Cell Transport Mechanisms and the Cell Cycle
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Physical (Passive) Mechanisms
Do not require cellular energy (ATP) and include diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and filtration.
Diffusion
Movement of atoms, molecules, or ions, from region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration, occurring due to constant motion of atoms, molecules, ions.
Example of Diffusion
A sugar cube dissolving in water.
Equilibrium in Diffusion
Solutes and water can diffuse across a membrane that is permeable to both of them until they reach equilibrium; at that point, the concentrations of water and the solute are equal in both compartments.
Osmosis
Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from region of higher water concentration to region of lower water concentration, often called 'diffusion of water'.
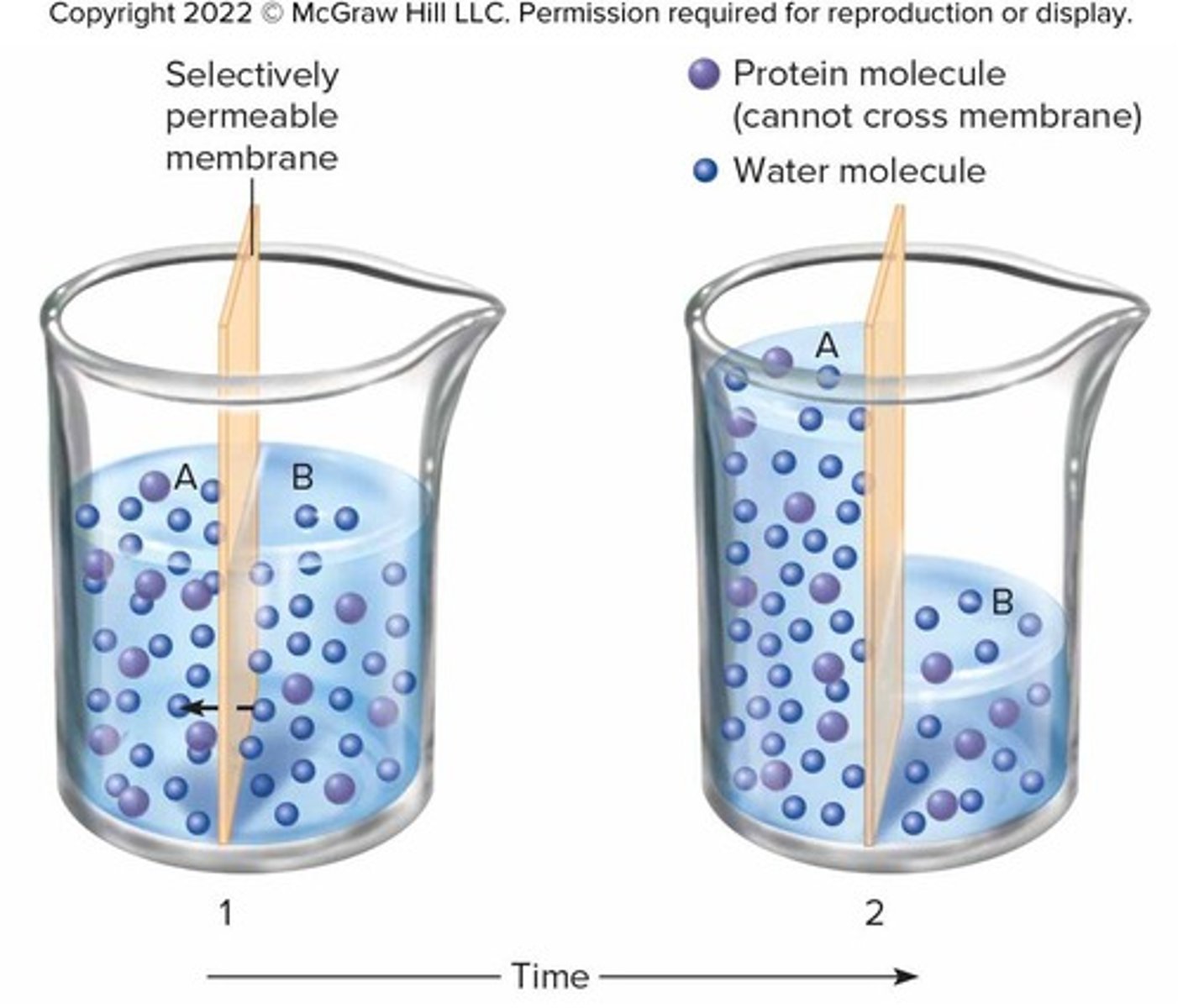
Passive Process of Osmosis
Water moves into a region containing higher impermeant solute concentration without requiring ATP.
