Med. Procedures Lec. - Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
What is an example of administering medication?
A medical assistant gives an IM injection to a patient.
2
New cards
The term parenteral refers to:
Sites located outside the gastrointestinal tract.
3
New cards
Which of the following is assigned by the pharmaceutical company that first develops a drug?
Generic Name
4
New cards
What is the name of a drug preparation that is applied externally to produce a feeling of heat or warmth?
Liniment
5
New cards
1 ml = ? cc
1 cc
6
New cards
Which system is used most often to prescribe and administer medication?
Metric
7
New cards
What is the term for the slanted edge at the top of a needle?
Bevel
8
New cards
Lumen sizes
The smaller the gauge number the larger the lumen. For example, an 18 G lumen is larger than a 27 G lumen.
9
New cards
Which of the following is a function of the flange of a syringe?
Helps in injecting the medication
10
New cards
Which of the following techniques should not be preformed when an ampule is used to administer medication?
Inject air into the ampule before removing the medication.
11
New cards
Which of the following is used to administer an intradermal injection?
Tuberculin syringe
12
New cards
The purpose of aspirating when administering an injection is to
Ensure that the needle is not in a blood vessel.
13
New cards
Which of the following needle lengths is used to administer an intramuscular injection into the dorsogluteal site on an average size adult?
1 1/2 inches
14
New cards
The vastus lateralis site is used most often to administer medication to
Infants and young children
15
New cards
What angle of needle insertion should be used to administer an IM injection?
90 degrees
16
New cards
The Z-track method is used to administer medications that are
irritating to the subcutaneous tissue
17
New cards
Which of the following is used to administer an intradermal injection? (what size?)
27 G, 1/2 inch
18
New cards
Erythema without induration occurring from a Mantoux test indicates a(n) ______ reaction
negative
19
New cards
What is done if a patient has a positive reaction to a Mantoux test?
Further diagnostic procedures are performed
20
New cards
Administered
given to a patient at the office
21
New cards
Prescribed
Physician provides patient with a handwritten or computer-generated Rx to be filled at a pharmacy
22
New cards
Dispensed
Medication given at the office for a patient to take home
23
New cards
Precise description of chemical composition. Example: n-acetyl-para-aminophenol
Chemical Name
24
New cards
Assigned by manufacturer who developed the drug. Example: Acetaminophen, paracetamol,
Generic Name
25
New cards
Name under which the drug is listed on official publications. Generic name is also used for this. Example: US Pharmacopeia (USP)
Official Name
26
New cards
Name under which pharmaceutical manufacturer markets the drug. Example: Advil, Tylenol
Brand Name
27
New cards
Sublingual tablet
dissolves under the tongue
28
New cards
Enteric-coated tablet
Coated with substance - prevents tablet from dissolving until it reaches the intestines
29
New cards
Sustained-release capsules
provides gradual and continuous release of medication
30
New cards
Basic Units
Gram (Weight), Liter (Volume), Meter (Linear)
31
New cards
Schedule I
Not available for prescribing; not used for treatment; high risk for abuse - examples: LSD, Heroin, MDMA
32
New cards
Schedule II
No refills allowed; currently accepted for tx; high risk for abuse - examples: Percocet, Adderall, Oxycontin
33
New cards
Schedule III
Moderate to low risk for abuse; can be refilled 5 times within 6 months - examples: Vicodin, Tylenol w codeine
34
New cards
Schedule IV
Low potential for abuse; limited psyche and physical dependence - examples: Xanax, Ambien, Valium
35
New cards
Schedule V
Low potential for abuse - Examples: Cough syrup
36
New cards
In order to administer, prescribe or dispense a controlled drug you must have a ________.
DEA Number
37
New cards
Superscription
Rx symbol; latin for recipe and take
38
New cards
Inscription
Name and dosage of drug - Example: Amoxil 250 mg
39
New cards
Subscription
Directions to pharmacist; designates number of doses to be dispensed
40
New cards
Signatura (sig)
Latin for write or label; directions for patient - Example: tab i po prn for pain (take one tab by mouth as needed for pain)
41
New cards
Which demographic of people are most affected by drugs?
