Module 9 - The Respiratory System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
1
New cards
What are 2 cyclic phases of breathing
1. Inspiration/Inhalation
2. Expiration/Exhalation
2
New cards
\
Functions of the Respiratory Systems (5)
Functions of the Respiratory Systems (5)
Gas Exchange, Gas Conditioning, Sound Production, Olfaction, Defense
3
New cards
Gas Exchange
movement of gases across membranes, Internal and external respiration
4
New cards
Internal Respiration
exchange of gases btwn blood and cells of body
5
New cards
External Respiration
exchange of gases btwn air and blood, CO2 & O2 btwn alveolus of lung & capillaries
6
New cards
Gas Conditioning
warm & cleanse gases entering lungs, prevent lung damage, in nasal cavities & paranasal sinuses, mucosal lining cleanses of particulate matter
7
New cards
Sound Production
from forceful expiration of air thru vocal cords in larynx → vibration, diff tensions of vocal cords → diff sounds
8
New cards
Olfaction
receptors for smell on olfactory epithelium, stimulated by airborne molecules dissolved in mucus
9
New cards
Defense
coarse hairs of nostrils, ciliated cells of respiratory epithelium, mucus lining → trap particles & microorganisms
10
New cards
Respiratory Tract Epithelium
defense, lines surfaces (nasal cavity → terminal bronchi),
11
New cards
type of cells in respiratory tract epithelium (2)
1. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
2. goblet mucus cells
12
New cards
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
apical surface is covered in cilia
13
New cards
function of cilia
increase surface area for conditioning, trap inhaled particles & microorganisms → sweep back out nose and mouth