Osmotic Pressure
Ability of osmosis to generate enough pressure to lift a volume of water, which increases as the concentration of impermeant solutes increases in a solution.
Tonicity
Ability of a solution outside cell to alter water volume inside cell.
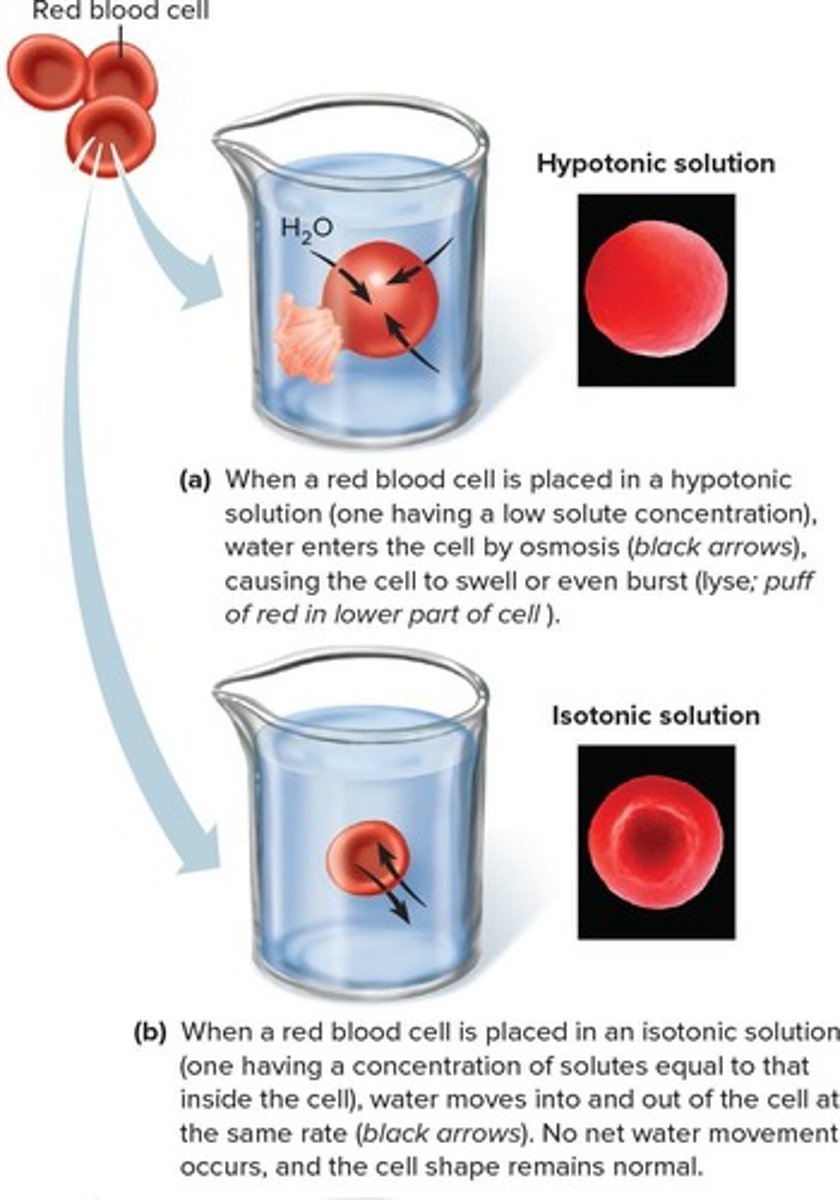
Isotonic Solution
A solution with the same osmotic pressure; cells in an isotonic solution have no net gain or loss of water.