The elderly and children
42
New cards
Factors affecting drug action
Age, route, size, time of administration and tolerance Ad
43
New cards
Adverse reactions
May be harmful; example: allergic reaction
May be harmless; referred to as side effects
May be harmless; referred to as side effects
44
New cards
Anaphylactic reaction symptoms
hives, vasodilation, angioedma (internal hives)
45
New cards
anaphylactic reaction - prevention
stay with patient after administration of meds
46
New cards
Idiosyncratic reaction
abnormal response to a drug that is unexplained and unpredictable (most often occurs in the elderly)
47
New cards
Seven rights
drug, dose, time, patient, route, technique, documentation
48
New cards
true or false: some vials require mixing
true
49
New cards
True or false: If a vial requires mixing shake it vigorously
False - shaking causes bubbles that may enter syringe; roll between hands
50
New cards
Ampule
small, sealed glass container holding a single dose
51
New cards
Diluent
Liquid used to reconstitute powder medication to liquid form
52
New cards
Hub - needle part
fits onto top of syringe
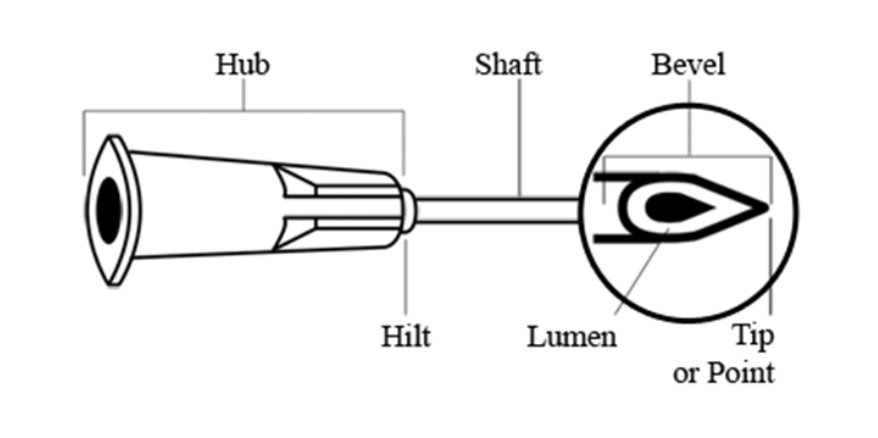
53
New cards
Shaft - needle part
inserted into body tissue
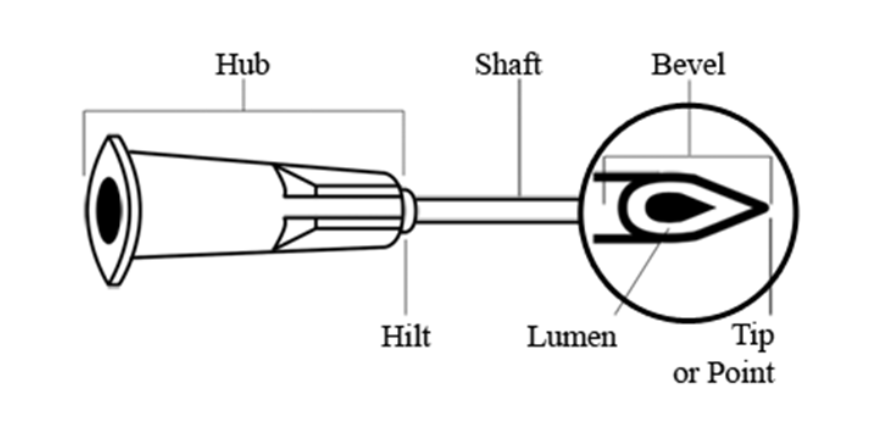
54
New cards
Lumen - needle part
opening in shaft of needle
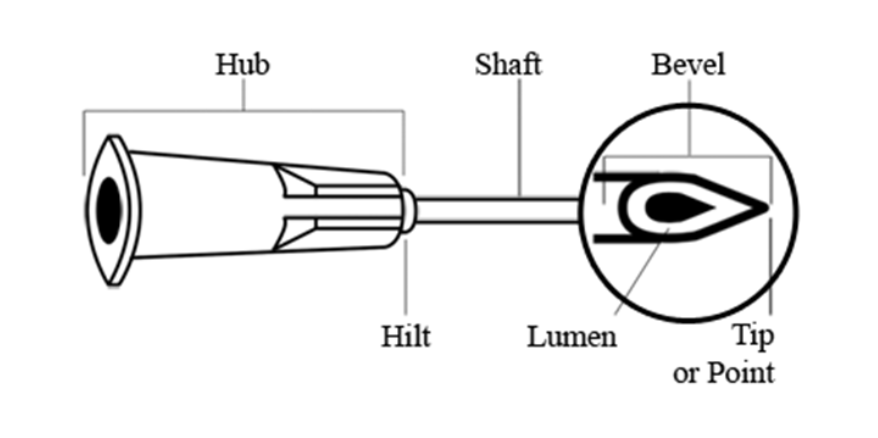
55
New cards
Gauge ranges
18 to 27
56
New cards
Needle length ranges
3/8 to 3 inches - depends on type of injection
57
New cards
Barrel - syringe part
holds medication
58
New cards
Flange - syringe part
rim at the end of the barrel
59
New cards
Plunger - syringe part
movable cylinder that slides back and forth in the barrel
