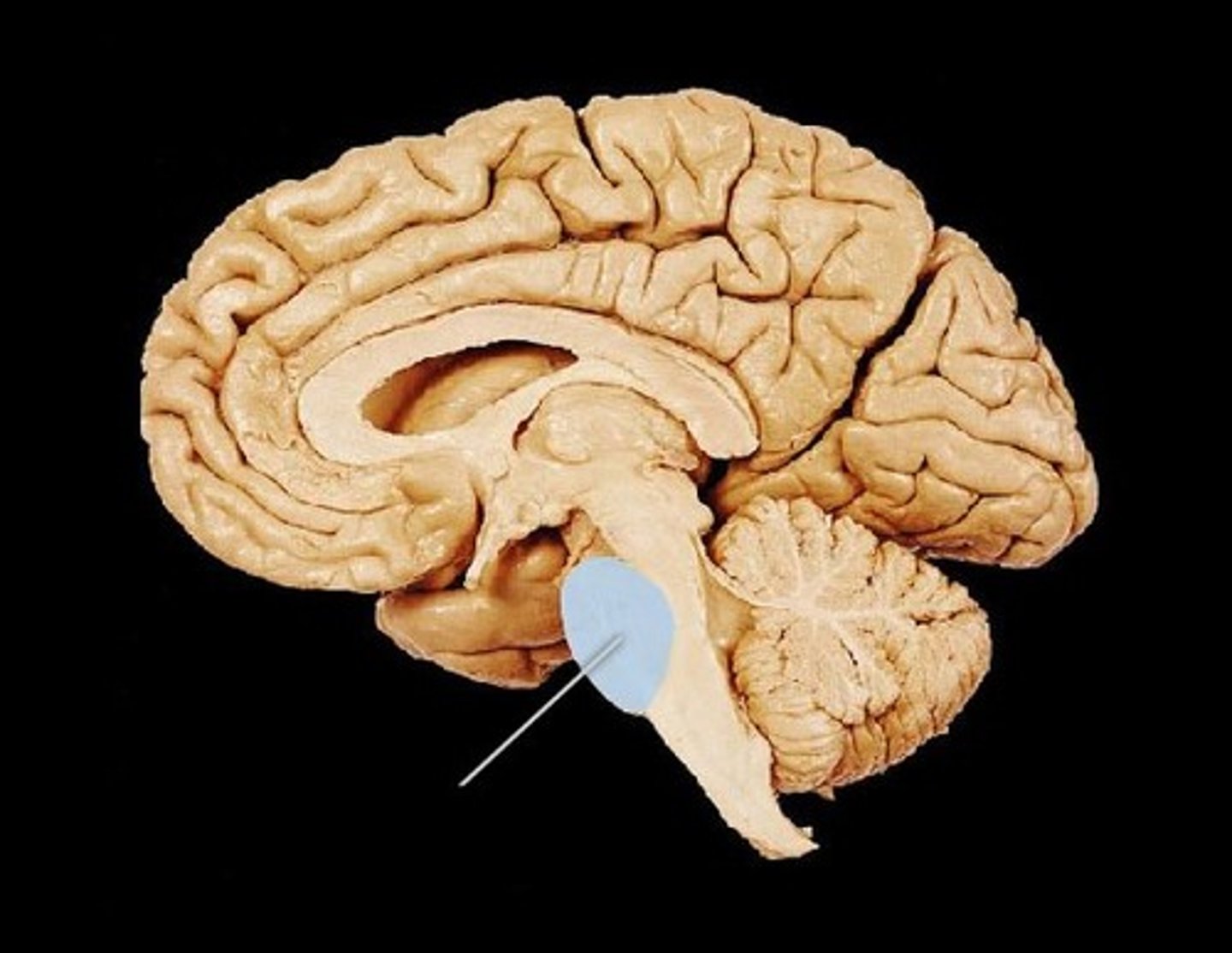
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain "bridge". Responsible for autonomic and sensory functions including arousal, respiratory processes, fine motor control, equilibrium, muscle tone, and the circadian cycle (sleep cycle)
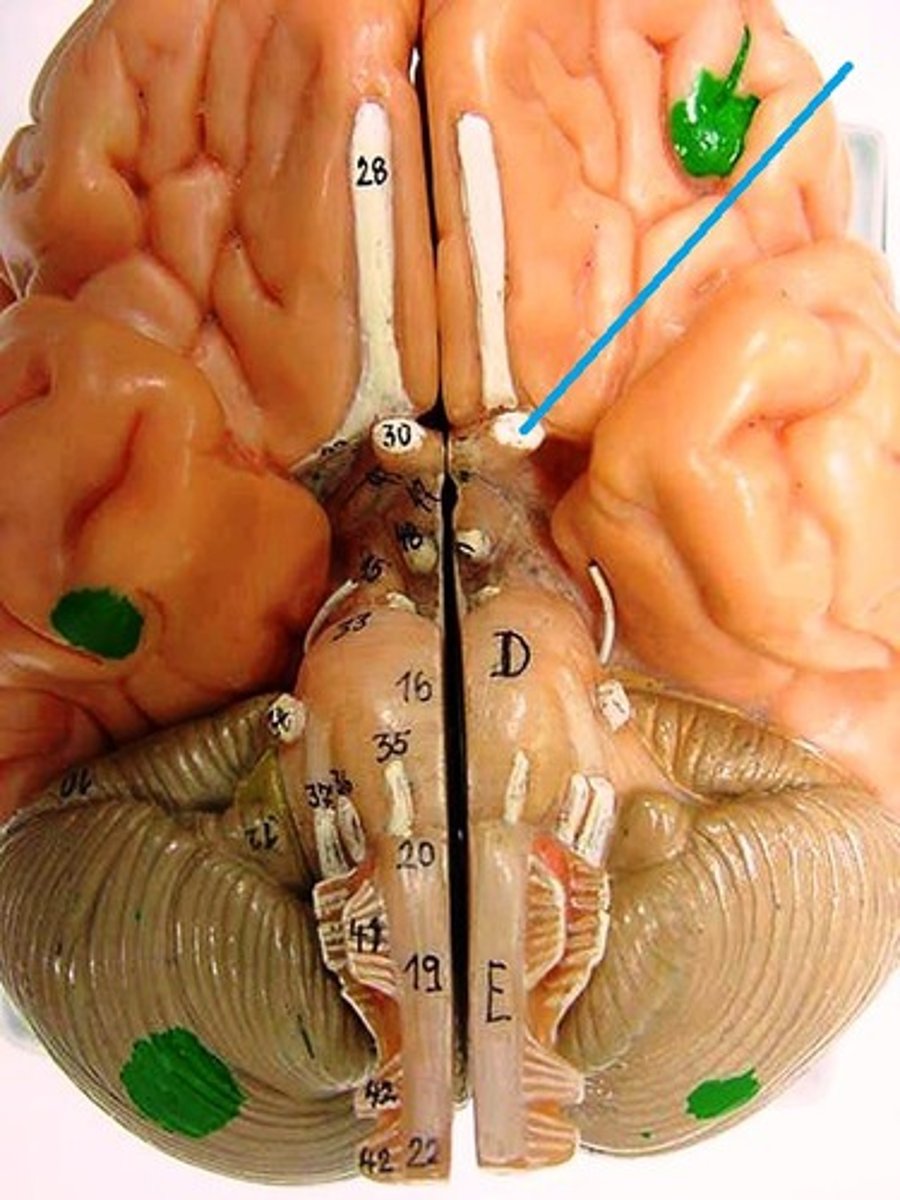
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
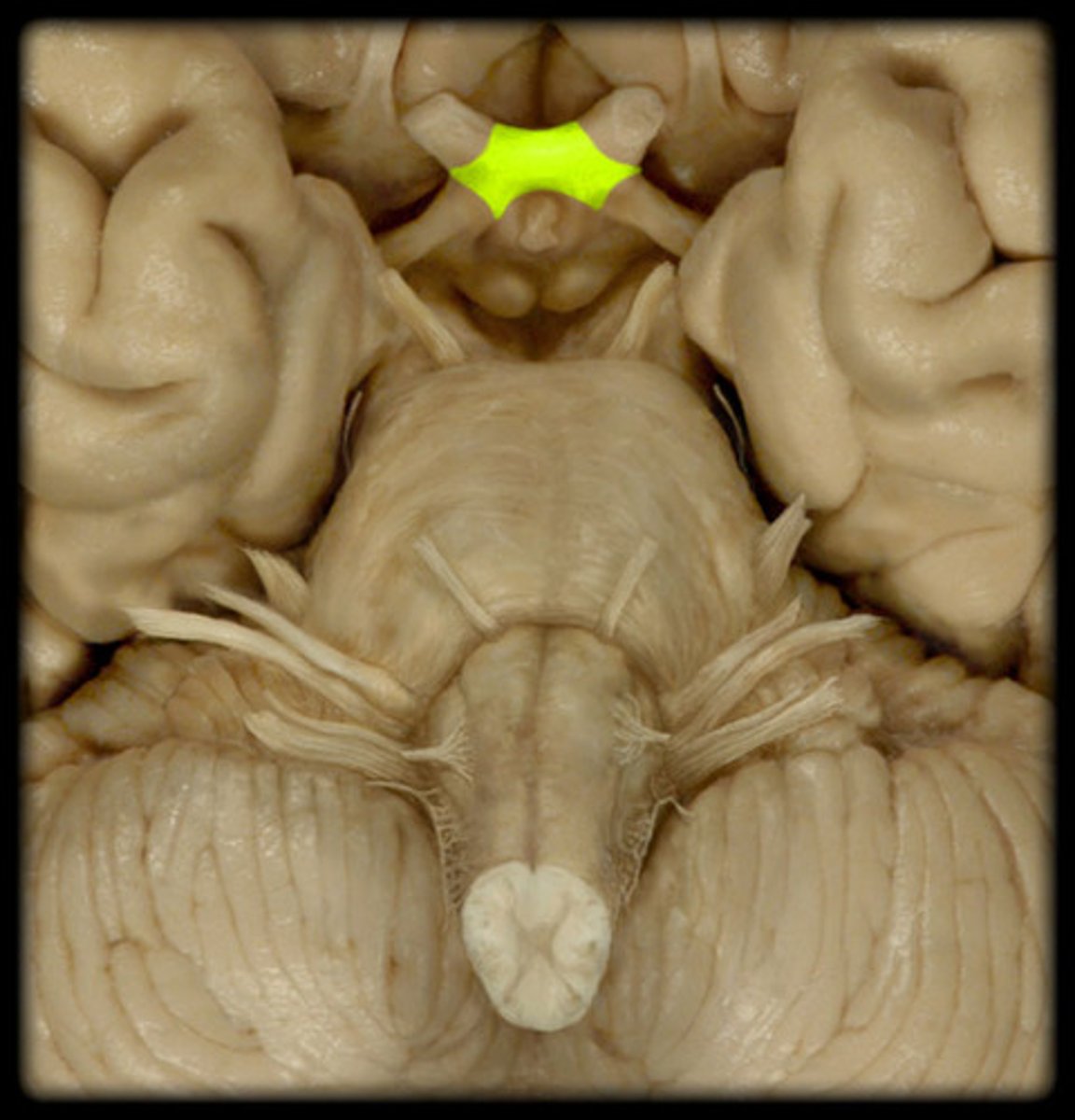
optic chiasm
the point in the brain where the visual field information from each eye "crosses over" to the appropriate side of the brain for processing
optic tract
Information from the optic nerve travels to occipital lobes (primary visual area)
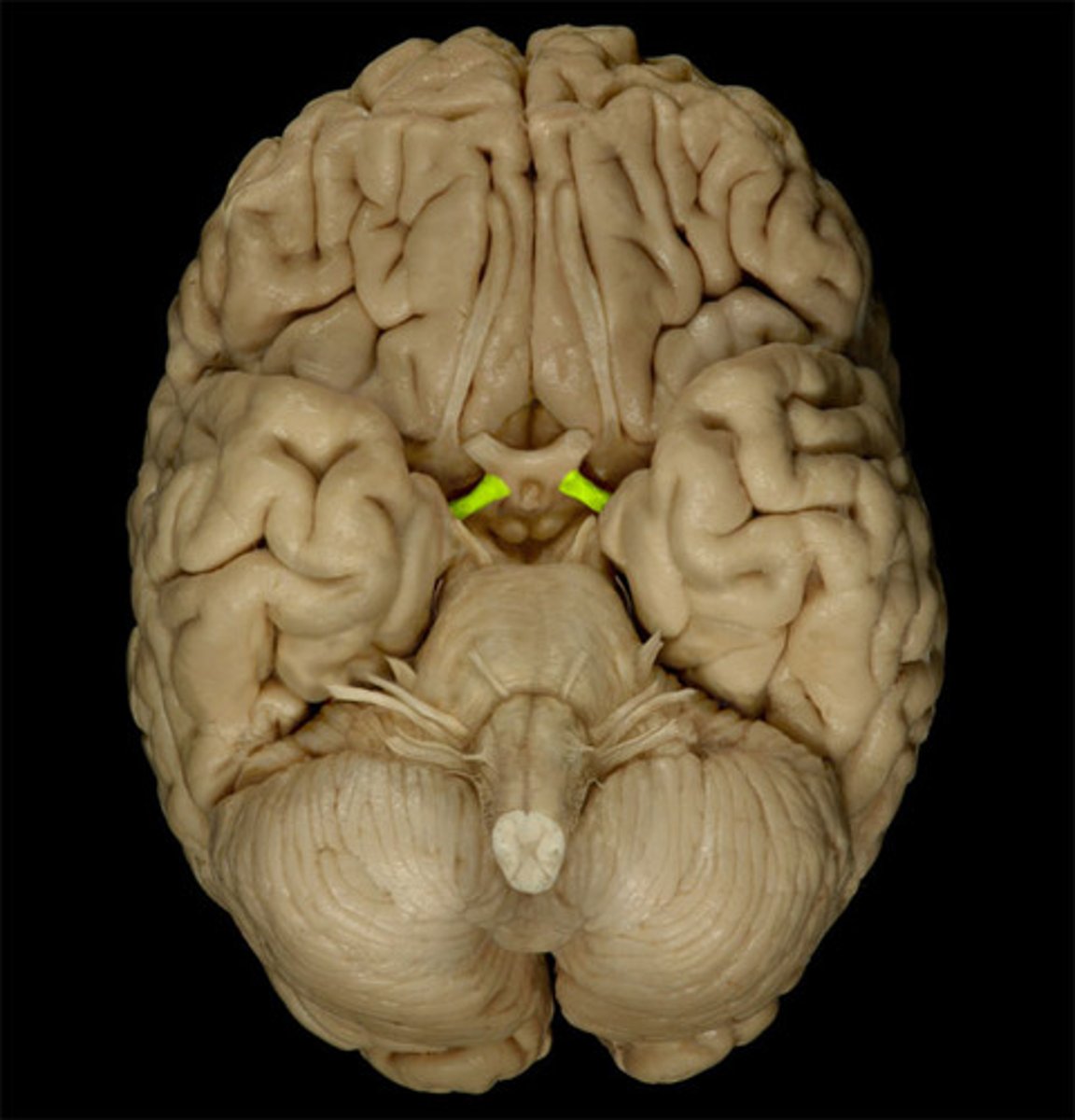
olfactory bulb
A brain structure located above the nasal cavity beneath the frontal lobes. Carries smell information to the olfactory nerve.
