micro importants
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
capital
manufactured goods used to make other goods and services.
command economy
an economy in which industry is publicly owned and a central authority makes production and consumption decisions.
economics
the study of scarcity and choice.
economy
a system for coordinating a society's productive and consumptive activities.
incentives
rewards or punishments that motivate particular choices.
individual choice
decisions by individuals about what to do, which necessarily involve decisions about what not to do.
macroeconomics
the branch of economics that is concerned with the overall ups and downs of the economy.
marginal analysis
the study of the costs and benefits of doing a little bit more of an activity versus a little bit less.
market economy
an economy in which the decisions of individual producers and consumers largely determine what, how, and for whom to produce, with little government involvement in the decisions.
microeconomics
the branch of economics that studies how individuals, households, and firms make decisions and how those decisions interact.
normative economics
the branch of economic analysis that makes prescriptions about the way the economy should work.
opportunity cost
the real cost of an item: what you must give up in order to get it.
positive economics
the branch of economic analysis that describes the way the economy actually works.
resource
anything that can be used to produce something else.
scarce
in short supply; when a resource is not available in sufficient quantities to satisfy all the various ways a society wants to use it.
efficient
describes a market or economy in which there is no way to make anyone better off without making at least one person worse off.
production possibilities curve
illustrates the trade
productive efficiency
achieved by an economy if it produces at a point on its production possibilities curve.
technology
the technical means for producing goods and services.
trade
off
absolute advantage
the advantage conferred by the ability to produce more of a good or service with a given amount of time and resources; not the same thing as comparative advantage.
comparative advantage
the advantage conferred by an individual if the opportunity cost of producing the good or service is lower for that individual than for other people.
gains from trade
an economic principle that states that people can get more of what they want through trade than they could if they tried to be self
specialization
each person specializes in the task that he or she is good at performing.
terms of trade
indicate the rate at which one good can be exchanged for another.
trade
when individuals provide goods and services to others and receive goods and services in return.
budget constraint
limits the cost of a consumer's consumption bundle to no more than the consumer's income.
budget line
shows the consumption bundles available to a consumer who spends all of his or her income.
consumption possibilities
the set of all consumption bundles that are affordable, given a consumer's income and prevailing prices.
marginal utility
the change in total utility generated by consuming one additional unit of a good or service.
marginal utility curve
shows how marginal utility depends on the quantity of a good or service consumed.
marginal utility per dollar
the additional utility from spending one more dollar on a good or service.
optimal consumption bundle
the consumption bundle that maximizes the consumer's total utility given his or her budget constraint.
optimal consumption rule
says that in order to maximize utility, a consumer must equate the marginal utility per dollar spent on each good and service in the consumption bundle.
principle of diminishing marginal utility
the idea that each successive unit of a good or service consumed adds less to total utility than does the previous unit.
util
a unit of utility.
utility
a measure of personal satisfaction.
economic profit
total revenue - opportunity cost
explicit cost
cost that involves moeny
implicit cost
cost that is measured in other value - other than money
marginal revenue curve
shows how marginal revenue changes as output changes
optimal output rule
profit is maximized y producing when MC=MR
fixed input
input whose quantity is fixed for a period of time and can not be changed during this time
long run
a time period in which all inputs can be changed
short run
the time period in which at least one input is fixed
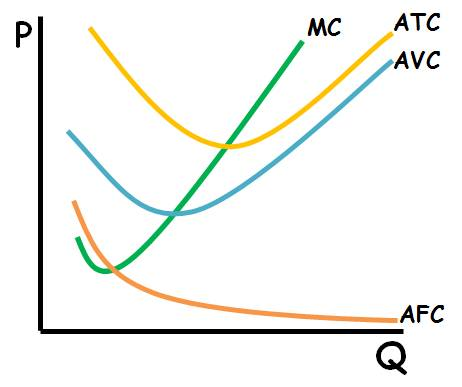
average fixed cost
the fixed cost per unit of output
average product
total product per unit of output
average total cost
total cost per unit of output
average variable cost
the variable cost per unit of output
fixed cost
a cost that doesn’t depend on the quantity of output produced
total cost
the sum of fixed and variable costs at any level of output
variable cost
cost that depends of quantity of output produced
constant returns to scale
when output increases in proportion to an increase in inputs
ex: increase in inputs by 20% and output increases by 20%
decreasing returns to scale
decreasing inputs your output will directly decrease in proportion
returns to scale
when i scale up, what do I get back?