14
New cards
goblet mucus cells
interspersed thru pseudostratified epithelium, produce mucus → protective layer to trap particulate matter & provide moisture
15
New cards
Regions of Respiratory system (2)
1. Conducting Portion
2. Respiratory Portion
16
New cards
Conducting Portion
conduct air from outside world → lung tissue & vice versa, were humidification & trapping of debris, no absorption of O2
17
New cards
parts of conducting portion (7)
1. nose & nasal cavity
2. paranasal sinuses
3. pharynx
4. larynx
5. trachea
6. primary, secondary, tertiary bronchi
7. terminal bronchioles
18
New cards
Respiratory Portion
transfer of gases from lungs → pulmonary capillaries
19
New cards
pulmonary capillaries
terminal structure within lungs, have thin walls for movement of gas
20
New cards
Parts of Respiratory Portion (4)
1. Respiratory Bronchioles
2. Alveolar ducts
3. Alveolar sacs
4. Alveoli
21
New cards
Paranasal Sinuses
collection of air filled spaces within bones of skull, communicate with nasal cavity, aid in conditioning, defense against pathogens, resonance chambers for speech
22
New cards
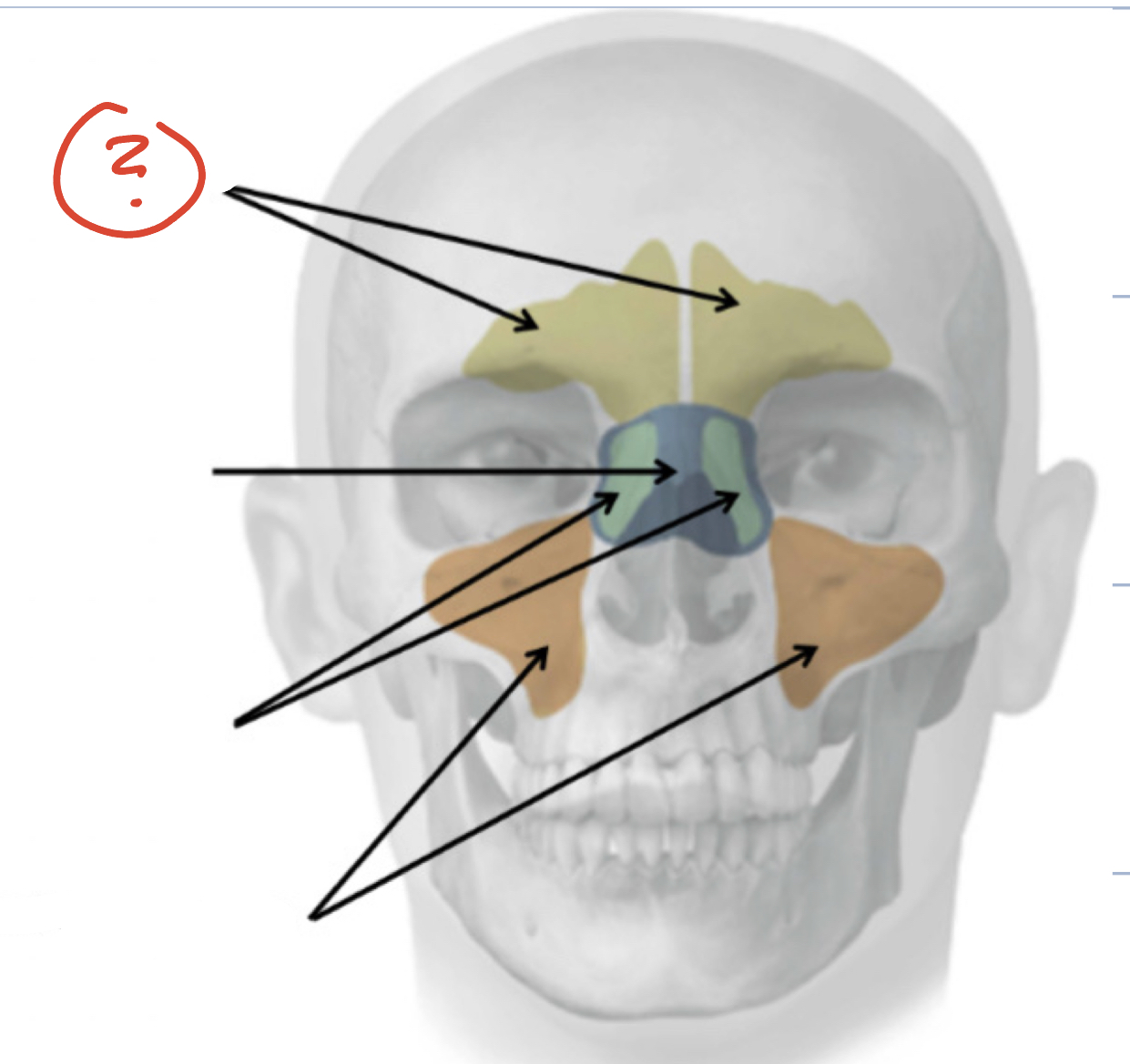
Frontal Sinuses
23
New cards
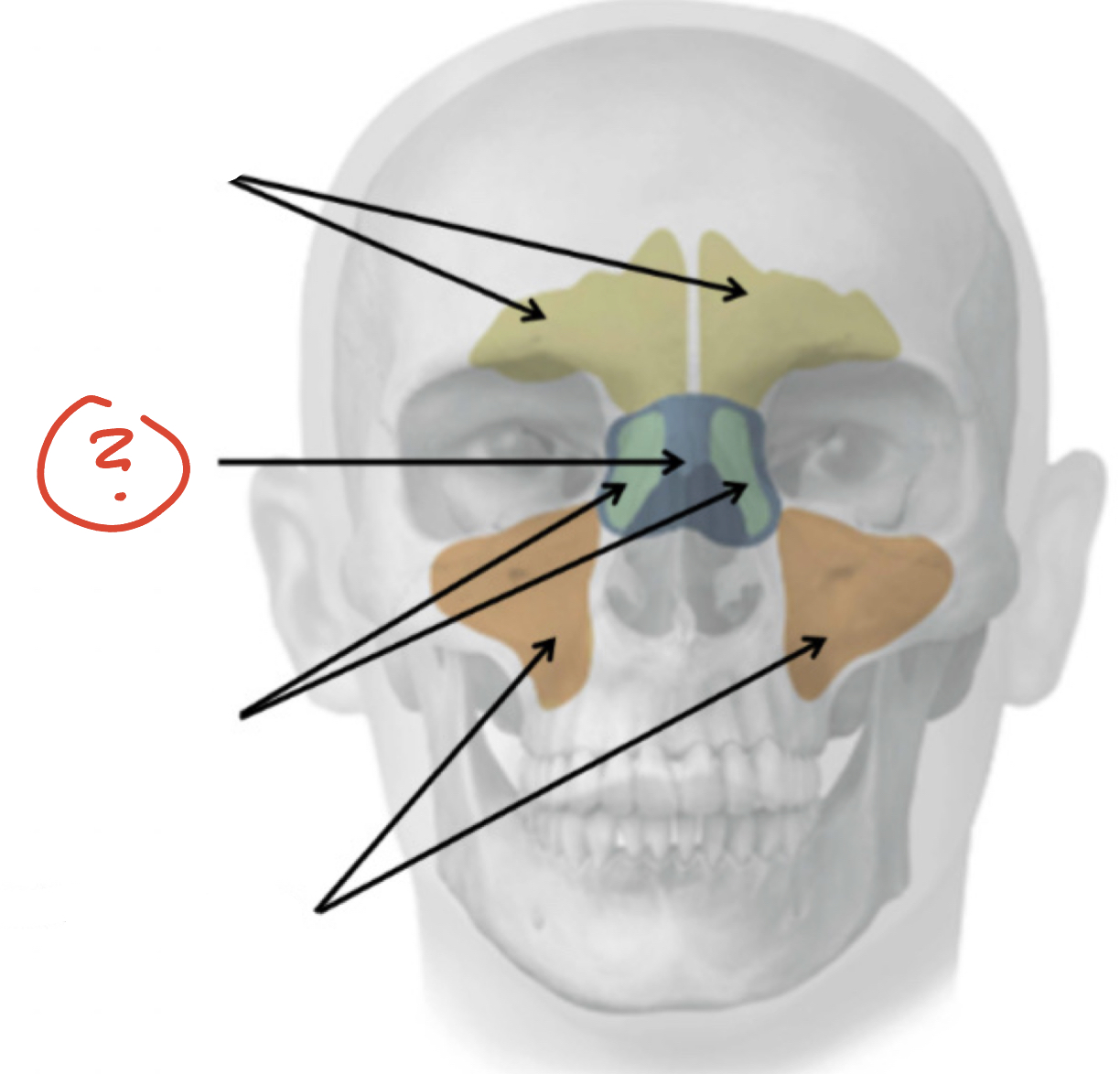
Sphenoid Sinus
24
New cards
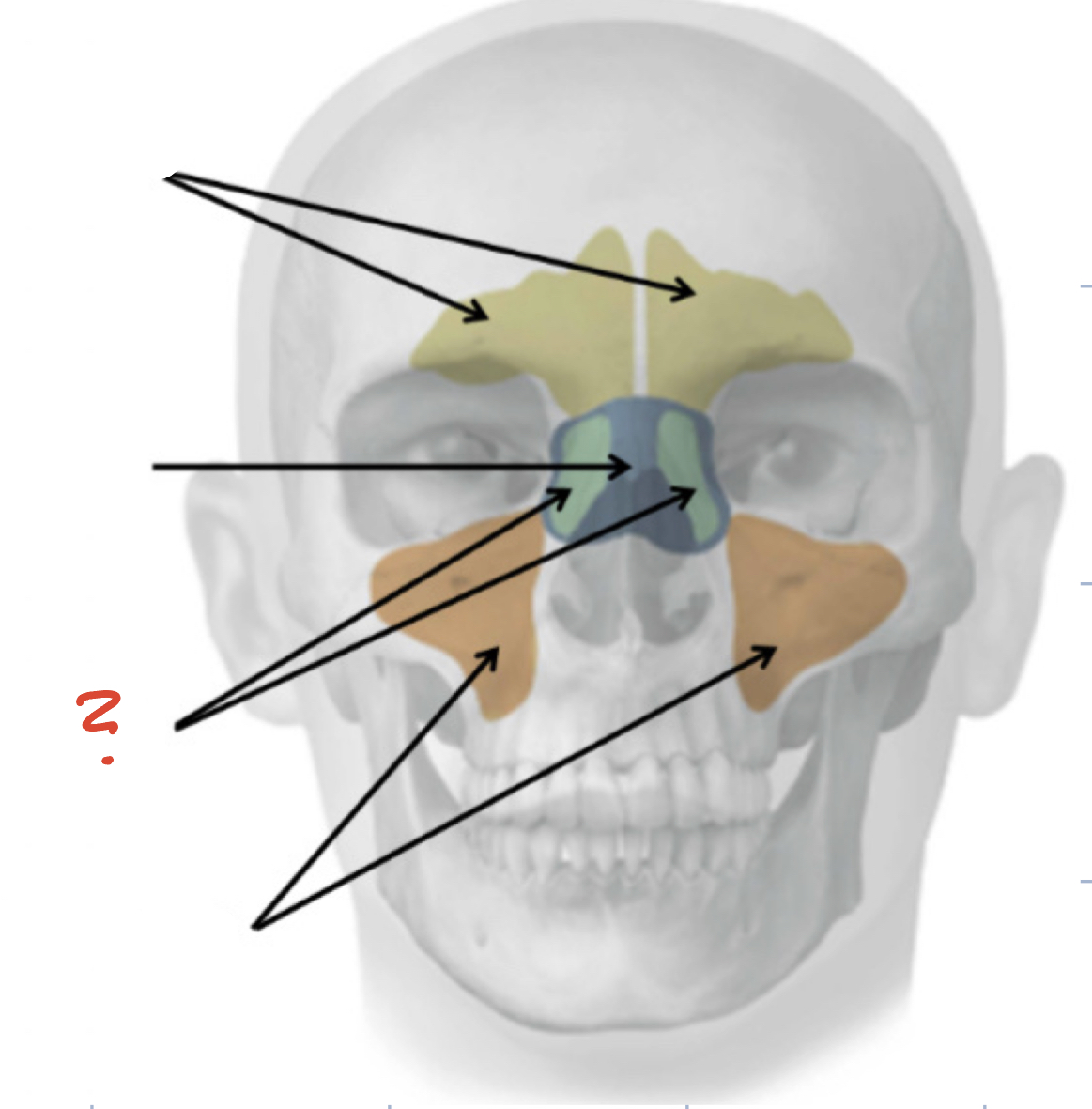
Ethmoid Sinuses
25
New cards
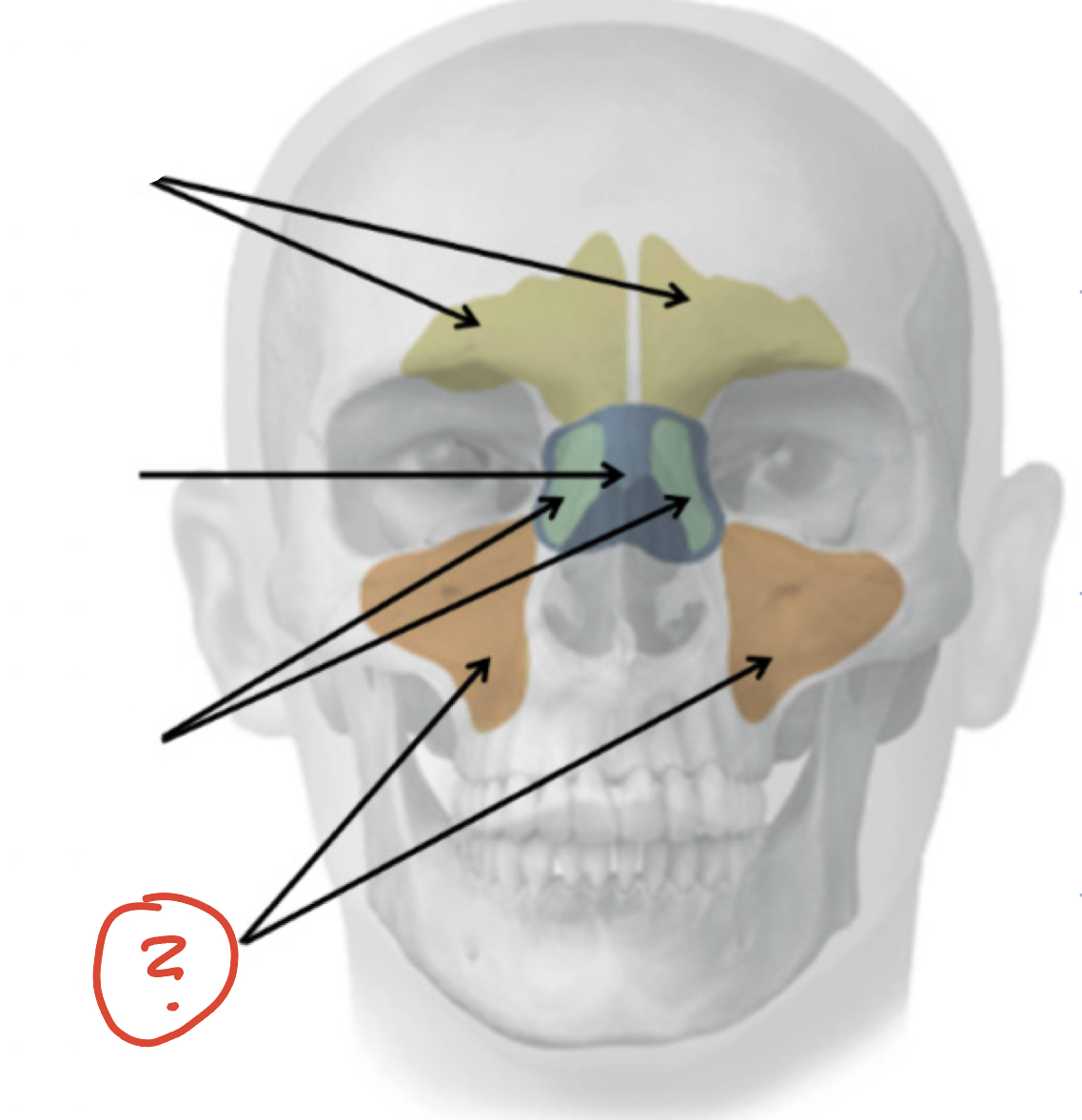
Maxillary Sinuses
26
New cards
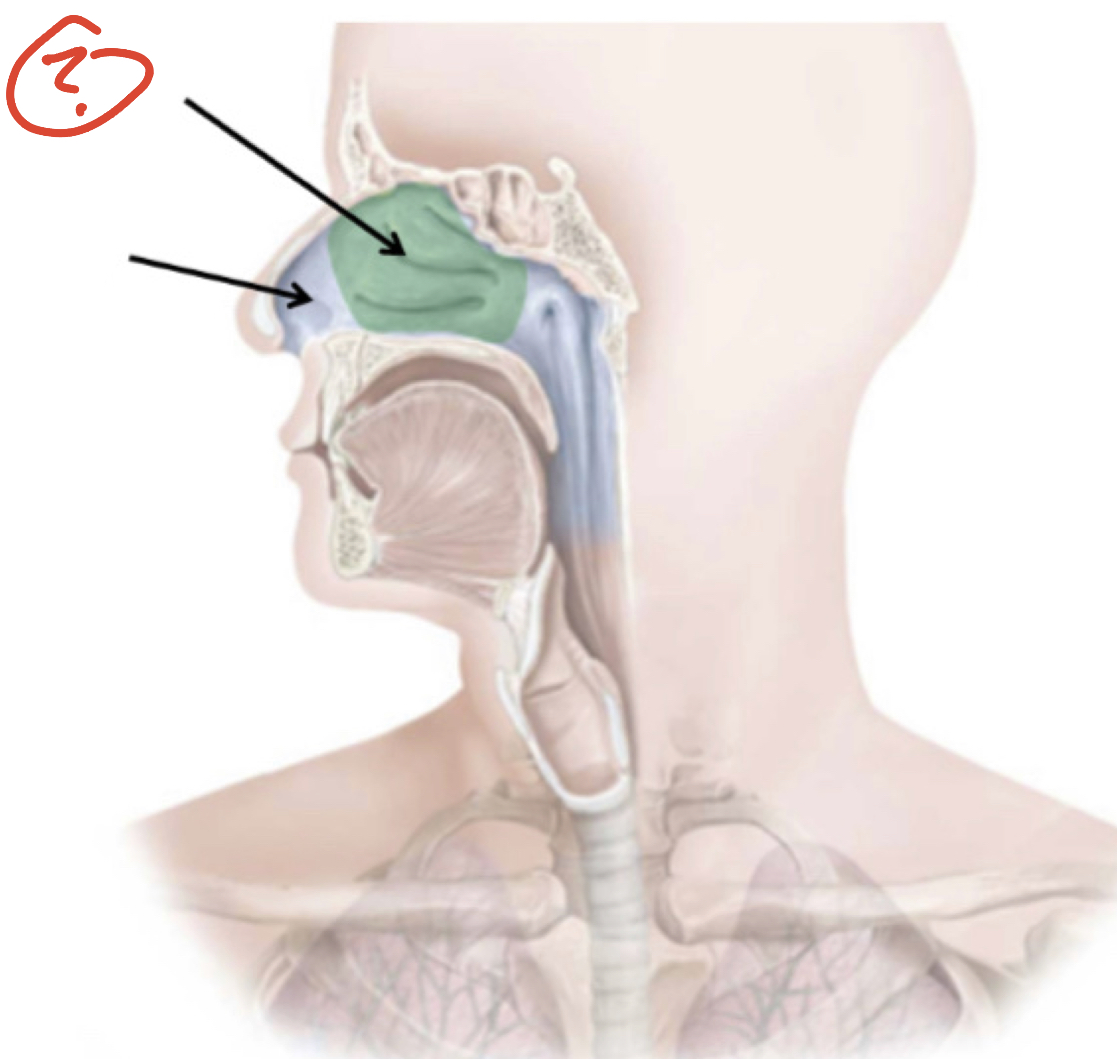
Nasal Cavity
27
New cards
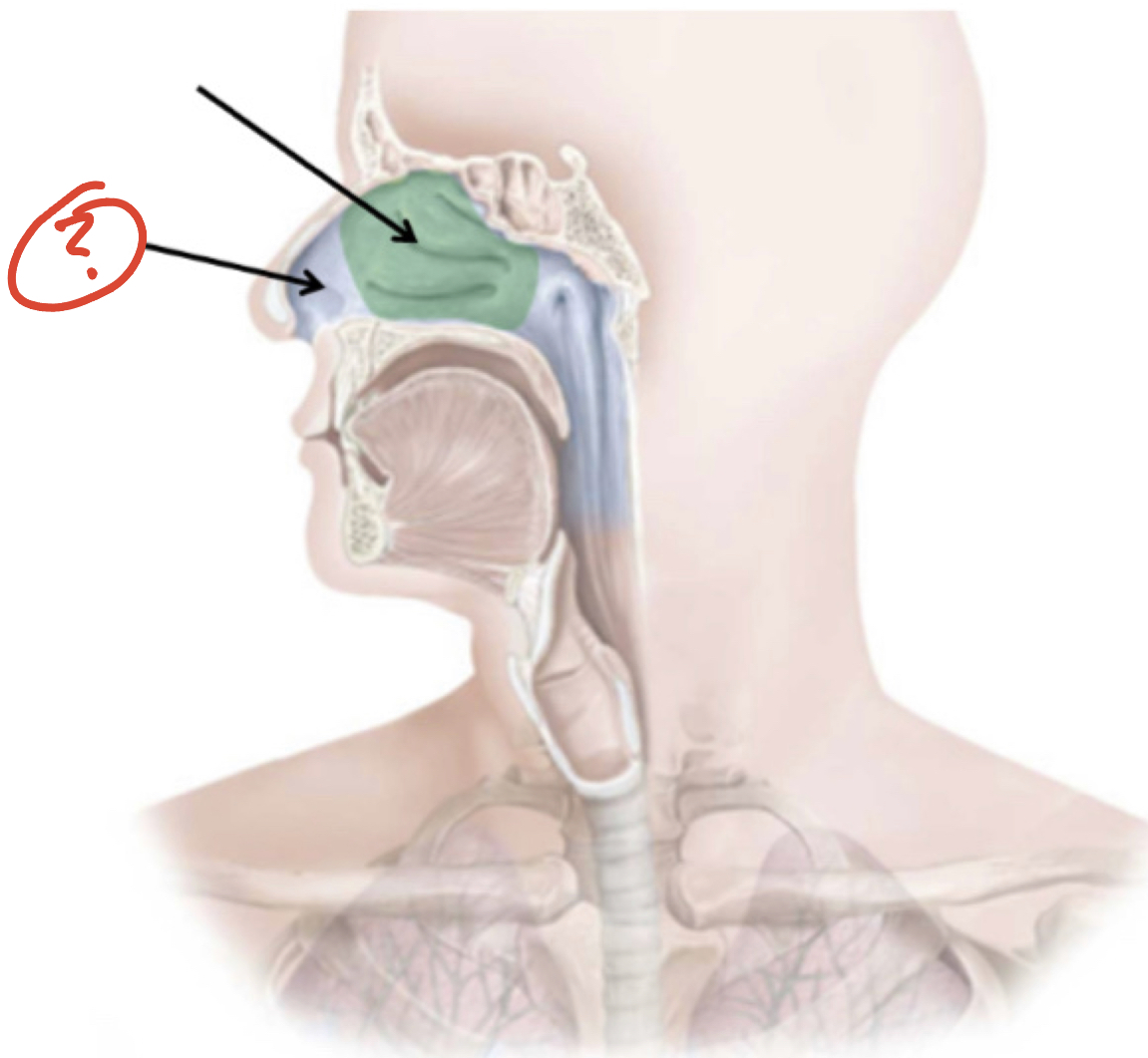
Vestibule
28
New cards
Nose & Nasal Cavity
1st line of defense against pathogens & debris (coarse hairs & mucus)
29
New cards
