Physics - Waves 1 and 2: Chapter 11 and 12
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Transverse Waves
Oscillations / vibrations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer. Examples:
Waves on the surface of water
Any electromagnetic wave
Waves on stretched strings
S-waves produced in earthquakes
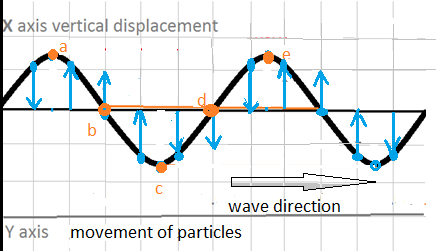
Longitudinal Waves
Oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer. They create a series of compressions and rarefactions as they travel through a medium. Examples:
Sound waves
P-waves produced by earthquakes
Progressive Wave
Waves that transfer energy from one place to another
The Wave Equation
V = F * λ
F = 1 / T
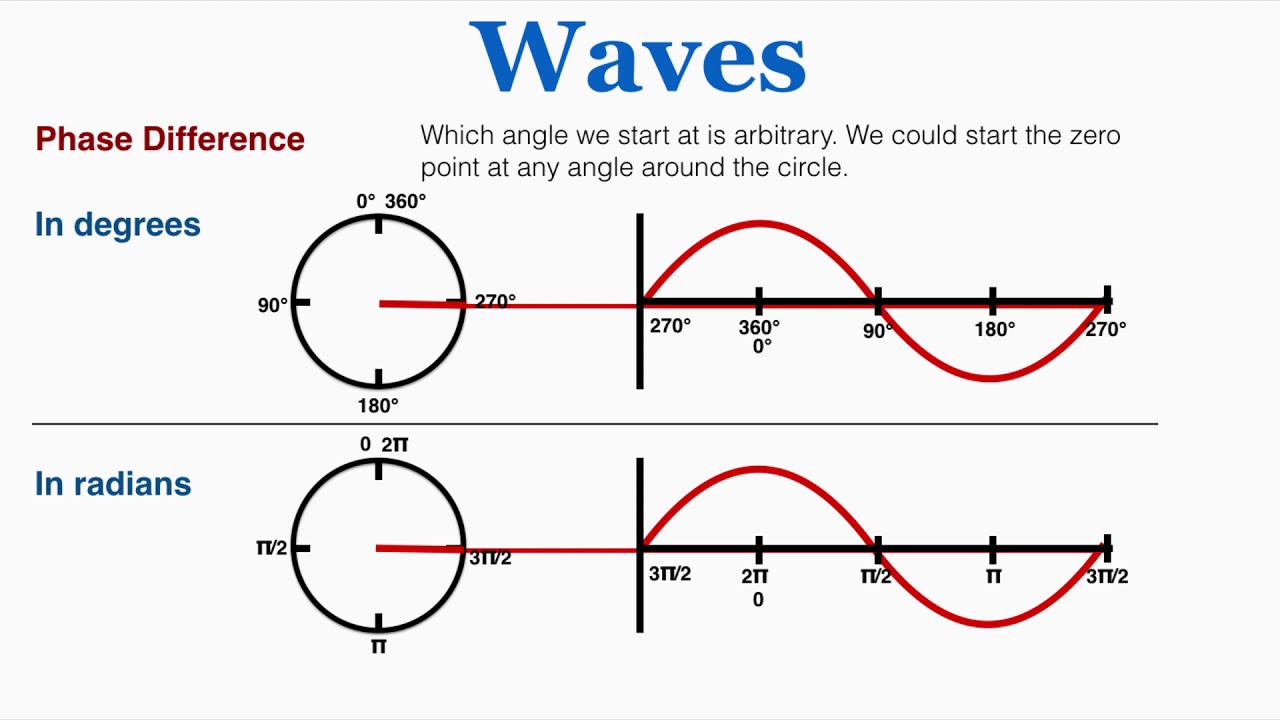
Phase Difference
The difference between the displacements of particles along a wave. It is most often measured in degrees or radians with each complete cycle representing 360° or 2π radians.