diseconomies of scale
when output increases less than in proportion to an increase in inputs
ex: increase in inputs by 30% and out put increases by 20%
economies of scale
when output increases more than in proportion to and increase in inputs
ex: increase inputs by 20% and output increases by 30%
increasing returns to scale
occurs when increasing inputs leads to a more than proportionate increase in output, resulting in reduced per-unit costs.
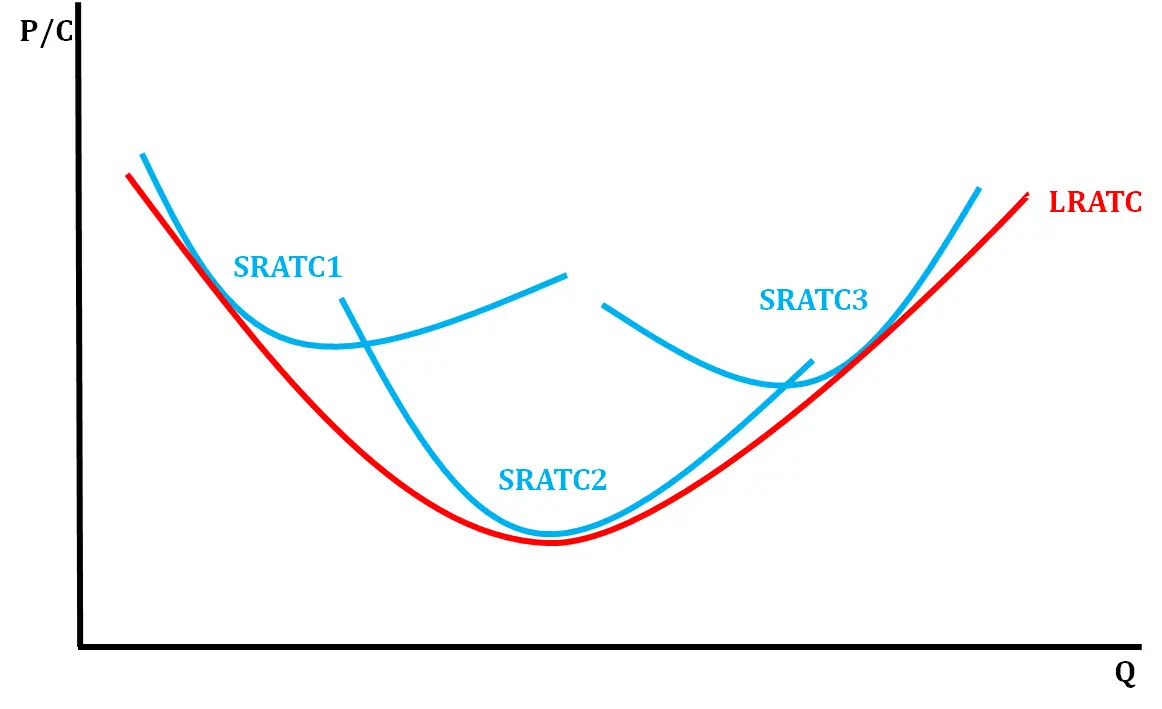
long run average total cost curve
lowest average total cost curve at each level of output
sunk cost
cost that has been incurred and cannot be recovered.