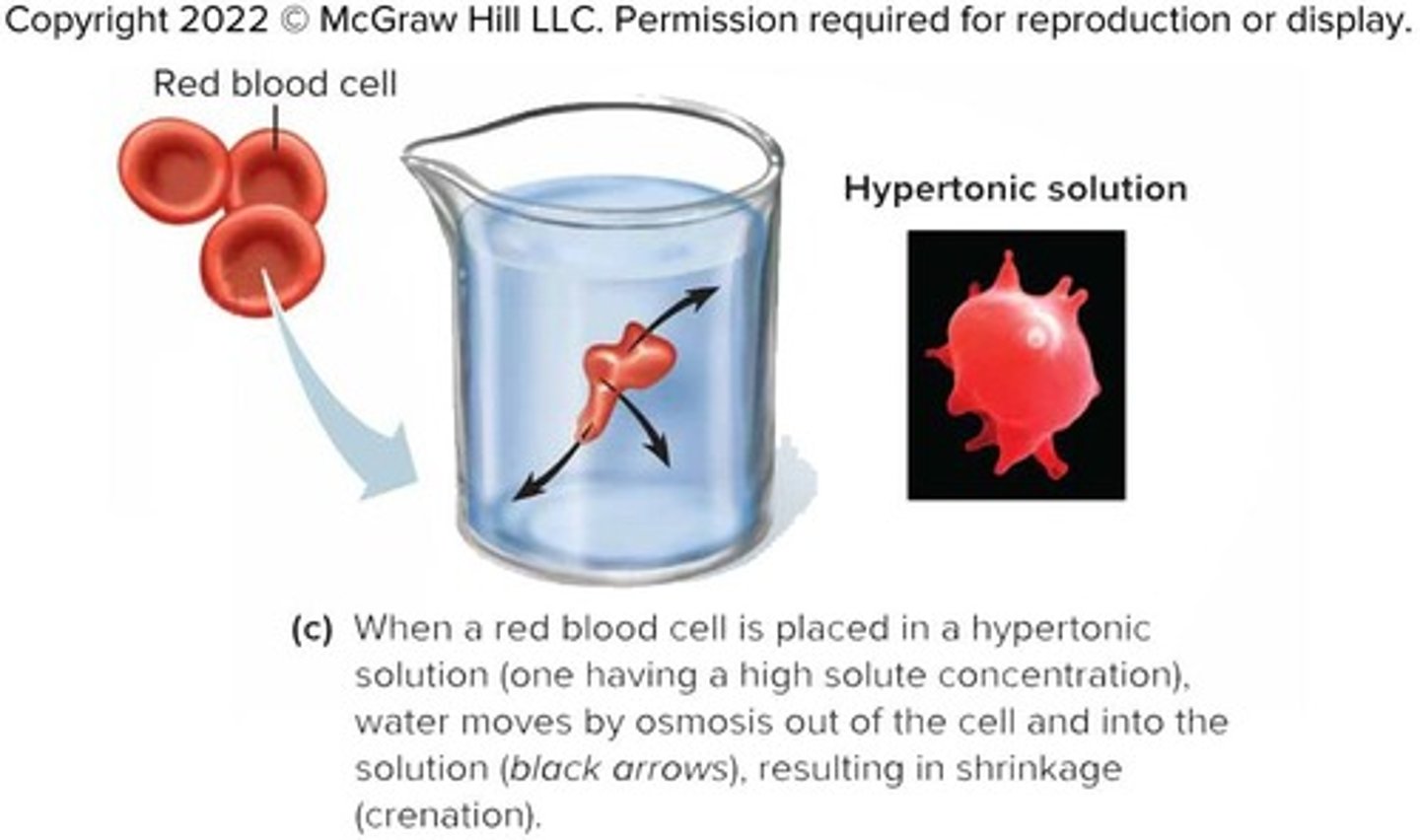
Hypertonic Solution
A solution with higher osmotic pressure; cells in a hypertonic solution lose water.