Term = ( x / wavelength ) * 360
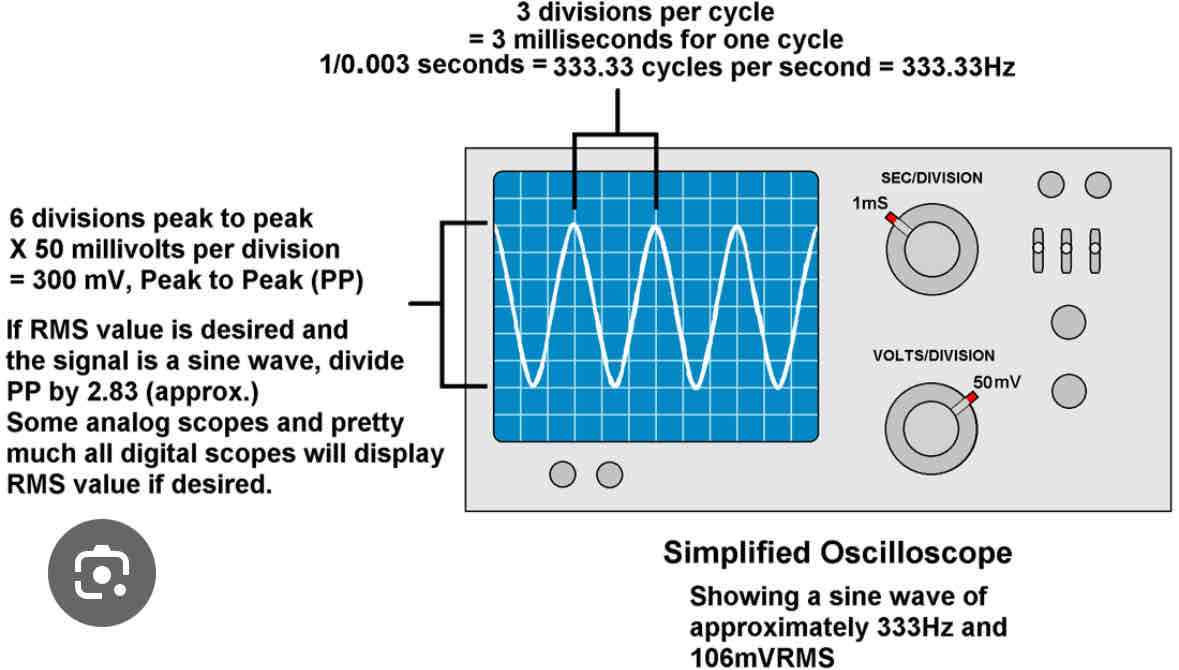
Oscilloscopes
Height - represents voltage
Horizontal - represents time interval
Reflection
Occurs when a wave changes direction at a boundary between two different media, remaining in the original media.
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Refraction
Occurs when a wave changes direction as it changes speed when passing from one medium to another.
If the wave slows down it will refract towards the normal, whereas if it speeds up it will refract away from the normal.
Law of refraction
n1Sinθ = n2Sinθ
n is the refractive index of each material.
What is the refractive index ?
Different materials refract light by different amounts. The angle at which the light is bent depends on relative speed of light between the two materials.
n = c / v
Total Internal reflection
Conditions Needed:
Light must be travelling from a material with a higher refractive index to a lower refractive index
The angle of incidence must be above the critical angle
sinC = 1 / n
Intensity
The power transmitted per unit area
Term = P / A
Term∝ A²
What is superposition ?
When two waves of the same type meet, they pass through each other. When the waves overlap, or surpose, they produce a single wave whose instantaneous displacement can be found using the principle of superposition of waves.
What is the principle of superposition of waves ?
when two waves meet at a point, the resultant displacement at that point is equal to the sum of the displacements of the individual waves.
Constructive Interference vs Destructive interference.
Two waves are in phase, resultant displacement with increased amplitude.
Two progressive waves are in antiphase, resultant displacement is smaller than for each individual wave.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radio waves 10³ m
Microwaves 10^-2 m
Infrared 10^-5 m
Visible 7×10^-7 to 4×10^-7 m
Ultraviolet 10^-8 m
X-ray 10^-10 m
Gamma 10^-12 m
Polarisation of EM waves
A wave is plane polarised if the particles (or EM fields) oscillate in a single plane. This is a property of transverse waves only.
