Respiratory Surfaces
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
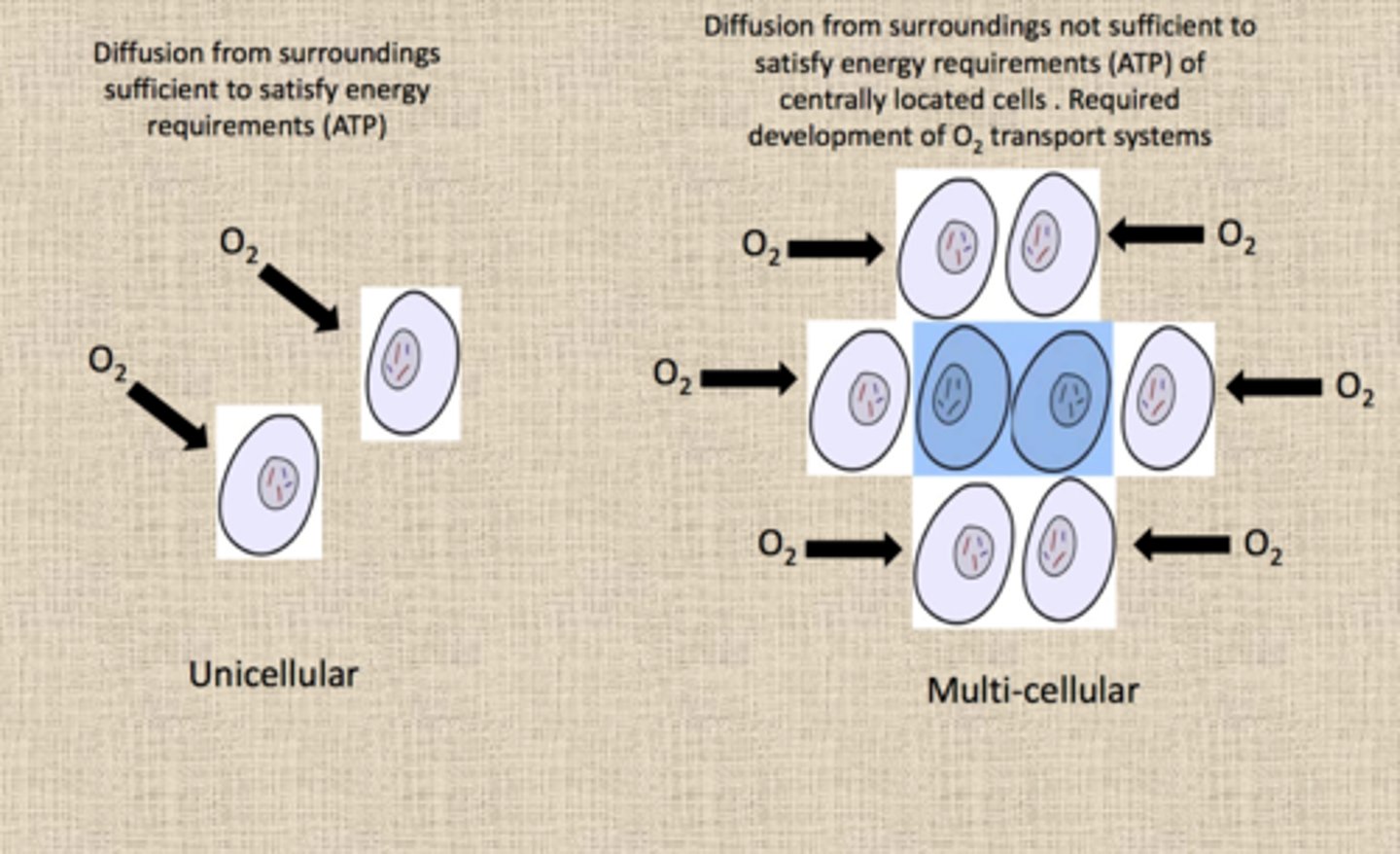
Need for transport and exchange systems
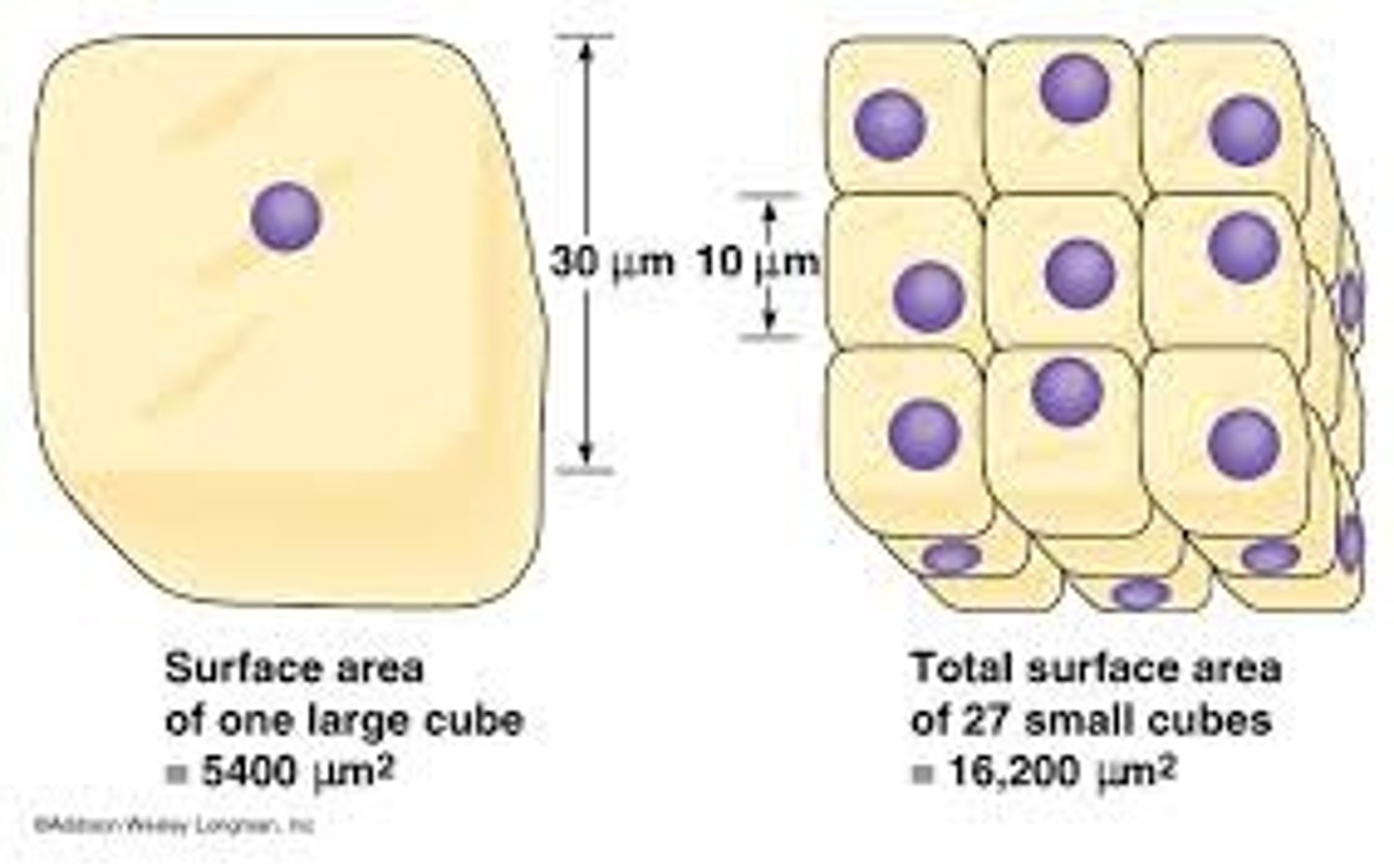
Larger organisms have smaller surface area to volume ratios and are unable to directly obtain useful substances from their environment like single-celled organisms can
Surface area
The total area of the surface of an object
Surface area to volume ratio
