Basic Cardiac Embryology - Module 4
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
3-7 weeks
What gestational age is the heart formed
True
T/F: the heart is the 1st organ to develop
Cardiogenic area
What first appears in week 3, marking the start of heart formation
Cardiogenic area
What does this image represent
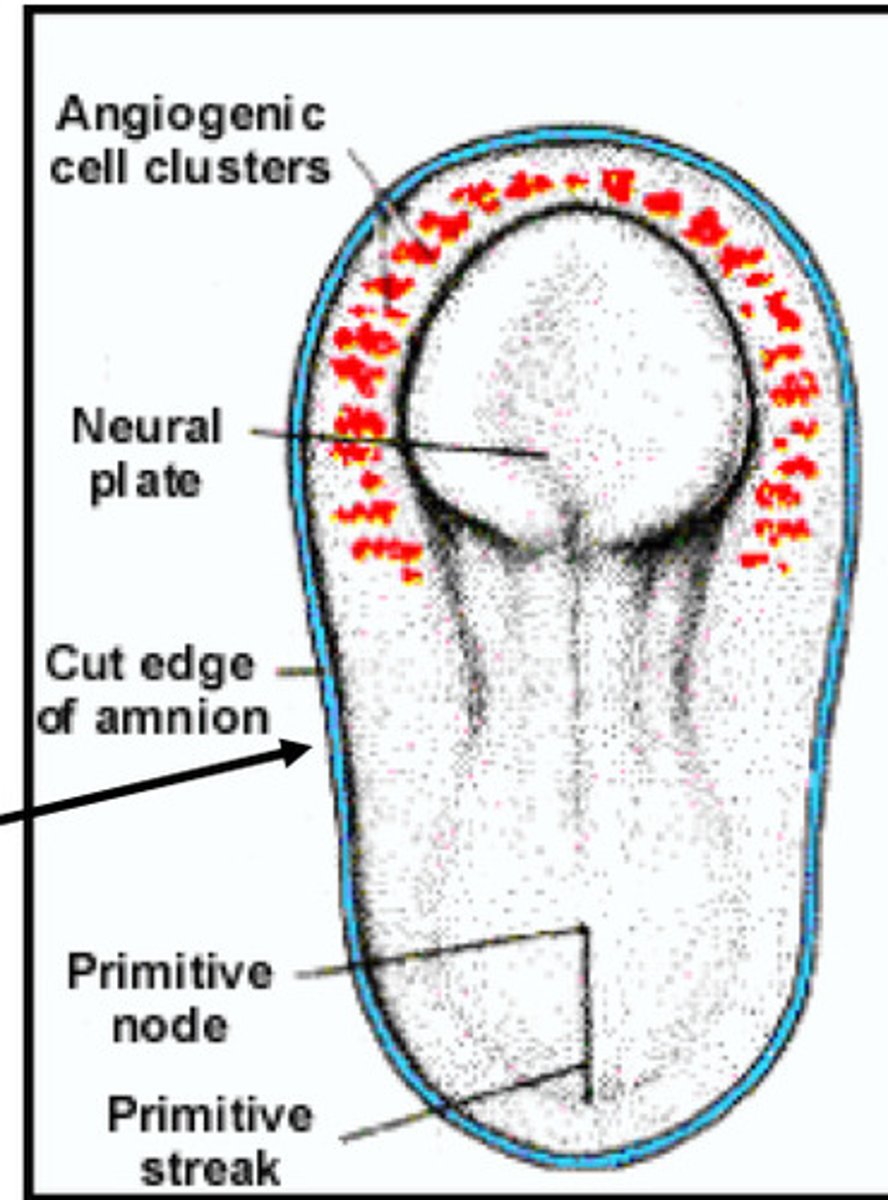
Pericardial cavity
Where does the heart lie
2 tubes
What does the heart start off as
Fuse and twist