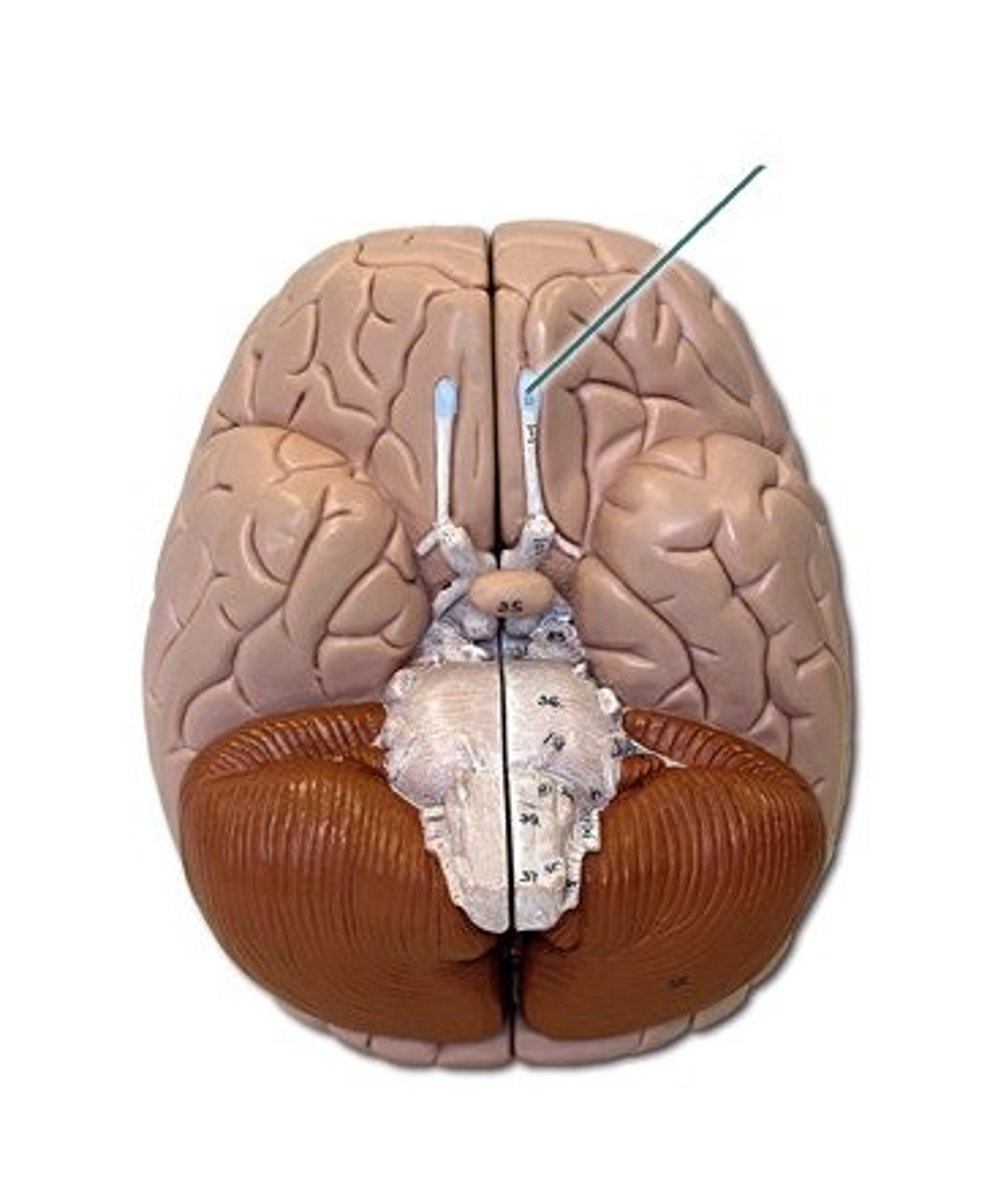
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
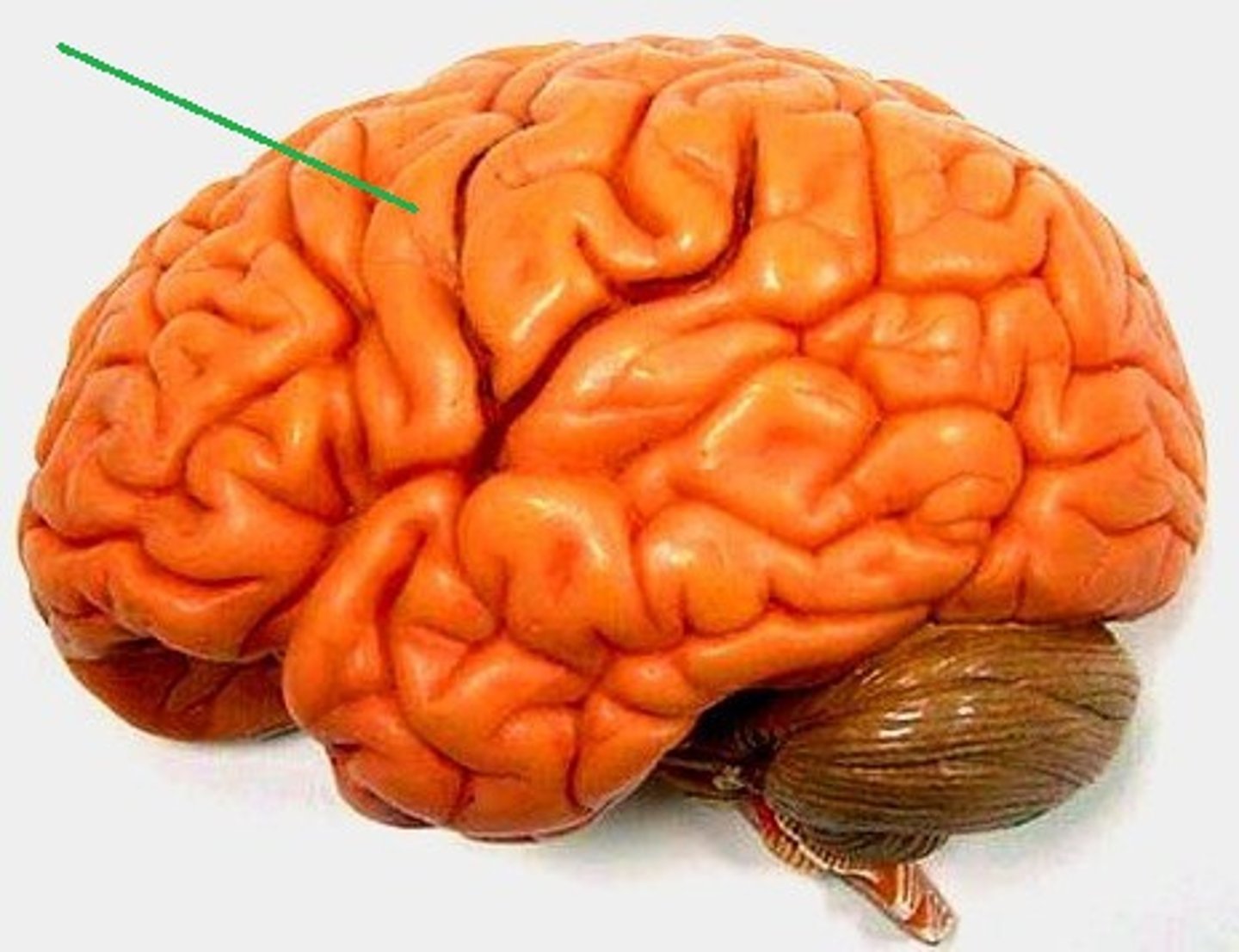
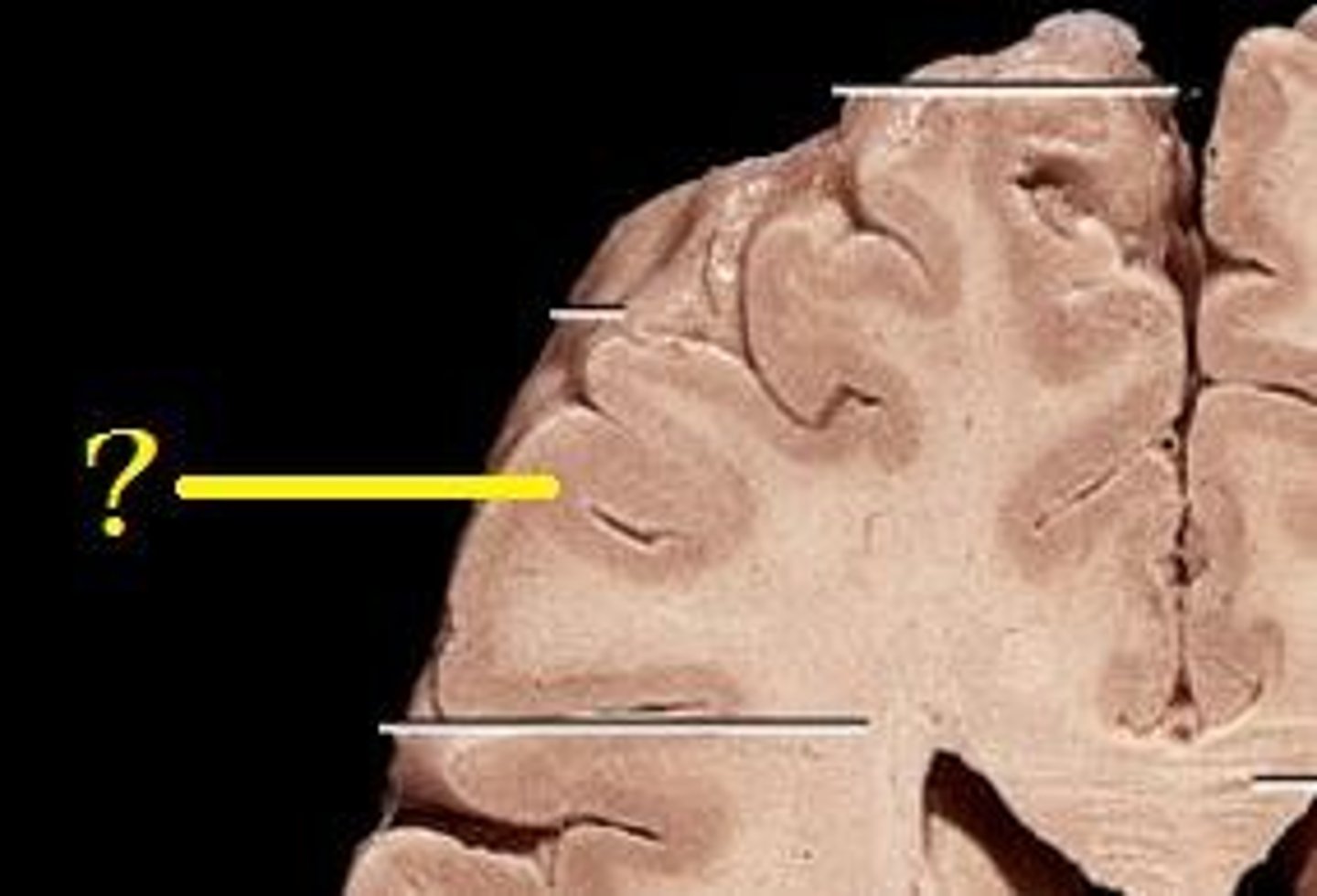
Sulci (sulcus)
shallow grooves

Gyri (gyrus)
ridges
septum pellucidum
thin membrane that separates lateral ventricles
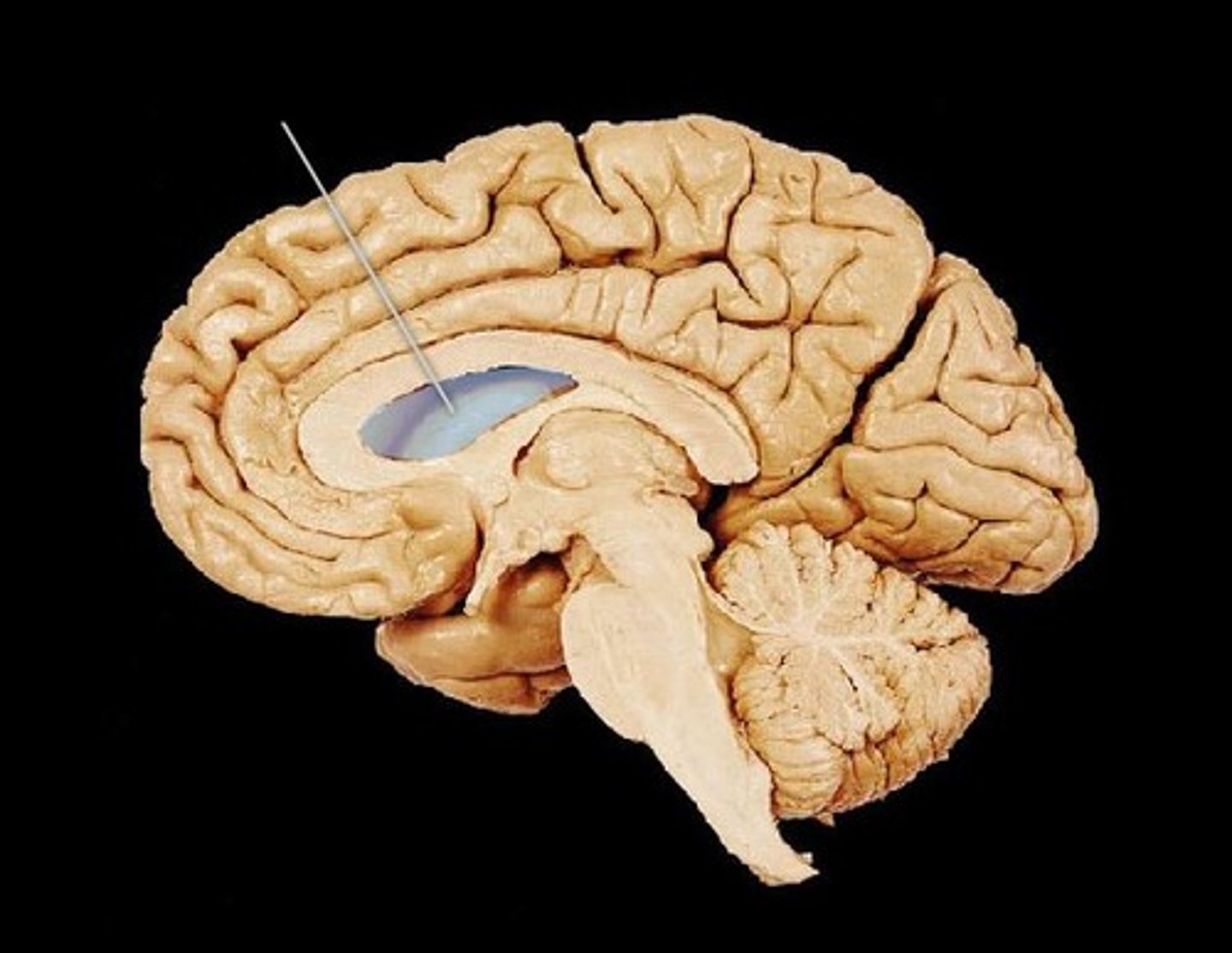
3rd ventricle
Found in the diencephalon and communicates with lateral ventricles via intraventricular foramen to produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