The amount of surface area in relation to how large something is
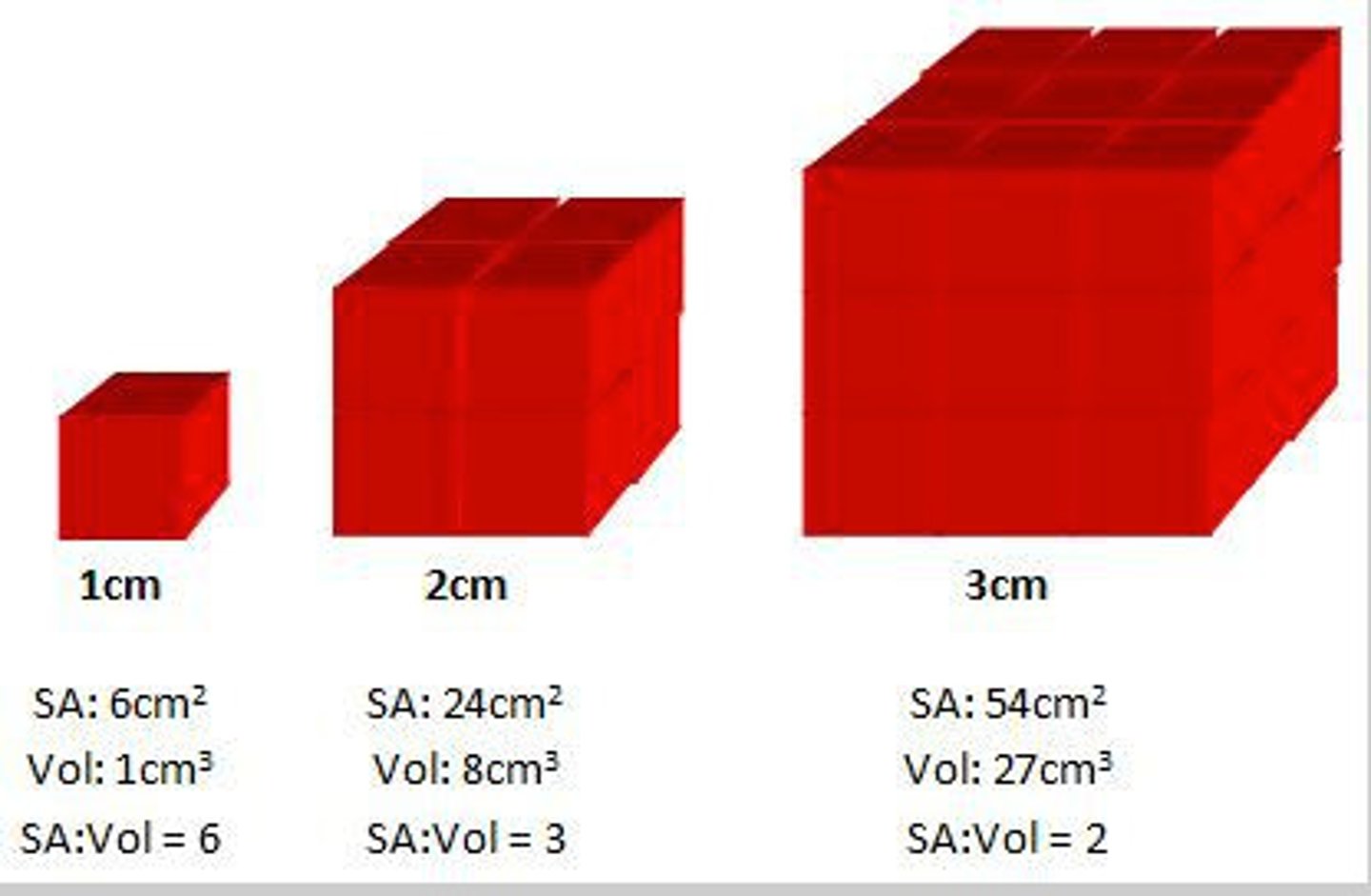
Large surface area to volume ratio
Leads to faster diffusion rates, as there is more room for particles to diffuse through a membrane
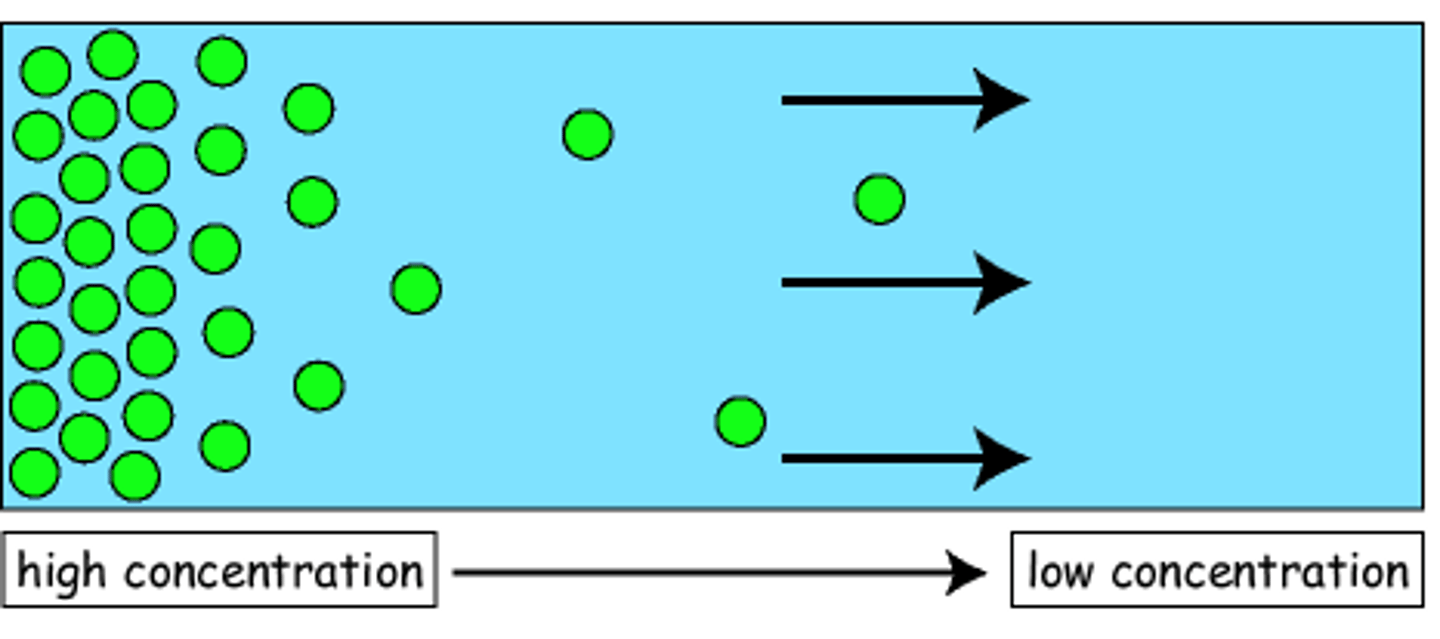
Diffusion
The movement of substances such as gas particles or substances in solution, from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
Gas exchange