Bone structures/ boundaries of nose & nasal Cavity (6)
1. Roof - Ethmoid Bone
2. Floor - Hard Palate
3. Medial Wall - nasal septum
4. Lateral wall - nasal conchae
5. Anterior Wall - nares
6. Posterior border - opening to nasopharynx
30
New cards
nasal septum
vertical bones in skull, separate halves of nasal cavity
31
New cards
nasal conchae
make turbulence in air, for conditioning & catching debris
32
New cards
nares
opening btwn nose & nasal cavity, nostrils
33
New cards
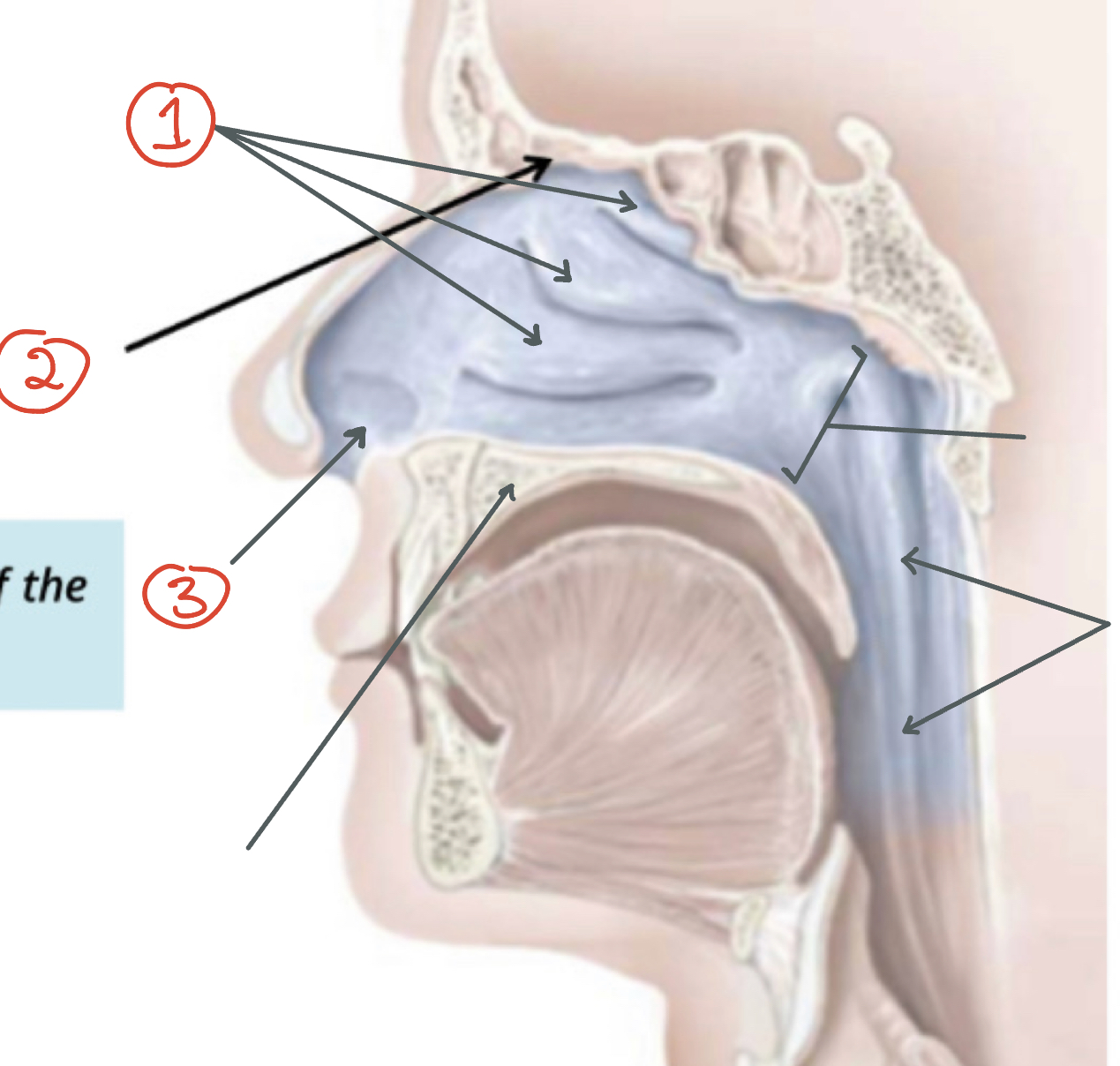
1) Nasal Conchae 2) Ethmoid bone 3) Anterior nares
34
New cards
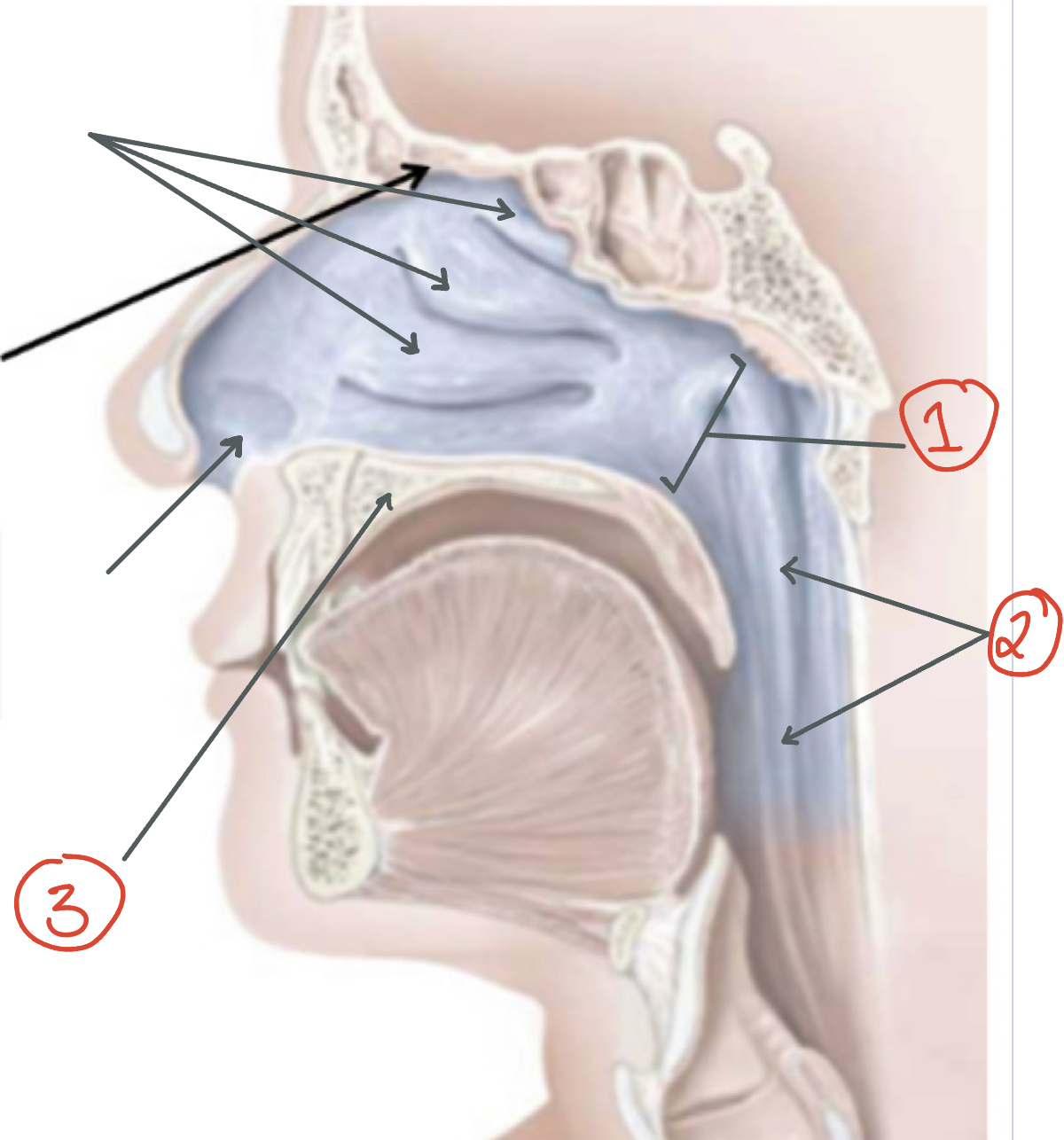
1) Opening to nasopharynx 2) Pharynx 3) Hard Palate
35
New cards
Pharynx
muscular tube, respiratory system: connect nasal cavity & larynx, digestive system: connect oral cavity & esophagus
36
New cards
parts of pharynx (3)
nasopharynx, oropharynx, langopharynx
37
New cards
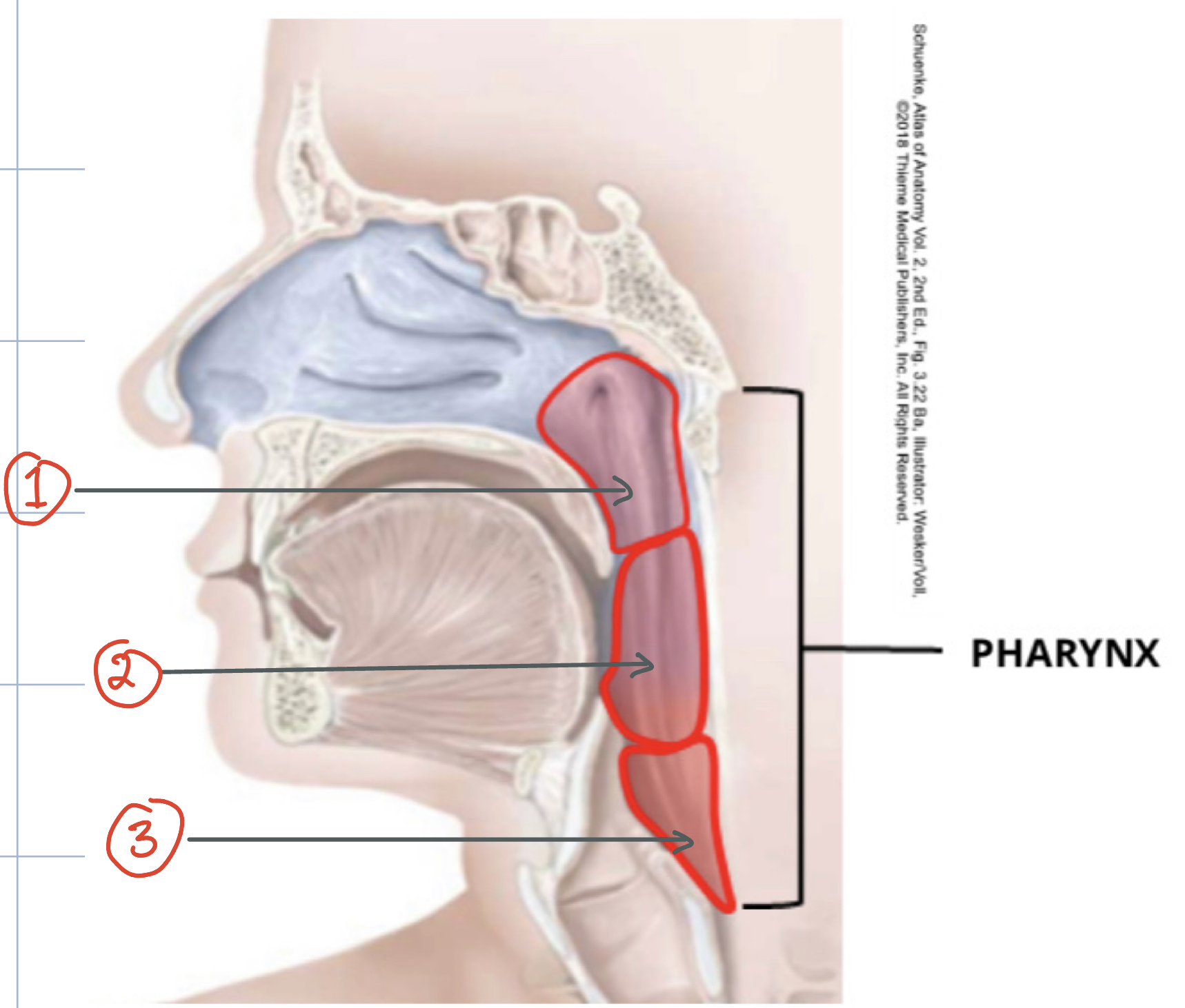
1) Nasopharynx 2) Oropharynx 3) Laryngopharynx
38
New cards
what parts of pharynx are in BOTH digestive & respiratory systems
oropharynx and laryngopharynx
39
New cards
histology of nasopharynx
respiratory tract epithelium
40
New cards
histology of oropharynx & laryngopharynx
stratified squamous epithelium → durability
41
New cards
histology of nasal cavity
respiratory tract epithelium → protect from airborne debris & microorganisms, condition air
42
New cards
histology of roof of nasal cavity
lined with olfactory epithelium → pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium + bipolar olfactory receptor neurons
43
New cards
Larynx
produce sound, made of cartilage, ligaments, associated muscles, anterior to esophagus, connect pharynx to trachea, prevent food entering trachea
