Y9 Physics - Sound and Light
0.0(0)Studied by 112 people
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:00 AM on 10/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
What are waves?
Waves involve the transport of energy without the transport of matter
2
New cards
What are electromagnetic waves?
A form of energy that can transmit its energy through the vacuum of space.
3
New cards
What are mechanical waves?
A form of energy that is not capable of moving its energy through a vacuum of space.
4
New cards
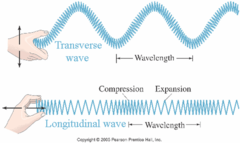
What are the two types of mechanical waves?
transverse and longitudinal waves
5
New cards
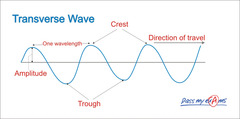
What are transverse waves?
Particles move at right angles to the direction of movement of the wave, eg. Ocean waves
6
New cards
What are longitudinal waves?
particles move in the same direction that the wave is moving, eg. Sound waves
7
New cards
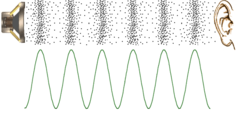
Why is sound a longitudinal wave?
The motion of the particles are parallel to the direction of energy transport.
Sound is a mechanical wave that results from the back and forth vibration of particles of the medium through which the sound wave is moving
Sound is a mechanical wave that results from the back and forth vibration of particles of the medium through which the sound wave is moving
8
New cards
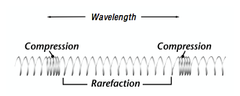
What are the parts of a longitudinal/sound wave?
Compressions- regions of high pressure due to particles being close together
Rarefractions- regions of low pressure due to particles being spread further apart
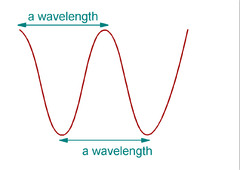
Wavelength- The distance between two consecutive points in a longitudinal wave
Amplitude- the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on the medium from its rest position (equilibrium)
Rarefractions- regions of low pressure due to particles being spread further apart
Wavelength- The distance between two consecutive points in a longitudinal wave
Amplitude- the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on the medium from its rest position (equilibrium)
9
New cards
What is the difference between periods and wavelengths?
Period - The time taken for one complete wave cycle.
Wavelengths are the distance between two points in a wave, while periods is the time taken for a complete oscillation to take place at a given point.
Wavelengths are the distance between two points in a wave, while periods is the time taken for a complete oscillation to take place at a given point.
10
New cards
What is the speed of sound through air?
343 m/s

11
New cards
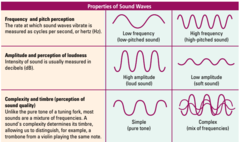
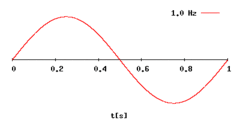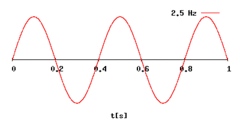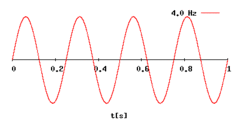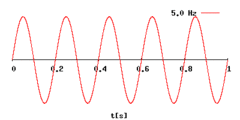
How does differing frequencies, wavelengths and amplitudes affect the properties of sound?
(Note: we haven't covered complexity + click the image to zoom)
12
New cards
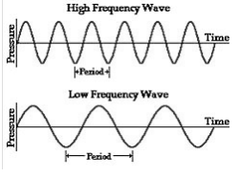
What is frequency?
The number of vibrations a sound makes each second.
13
New cards
What is the measurement of frequency?
Hertz (Hz)
14
New cards
What unit of measurement are wavelengths measured by?
Metres (m)
15
New cards
What is loudness measured in?
Decibels (dB)

16
New cards
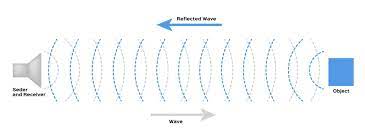
What is an echo?