When oxygen and carbon dioxide move in and out of cells by diffusion
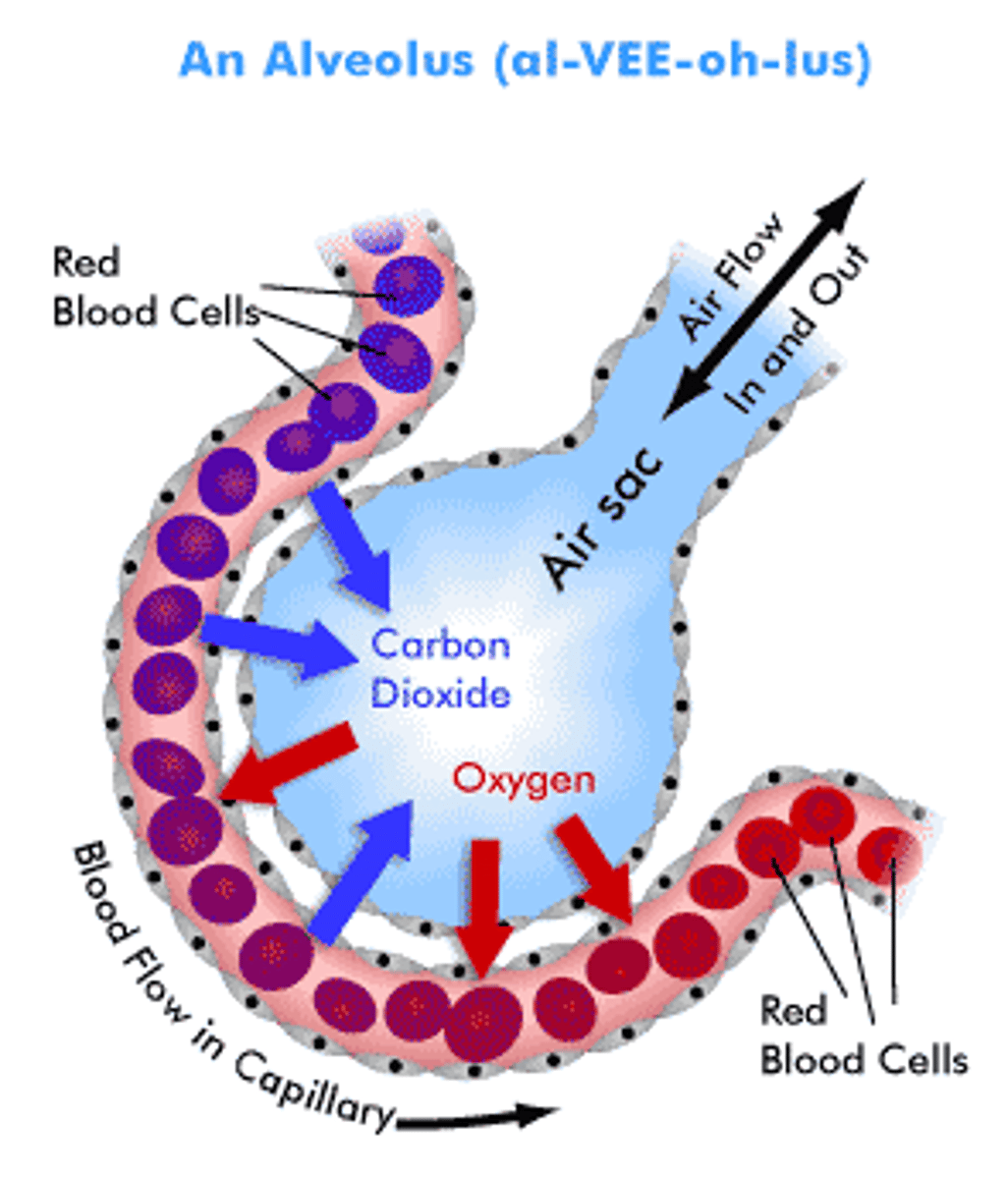
Purpose of gas exchange
Organisms need oxygen for aerobic respiration, they also need to remove carbon dioxide which is a waste product in some organisms

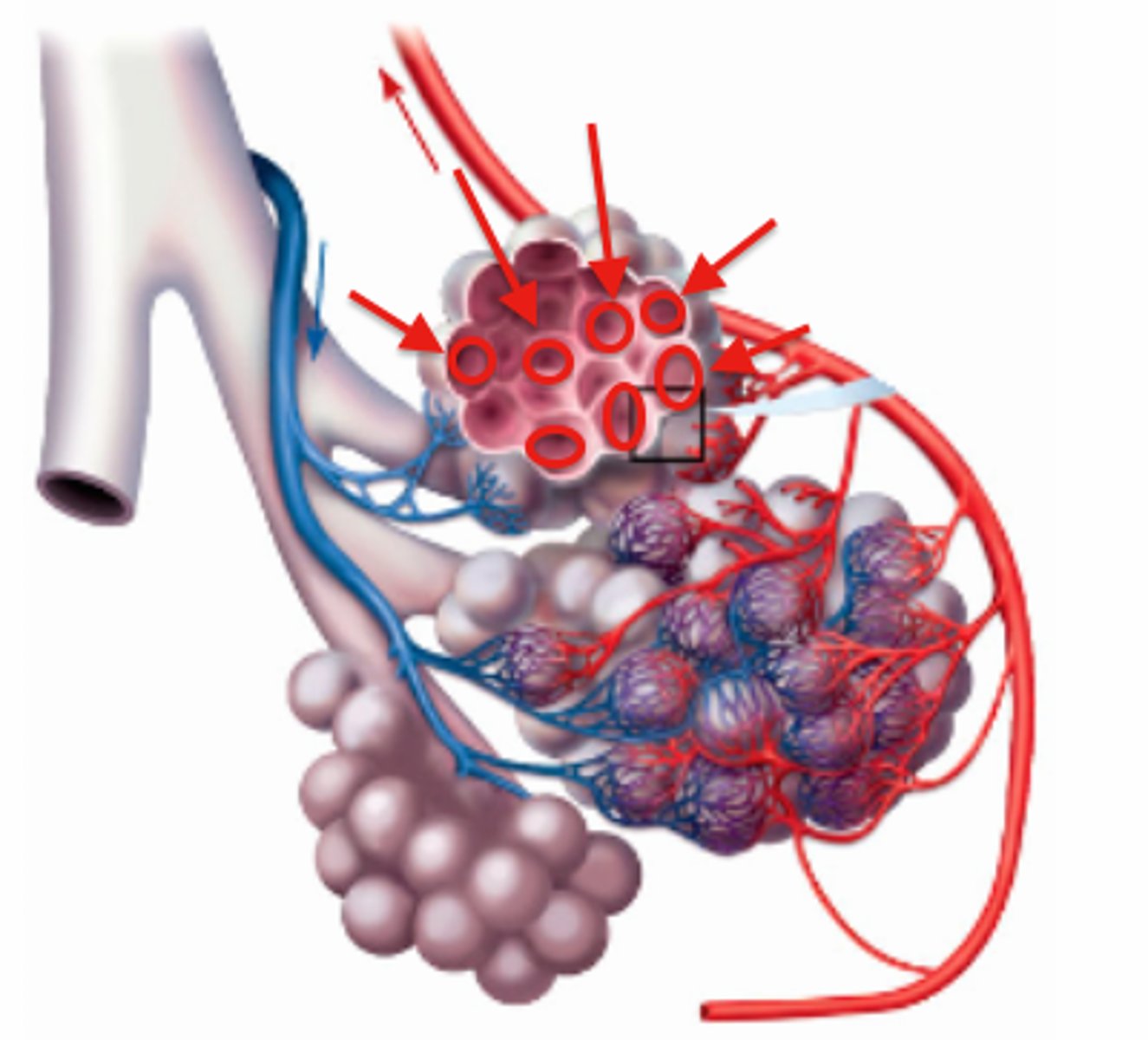
Sites of gas exchange
The alveoli of the lungs and respiring cells around the body
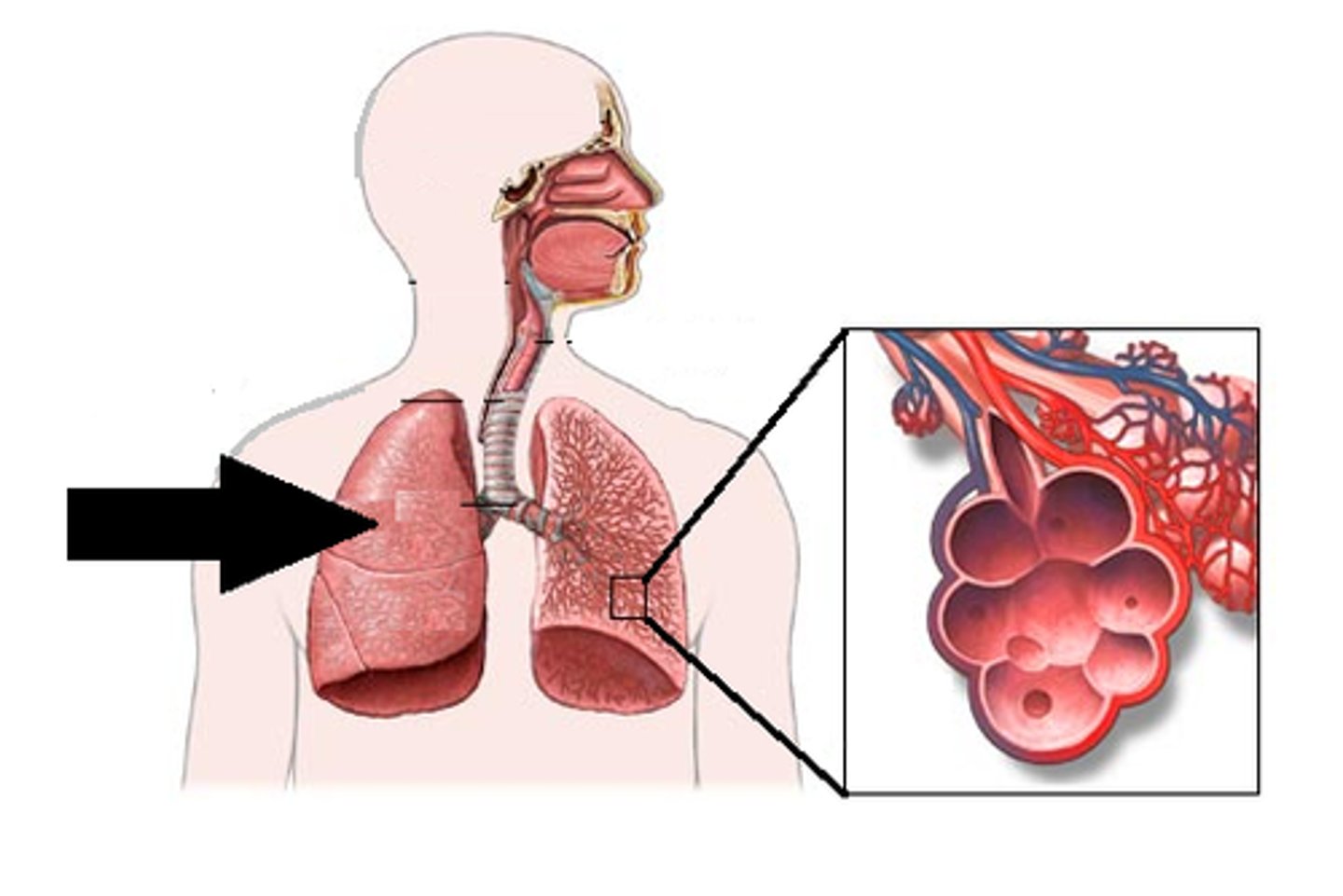
Alveoli adaptations