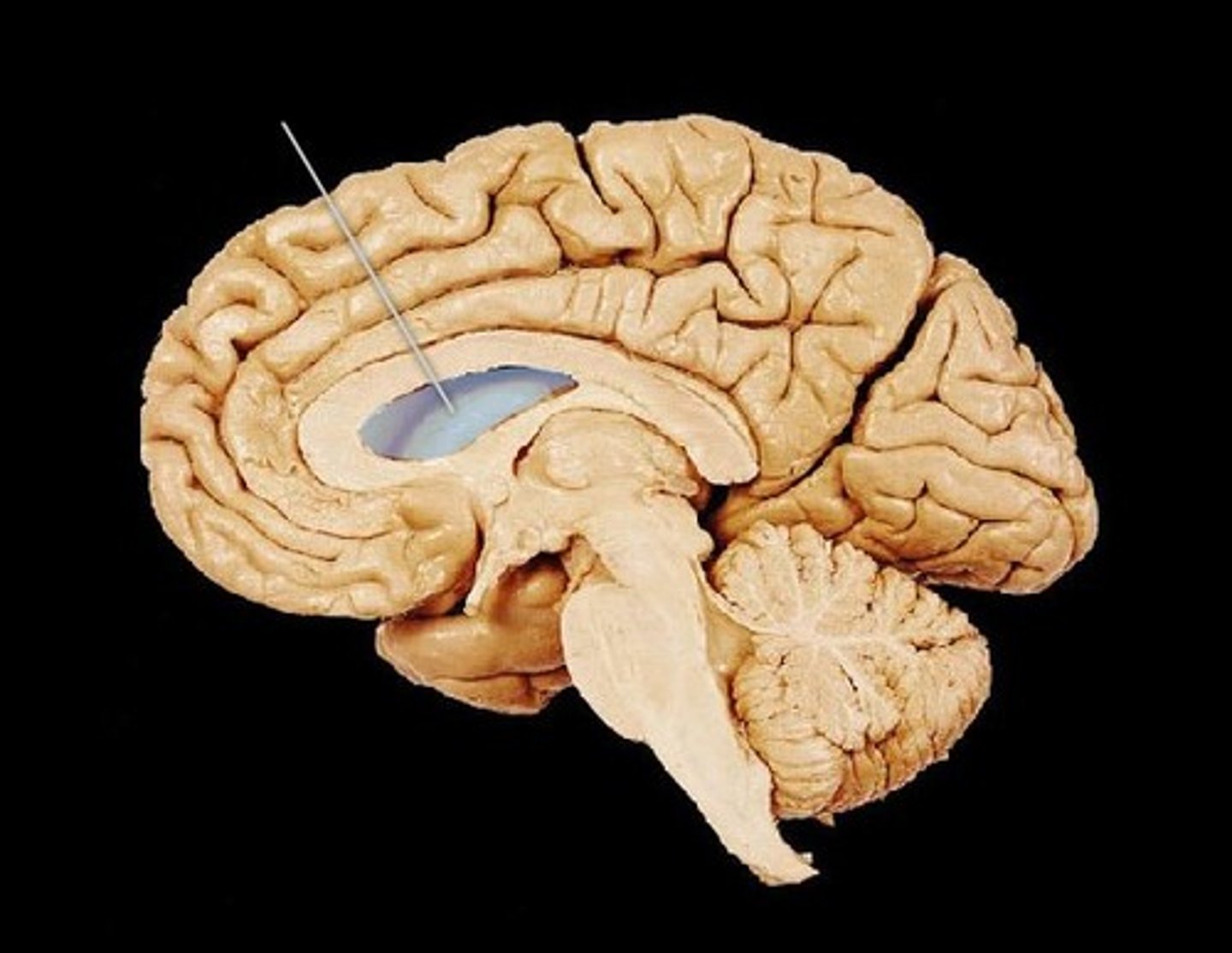
Lateral ventricles (left / right)
A set of large paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres that circulates cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
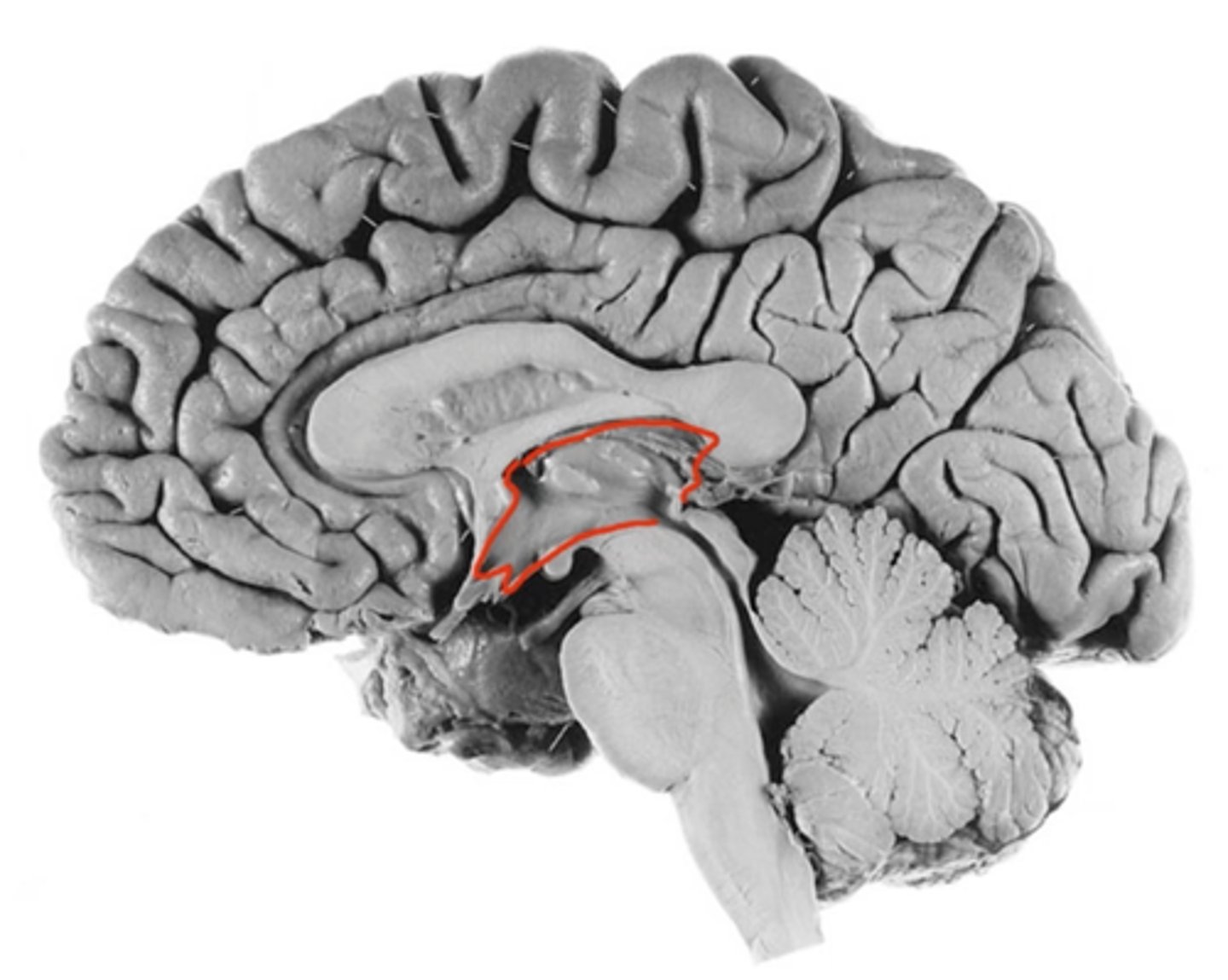
4th ventricle
Ventricle floor formed by medulla and pons and roof form by the cerebellum. It protects the human brain from trauma by cushioning it with cerebrospinal fluid. It drains into the central canal of the spinal cord.
