L33 How DNA is transferred between materials
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from the Microbial Genetics lecture on how DNA is transferred between microbes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Transfer of genetic material directly from one organism to another. This is a process specific to bacteria.
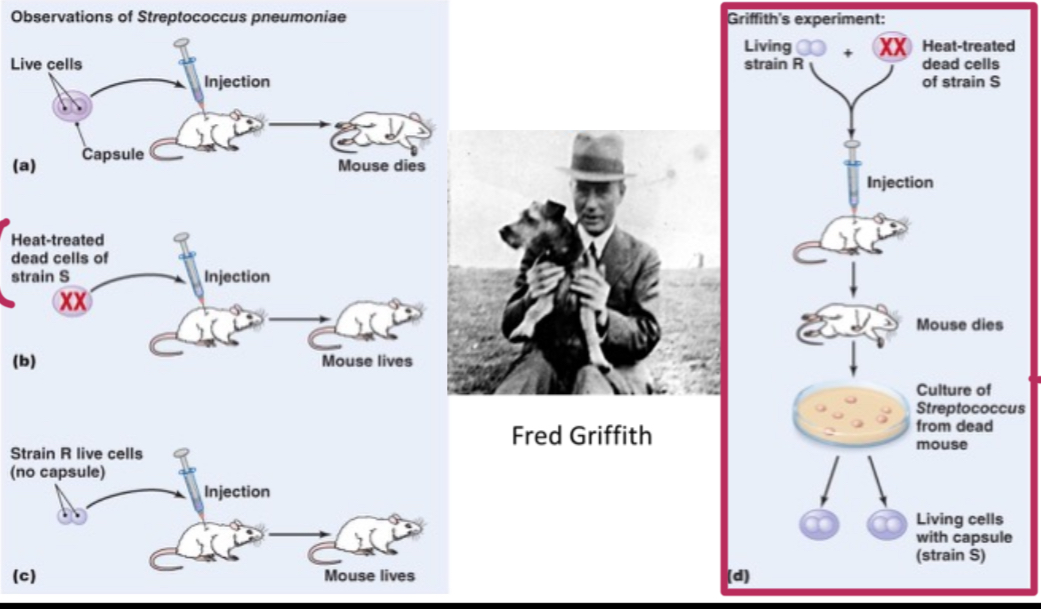
Griffiths experiment demonstrating horizontal gene transfer
Streptococcus had S strain (fatal) and R strain (negligable). He heat treated S strain cells which were then negligible (mouse lived). Then he injected mouse with both heat treated S strain and R strain and mouse died. Culture shows living cells with S strain.
Properties of bacterial genome
Single, circular chromosome, nucleoid, and plasmids (self replicating DNA molecules in cytosol)
Vertical Gene Transfer
Transfer of genetic material from parent to offspring.
Virulence Factors
Attributes that help bacteria survive in the host, sometimes at a cost to the host. Eg capsules on streptoccocus pnuemonia.
Antibiotic Resistance
Attributes that reduce the effectiveness of antibiotics against the targeted bacteria. Eg plasmid carrying Beta-lactamase enzyme (inactivates penicillin)
Types of horizontal gene transfer
Transformation, transduction, conjugation.
Transformation
Uptake of short fragments of naked DNA from the environment by naturally transformable bacteria.
Transduction
Transfer of DNA between bacteria via bacteriophages (virus). During assembly of bacteriophage, instead of being filled with its own DNA it takes in plasmids. Then goes on to replicate.
Conjugation
Direct transfer of DNA between live bacterial cells via sexual pilus, requires cell to cell contact. Pilus attaches to other cell, plasmid unwinds and travels across pilus.
Bacteriophages
Viruses that specifically target and kill bacteria; used in phage therapy.
Phage Therapy
The therapeutic use of bacteriophages to treat pathogenic bacterial infections.