Has a large surface area, a good blood supply, is moist, is well ventilated for gas exchange and has a thin membrane for diffusion
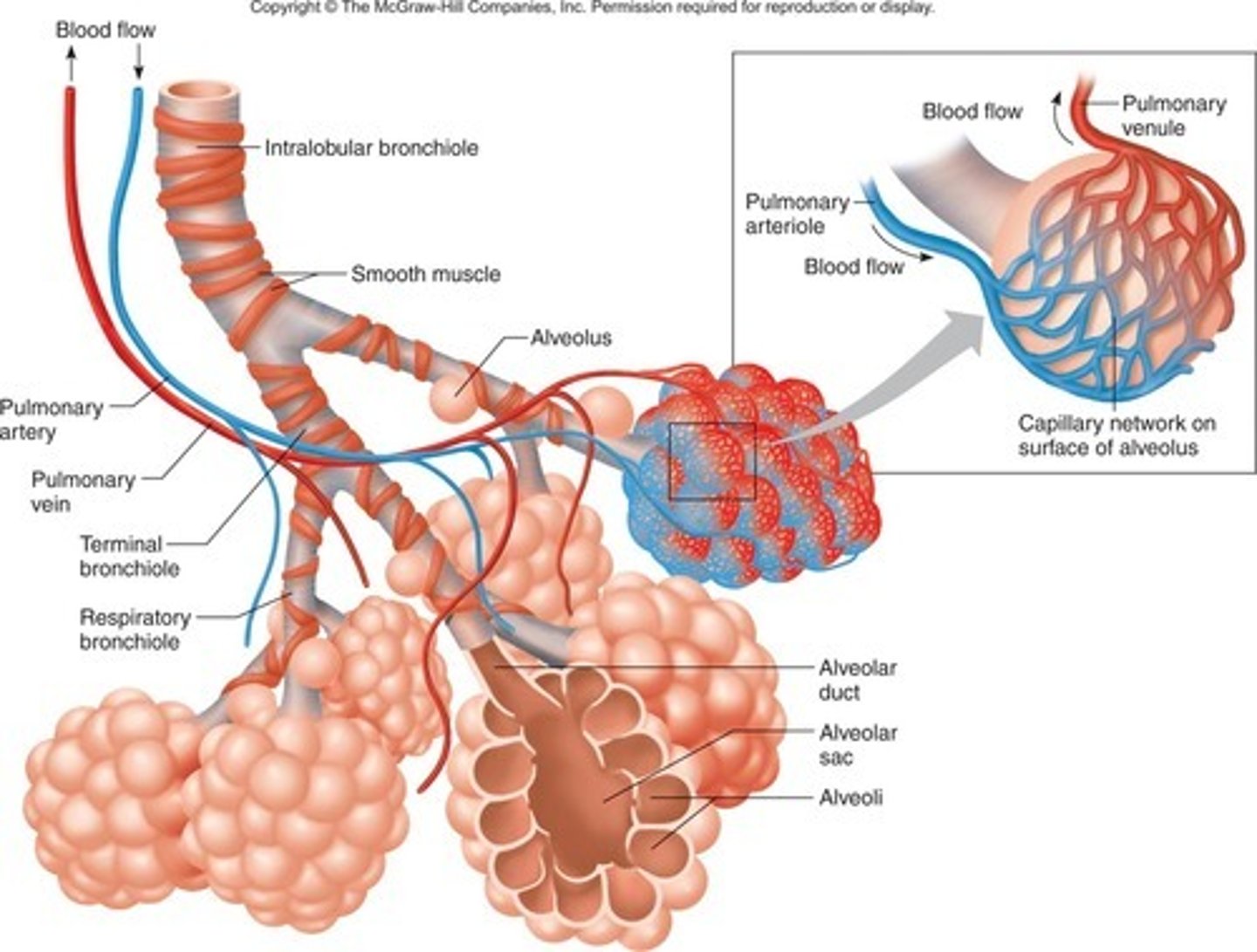
Moist lining of alveolus
The lining of the alveolus is moist, which increases the rate of diffusion
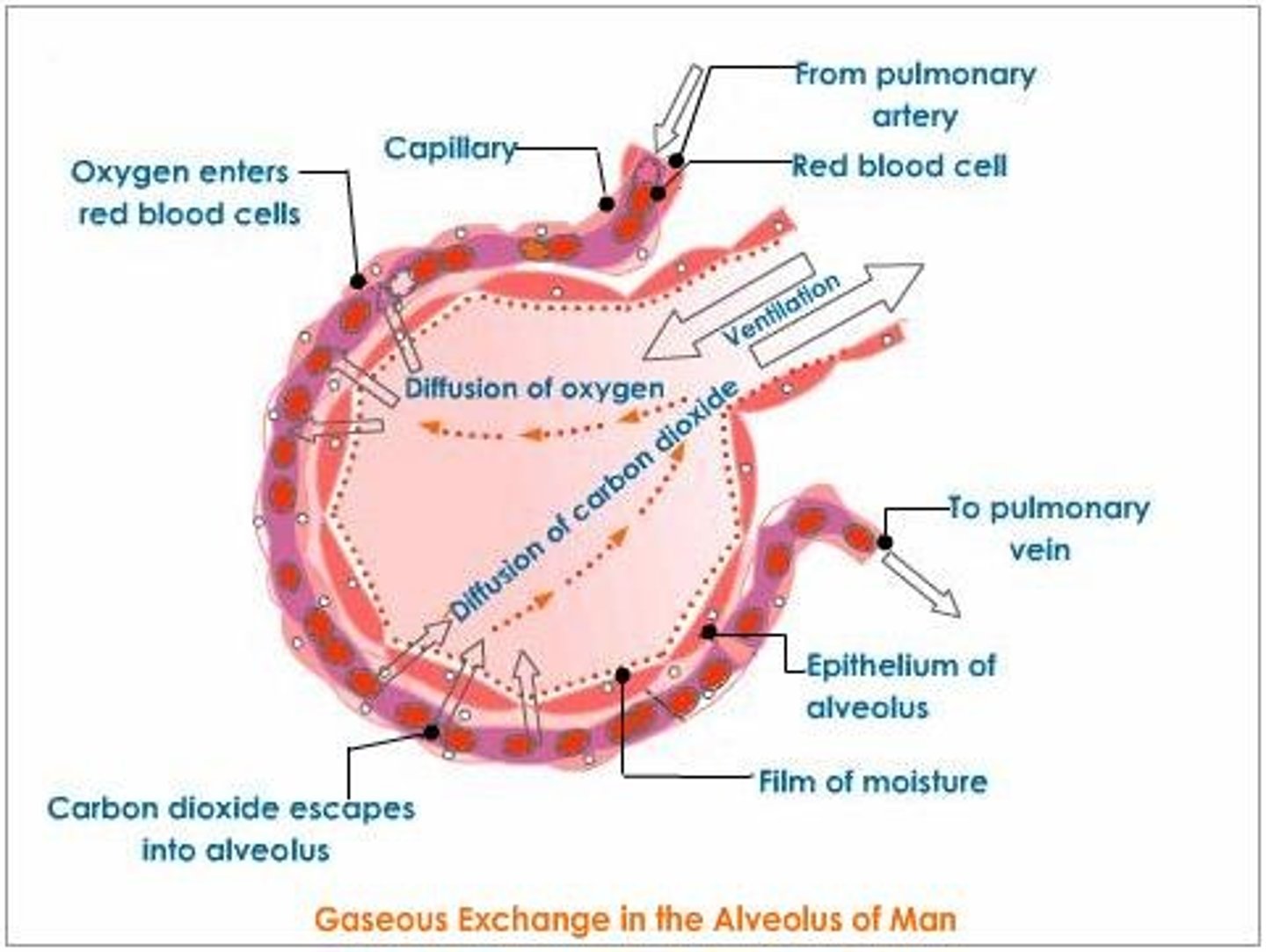
Wall of capillary
The capillary walls are thin and one cell thick to optimise diffusion between the alveoli and the blood
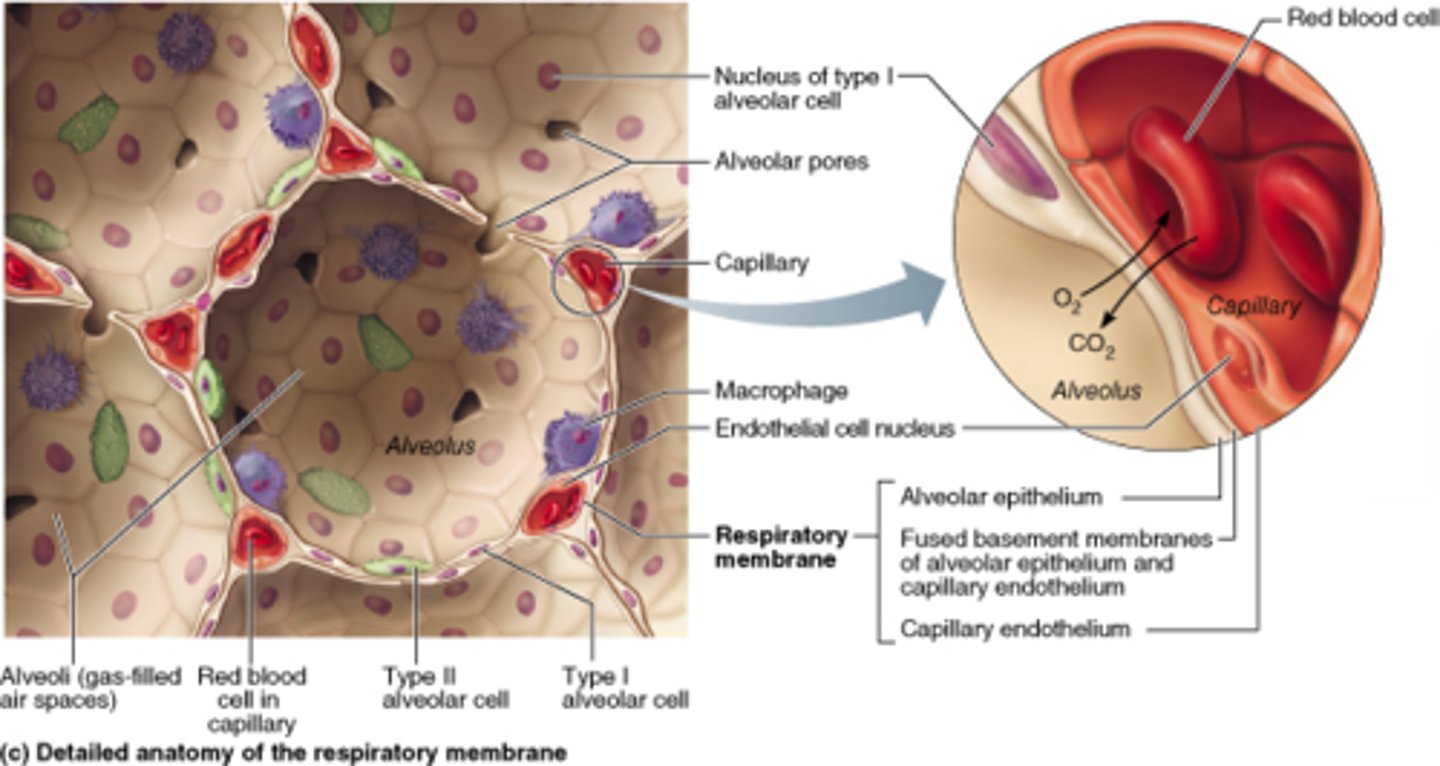