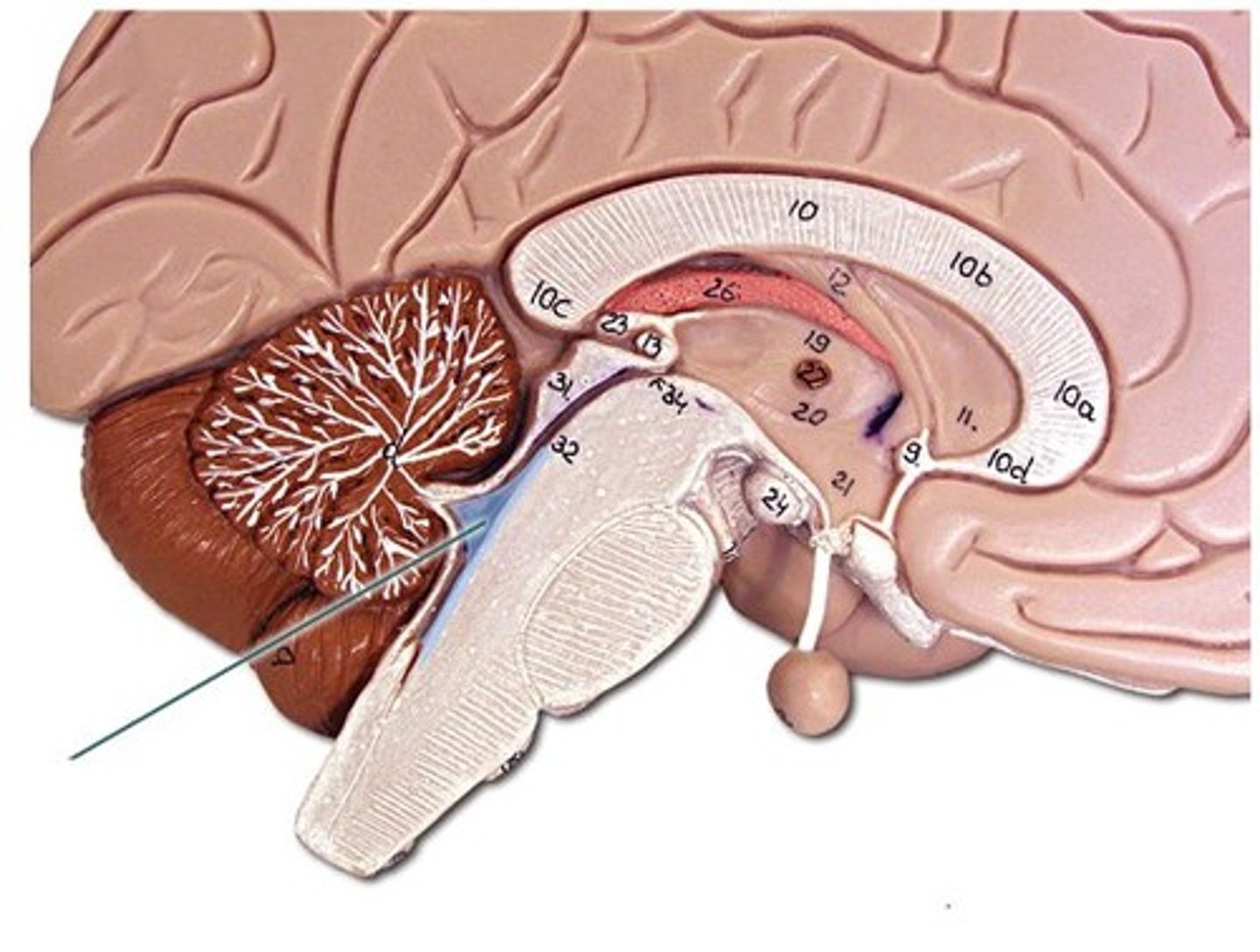
Superior colliculus
Receives visual sensory input (midbrain)
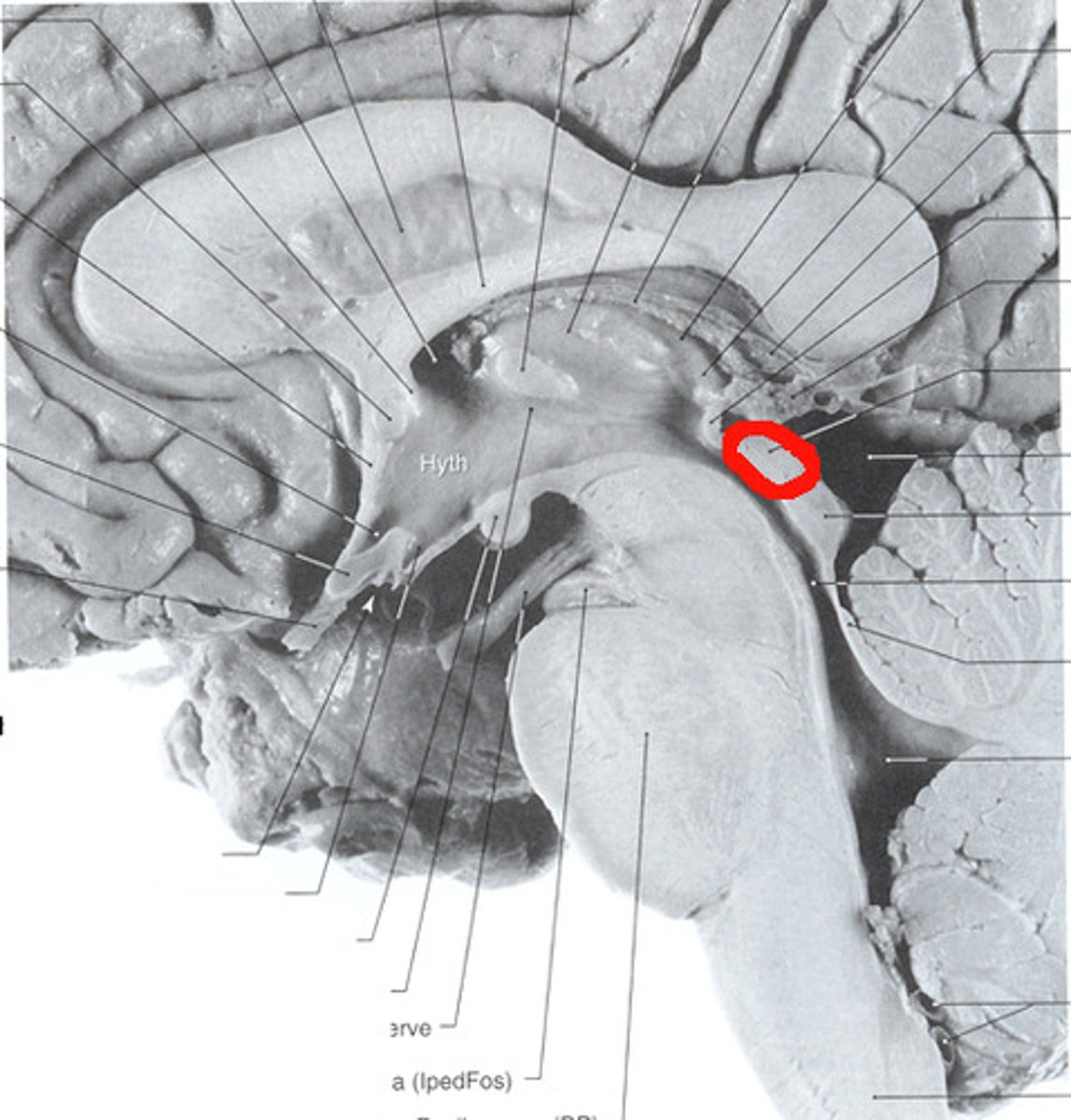
Inferior colliculi
Auditory reflex centers, which are a part of the auditory relay from the hearing receptors to the sensory cortex
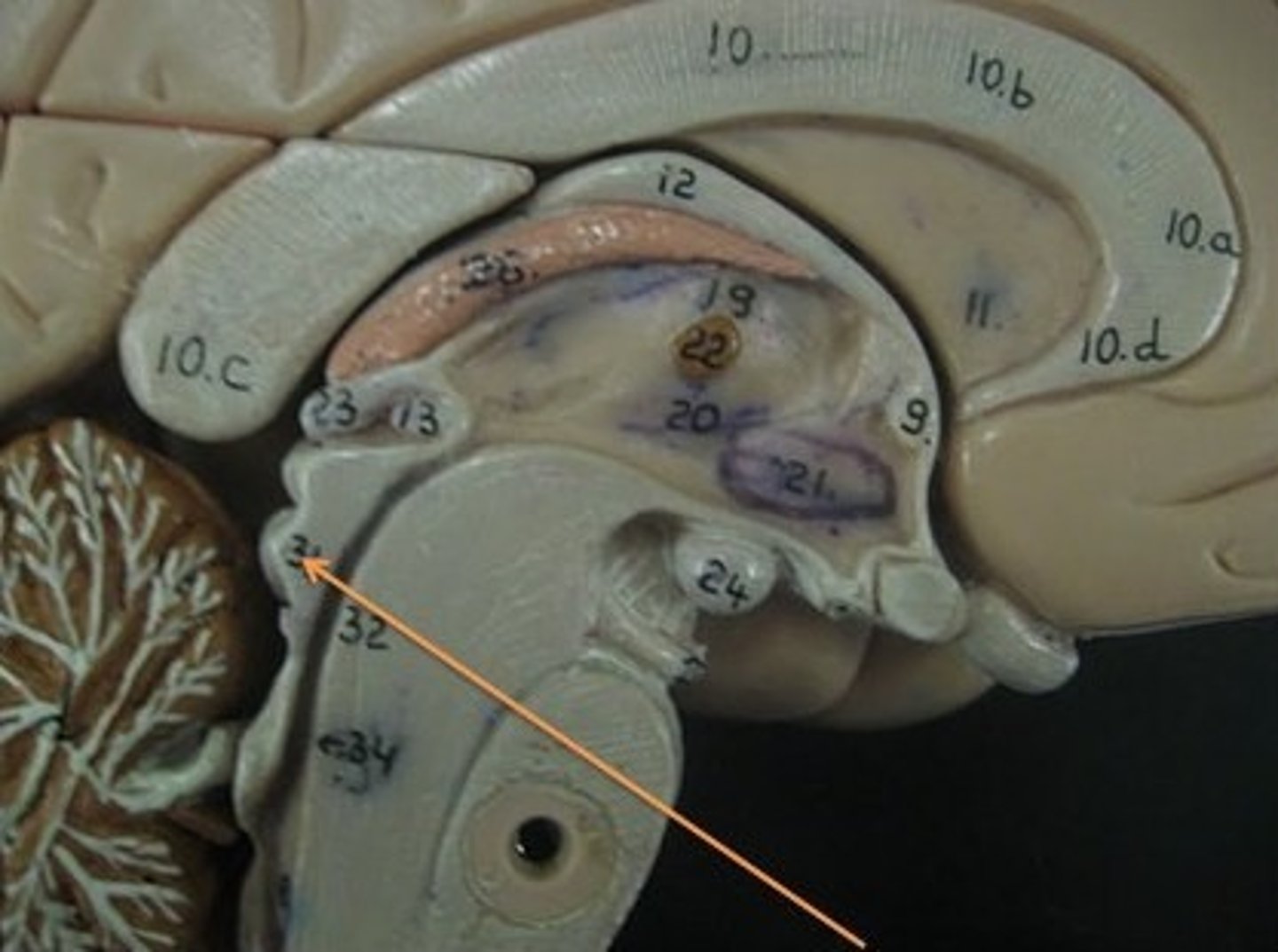
Pineal gland
Produces melatonin, which helps maintain circadian rhythm (sleep cycle) and regulate reproductive hormones