44
New cards
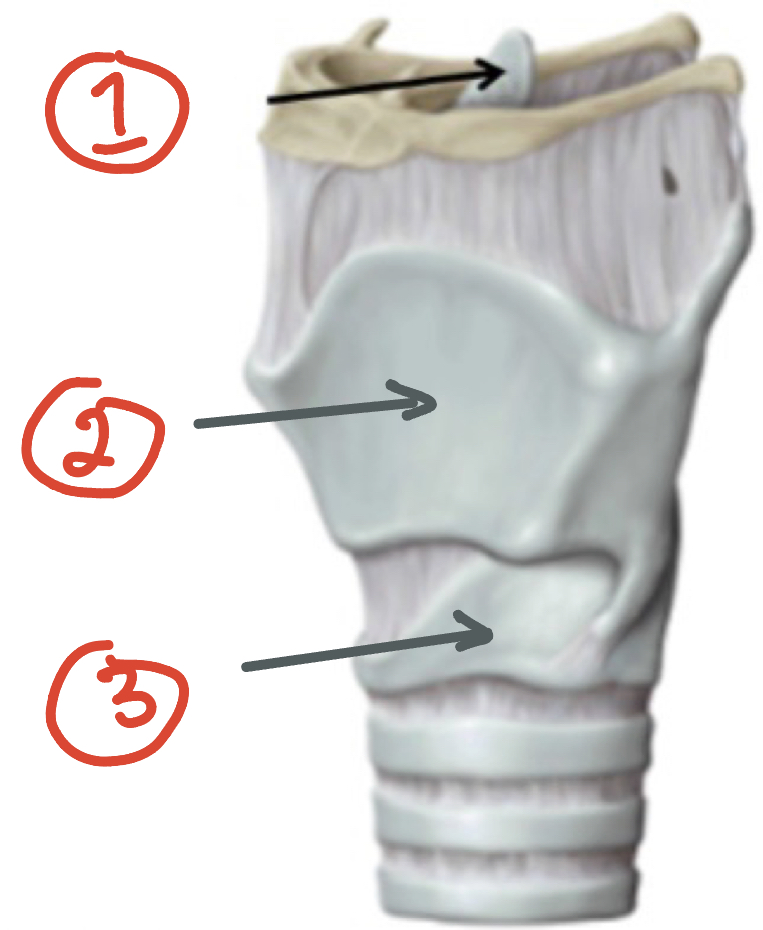
Cartilage of larynx (3) + function
1. Epiglottis
2. Thyroid Cartilage
3. Cricoid Cartilage
protect, attach, aid in function of vocal cords
45
New cards
epiglottis
spoon shaped, elastic, flip and cover trachea when swallow → prevent food enter
46
New cards
thyroid cartilage
shield shaped, hyaline cartilage, attachment for muscles + vocal cords
47
New cards
cricoid cartilage
complete ring, hyaline cartilage, narrow anteriorly & broad posteriorly, attachment for muscles + vocal cords
48
New cards
Trachea/Windpipe
from larynx to T4/5 level, slits at carina (junction), conduction of air into lungs
49
New cards
What is trachea made up? + function
15-20 C shaped cartilaginous rings → incomplete posteriorly, keep airway open, trachealis muscle connect posteriorly
50
New cards
Histology of trachea (3 layers)
1. Mucosa
2. Submucosa
3. Adventitia
51
New cards
Mucosa
lined with respiratory tract epithelium, clears debris/pathogens
52
New cards
submucosa
loose areolar connective tissue, have large vessels & nerves & mucus secreting glands
53
New cards
Adventitia
enclose C-shaped cartilaginous rings, make trachea flexible & durable → shift with breathing movements
54
New cards
Vocal Cords
small ligaments attached to laryngeal cartilage, true vocal cords = produce sound, false vocal cords = membranous flap that protect true vocal cords
55
New cards
What does trachea split into?
2 primary bronchi (L & R), same histology & function as trachea
56
New cards
Hilus
where primary bronchi enter lung on medial side
57
New cards
how is right primary bronchi different?