When sound bounces off an object (the reflection of sound)
17
New cards
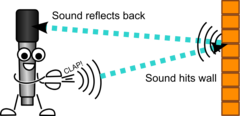
How do different surfaces reflect sound waves and create echoes?
Hard surfaces reflect sound well, making echoes
Soft substances, like curtains and carpets, reflect very little sound. Instead, they absorb the sound instead, so there are no echoes.
Soft substances, like curtains and carpets, reflect very little sound. Instead, they absorb the sound instead, so there are no echoes.
18
New cards
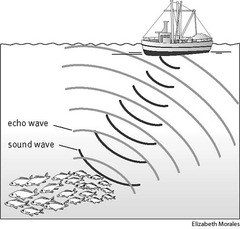
What does SONAR stand for?
SOund NAvigation & Ranging
19
New cards
How do wind instruments make sound?
The vibrating air makes sound. The air particles move back and forth making sound waves.
Different pitches are created by pressing keys that open or close holes in the tube, making the air column inside the tuber longer or shorter.
The longer the air columns, the lower the pitches.
Different pitches are created by pressing keys that open or close holes in the tube, making the air column inside the tuber longer or shorter.
The longer the air columns, the lower the pitches.
20
New cards
How do string instruments produce sound?
They are played by pressing fingers down on the strings.
Pressure changes the string's length, causing them to vibrate at different frequencies (different pitches). Shortening the pitch makes the sound higher.
Pressure changes the string's length, causing them to vibrate at different frequencies (different pitches). Shortening the pitch makes the sound higher.

21
New cards
What is the wave length equation?
v= m/s
f= Hz
λ = m
f= Hz
λ = m
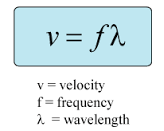
22
New cards
What is the Doppler effect?
A change in sound frequency caused by motion of the sound source, motion of the listener, or both.
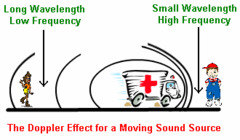
23
New cards
What does EMS stand for?
Electromagnetic spectrum
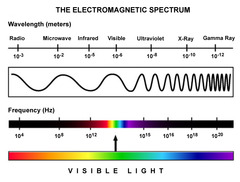
24
New cards
List the components of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing energy.
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Gamma rays
(Remember: RMIVUXG)
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Gamma rays
(Remember: RMIVUXG)
25
New cards
What are gamma rays?
Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies.
They are produced by the hottest and most energetic objects in the universe.
On Earth, gamma waves are generated by nuclear explosions, lightning and the less dramatic activity of radioactive decay.
They are produced by the hottest and most energetic objects in the universe.
On Earth, gamma waves are generated by nuclear explosions, lightning and the less dramatic activity of radioactive decay.
26
New cards
What are Isotopes?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
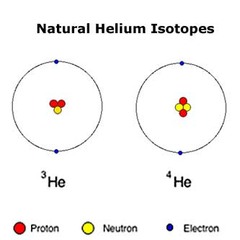
27
New cards
What are unstable isotopes considered as?
Radioactive
28
New cards
What happens when unstable isotopes decay?
They turn into another isotope or element
29
New cards
What is the process of radiation?
The nuclei of radioactive atoms emit charged particles and energy which are called by the general term, radiation.
30
New cards
What is radioactive decay?
The process in which unstable isotopes decay into other elements and emit radiation as they attempt to become more stable.
31
New cards
Is radioactive decay a nuclear or chemical reaction? Why?
It is a nuclear reaction because it only involves the nuclei of the atoms.
32
New cards
What charge are alpha, beta and gamma particles?
Alpha- Positive
Beta- Negative
Gamma- Neutral
Beta- Negative
Gamma- Neutral
33
New cards
What are alpha particles made of?
2 protons and 2 neutrons
34
New cards
What is alpha decay caused by?
Alpha decay is caused when there are too many protons in a nucleus. In this case, the element will emit radiation in form of positively charged particles called an alpha particle.
35
New cards
What are beta particles made of?
One electron
36
New cards
What is beta decay caused by?
Beta decay is caused when there are too many neutrons in a nucleus. In this case, the element will emit radiation in the form of negatively charged particles called beta particles
37
New cards
What are gamma particles made of?