Many blood vessels surrounding the aveoli
Provide a constant blood supply to maintain a constant diffusion gradient for gas exchange
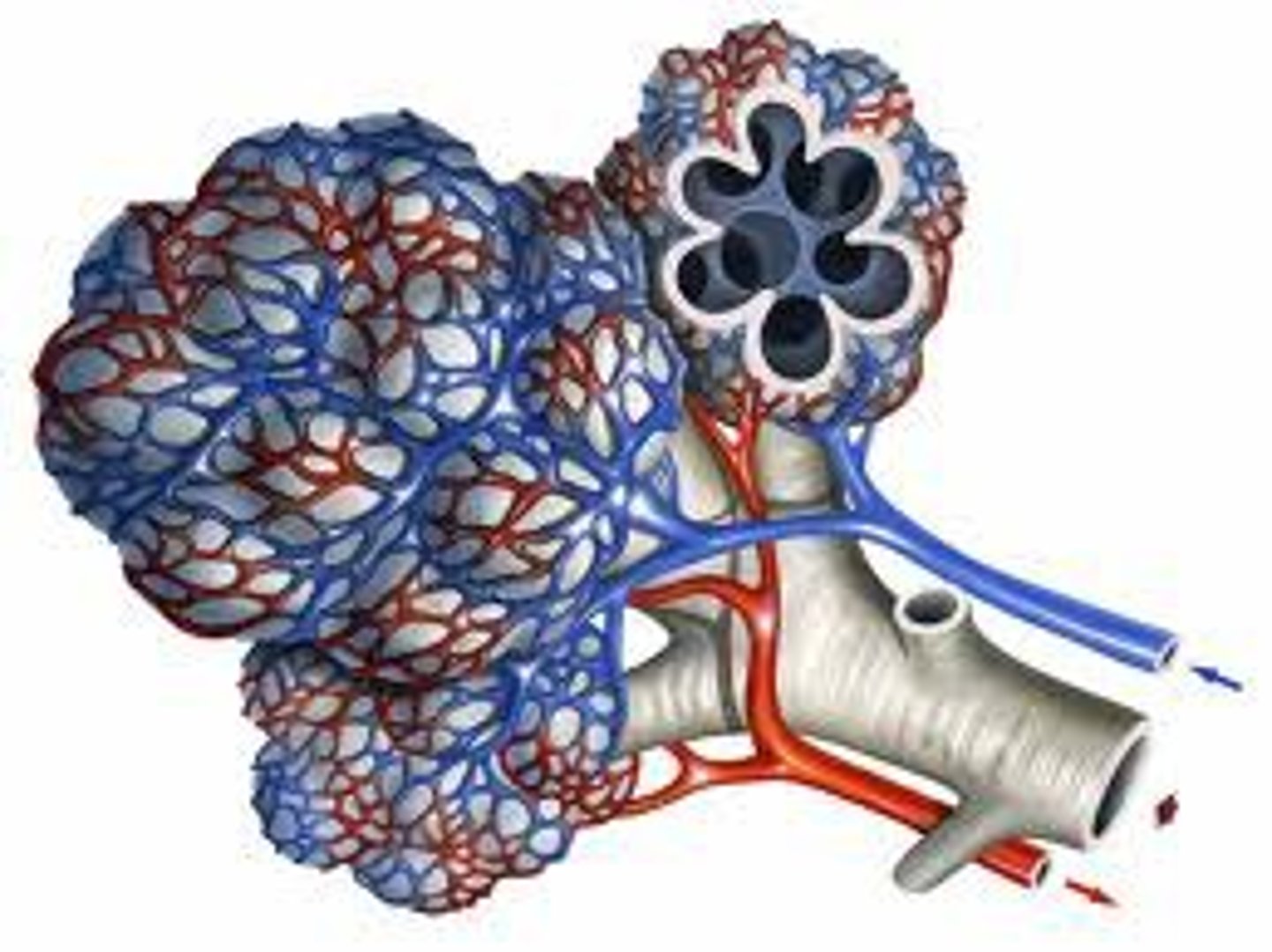
Specific cells, tissue and sacs adapted for exchange
Alveoli in mammal lungs, guard cells in plants, spongy mesophyll cells in plants
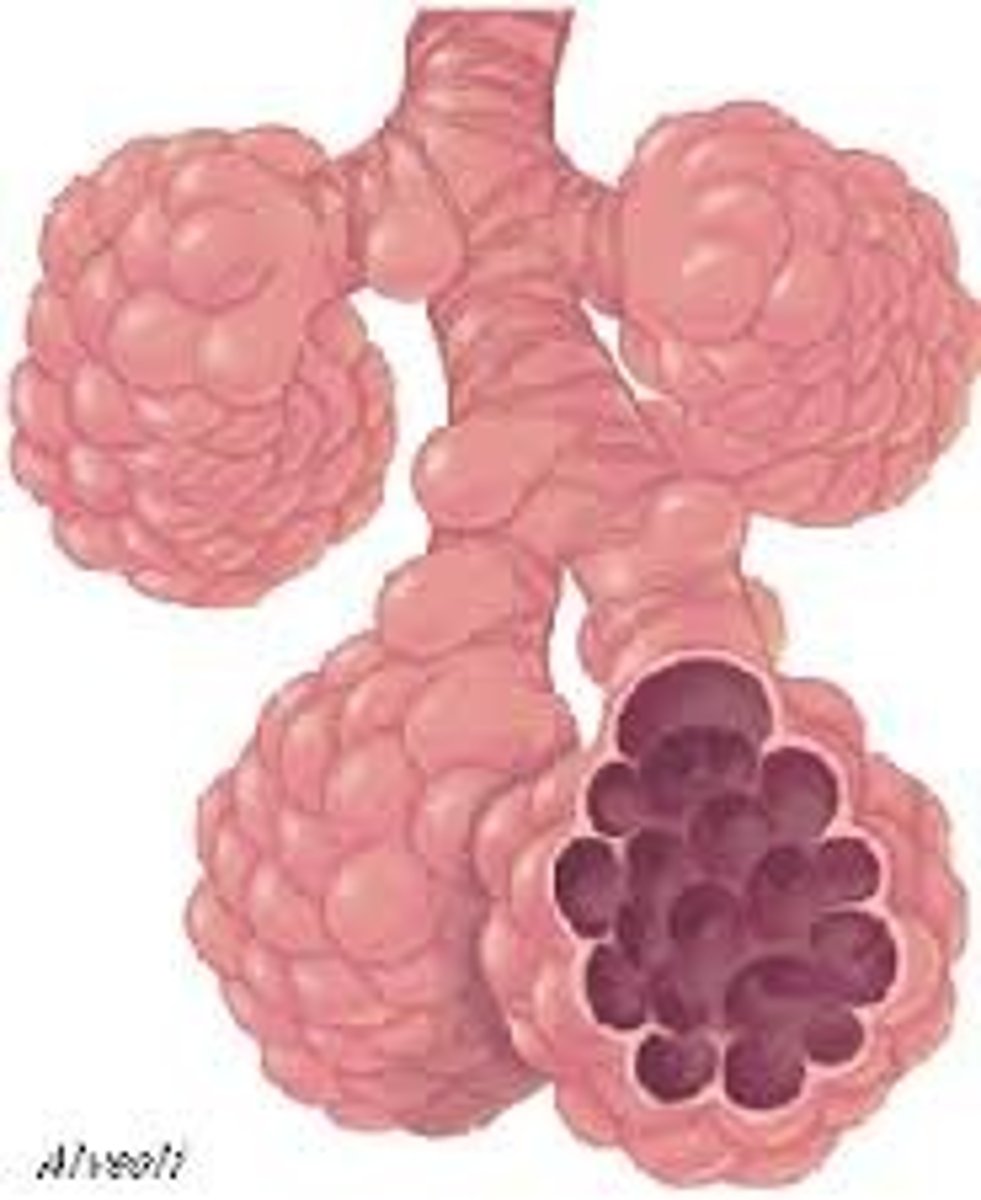
Oxygen
A gas that is needed for aerobic respiration to release energy, oxygen is transported into the body by the respiratory system and around the body by the circulatory system