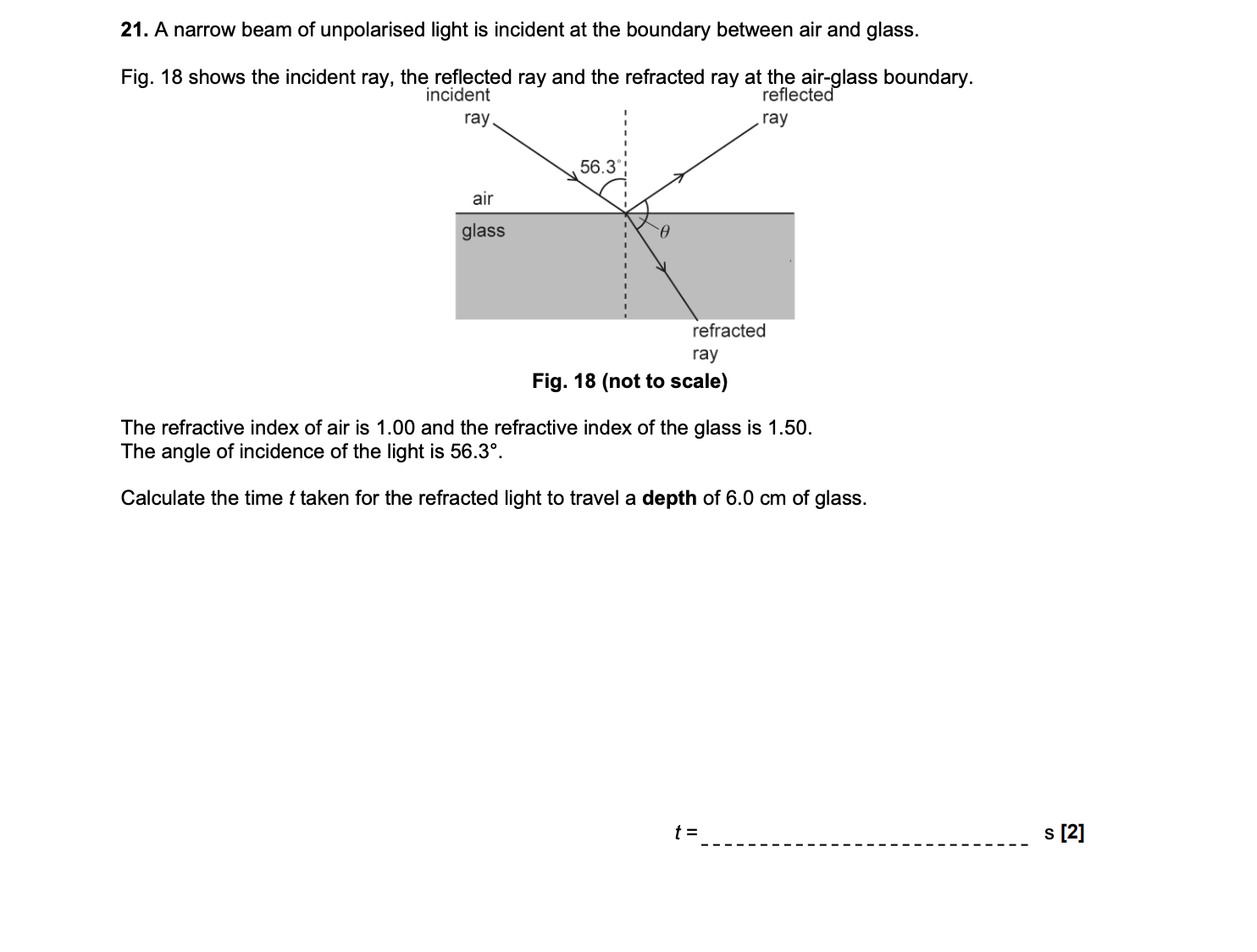
EXAM Q (refracted wave speed)
Distance = 6 / cos33.7 = 7.2 cm
v = 3×10^8 / 1.5 = 2×10^8
t = 7.2×10^-2 / 2×10^8
t = 3.6×10^-10(s)
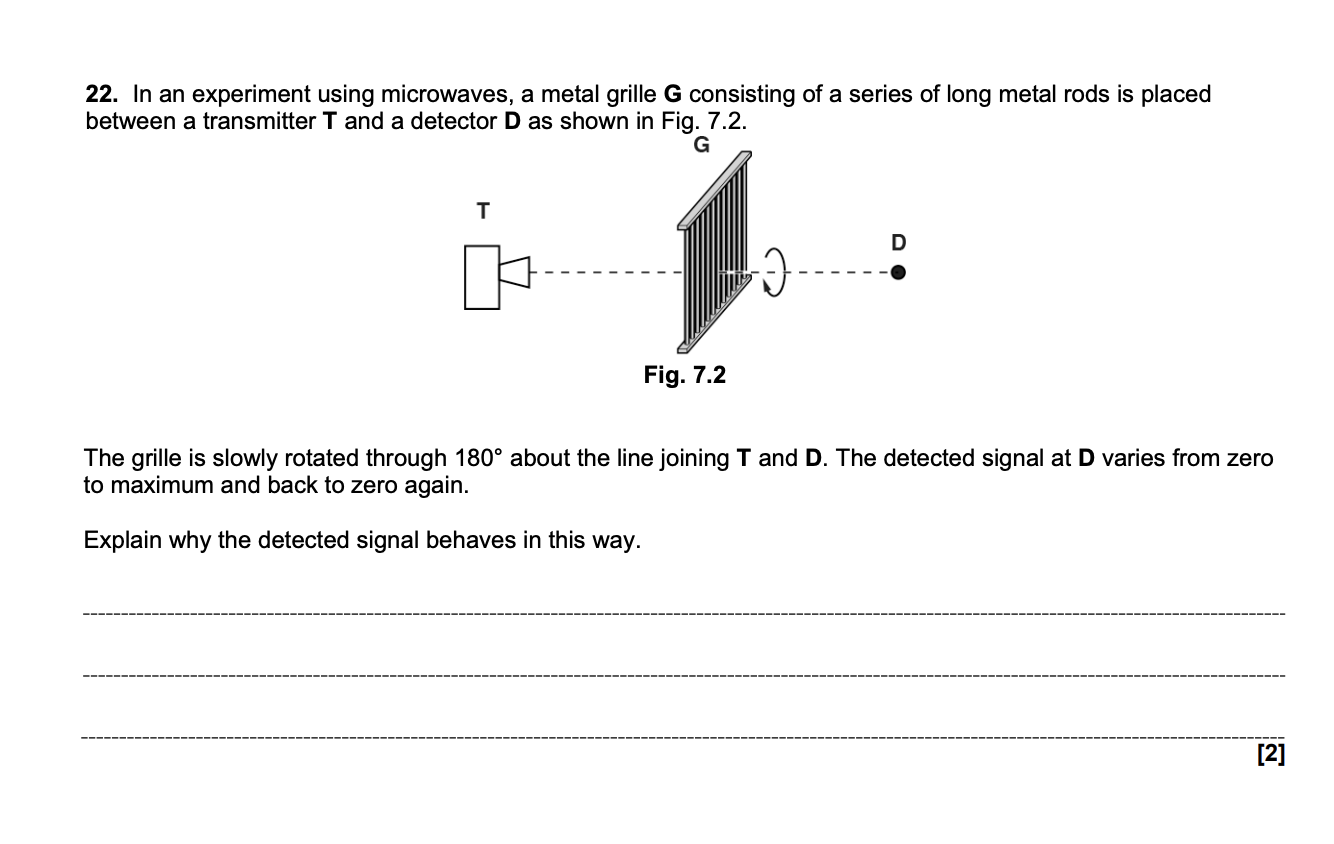
EXAM Q (polarisation of microwaves)
Microwaves from T are transverse. At 0° the grille blocks all the polarised waves and at 90° the grille allows the microwaves to pass through it.
Diffraction
The spreading out of a wave front as it passes through a gap.Maximum diffraction will occur when the gap the wave passes through is the same size as the wavelength of the incident wave.
Young’s Double Slit Experiment
Used to investigate superposition of light.
A laser is placed behind a sheet with two small slits in it, a distance “a” apart. The two coherent waves produced by the double slit overlap and superpose each other. This creates alternating bright (maxima) and dark (minima) fringes on a screen, distance “d” from the double slit. The distance between two adjacent maxima is “x”.
Using the equation:
λ = ax/d we can then determine the wavelength.