Electromagnetic Waves
38
New cards
What is gamma decay caused by?
Gamma decay occurs when there is too much energy in the nucleus. In this case, gamma particles, with no overall charge are emitted from the element.
39
New cards
How fast does light travel?
300,000,000 m/s
40
New cards
Can light move through empty space?
Yes, light does not require a medium to be transmitted and can move through space.
41
New cards
Is light transverse or longitudinal?
transverse
42
New cards
What is the name of the narrow band of light that humans can see?
The visible light spectrum.
43
New cards
What type of fields do light waves consist of?
They consist of alternating electric and magnetic fields.
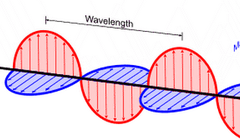
44
New cards
How does polarisation of light occur?
Polarised light can be produced by passing up polarised light through a polarising filter, which allows waves of only polarisation to pass through.
When unpolarised light is transmitted through those filters, it emerges with one-half intensity and with vibrations in a single plane; it is now polarised light
When unpolarised light is transmitted through those filters, it emerges with one-half intensity and with vibrations in a single plane; it is now polarised light
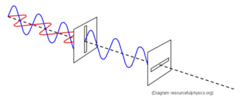
45
New cards
What is reflection?
Reflection is when light bounces off an object.
46
New cards
What is an incident ray?
A ray of light that strikes or is approaching a surface
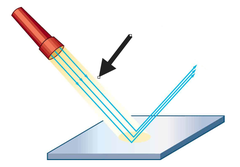
47
New cards
What is a reflected ray?
The light ray that leaves the surface.
48
New cards
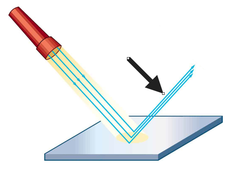
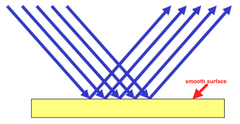
What is specular reflection?
This happens when a wave is reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface
E.g. when light is reflected by a mirror, you get a nice, clear reflection
E.g. when light is reflected by a mirror, you get a nice, clear reflection
49
New cards
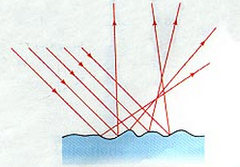
What is diffuse reflection?
When a wave is reflected by a rough surface & the reflected rays are scattered in lots of different directions - happens due to the normal being different for each incoming ray, therefore the angle of incidence is different for each ray
50
New cards
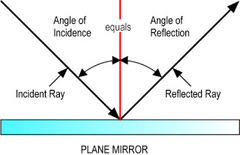
What is the law of reflection?
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
51
New cards
What is the normal line?
An imaginary line that's perpendicular to the surface at the point where the wave hits the surface.
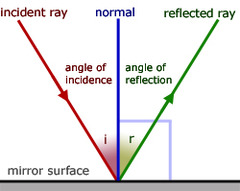
52
New cards
What are plane mirrors?
A mirror that has a flat reflective surface
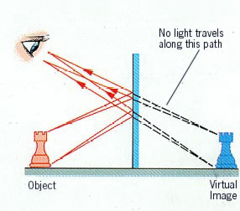
53
New cards
What are convex mirrors?
A mirror with the reflective surface curved outward
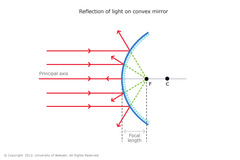
54
New cards
What are concave mirrors?
A mirror where its reflective surface is curved inward
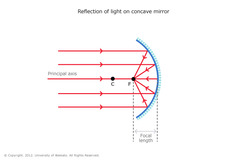
55
New cards
Define transparent
A surface allowing light to pass through so that objects behind can be distinctly seen.

56
New cards
Define translucent
A material that allows some light to pass through in a scattered manner

57
New cards
Define opaque
A material where light is either reflected or absorbed into the substance

58
New cards
how do our ears hear sound?