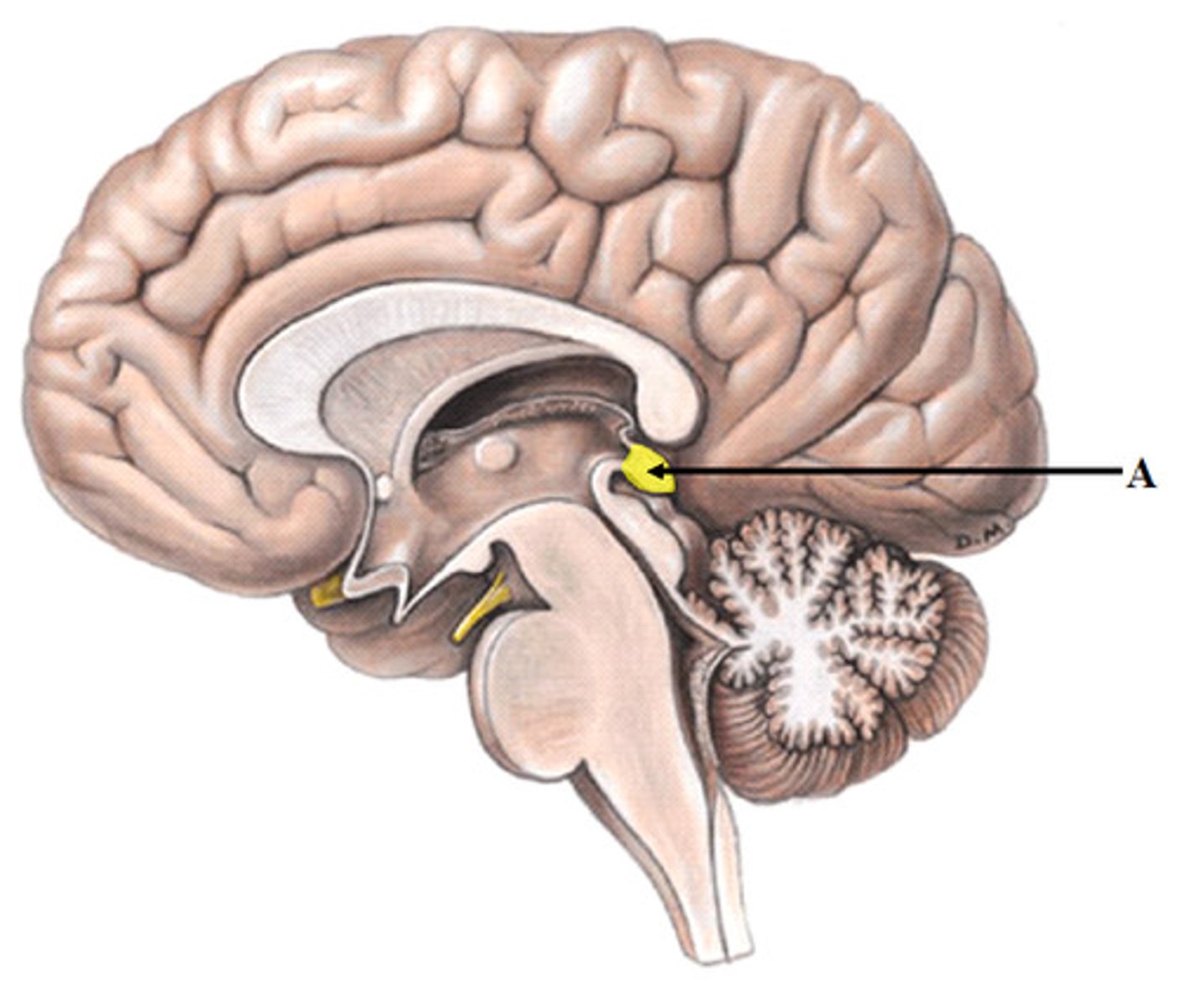
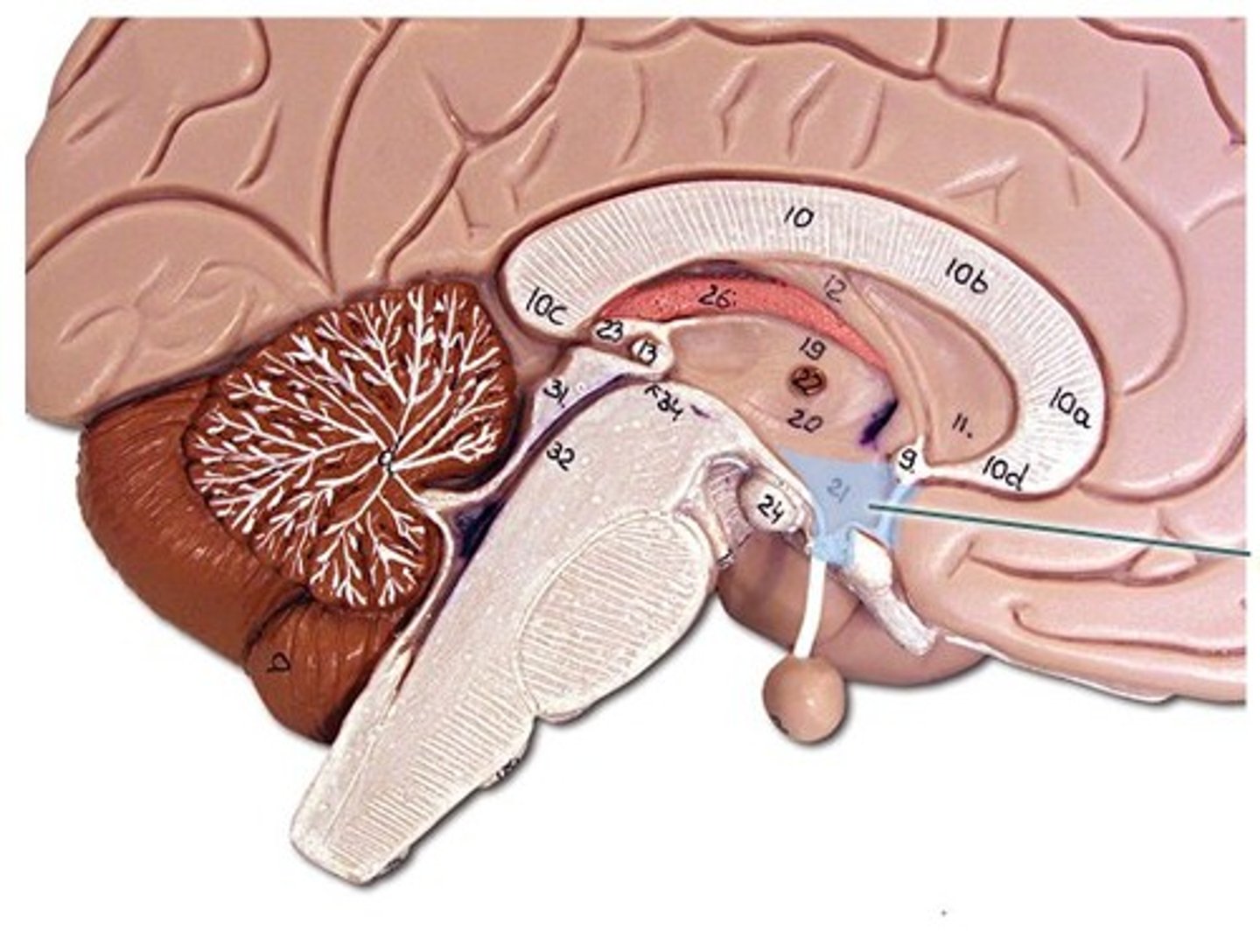
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
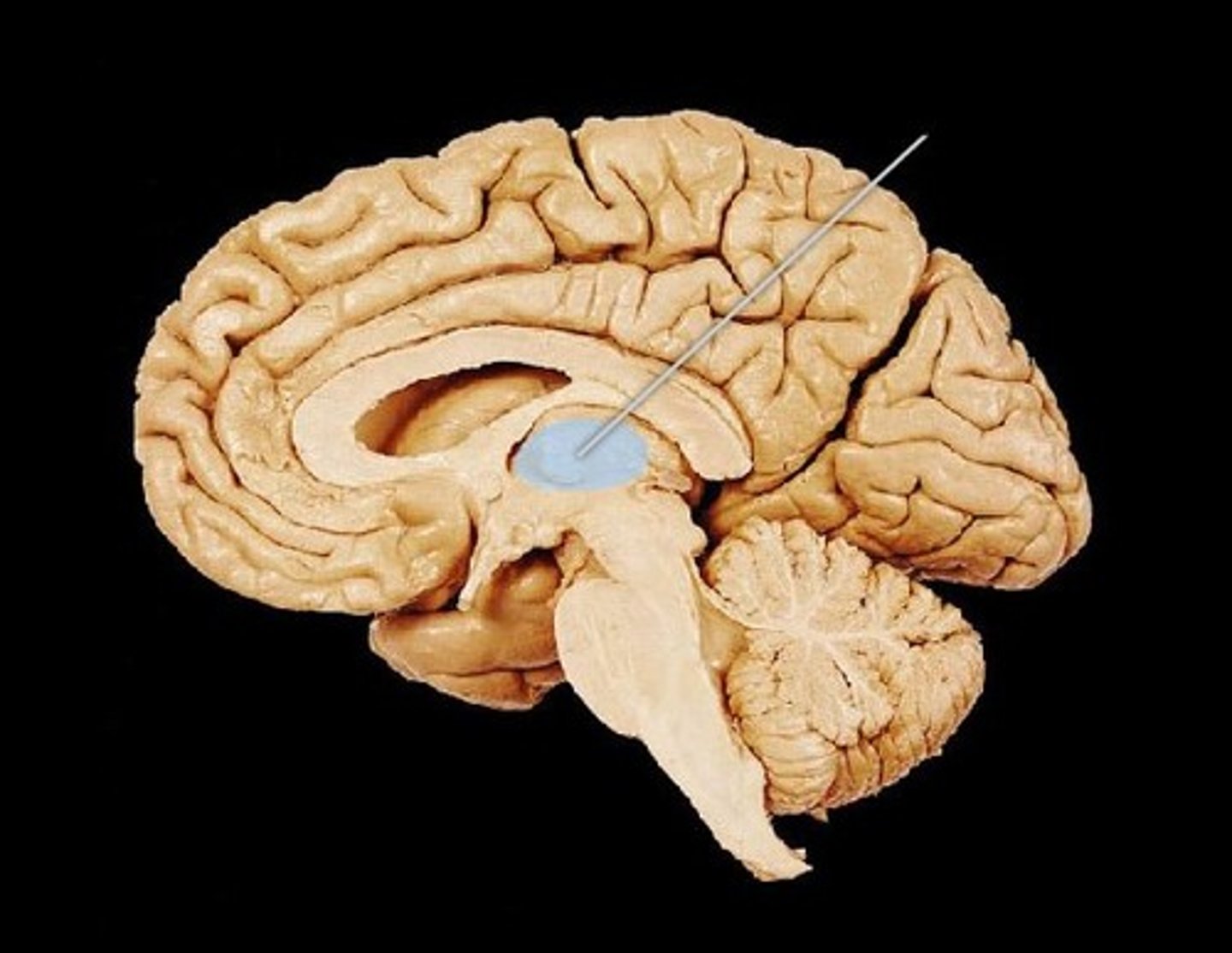
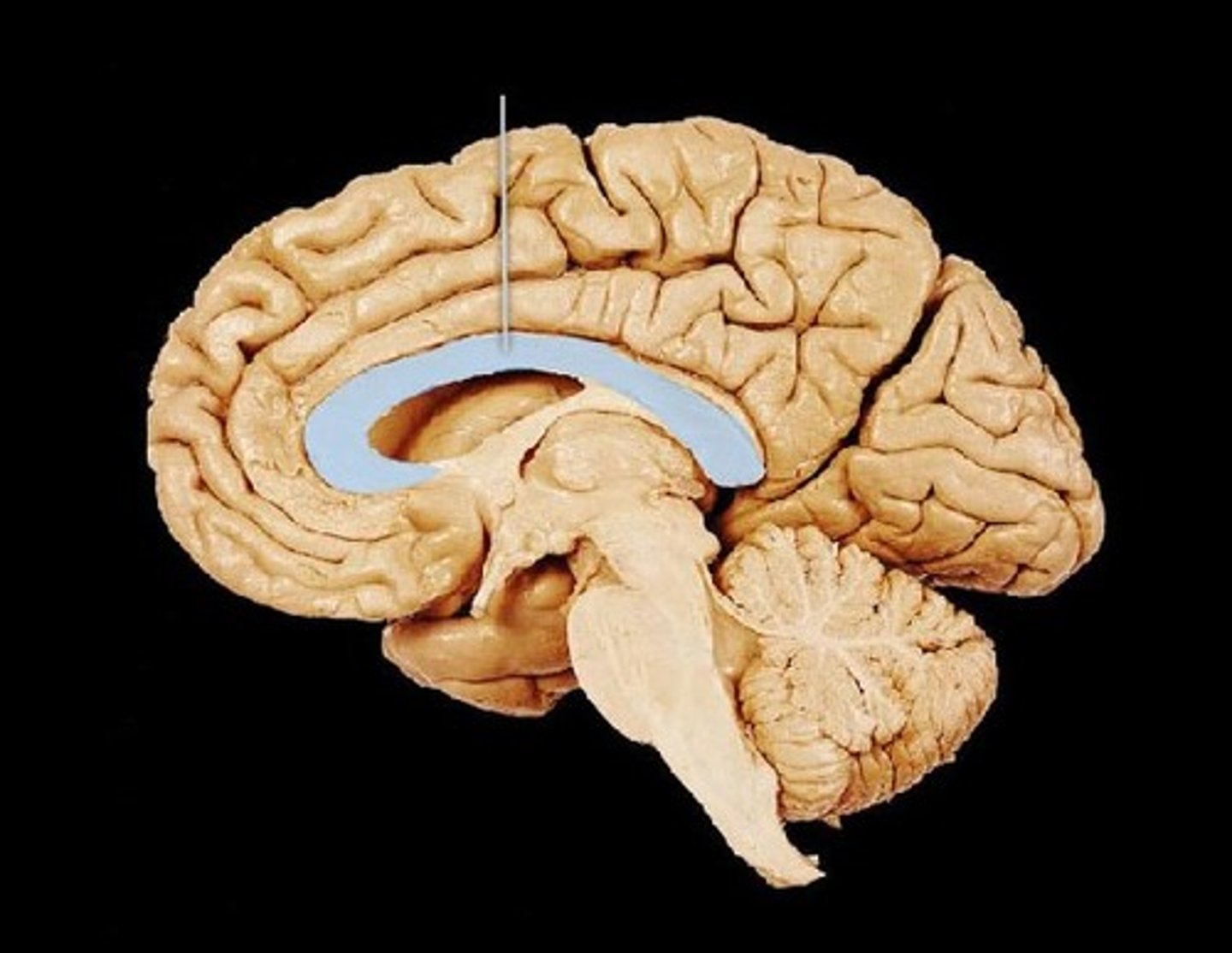
Corpus callosum
The large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
White matter
Myelinated axons of neurons
Gray matter
Cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers