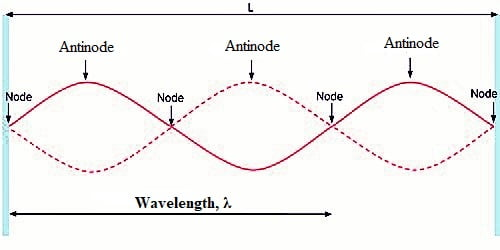
Stationary Waves
Formed when two progressive waves with the same frequency, travelling in opposite directions, superpose.
Has a series of alternating nodes (points that always have 0 amplitude) and antinodes (points which always have maximum displacement).
Two adjacent nodes are 1/2 λ apart
Producing Stationary Waves
String Method
String is held taught over a pulley. Vibration generator is used to oscillate the string in a coherent manner. Adjust frequency until stationary wave is produced. Initial wave produced is reflected at the pulley, producing two waves with the same frequency travelling in opposite directions. These waves superpose to produce a stationary wave.
Microwave Method
Microwave transmitter is used to produce a wave. This wave is then reflected off a metal plate. The incident and reflected waves superpose to make a stationary wave. A microwave receiver can be moved between the transmitter and the plate to observe minima and maxima.
Tuning Fork Method
Place a tube in a container of water (this allows you to effectively vary the length of the tube). Hit the tuning fork on the table and hold it just above the top of the tube. Adjust the length of the tube until a stationary wave is formed.
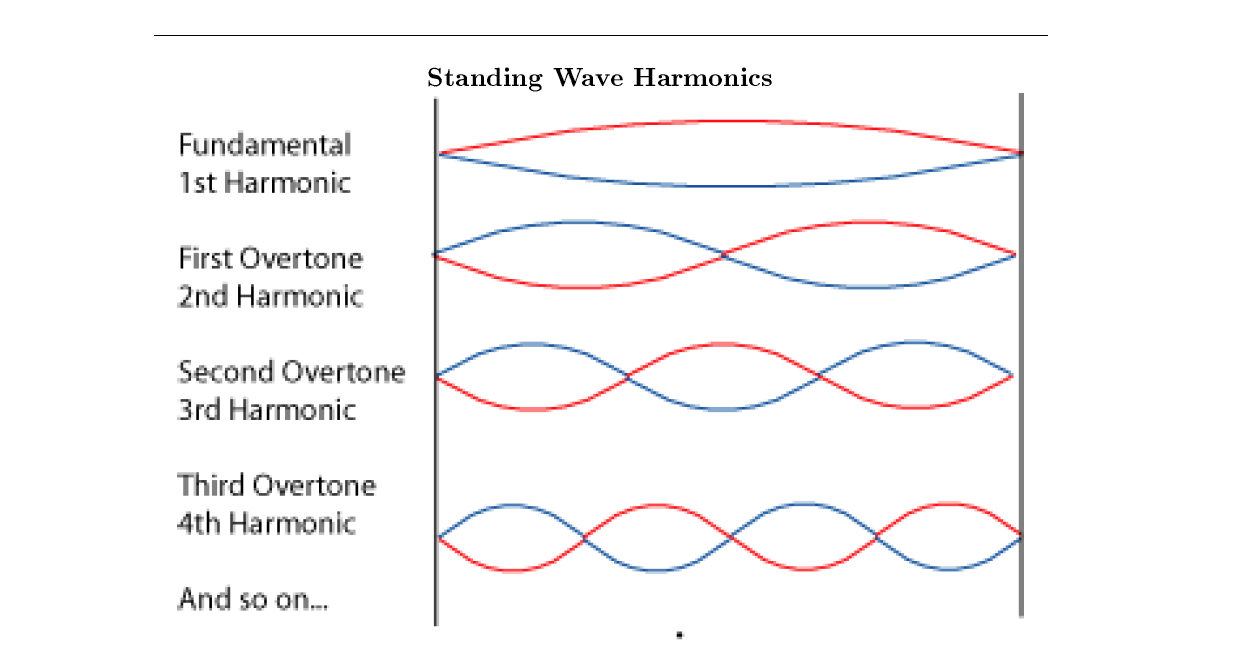
Fundamental Frequency
The lowest frequency which is produced by the oscillation of an object. When the wave vibrates at this frequency it is called the first harmonic.
Draw the first 4 harmonics