What must the 2 heart tubes to in order to from the adult heart
Heart tube fusion
What does this image show
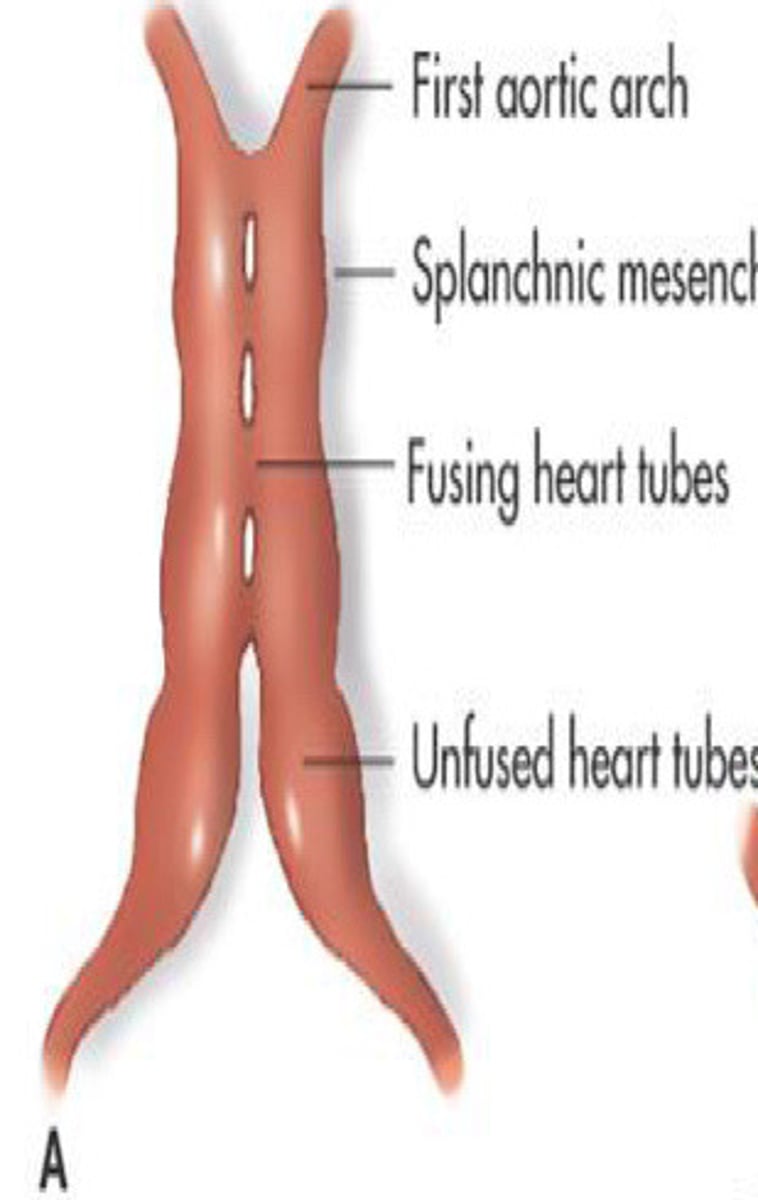
Heart tube begins to fold and twist
What does this image show
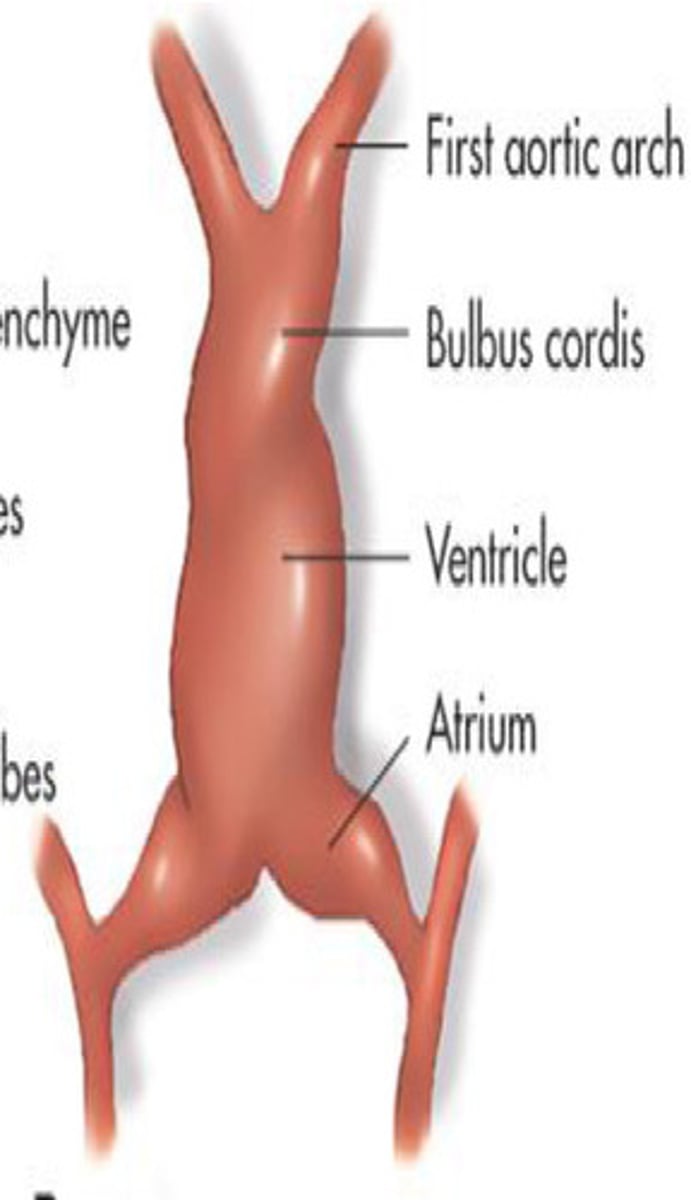