- Make up the cerebral cortex in the brain
brain stem
Connection to the spinal cord. Filters information flow between the peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain (contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla).
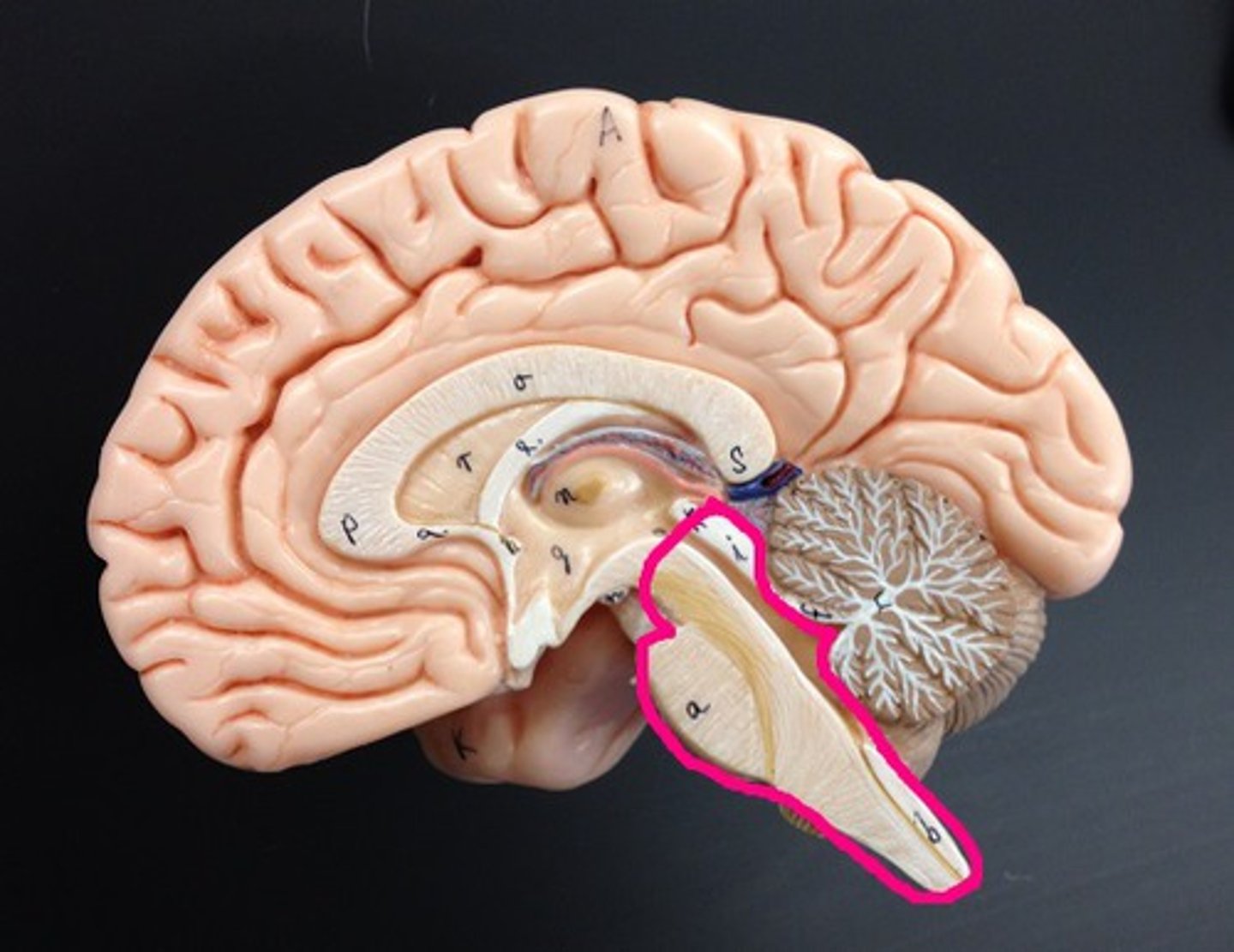
Diencephalon
Contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, & epithalamus
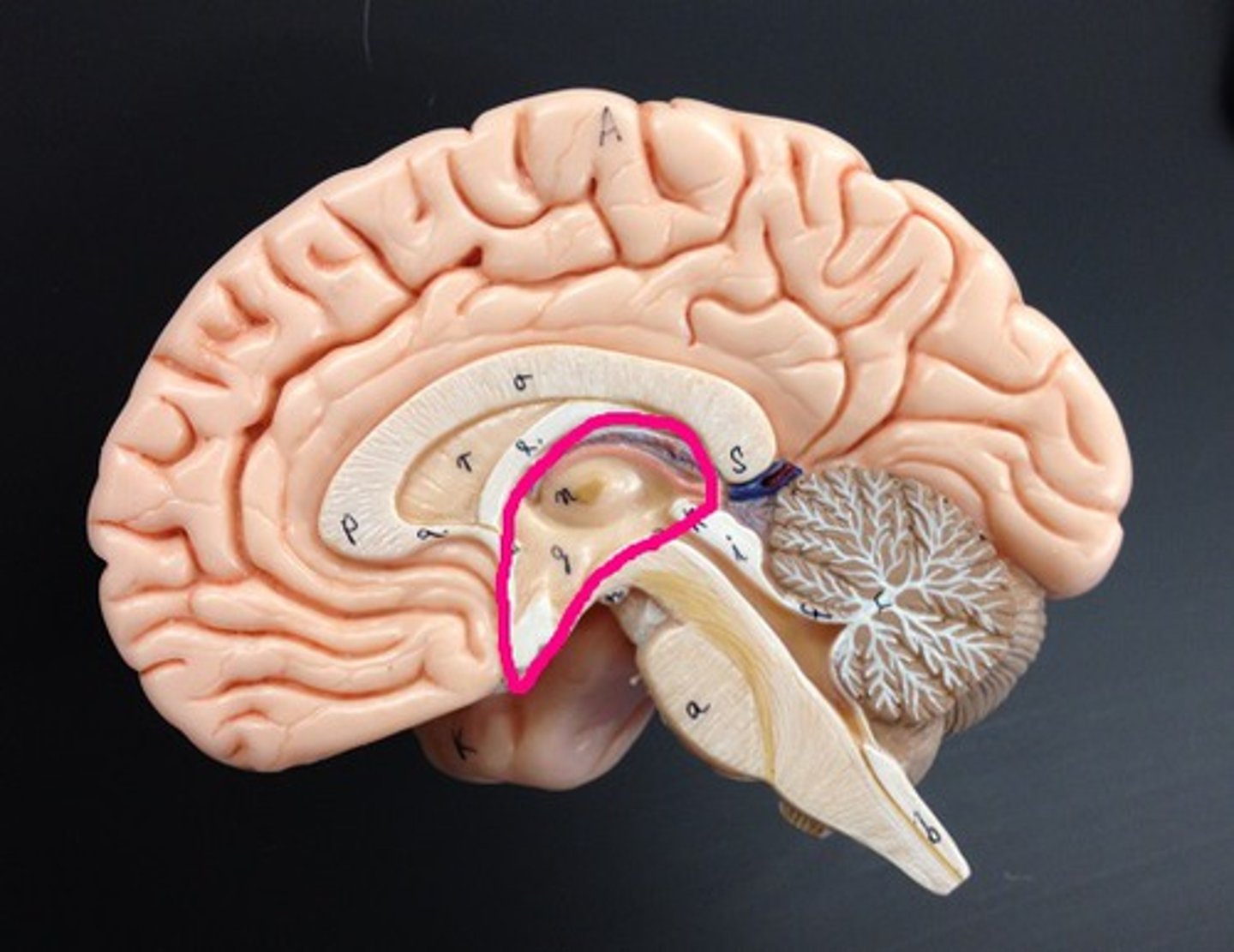
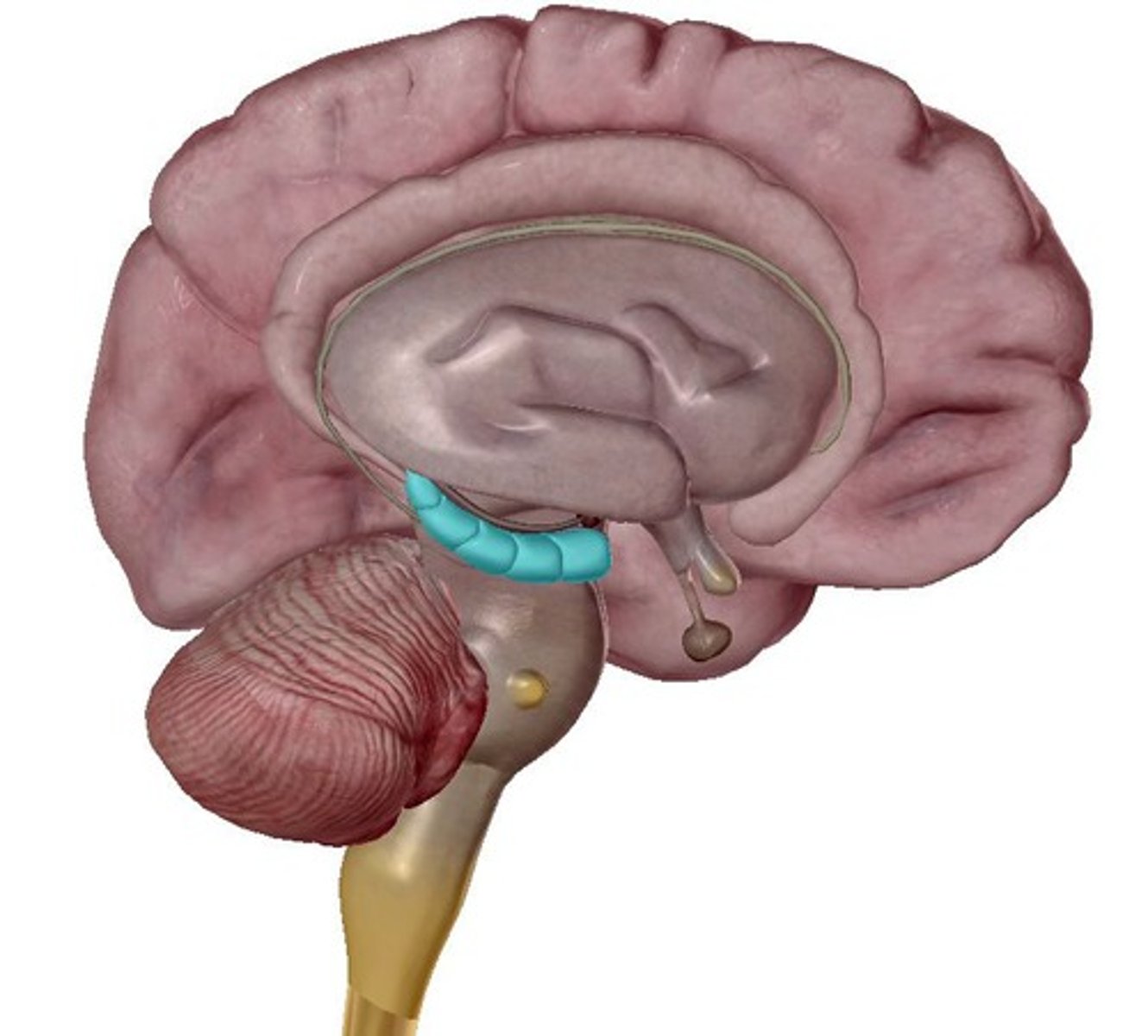
