Chapter 3 (The chemical basis of life)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
macromolecules
enormous molecules are always synthesized by living things called _
2
New cards
inorganic molecules
substances that do not contain carbon; found in the physical environment
3
New cards
55 to 90
water constitutes _ to _% of the cell
4
New cards
polar molecule
water is a _, meaning it has charges on opposite side
5
New cards
hydrophilic
substances that readily dissolve in water are called _
6
New cards
cohesion
tendency of water molecules to stick together
7
New cards
surface tension
measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
8
New cards
organic molecules
chemical compounds that contain carbon
9
New cards
carbon chains
In which carbon atoms are linked together, form the framework of biological molecules
10
New cards
carbohydrates
_ are organic molecules, which are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with the ratio 1:2:1; Include sugars and starches.
include simple sugars and sugar polymers. – They serve as energy storage molecules, structural components, and also function as membrane receptors
include simple sugars and sugar polymers. – They serve as energy storage molecules, structural components, and also function as membrane receptors
11
New cards
disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined by condensation (dehydration) reaction
12
New cards
polysaccharides
_ are carbohydrates consisting of hundreds to few thousands of monosaccharide units linked together by dehydration synthesis.
13
New cards
starch
polysaccharide stored in the roots, tissues, and other parts of the plant body. It is composed purely of glucose units.
14
New cards
glycogen
referred to as “animal starch,” is stored in the liver and muscles of animals.
15
New cards
cellulose
_ is the tough, rigid material that encloses plant cell and the major component of the woody parts of plants; serves as the bundles of “fibers” that cleans our digestive tract.
16
New cards
chitin
polysaccharide that forms outer covering of arthropods
17
New cards
lipids
non-polar, organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen with some forms containing small amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus
18
New cards
complex lipids
type of lipids:
contain fatty acids such as triglycerides and phospholipids
contain fatty acids such as triglycerides and phospholipids
19
New cards
simple lipids
type of lipids:
do not contain fatty acids such as cholesterol, plant pigments, some vitamins, and hormones.
do not contain fatty acids such as cholesterol, plant pigments, some vitamins, and hormones.
20
New cards
fatty acid
the basic building block of fats; non-polar molecules which is not soluble in water (hydrophobic, water-fearing)
21
New cards
triglyceride
glyceride occurring naturally in animal and vegetable tissues; it consists of three individual fatty acids bound together in a single large molecule; are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood
22
New cards
phospolipid
_ composes the plasma membrane of the cell.
23
New cards
insoluble
Characteristics of Fats:
Fats are _ in water
Fats are _ in water
24
New cards
vary
Characteristics of Fats:
Fat molecules _
Fat molecules _
25
New cards
length
Characteristics of Fats:
The fatty acid bonded to a glycerol molecule varies in _.
The fatty acid bonded to a glycerol molecule varies in _.
26
New cards
saturated or unsaturated
Characteristics of Fats:
ii may be _ or _
ii may be _ or _
27
New cards
saturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
No double bonds between carbon atoms
in the fatty acid chain
No double bonds between carbon atoms
in the fatty acid chain
28
New cards
saturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
Contain more hydrogen atoms
Contain more hydrogen atoms
29
New cards
saturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
Usually solid at room temperature since
the carbon atoms pack closely
Usually solid at room temperature since
the carbon atoms pack closely
30
New cards
unsaturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
With one or more double bonds between carbon
atoms in the fatty acid chain
With one or more double bonds between carbon
atoms in the fatty acid chain
31
New cards
unsaturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
With less Hydrogen atoms
With less Hydrogen atoms
32
New cards
unsaturated
Determine if saturated or unsaturated fatty acid:
Liquid at room temperature. The presence of double bonds in the carbon atoms causes the formation of kinks that prevent the carbon atoms from packing together
Liquid at room temperature. The presence of double bonds in the carbon atoms causes the formation of kinks that prevent the carbon atoms from packing together
33
New cards
Structural protein
Types of Proteins:
Support; ex. Collagen, elastin, and keratin
Support; ex. Collagen, elastin, and keratin
34
New cards
Enzymatic protein
Types of Proteins:
Catalyze metabolic reactions; ex. Digestive enzymes
Catalyze metabolic reactions; ex. Digestive enzymes
35
New cards
Storage protein
Types of Proteins:
Stores amino acids; ex. Albumin in egg white, casein in milk
Stores amino acids; ex. Albumin in egg white, casein in milk
36
New cards
Transport protein
Types of Proteins:
Transport of substance; ex. Hemoglobin, membrane transport
proteins
Transport of substance; ex. Hemoglobin, membrane transport
proteins
37
New cards
Contractile protein
Types of Proteins:
Movement; ex. Actin and myosin in muscles
Movement; ex. Actin and myosin in muscles
38
New cards
Defensive protein
Types of Proteins:
Protective/Immunity; ex, Antibodies of the immune system
Protective/Immunity; ex, Antibodies of the immune system
39
New cards
Hormonal protein
Types of Proteins:
Coordination of activities; ex, Glucagon, adrenalin, testosterone, estrogen
Coordination of activities; ex, Glucagon, adrenalin, testosterone, estrogen
40
New cards
amino acids
building block in the synthesis of protein
41
New cards
nucleic acids
_ are important in the synthesis of protein and play as the "Information" molecules of living organisms.