Vibrations travel through to the ear drum. These convert into electrical signals, which are sent to the brain where the information is processed
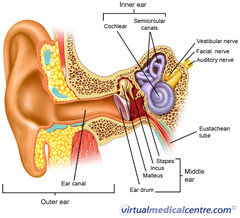
59
New cards
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another with a different desnity.
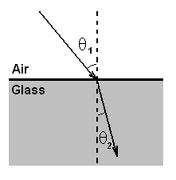
60
New cards
What is FST?
Fast to Slow, towards the normal line.
Happens when a fast wave goes through a medium & travels slower and will bend towards the normal line more
Happens when a fast wave goes through a medium & travels slower and will bend towards the normal line more
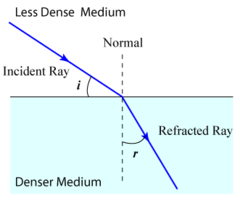
61
New cards
What is SFA?
Slow to fast, away from the normal line.
Slow into a material, then faster, light bends away from normal line.
Slow into a material, then faster, light bends away from normal line.
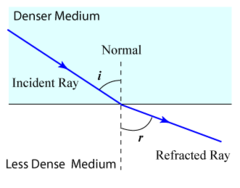
62
New cards
What is the dispersion of white light?
When white light passes through a prism it is dispersed and the different colours of the spectrum seperate
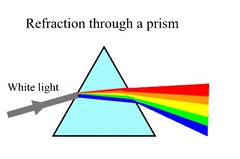
63
New cards
Why does dispersion occur?
Dispersion occurs due to the different spectral colours travel at the same speed in a vacuum but at different speeds in the medium such as glass
64
New cards
List the spectral colours in decreasing wavelength
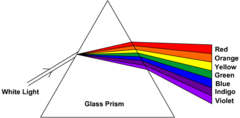
65
New cards
What is a lens
An optical transparent material which focuses or disperses light by means of refraction.
66
New cards
What are convex lenses
A lens with the glass surface curved outward
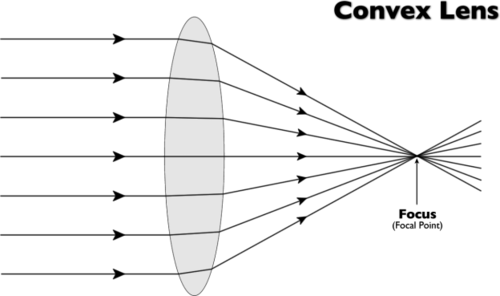
67
New cards
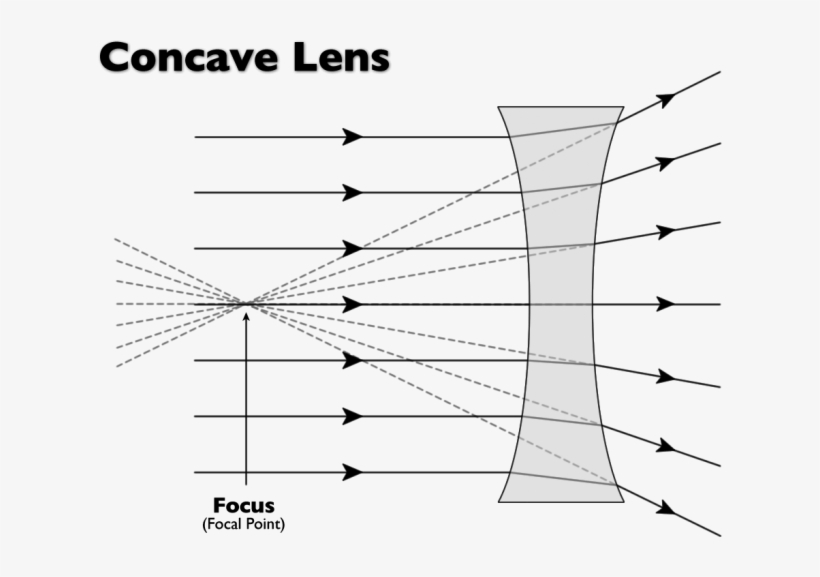
What are concave lenses
A lens with the glass surface curved inward