60
New cards
Hypodermic needle
Small capacity; ranges from 2, 2.5, 3 and 5 ml
61
New cards
Insulin syringe
calibrated in units; most common U-100
62
New cards
Tuberculine syringe
administers a small dose of medication; capacity of 1 ml
63
New cards
SQ sites commonly used
upper lateral part of arms, anterior thigh, upper back, abdomen
64
New cards
Angle of insertion for a SQ injection
45 degrees
65
New cards
True or False: a SQ injection has a slower absorption rate than IM
True
66
New cards
Do not give SQ injection into tissue that is
hardened, inflamed SQ nee
67
New cards
SQ needle length range
1/2 to 5/8 inch - 45 degree angle for 5/8 in needle - 90 degree angle for 1/2 in needle
68
New cards
Medications administered via SQ
epinephrine, insulin, allergy injections
69
New cards
SQ injections shoulder no exceed ___ml
1 ml
70
New cards
Intramuscular injections
located below skin and SQ layer
71
New cards
Amount that can be injected into gluteal and vastus lateralis sites
Adults: 3ml
Very thing or older adults: 2 ml
Very thing or older adults: 2 ml
72
New cards
Amount that can be injected into deltoid site
no more than 1 ml
73
New cards
IM needle length range
1 to 3 inches
average adult: 1 1/2 in
Child or thin adult: 1 in
Obese: 2 to 3 in
average adult: 1 1/2 in
Child or thin adult: 1 in
Obese: 2 to 3 in
74
New cards
IM needle gauge range
18 to 23 - depends on viscosity of medication
75
New cards
IM injection sites
Dorsogluteal - square on the ass cheek
Deltoid - upper arm
Vastus Lateralis - mid thigh
Ventrogluteal - closer to hip
Deltoid - upper arm
Vastus Lateralis - mid thigh
Ventrogluteal - closer to hip
76
New cards
What is the iliac?