price taking firms optimal rule
produce where P = MC
break-even point
where you are neither loosing or gaining money for the price that you are selling at
shut down price
P ≦ AVC; point where firm should stop producing
total fixed cost
cost of fixed inputs
total variable cost
cost depending on quantity produced
total cost
sum of fixed cost and variable cost of producing a given quantity of output
what does a “average cost curve” look like
characteristics of perfect competition
many small firms
identical goods
low barrier to entry
firms are PRICE TAKERS
firms break even in the LR
perfect competition
many firms produce identical products
accounting cost
all explicit costs
economic costs
implicit and explicit costs
perfect competition equalibrium point
ATC = MR = MC
perfect competitive market profit loss
when min ATC > MR
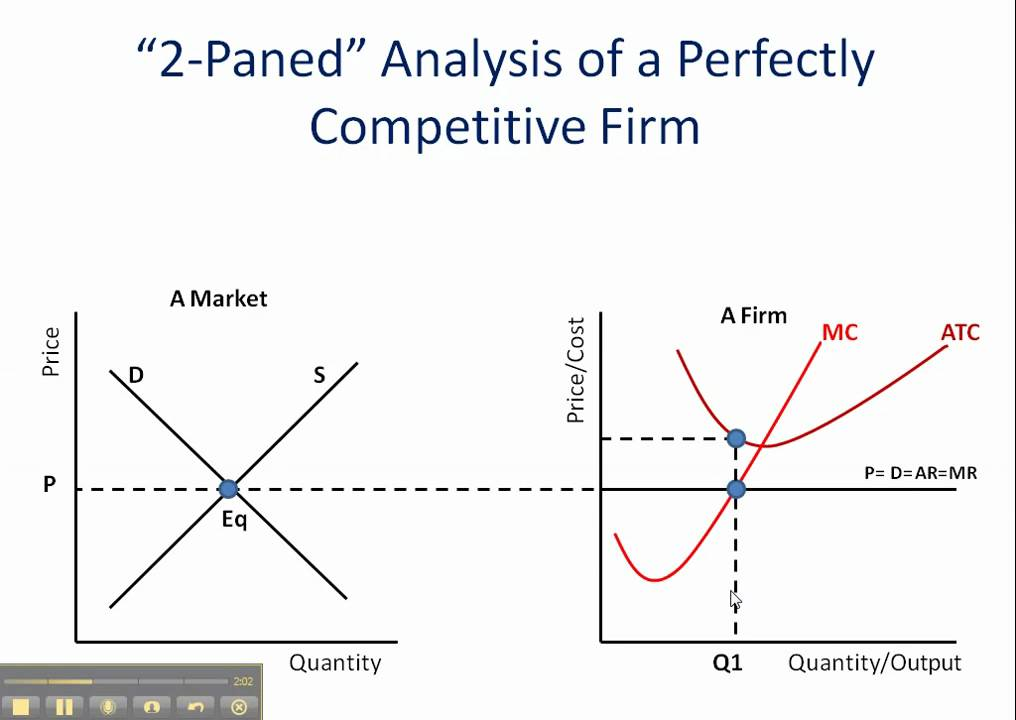
perfectly competition market profit gain
when min ATC < MR
long run supply curve
how quantity supplied responds to the price once producer have had the time to exit/enter the industry
constant cost industry
newly entered firms don’t increase costs for firms already in the market
increasing cost industry
newly entered firms increase the cost for other firms already in the market
decreasing cost industry
newly entered firms decrease costs for existing firms in the market
normal profit
when economic profit is 0
monopoly
one firm which controls the market
oligopoly
when multiple firms dominate th emarket
monopolistically competitive markets
large # of seller w differentiate products
differentiated products
companies selling very similar products with with distinct differences
imperfectly competitive market characteristics
few large frism
firms are price makers
high parriers to enter
earn long-run profit
subsidy
gift of money from government to help firms produce more l
lump-sum subsidy
one -time payment provided to firms to support their production efforts.
per-unit subsidy
financial assistance given by the govt for each unity of good sold —> leads to and increase in supply because marginal costs are reduced
prices discrimination
when specific products are sold to different groups of people for different prices
characteristics of price descrimination
has to ve a monopolistic power
has to be able to group people together to discriminated against
no consumer surplus
allocatively efficient ; productively inefficient