Hypotonic Solution
A solution with lower osmotic pressure; cells in a hypotonic solution gain water.
Active Mechanisms
Require ATP to move substances across cell membrane
Active Transport
Movement of substances across a membrane from region of lower concentration to region of higher concentration (against concentration gradient)
Carrier Molecules
Molecules in cell membrane, often called 'pumps', that facilitate active transport
Endocytosis
Process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment
Exocytosis
Process by which cells expel substances to the external environment
Transcytosis
Process that involves the transport of substances across a cell
Secondary Active Transport
A carrier protein uses a Na+ gradient to transport another substance across a cell membrane; this process does not require ATP energy
Cell Cycle
Series of changes a cell undergoes from the time it forms until the time it divides
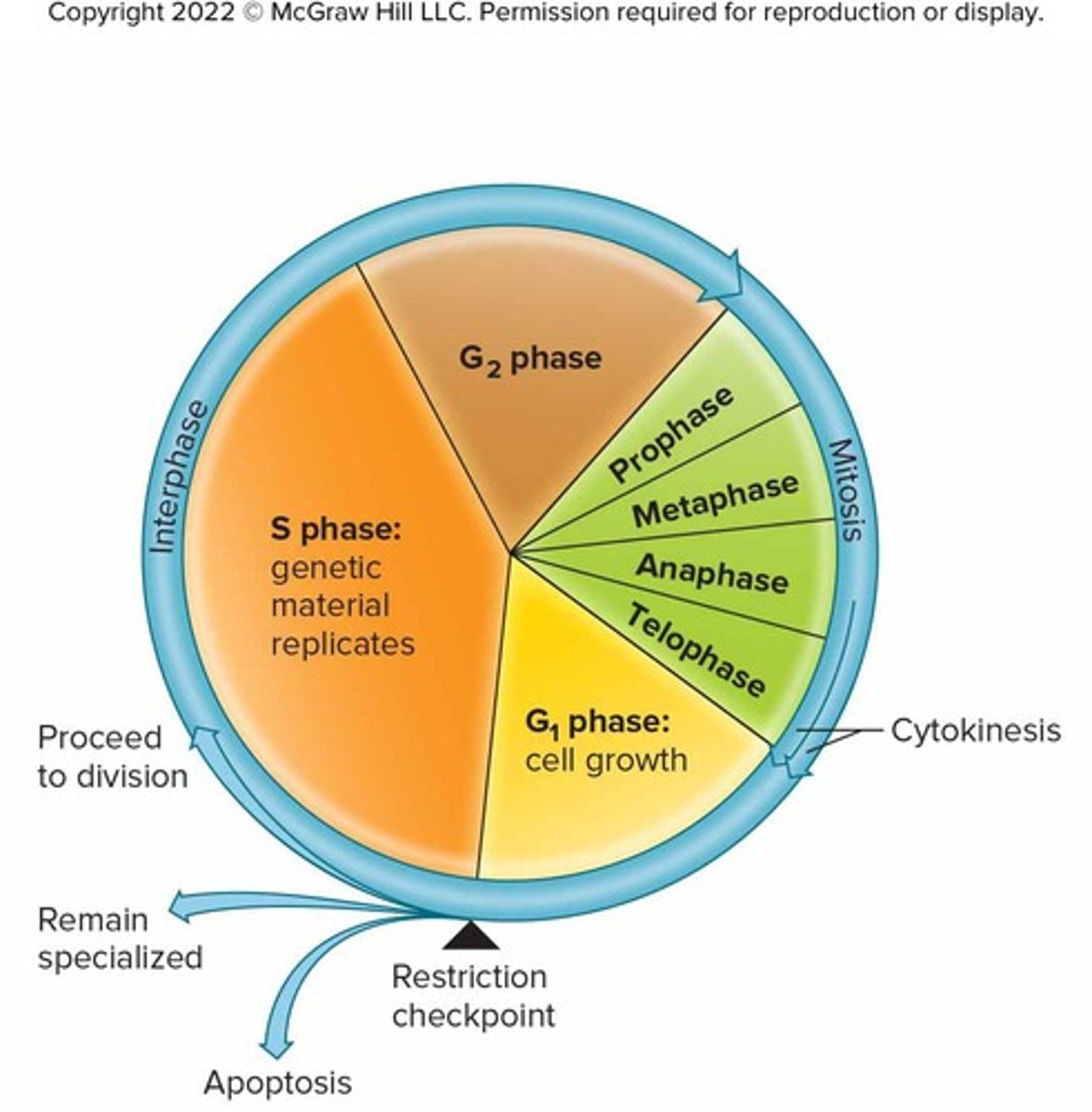
Interphase
Growth of cell, maintenance of normal functions, and preparation for mitosis and cytokinesis
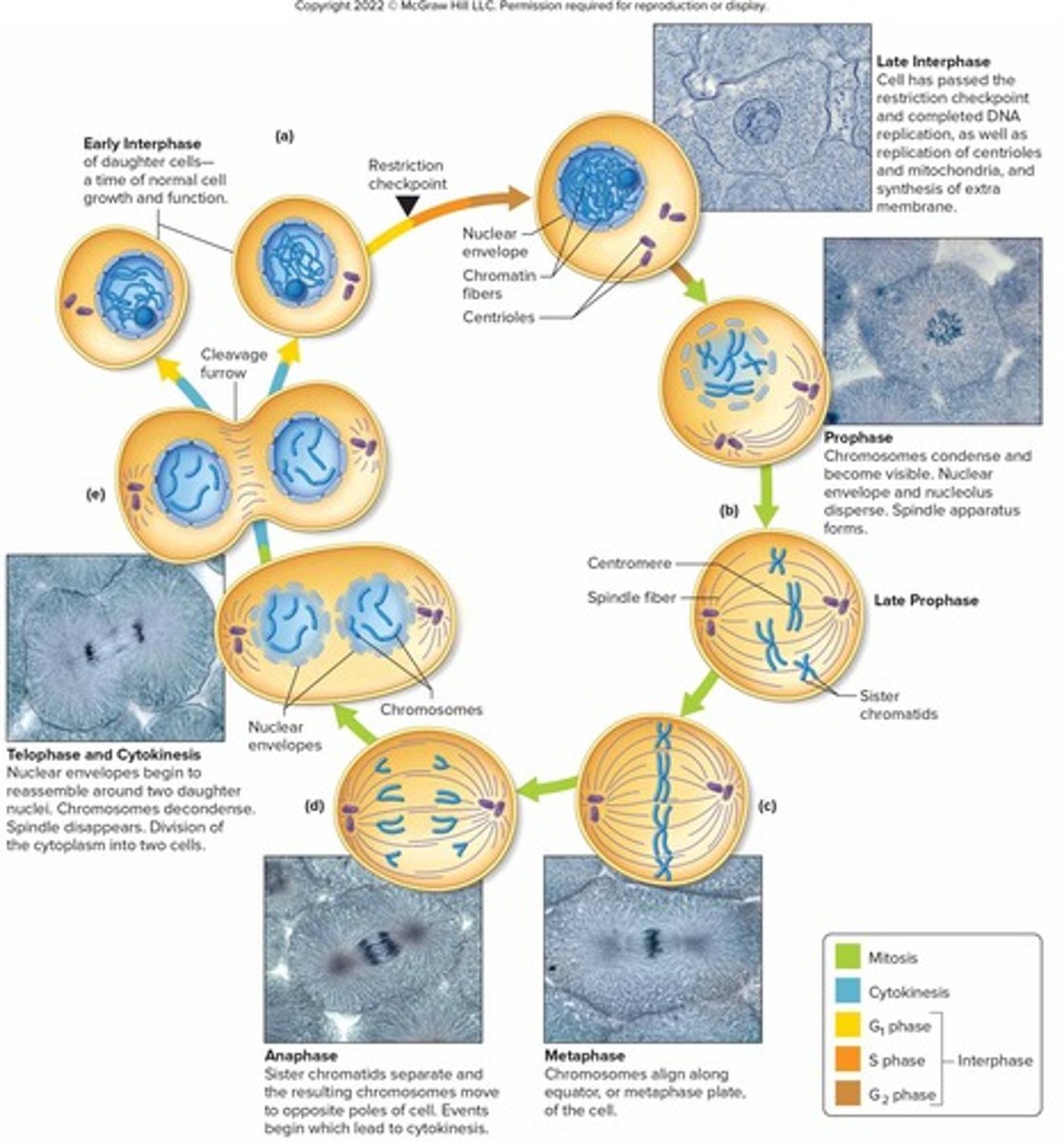
Mitosis
Division of the nucleus via karyokinesis
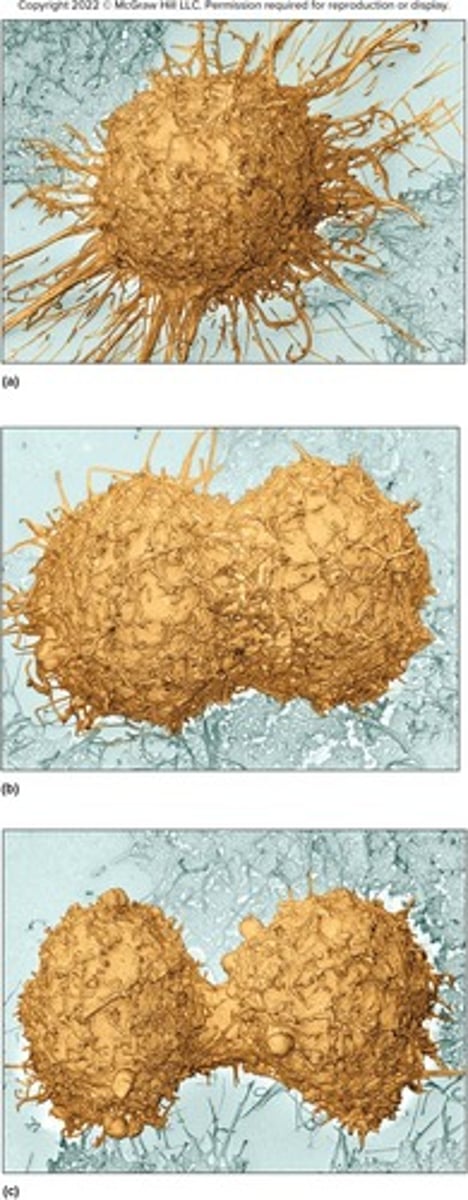
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
S Phase
Phase of interphase where DNA is replicated
G1 and G2 Phases
Phases of interphase where structures and other molecules are duplicated
Prophase
Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite sides of cytoplasm, nuclear envelope and nucleolus disperse
Metaphase
Spindle fibers from centrioles attach to chromosomes and align them midway between centrioles
Anaphase
Chromosomes separate and move in opposite directions toward centrioles as the spindle fibers shorten
Telophase
Chromosomes return to chromatin structure, nuclear envelope forms around each chromosome set, and nucleoli become visible
Cytoplasmic Division
Cytokinesis, which begins during anaphase and continues through telophase
Contractile Ring
Structure of actin filaments that pinches cytoplasm in half during cytokinesis
Cleavage Furrow
Constriction formed during cytokinesis as the contractile ring pinches the cytoplasm
Daughter Cells
Newly formed cells that will have identical DNA, may have slightly different size and number of organelles