wider, shorter, more vertical
58
New cards
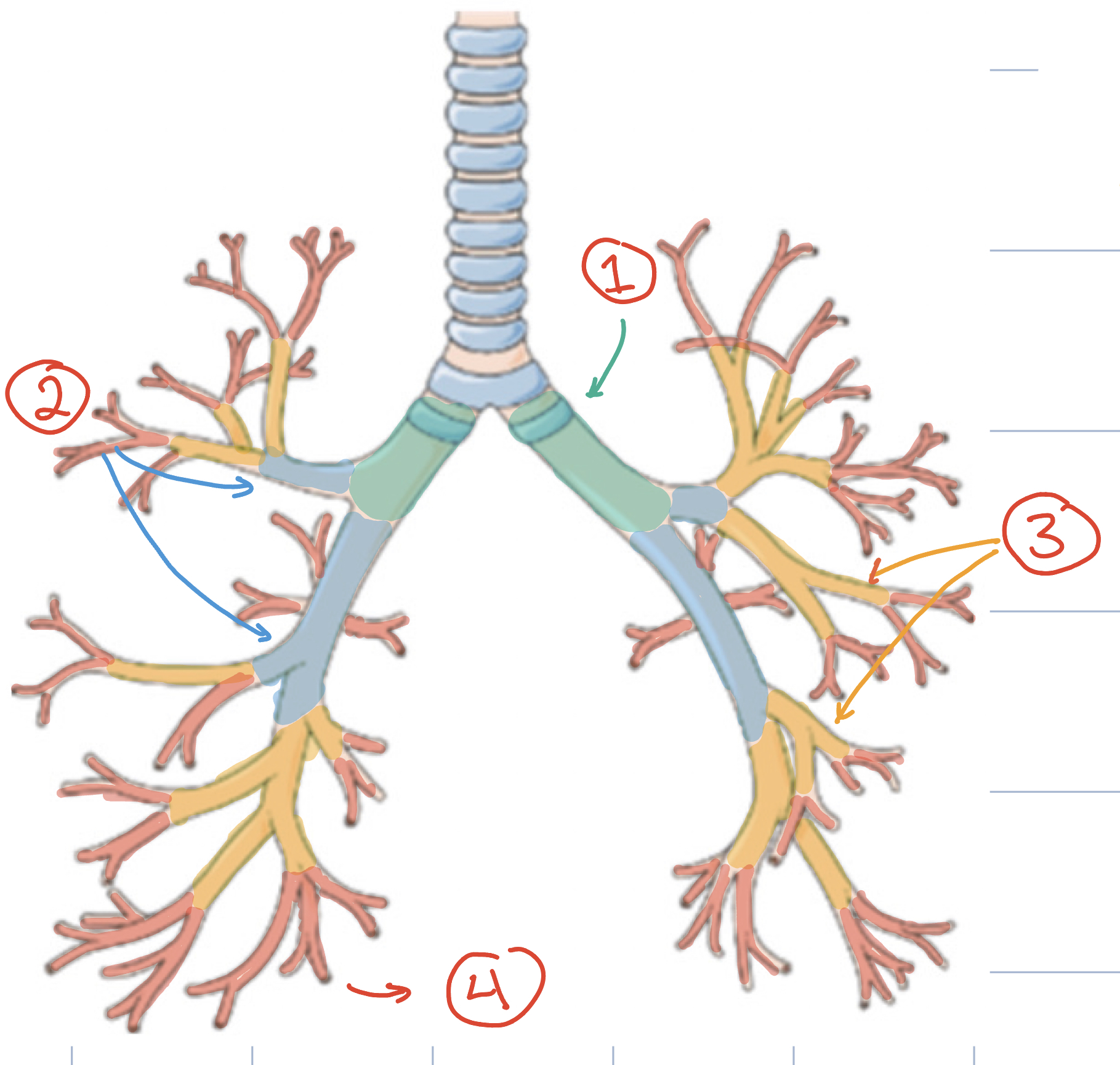
1) primary bronchi 2) secondary bronchi 3) tertiary bronchi 4) terminal bronchioles
59
New cards
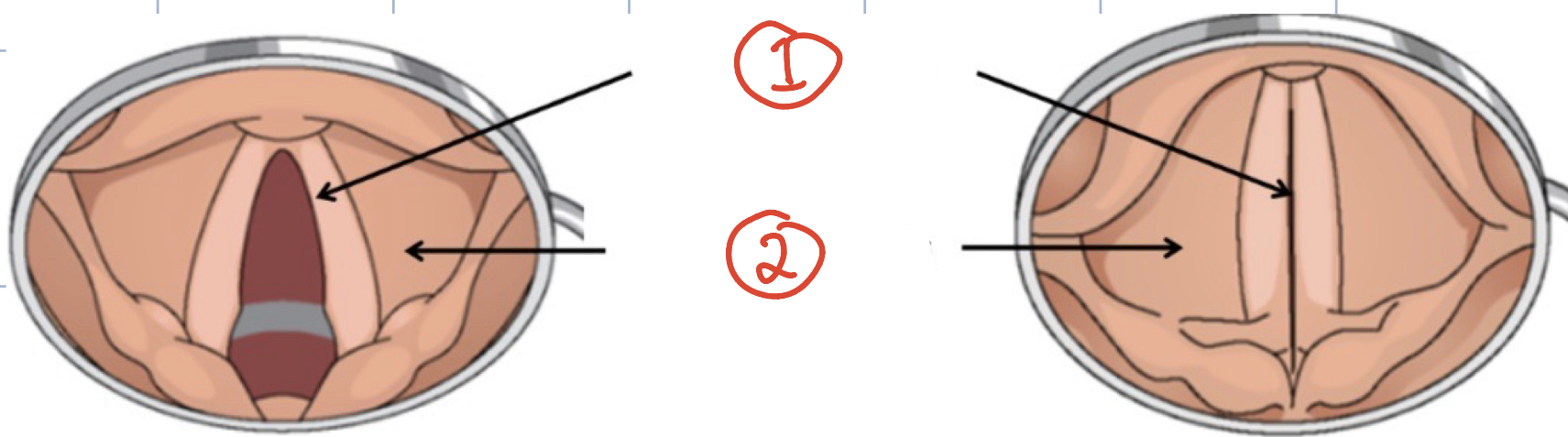
1) True vocal cords 2) False vocal cords
60
New cards
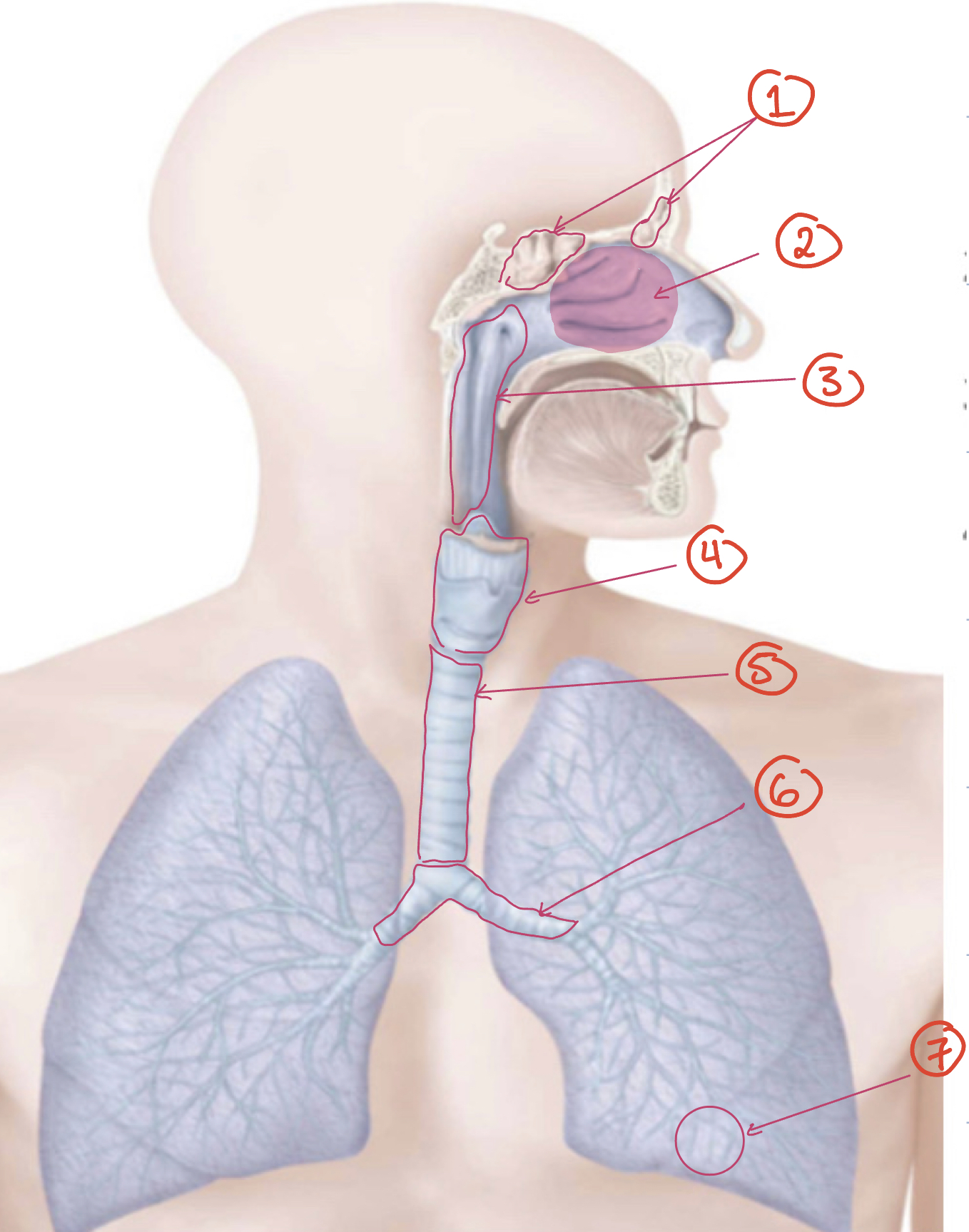
1) paranasal sinuses 2) nose & nasal cavity 3) pharynx 4) larynx 5) trachea 6) primary bronchi 7) end of conducting portion
61
New cards
Respiratory Portion
allow gas exchange btwn air & blood, walls = 1 cell layer thick, make up majority of lung tissue
62