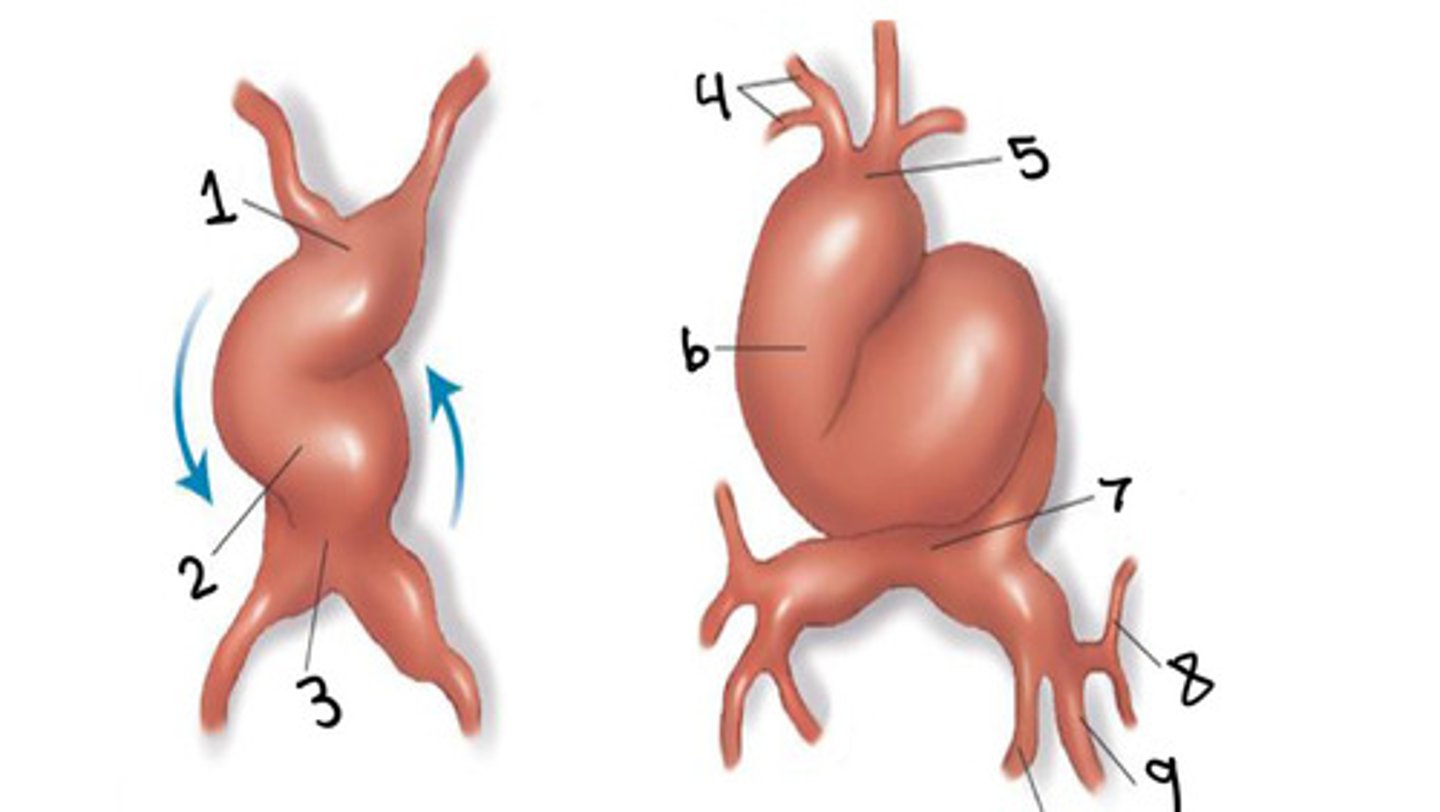
First aortic arch
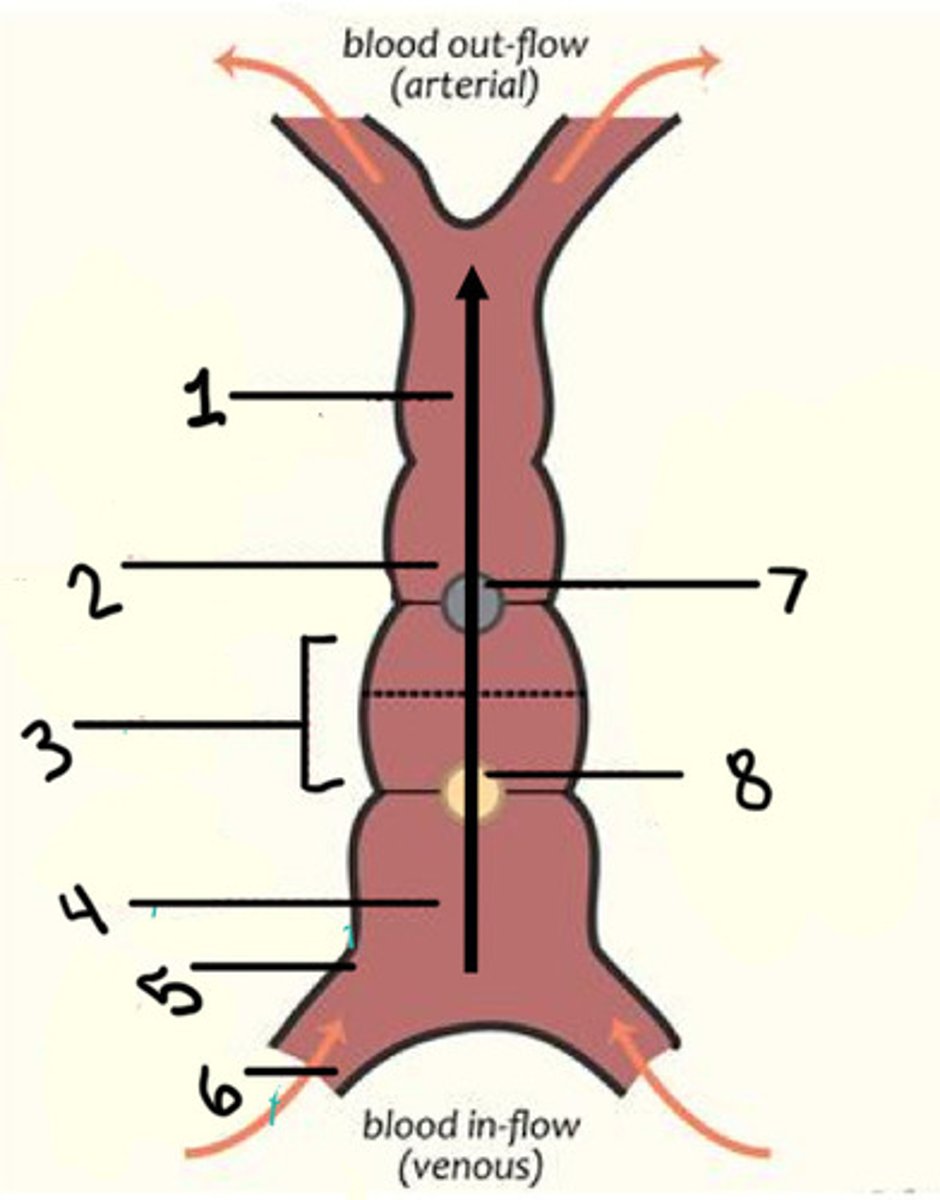
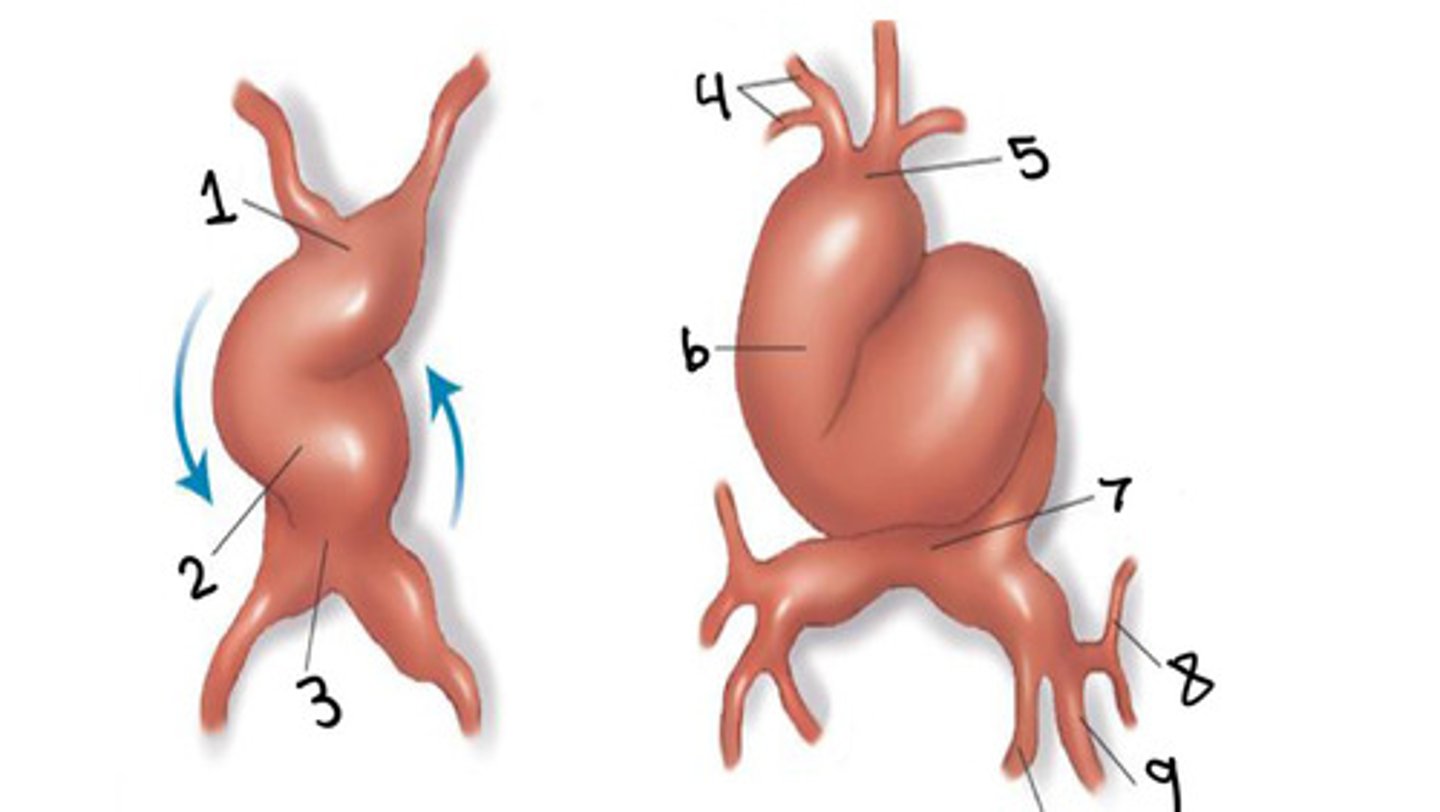
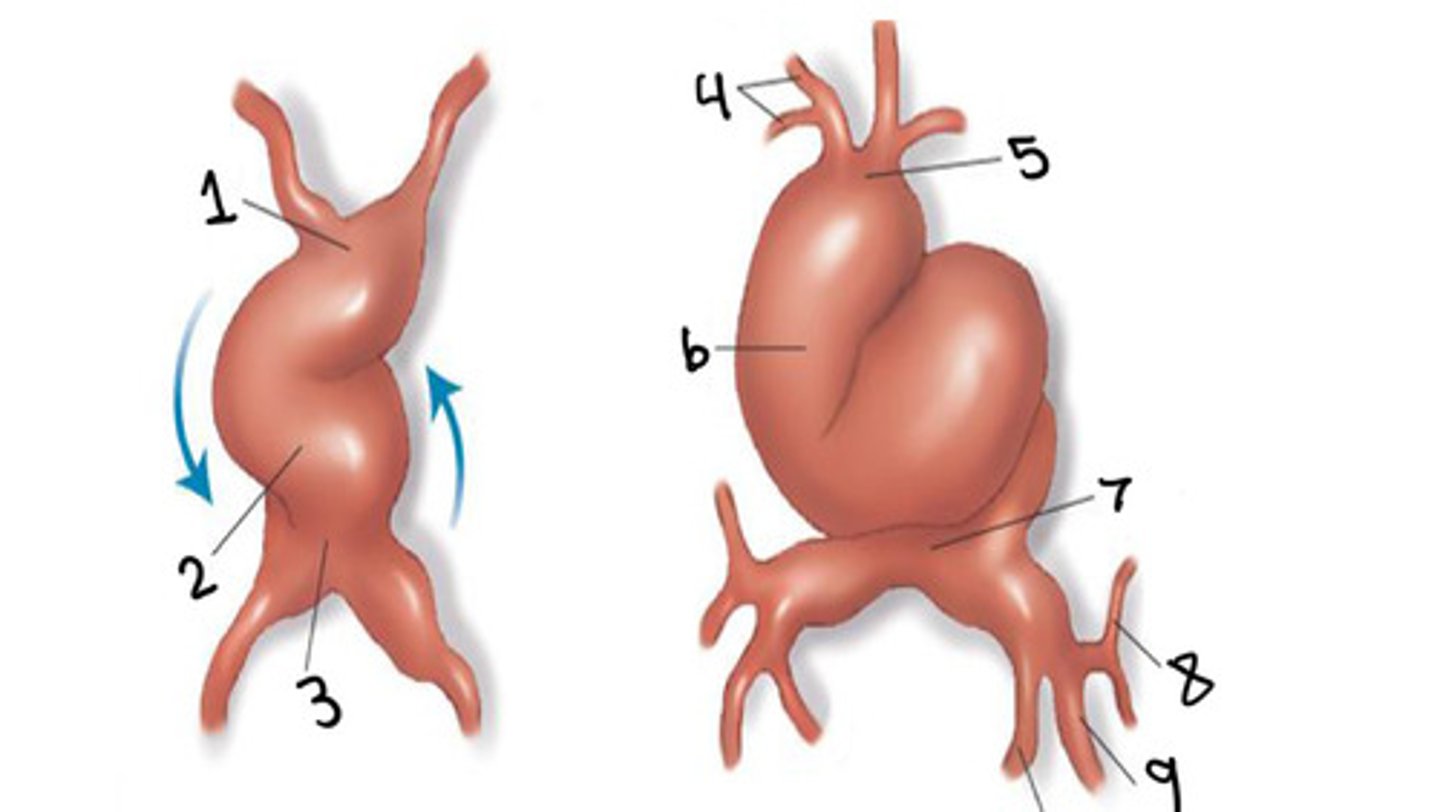
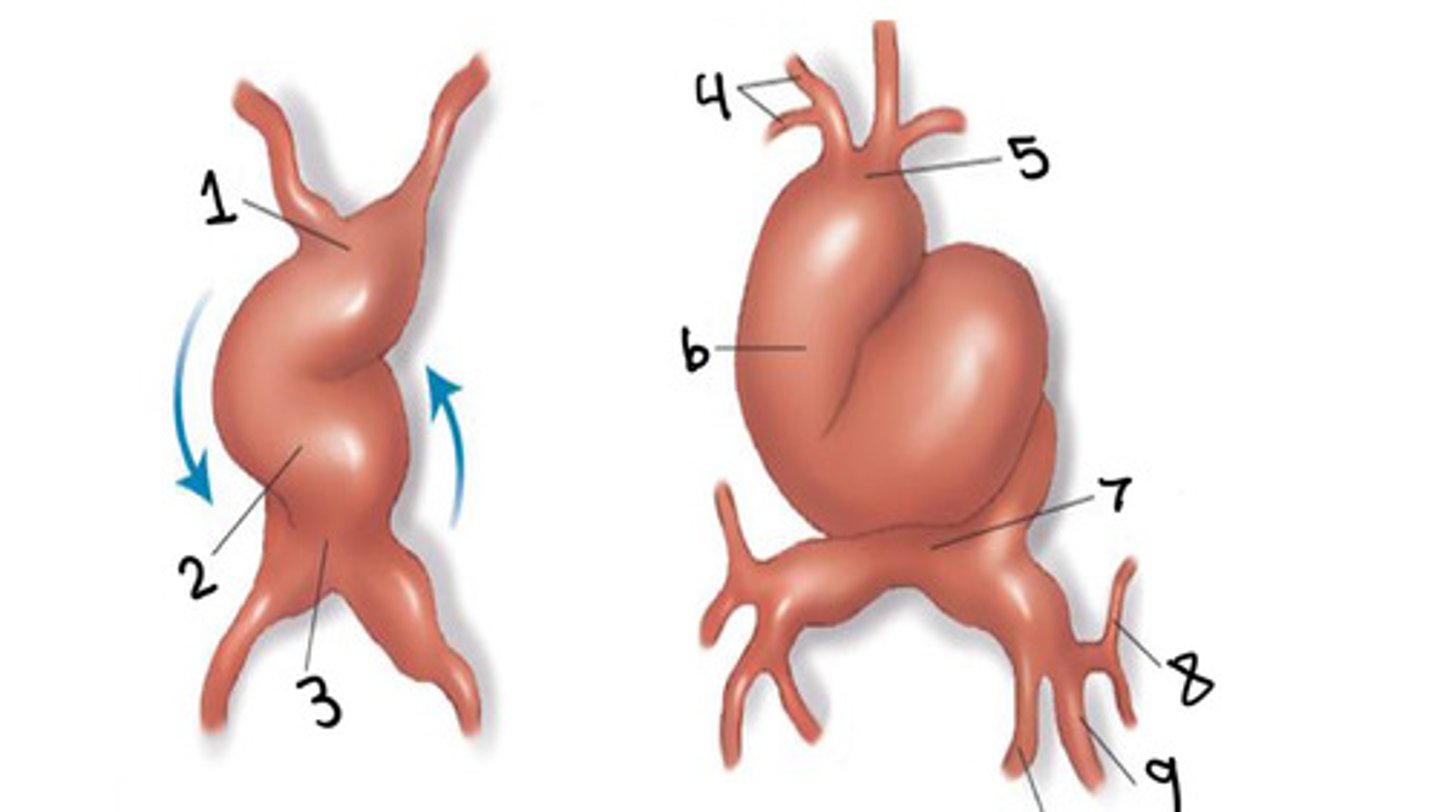