42
New cards
nucleotides
nucleic acids are composed of a long chain of similar but not identical building blocks called _
43
New cards
pentose, phosphate group, and nitrogen-containing base
A nucleotide molecule is composed of three parts: _ or a five-carbon sugar which maybe ribose or deoxyribose, a _, and a _.
44
New cards
deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid
two types of nucleic acids
45
New cards
ribonucleic acid
key material in the synthesis of protein; manufactured in the nucleolus of the cell as directed and coded by the DNA molecule
46
New cards
adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
nucleotide
(called ribonucleotide) is composed of the sugar ribose that chemically bonds with phosphate on
one side and to any one of the following bases: _, _, _, and _
(called ribonucleotide) is composed of the sugar ribose that chemically bonds with phosphate on
one side and to any one of the following bases: _, _, _, and _
47
New cards
deoxyribose nucleic acid
material that composes the genes that are passed on from one generation of cells to the next.
48
New cards
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
deoxyribose nucleotide is composed of the sugar deoxyribose that can bond to a phosphate on one side and to any one of the
following bases: _, _, _, and _.
following bases: _, _, _, and _.
49
New cards
thymine
Pairing rule:
Adenine always pair with _
Adenine always pair with _
50
New cards
guanine
Pairing rule:
_ always pair with cytosine
_ always pair with cytosine
51
New cards
hydrolysis reactions
involve the usage of water in order to split a particular material. By doing so, two portions of the water molecule will be combined with the material
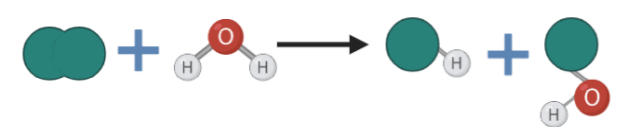
52
New cards
Hydrocarbons
contain only carbon and hydrogen
53
New cards
Biochemicals
carbon-containing molecules produced by living organisms
54
New cards
Functional groups
groups of atoms giving organic molecules different characteristics and properties
55
New cards
polymerization
any process in which relatively small molecules, called monomers, combine chemically to produce a very large chainlike or network molecule, called a polymer.
56
New cards
Sucrose
(table sugar), major component of plant sap; carries chemical energy from one part of t
57
New cards
Lactose
(milk sugar) fuel for early growth and development of newborns.
a. lactase that hydrolyzes it is found in membranes of cells lining intestines
b. if lose this enzyme after childhood, eating dairy products cause digestive discomfort
a. lactase that hydrolyzes it is found in membranes of cells lining intestines
b. if lose this enzyme after childhood, eating dairy products cause digestive discomfort
58
New cards
Non-covalent bonds
attractive forces that are weaker than covalent bonds.
59
New cards
Ionic bonds
attractions between charged atoms.
60
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
enhance solubility in and interactions with water
occurs when covalently bound hydrogen has a partial positive charge and attracts electrons of a second atom
determine the structure and properties of water
occur between polar groups in biological molecules, such as between the strands of DNA.
occurs when covalently bound hydrogen has a partial positive charge and attracts electrons of a second atom
determine the structure and properties of water
occur between polar groups in biological molecules, such as between the strands of DNA.
61
New cards
Glycosaminoglycans
composed of two different sugars repeating disaccharides (2 different sugars; —A—B—A—B—); found in extracellular space and in connective tissues
62
New cards
Peptidoglycans
polymer of NAG-NAM (N-acetyl glucosamine & N acetyl-muramic acid); structural component of bacterial cell wall
63
New cards
Steroids
four C fused rings animal lipids that have been implicated in atherosclerosis; component of cholesterol, steroid hormones, vit D and bile acids