ib physics farady's + lenz's law
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
faraday's, lenz's law ib definition, rules, sample problems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
faraday’s law
The induced EMF for a magnet in a coil is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux
lenz’s law
This voltage induced due to Faraday's law will oppose the original change that created it.
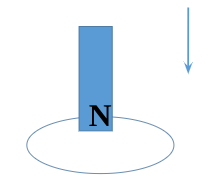
lenz’s law rules:
when a changing magnetic field ENTERS a wire loop for the first time…
the wire produces a current/magnetic field to OPPOSE
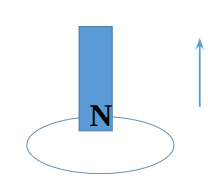
lenz’s law rules:
when a changing magnetic field ALREADY IN a wire loop changes or leaves…
the wire produces a current/mag field that MATCHES
lenz’s law rules:
if the magnetic field is near a wire and is NOT CHANGING…
NO CURRENT is produced, nothing happens
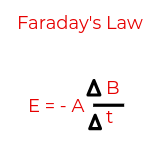
faraday’s law formula (WIRE LOOP)
E = Voltage
A = Area of wire loop (pi*r²)
B = Magnetic field
t = Time
area formula
r = radius
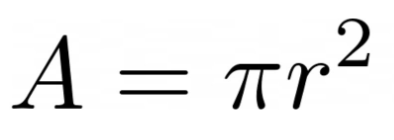
farday’s law formula (single wire)
E = vBl
v = Velocity
B = Magnetic Feild
L = length of wire
right hand rule (WIRE COILS)
Fingers = Current direction
Thumb = Magnetic field
If you wrap your fingers around the coil in the direction of the current, your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field
right hand rule (MAGNETS)
Thumb = North end of Magnet
Fingers= EMF Direction
Switches direction if entering wire