New cards
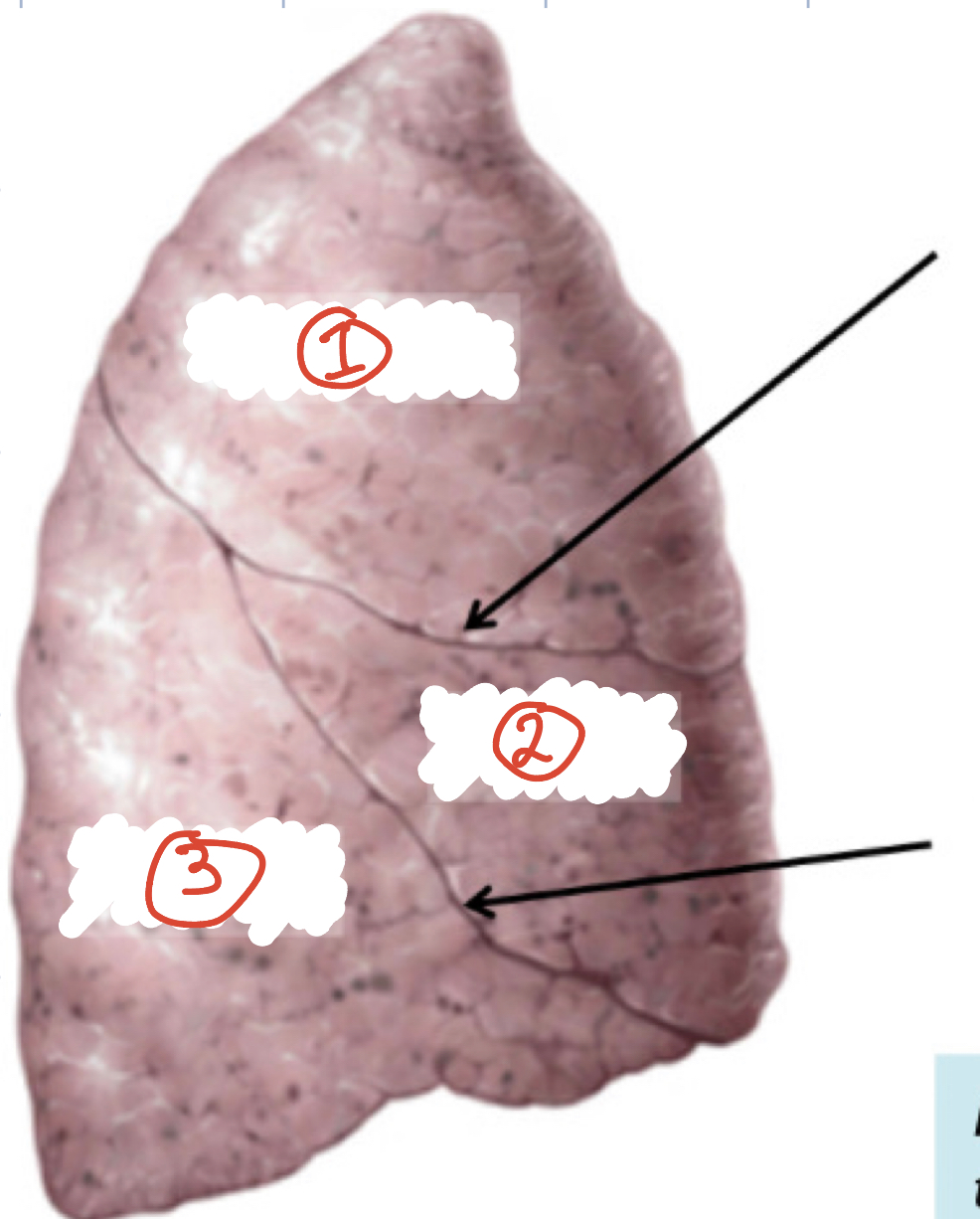
Lobes of Right lung: (3)
1) Superior 2) Middle 3) Inferior
63
New cards
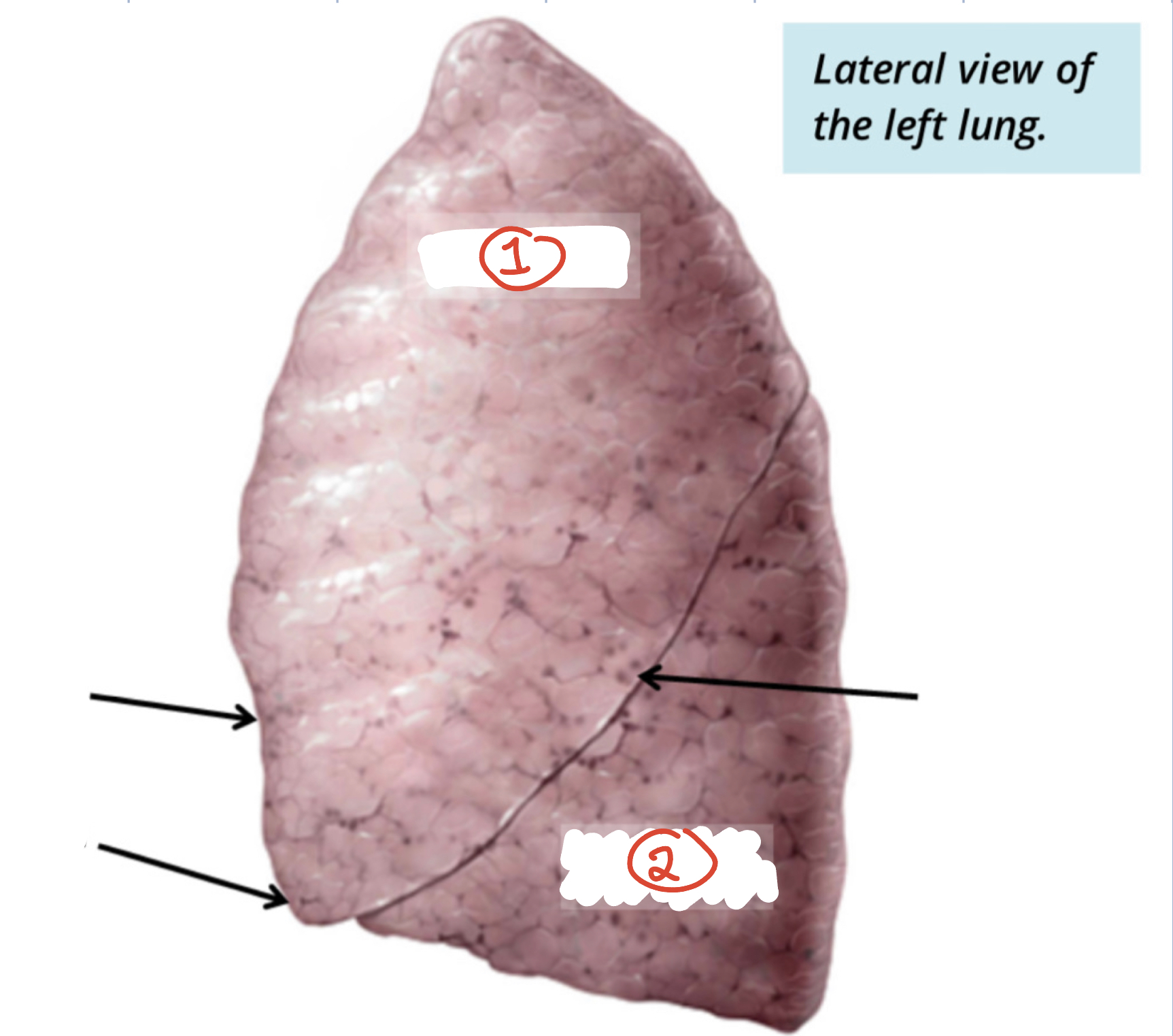
Lobes of Left Lung (2)
1) Superior 2) Inferior
64
New cards
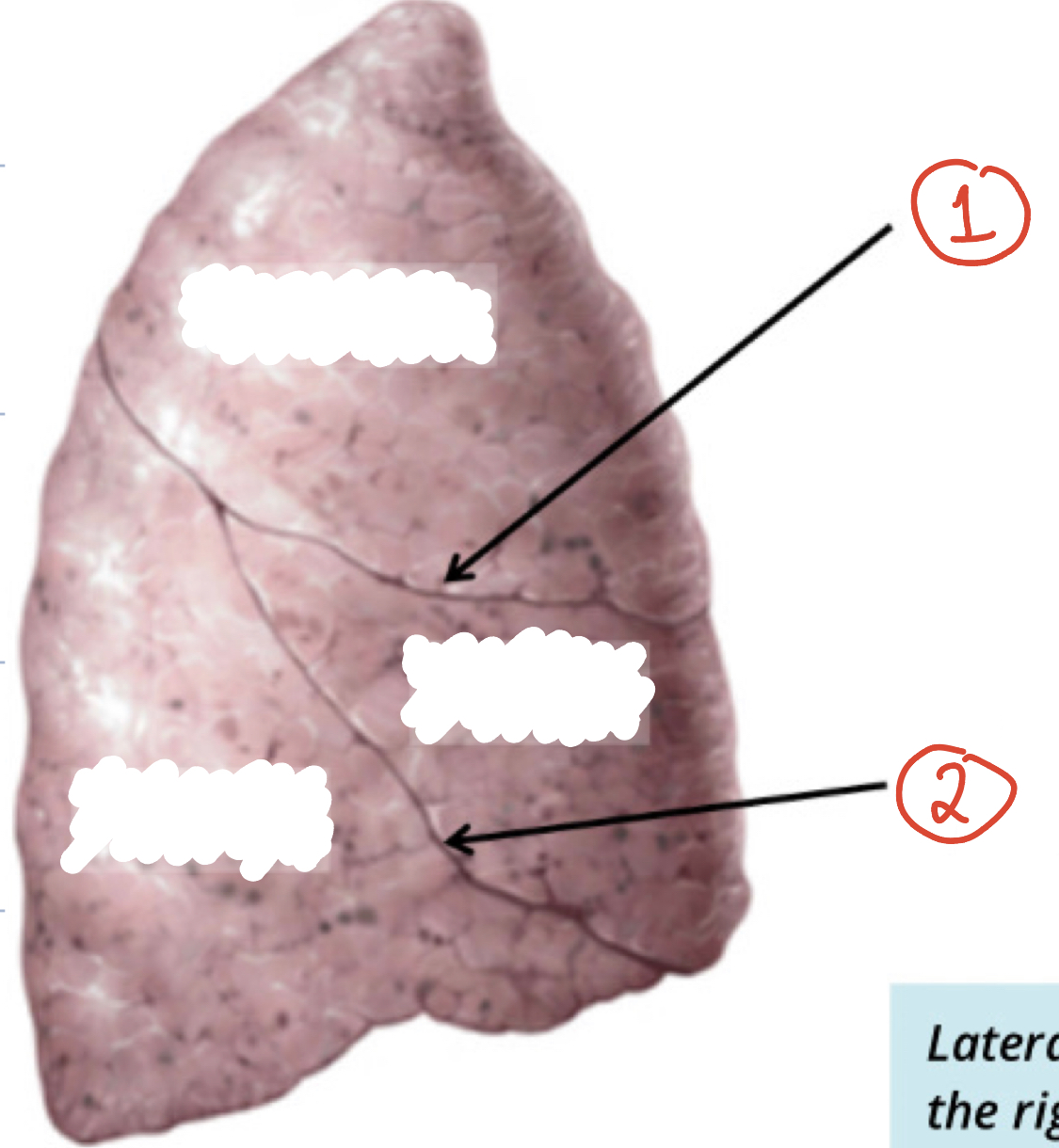
fissures of right lung (2)
1) Horizontal Fissure 2) Oblique Fissure
65
New cards
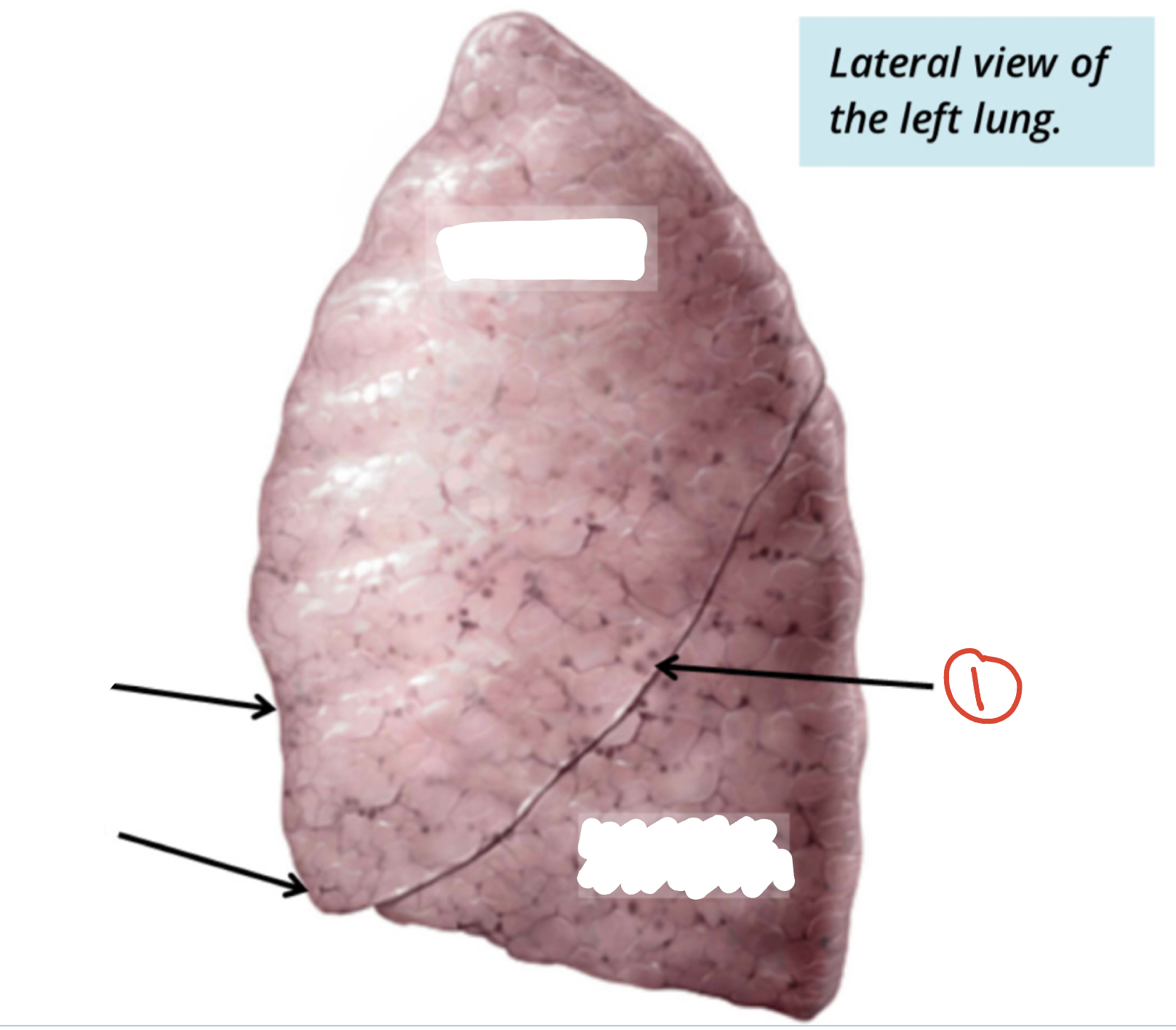
fissures of left lung (1)
1) oblique fissure
66
New cards
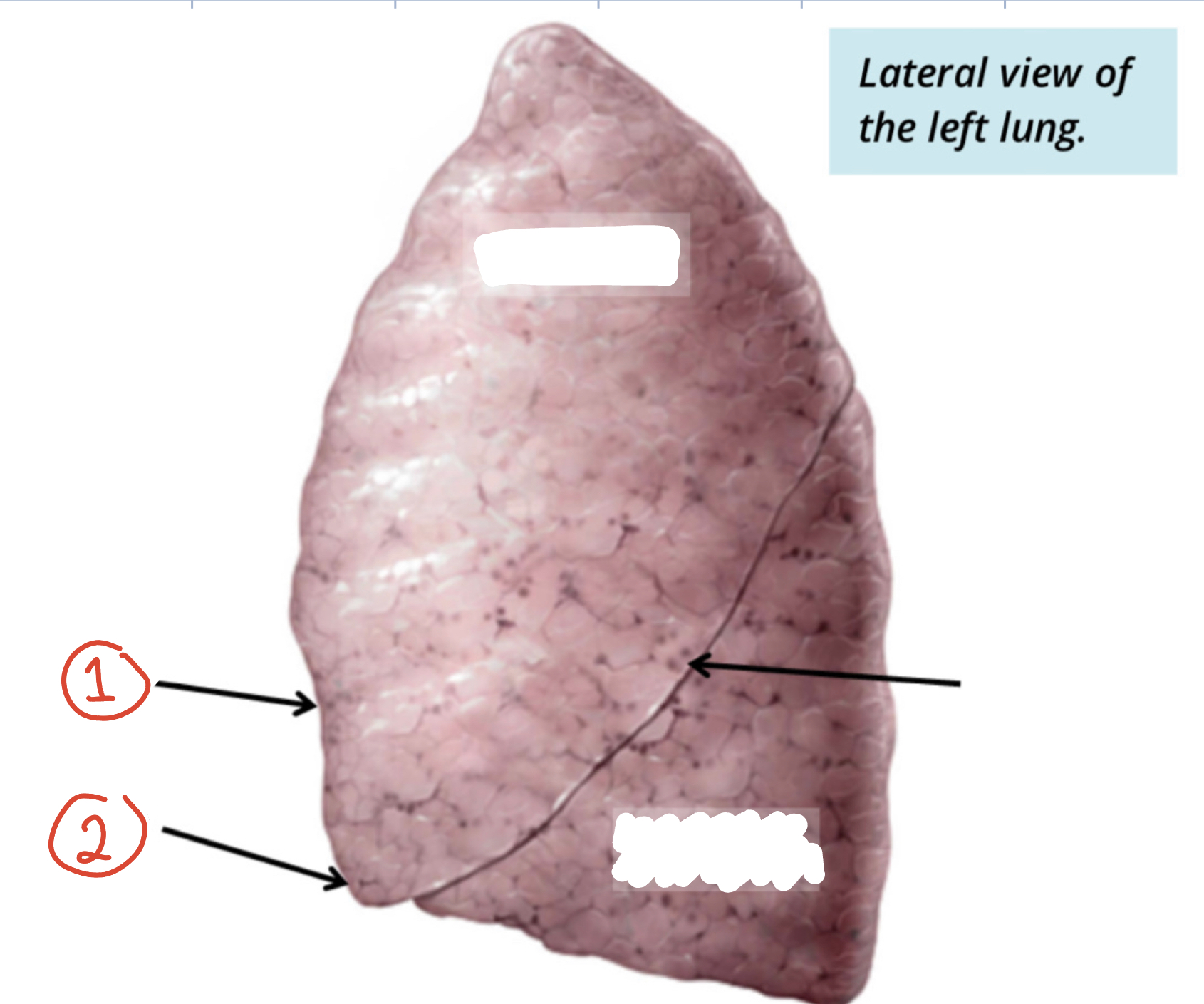
features of left lung
1) Cardiac Notch 2) lingula
67
New cards
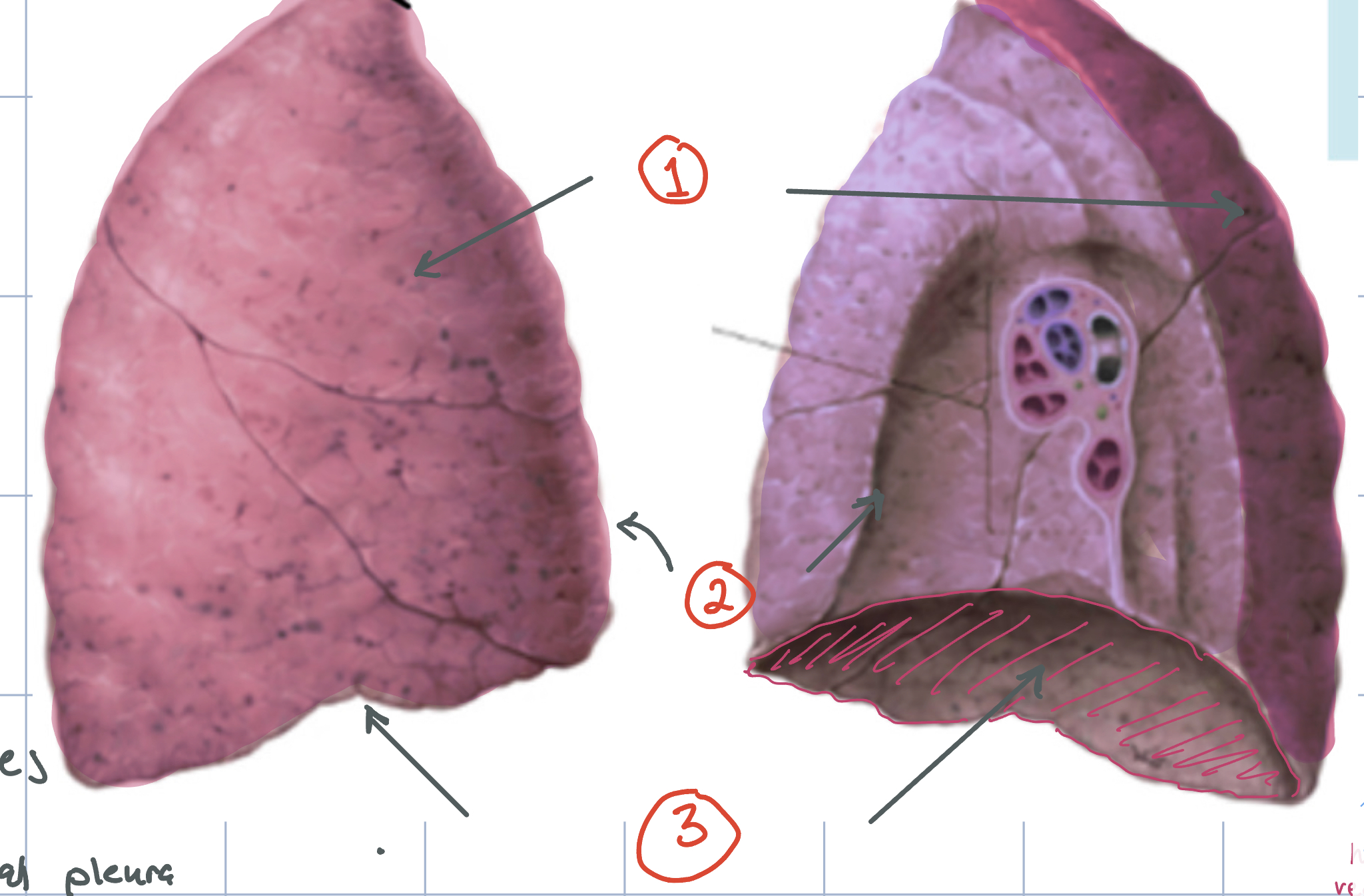