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
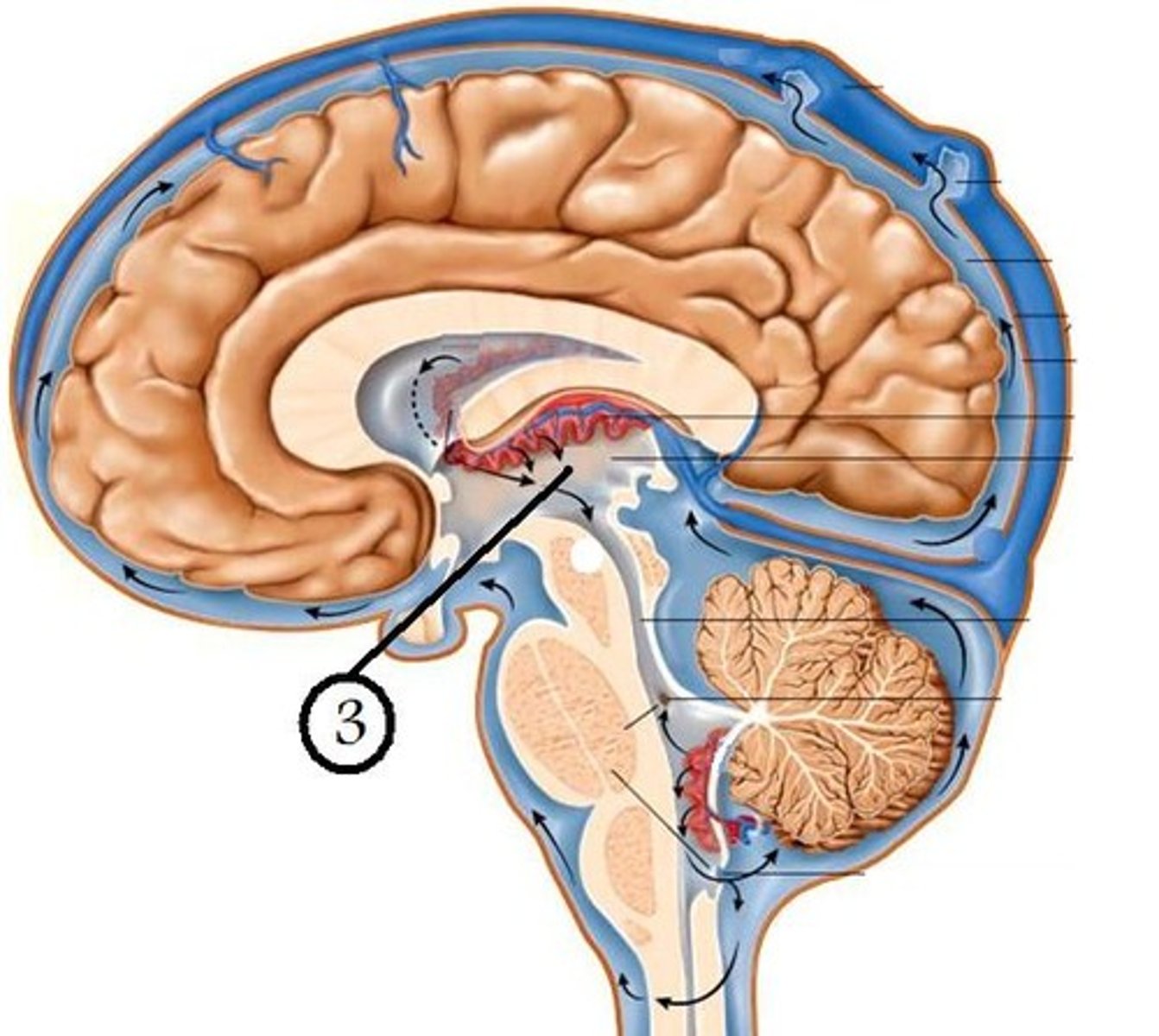
Choroid plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
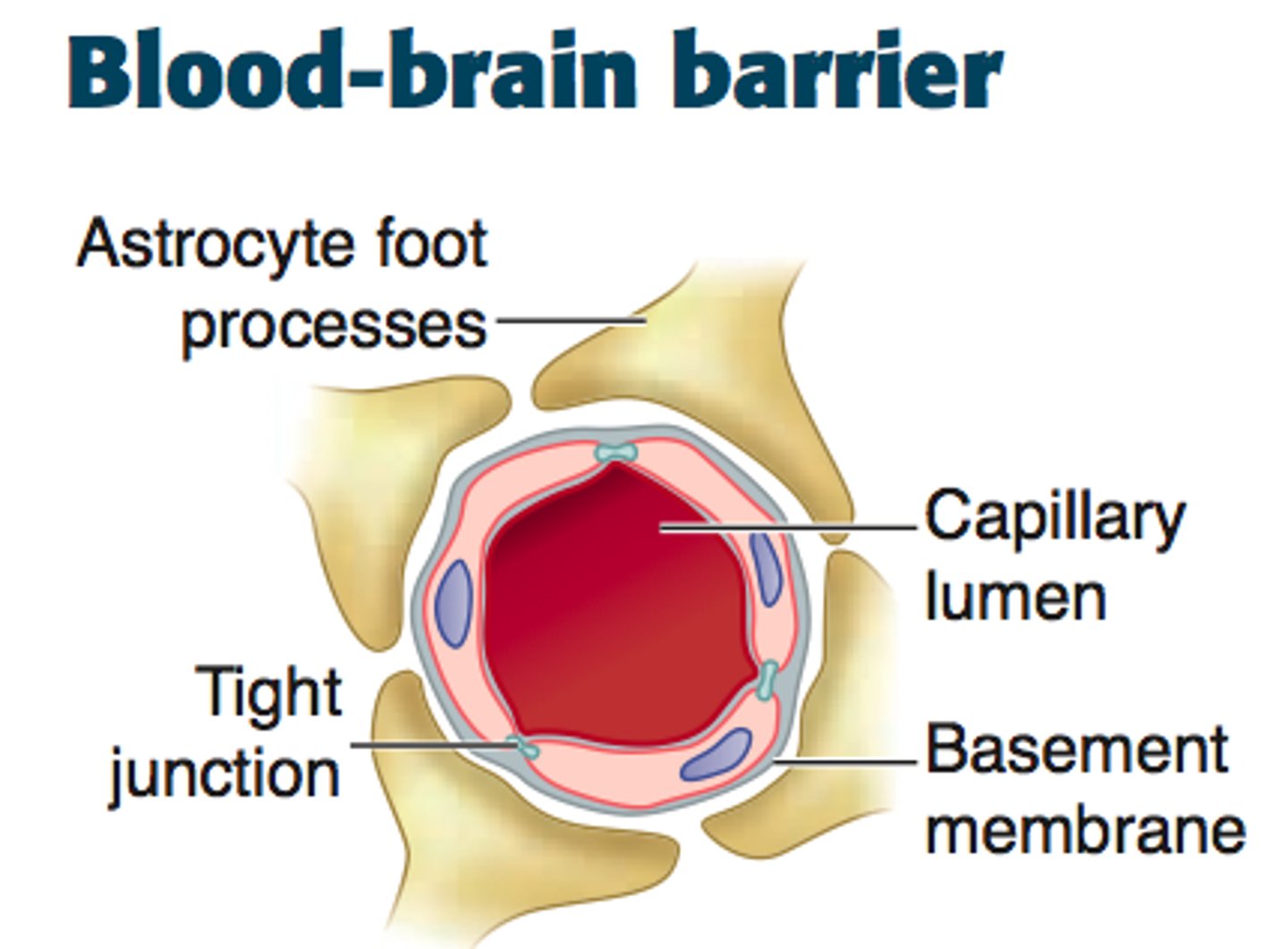
Blood Brian Barrier
The barrier system restricts the passage of various chemicals and microscopic entities between the bloodstream and the central nervous system. It sti
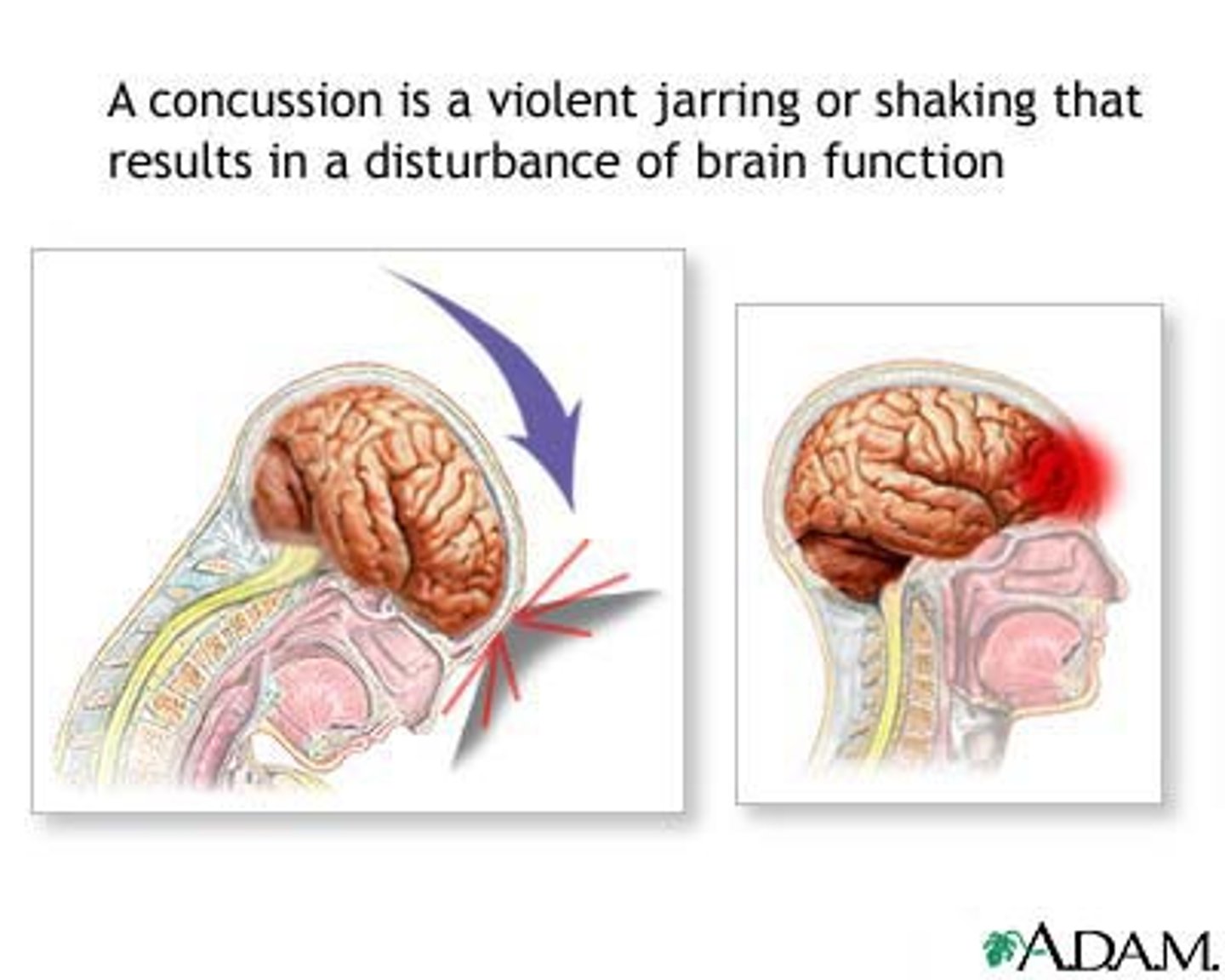
concussion