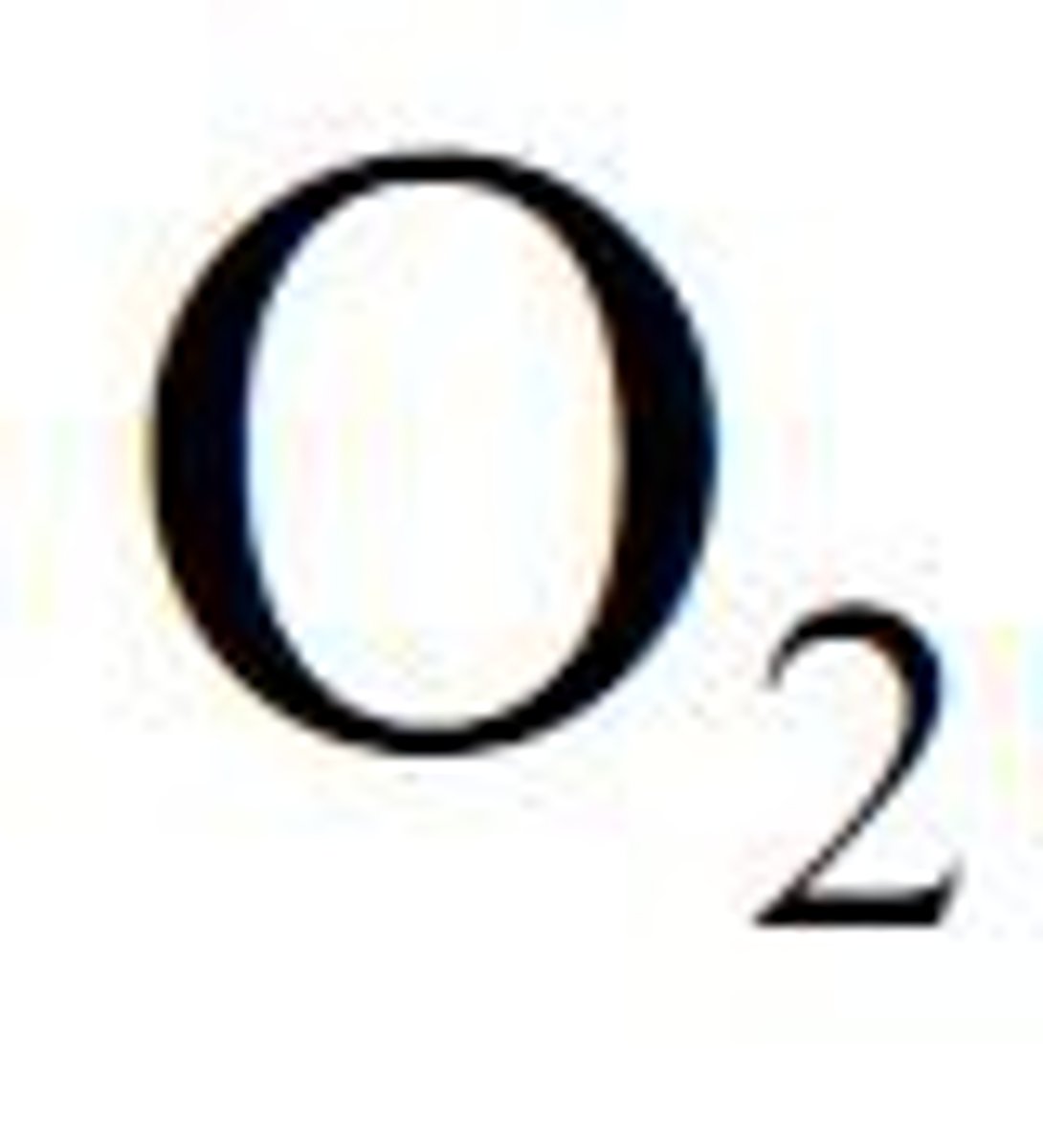
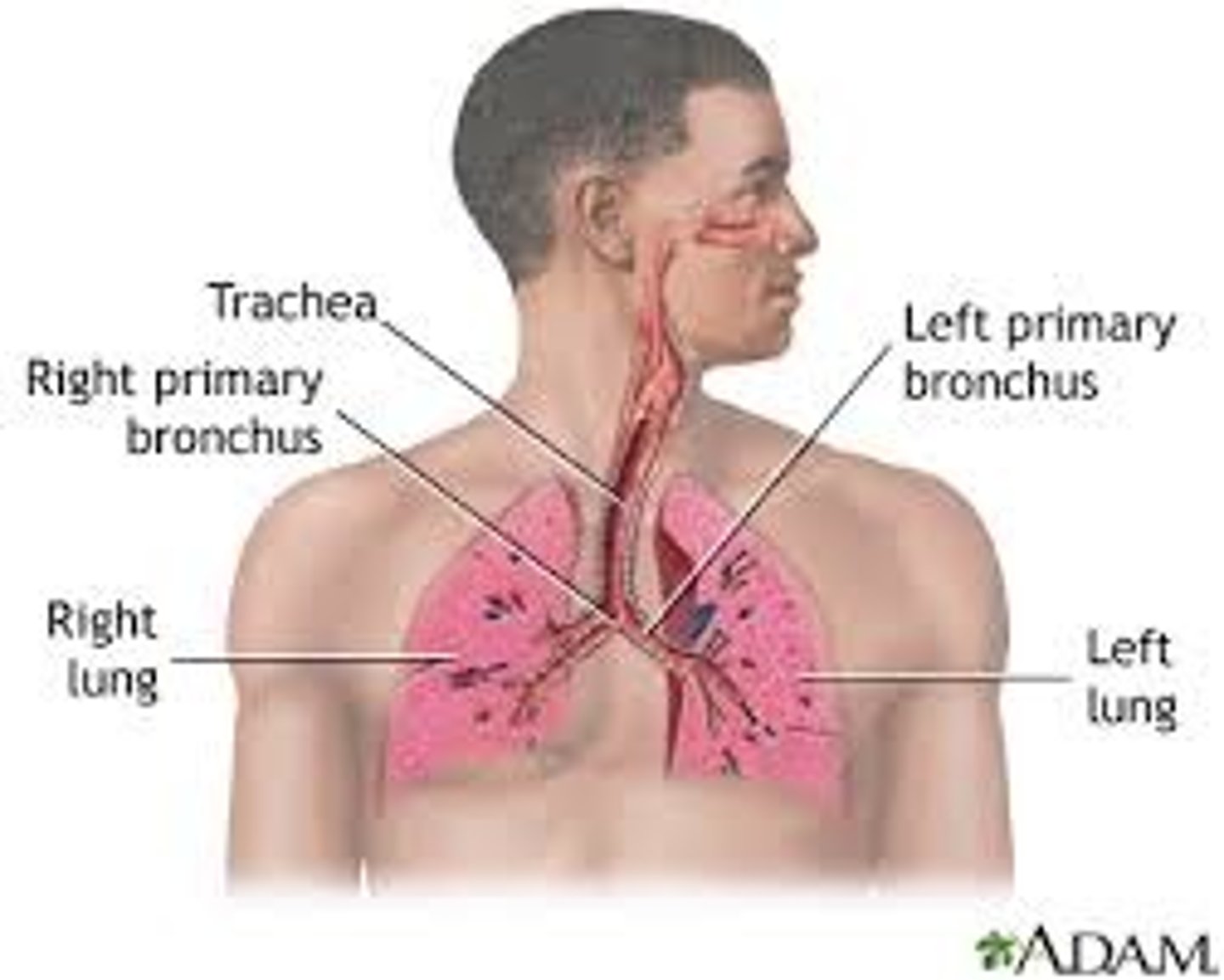
Respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting of the trachea, bronchi and lungs
Carbon dioxide
A waste product of respiration that needs to be removed from the body via the circulatory system, also an essential reactant in plants that is transported in to plant leaves via the stomata
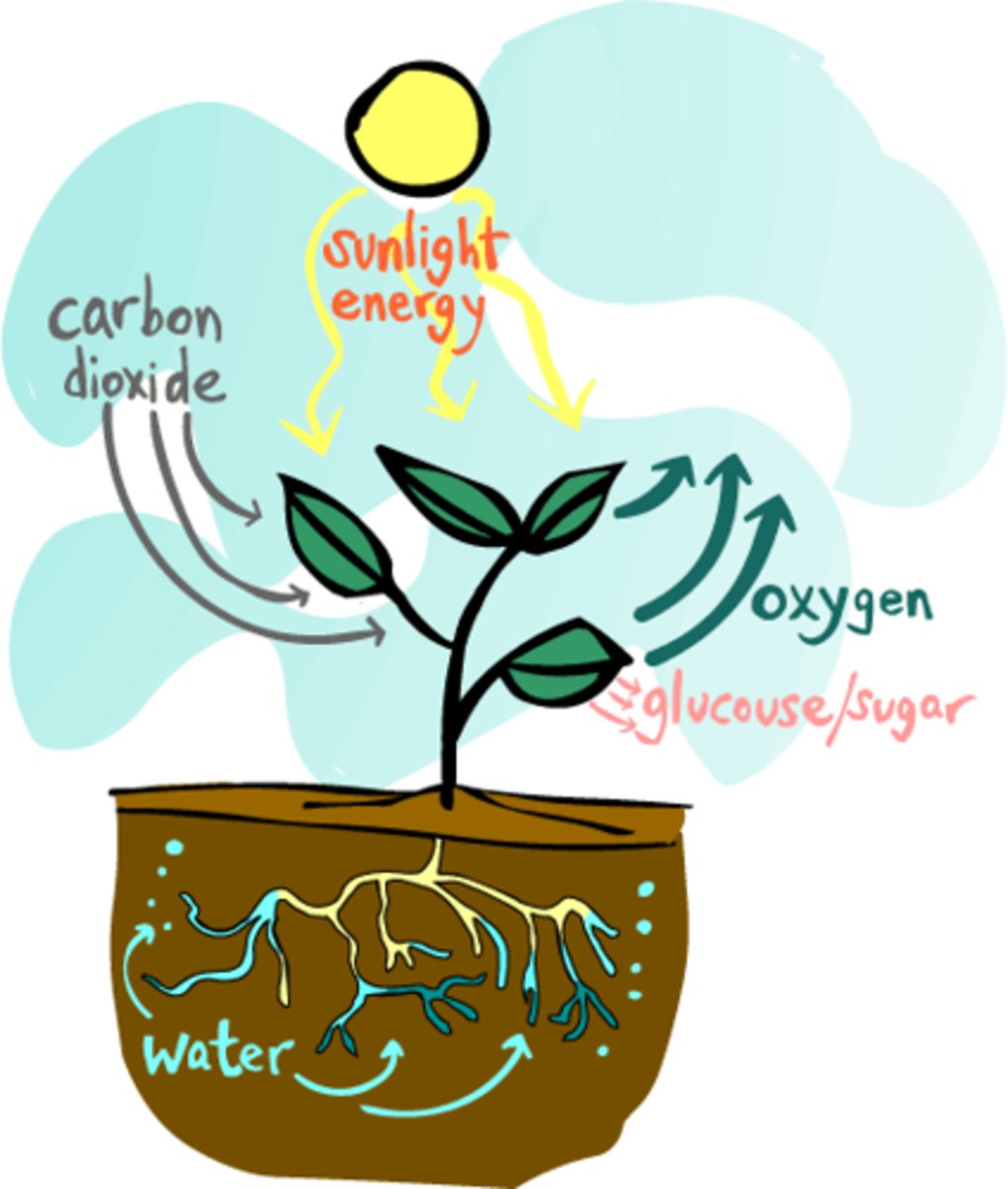