Surfaces of lungs
1) Coastal Surface 2) Mediastinal Surface 3) Diaphragmatic Surface
68
New cards
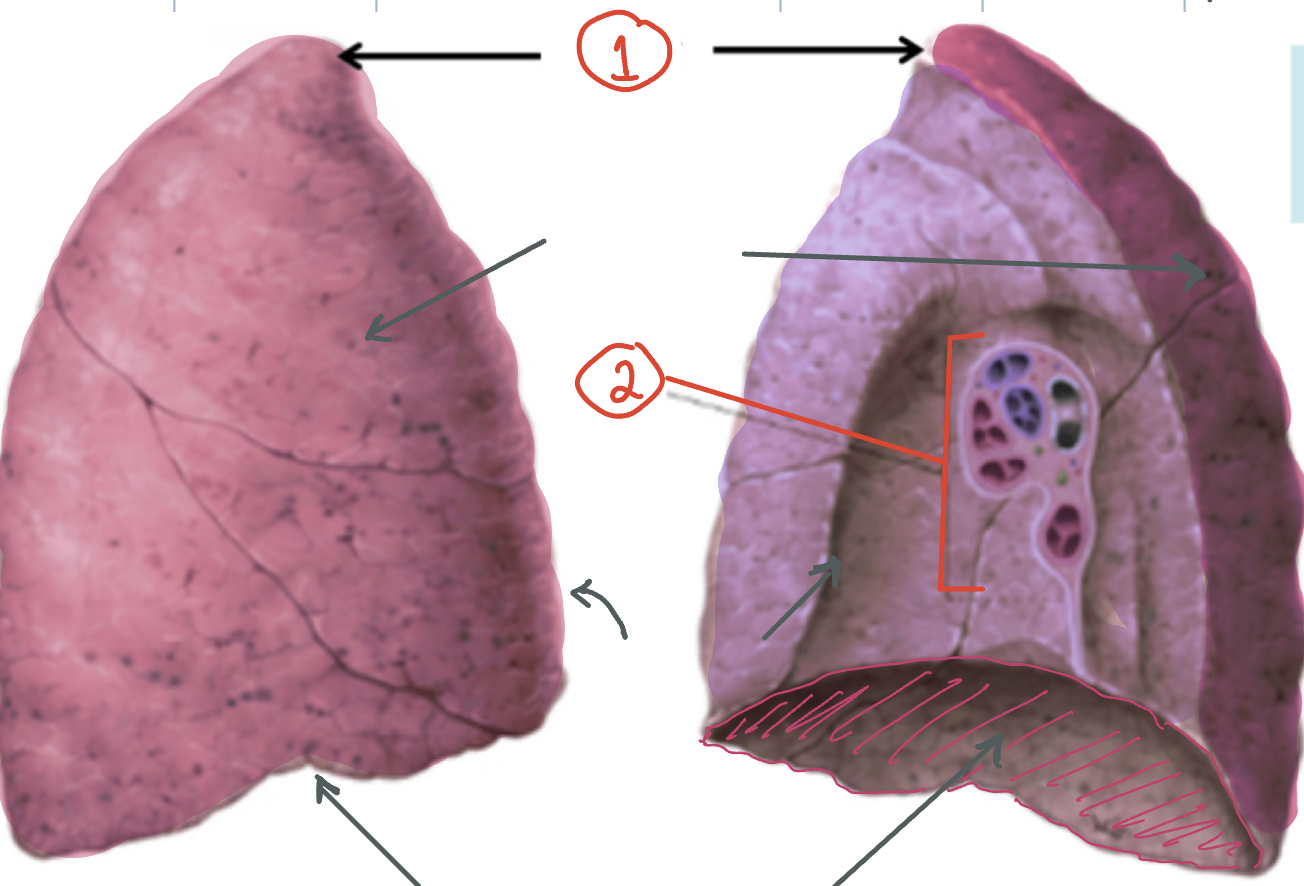
1) Apex 2) Hilus
69
New cards
Pleural Membranes (2) + function
1. parietal pleura
2. visceral pleura
serous membranes, protect lungs, secrete pleural fluid → fill pleural space btwn membranes, lubricant for sliding during inflation & deflation, are continuous w/ each other at hilus
70
New cards
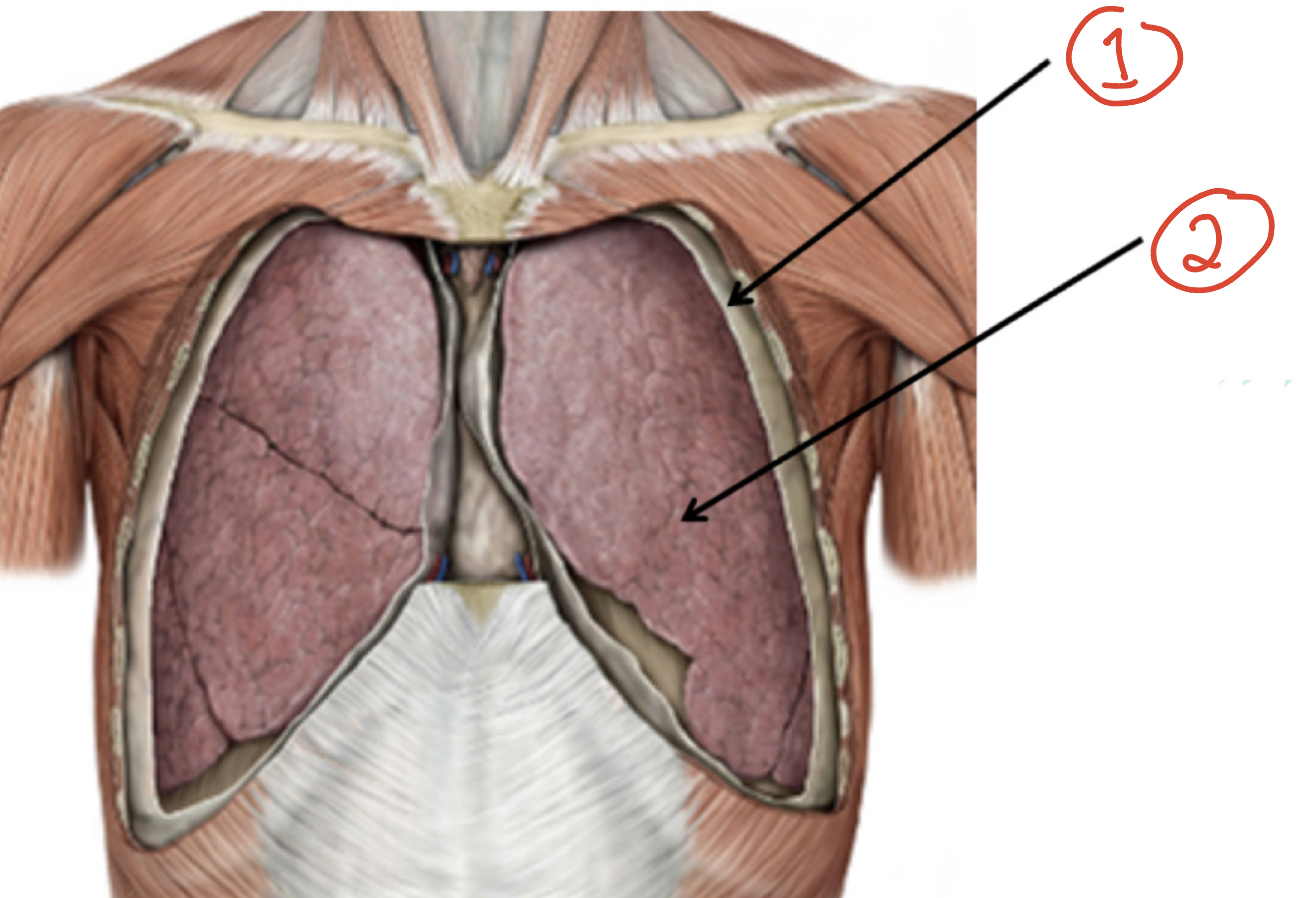
1) Parietal Pleural (outer) 2( Viscera pleura (inner)
71
New cards