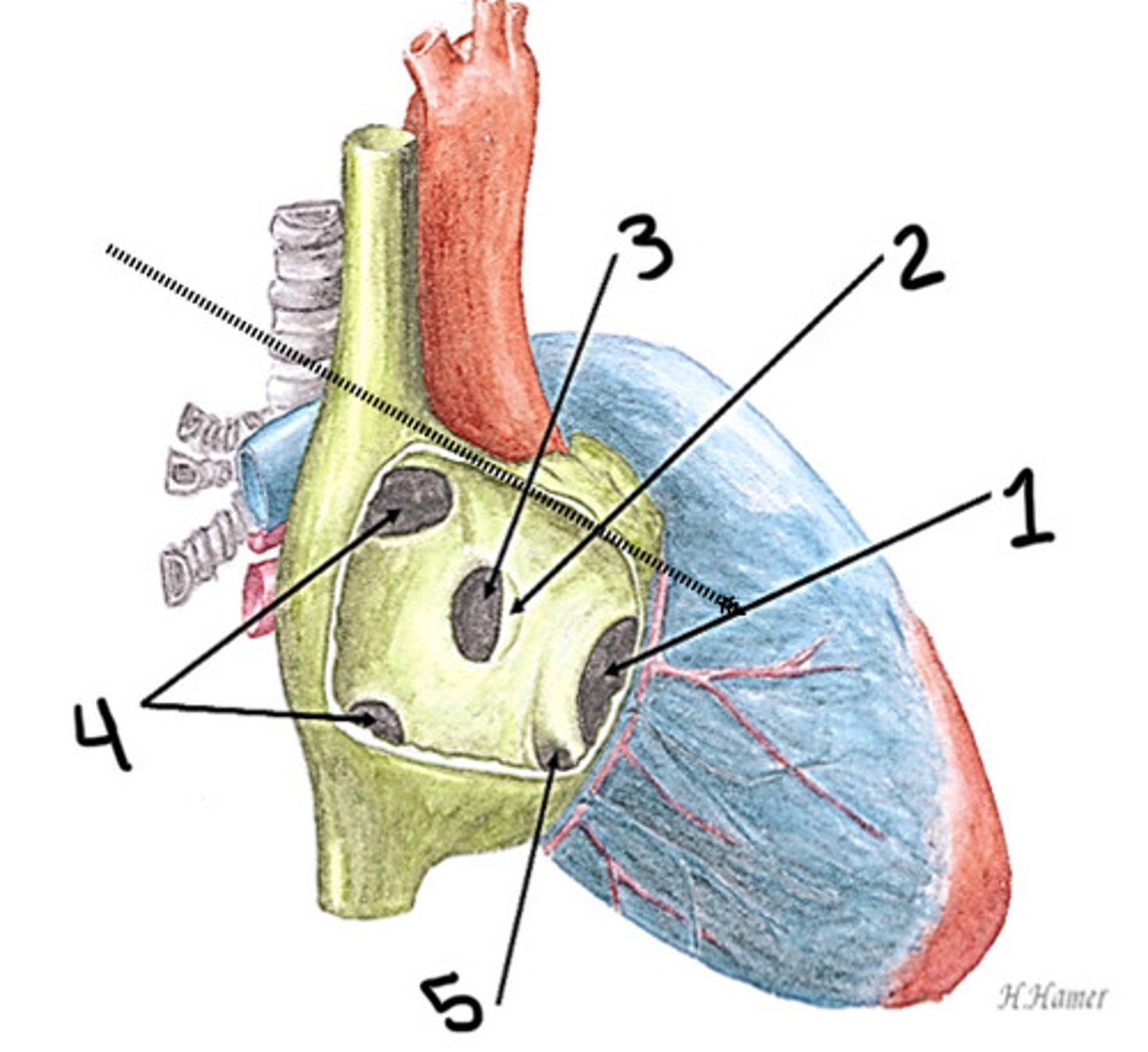
What is 1
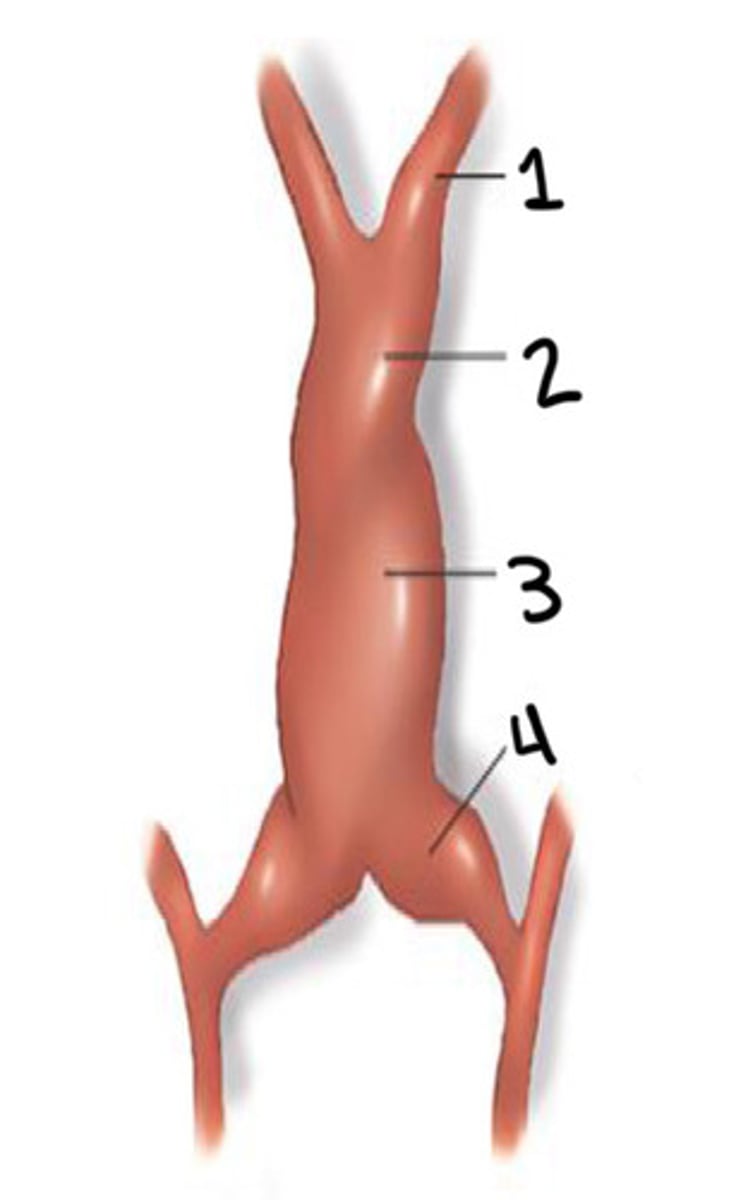
Bulbus cordis
What is 2
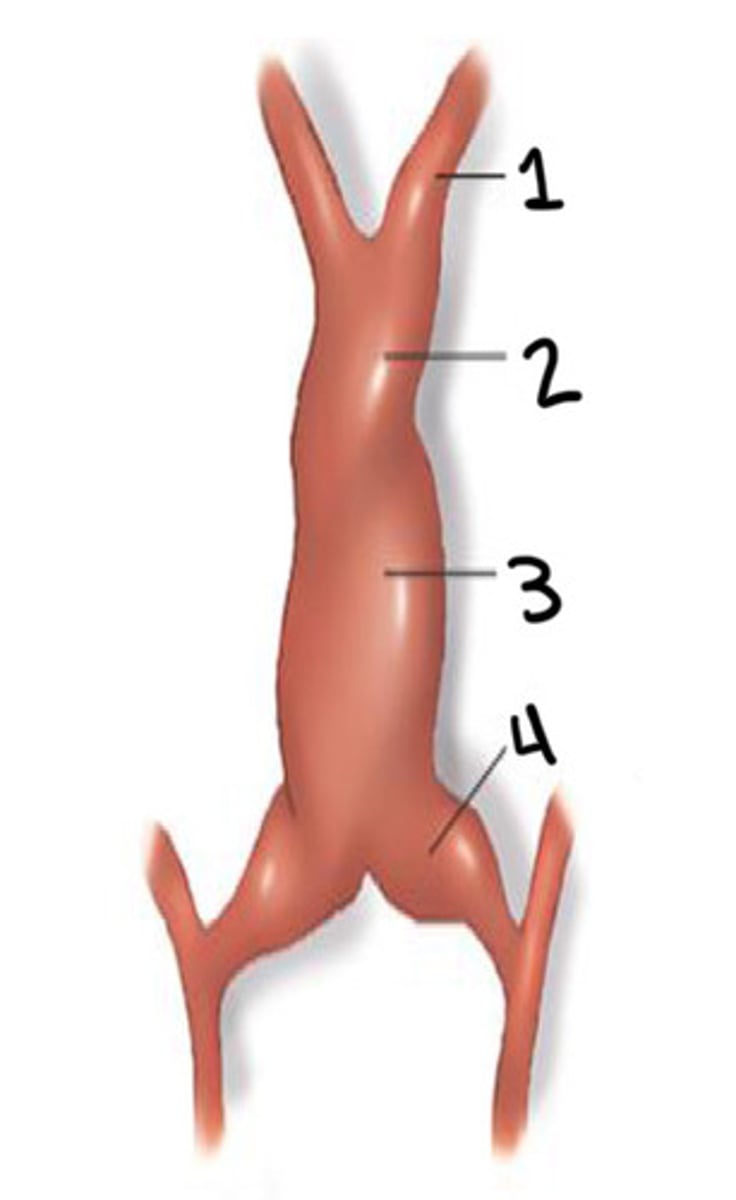
Ventricle
What is 3
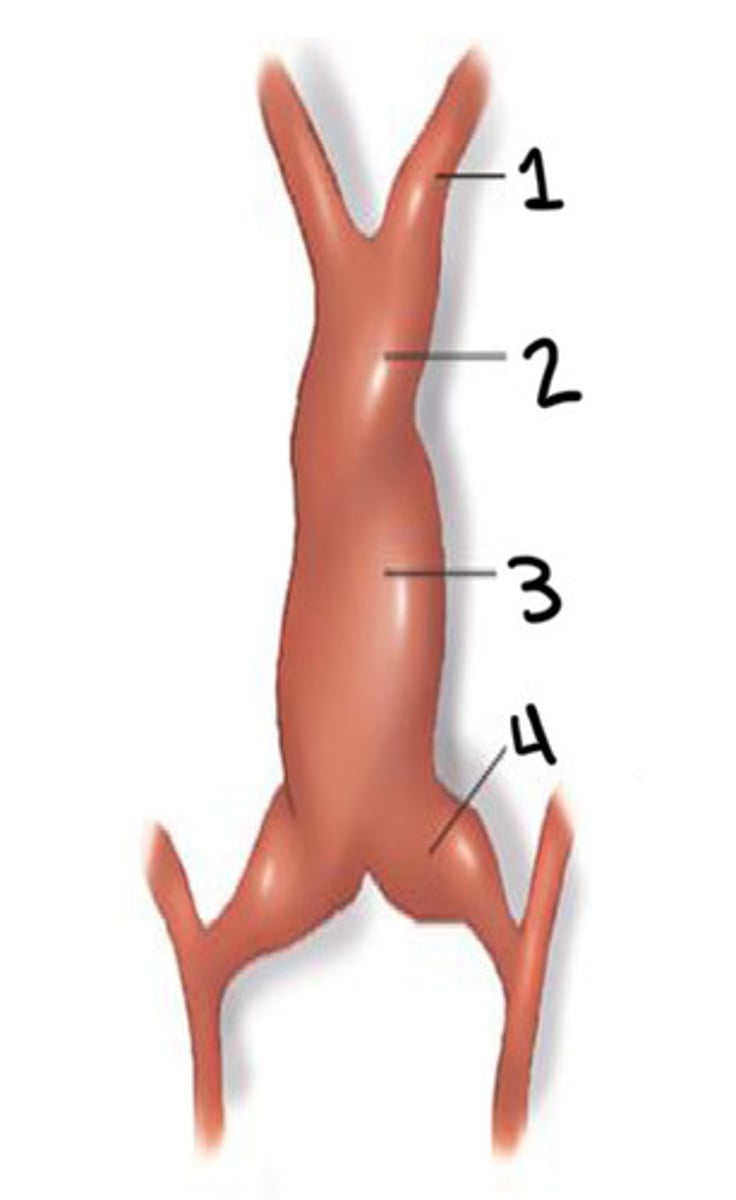
Atrium