Gas exchange in plants
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant in exchange for oxygen that diffuses out of the plant, this process is regulated by guard cells in the leaves that can open and close the stomata efficiently
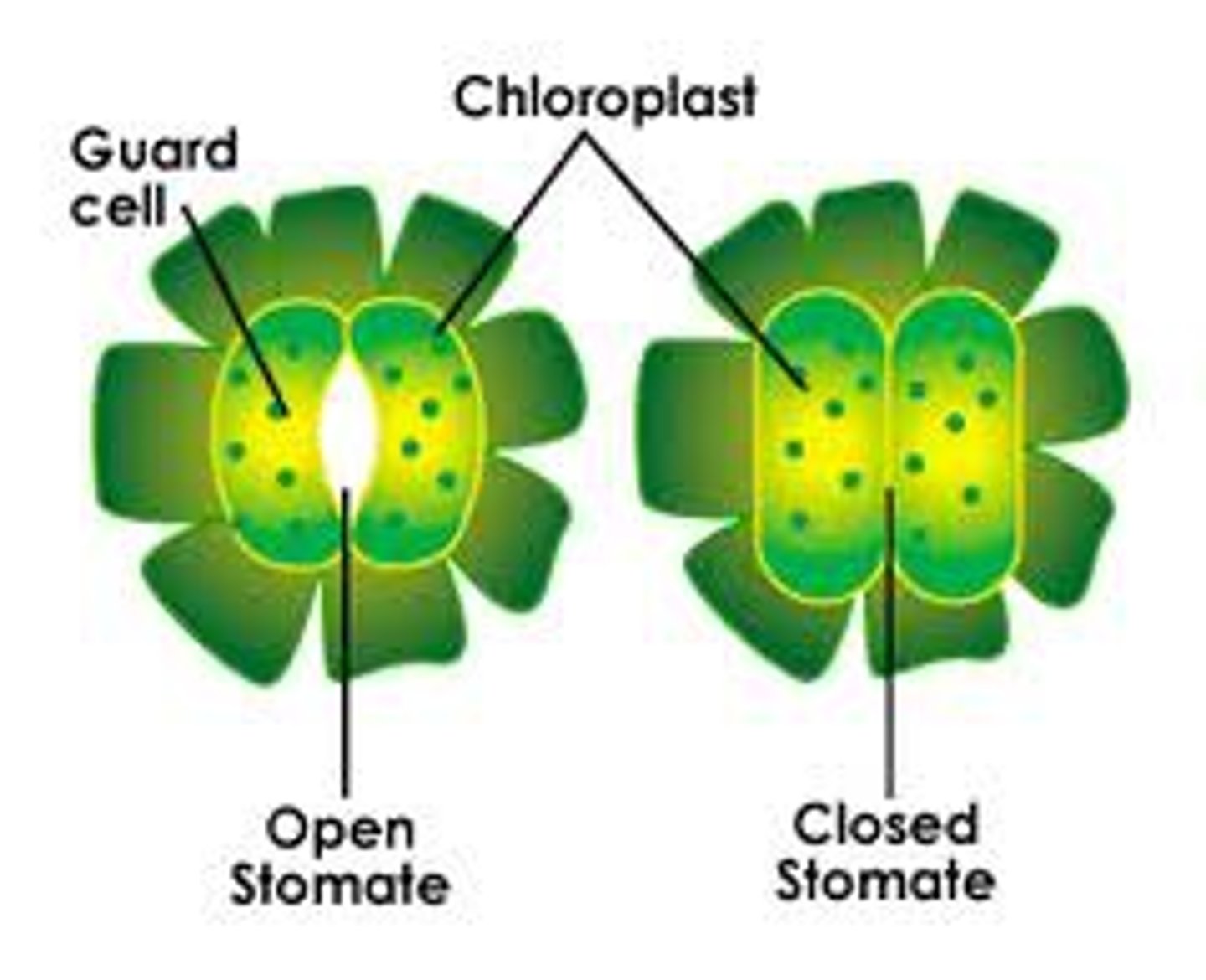
Leaf adaptations as a respiratory surface
Leaves have pores called stomata that can open and close to regulate gas exchange, they also have a layer of cells called the