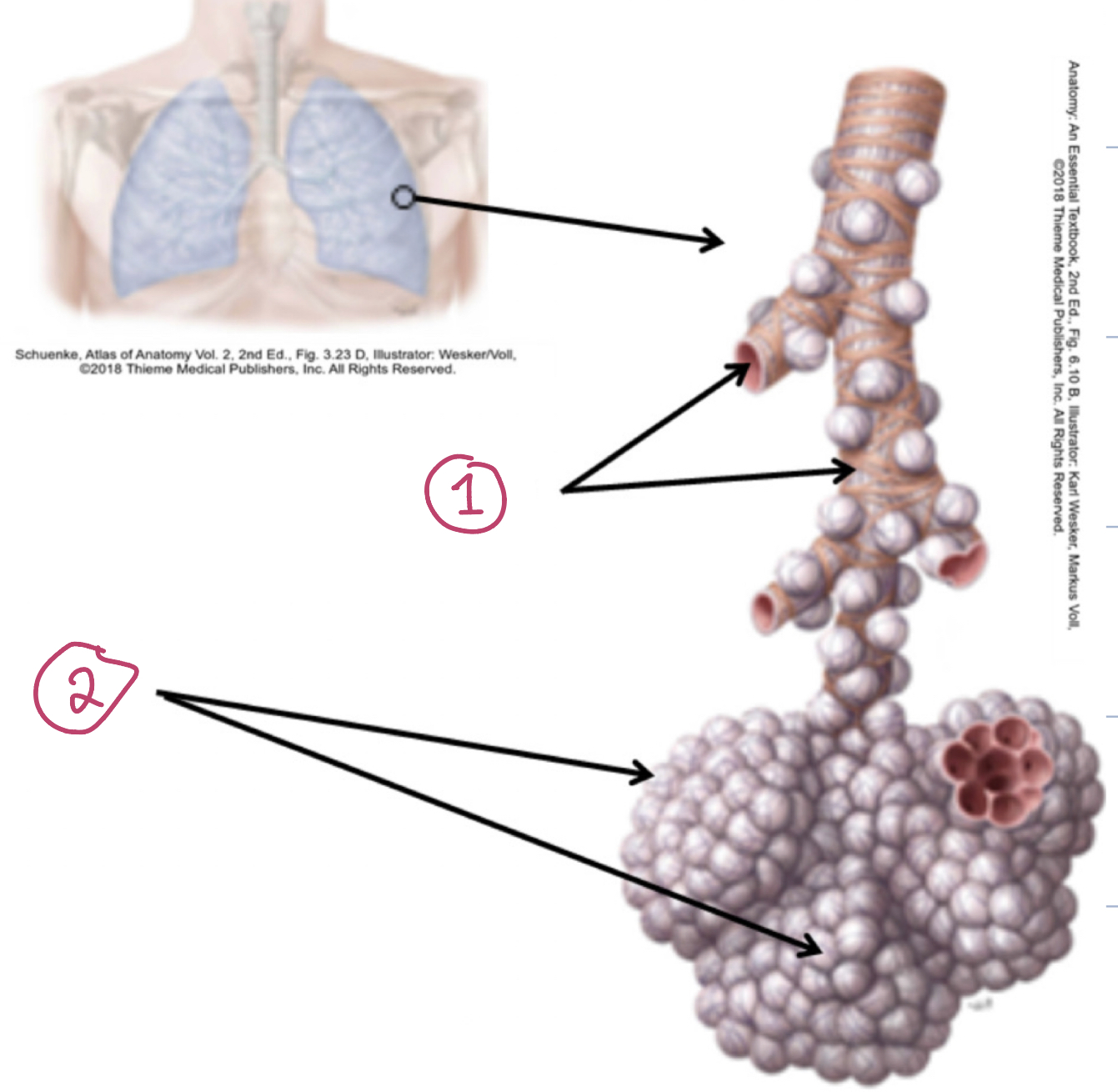
1) Respiratory Bronchioles 2) Alveoli
72
New cards
Respiratory Bronchioles
Branch out from terminal bronchioles, 1st structure for gas exchange, thin walled ducts, simple ciliated cuboidal epithelium, branch into alvelo
73
New cards
Alveoli
functional unit of lung, gas exchange take place here, surrounded by capillaries
74
New cards
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
inflammation of airways → limit air flow, produce more mucus (clog airways, hard to breathe), smaller & constricted lumen, damaged air sacs → lose elasticity