tip of hip bone
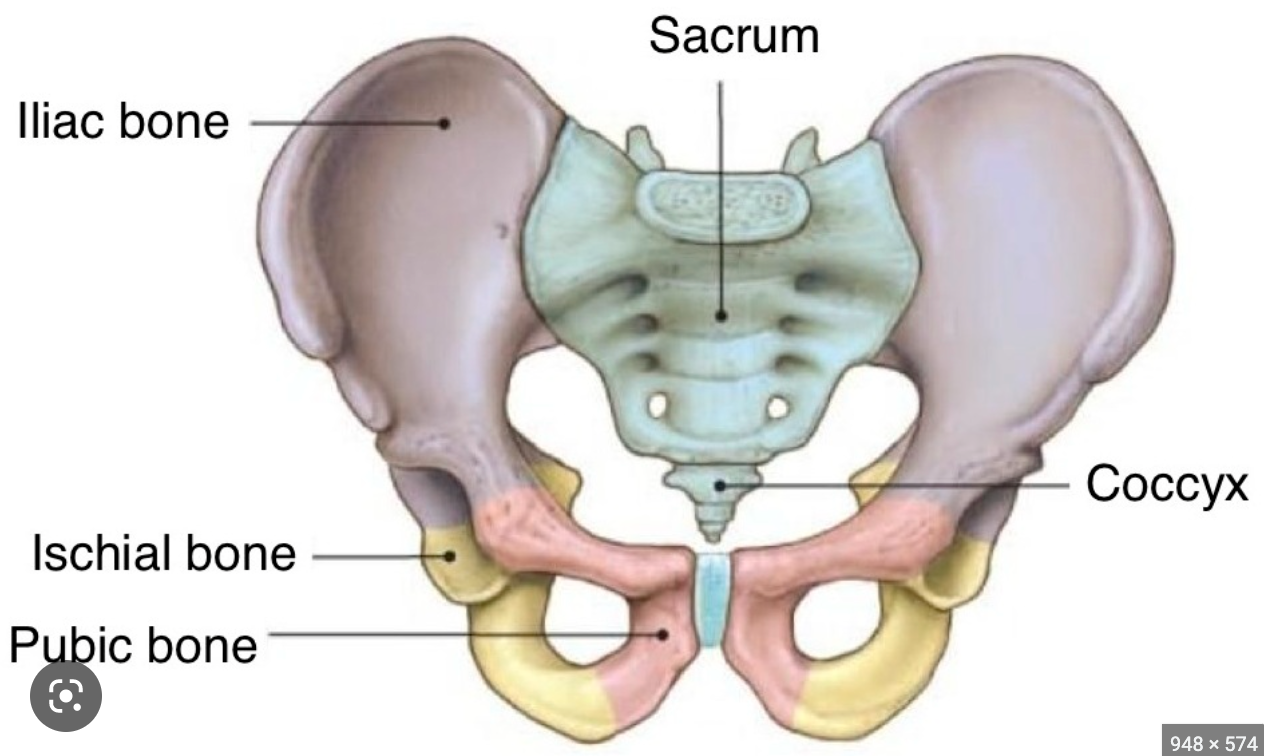
77
New cards
To locate injection site for a deltoid injection you must palpate the____
Acromion process
78
New cards
Vastus lateralis site - recommended for
infants and children younger than 3
79
New cards
What angle of insertion do you administer intradermal injections?
almost parallel to skin
80
New cards
Amount allowed to be injected for intradermal
0\.01 to 0.2 ml
81
New cards
Intradermal needle length range
3/8 to 5/8 inch
82
New cards
Needle gauge for intradermal
25 to 27
83
New cards
Types of tuberculosis
Active (w symptoms) and Latent (no active symptoms)
84
New cards
When should you read a tuberculin test?
48 to 72 hours
85
New cards
Tuberculosis is caused by what bacteria?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
86
New cards
Latent TB affects what percent of people infected?
90%
87
New cards
What does tuberculin consist of?
Purified protein derivative (PPD)M
88
New cards
Mantoux test
Most common - administer PPD into skin - the good old skin test bb
89
New cards
Tine test
four prong thingy
90
New cards
What is the dose of PPD?
0\.1 ml
91
New cards
PPD solution expires how long after opening?
30 days
92
New cards
What does it mean if the second skin test is positive?
likely caused by boosted reaction
93
New cards
True or False: the Quantiferon TB Gold blood test cannot determine if active or latent
true
94
New cards
What is a disadvantage of the Quantiferon test?
Must deliver blood specimen within 12 hour to lab
95
New cards
Allergen
a substance that is capable of causing an allergic reaction
96
New cards
Which immunoglobulin is present during an allergic reaction?
IgE
97
New cards
Skin punctures capture what type of blood?
capillary blood
98
New cards
Another name for skin puncture
capillary puncture
99
New cards
Examples of skin puncture tests
hemoglobin, hematocrit, blood glucose, mononucleosis
100
New cards
Skin puncture site
Adult: third or fourth finger
Infant: plantar surface of heel (can perform up until child is walking) De
Infant: plantar surface of heel (can perform up until child is walking) De