spongy mesophyll that is very spacious allowing room for diffusion and gas exchange
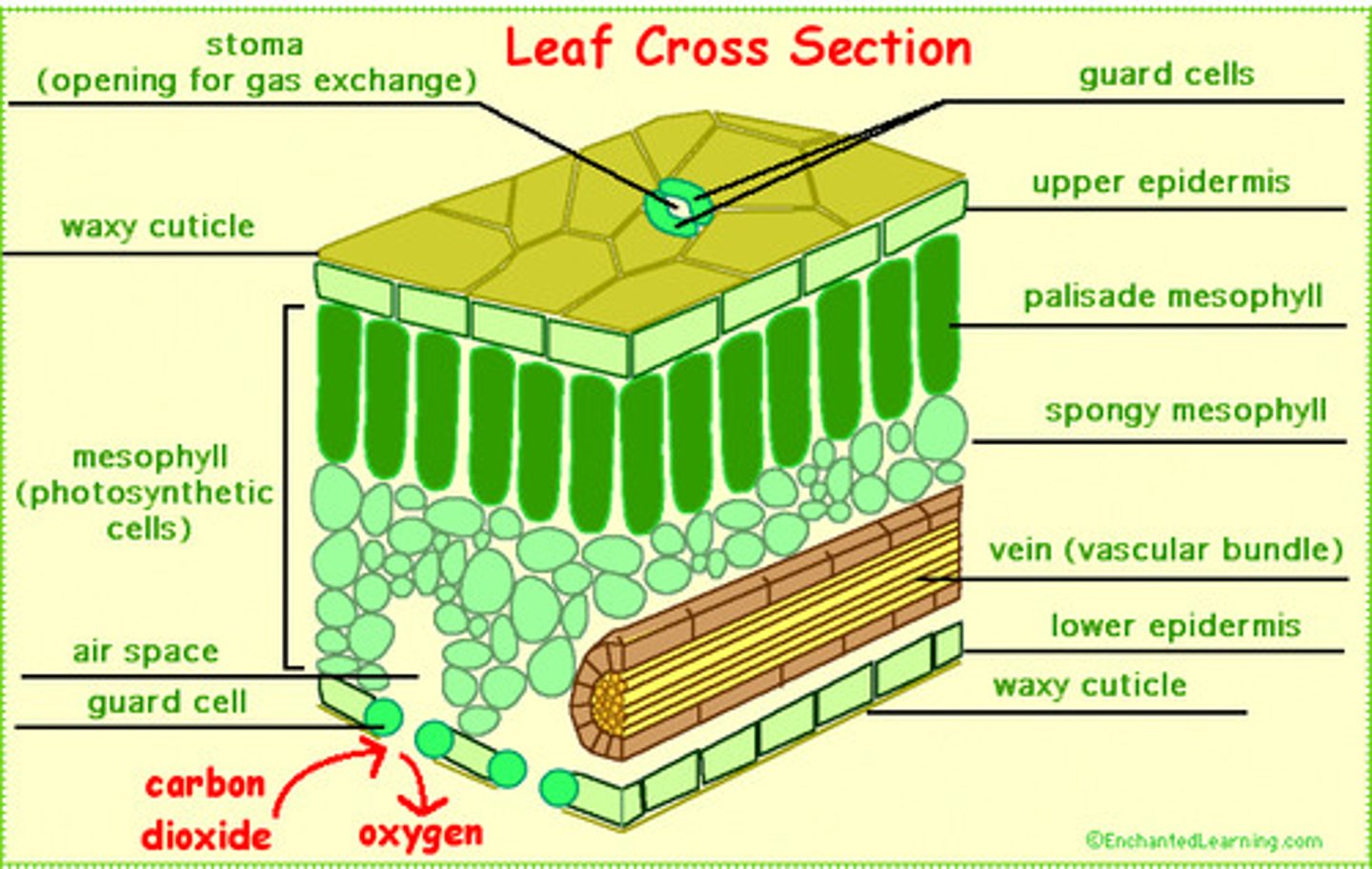
Spongy mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf, has many air spaces between its cells and an increased surface area for diffusion
Lungs
Are specialised in gas exchange due to the presence of many tiny sacs called alveoli that are adapted for diffusion due to being moist, one cell thick and surrounded by capillaries