A violent shaking up or jarring of the brain may result in a temporary loss of awareness and function
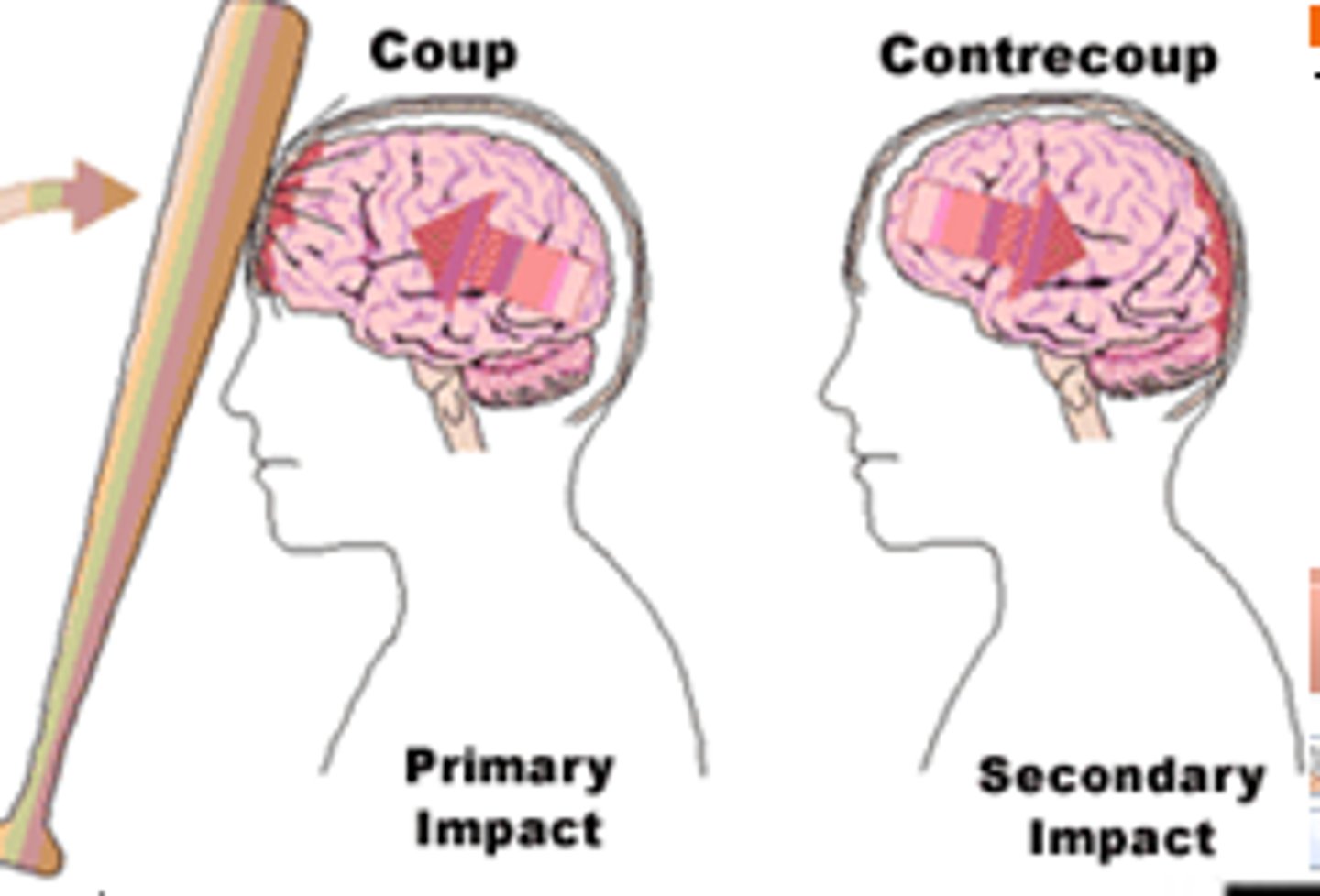
Contusion (bruise)
A blow from an external object causes soft tissue damage resulting in pain, ecchymosis, swelling
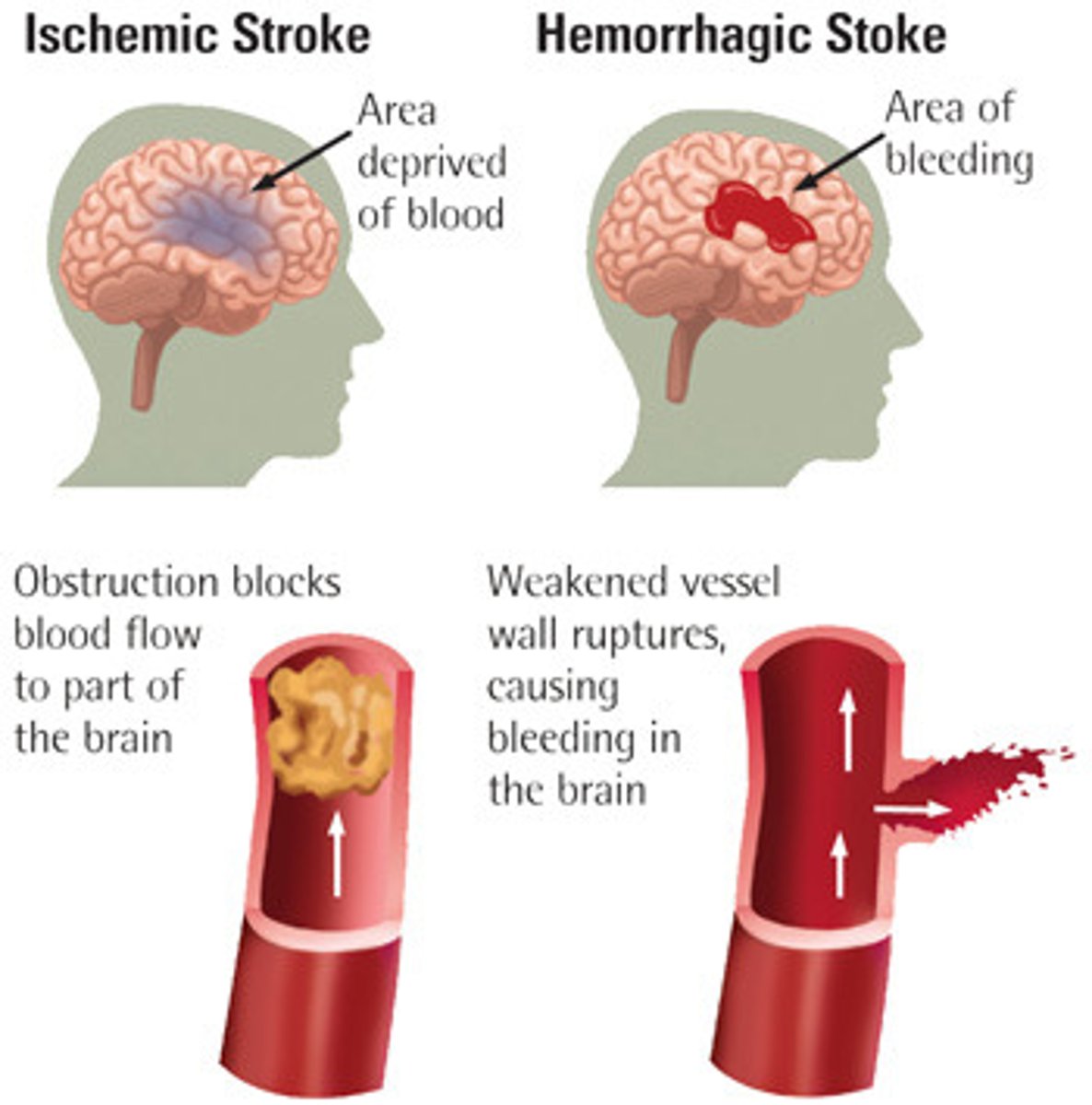
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
a.k.a. "Stroke". Lack of blood supply to the brain causes brain damage