What is 4
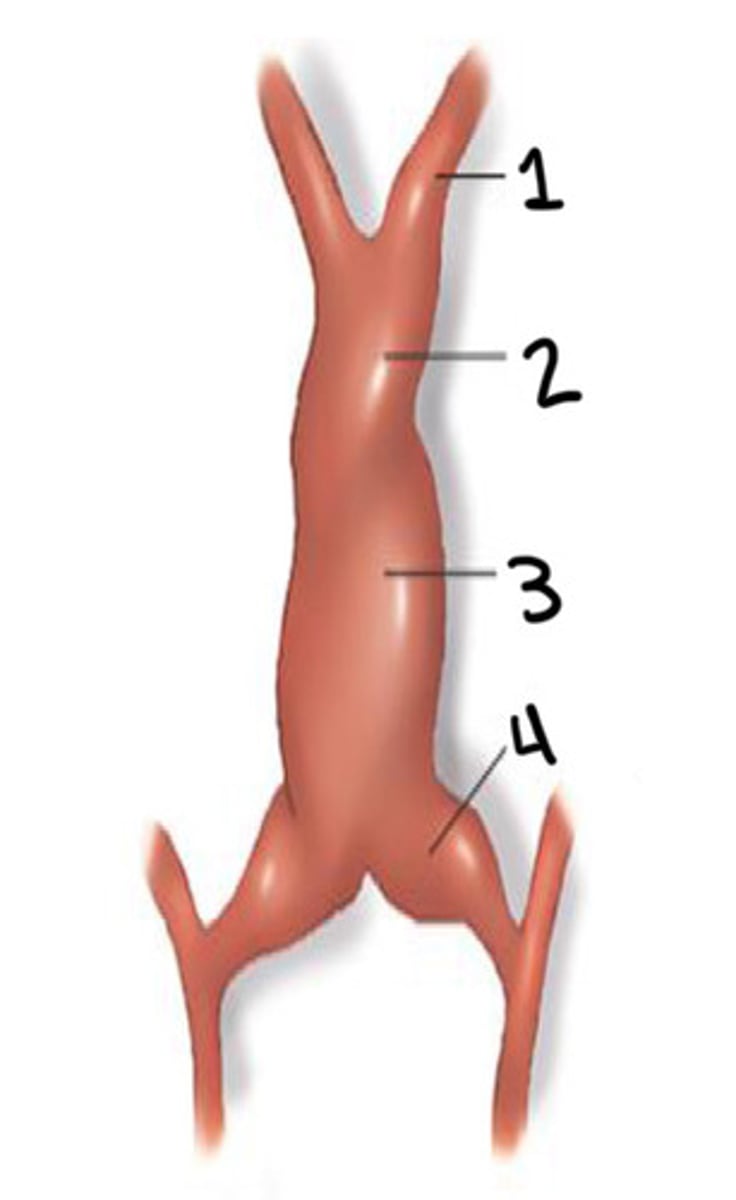
Unidirectional
Describe the blood flow in the fetal heart tube when it first forms
Ascending ao and pulmonary trunk
What does truncus arteriosus develop into
Infundibulum and LVOT
What does bulbus cordis develop into
LV
What does primitive ventricle develop into
Atrium
What does primitive atrium develop into
Coronary sinus
What does sinus venosus develop into
Heart now a more complex structure with two atria and two ventricles
What does looping of the heart transform the single heart tube into
Rightwards
What is normal looping
Leftwards
What is ABNORMAL looping
Top twists to the RT of fetus
Describe how a normal rightwards looping occurs
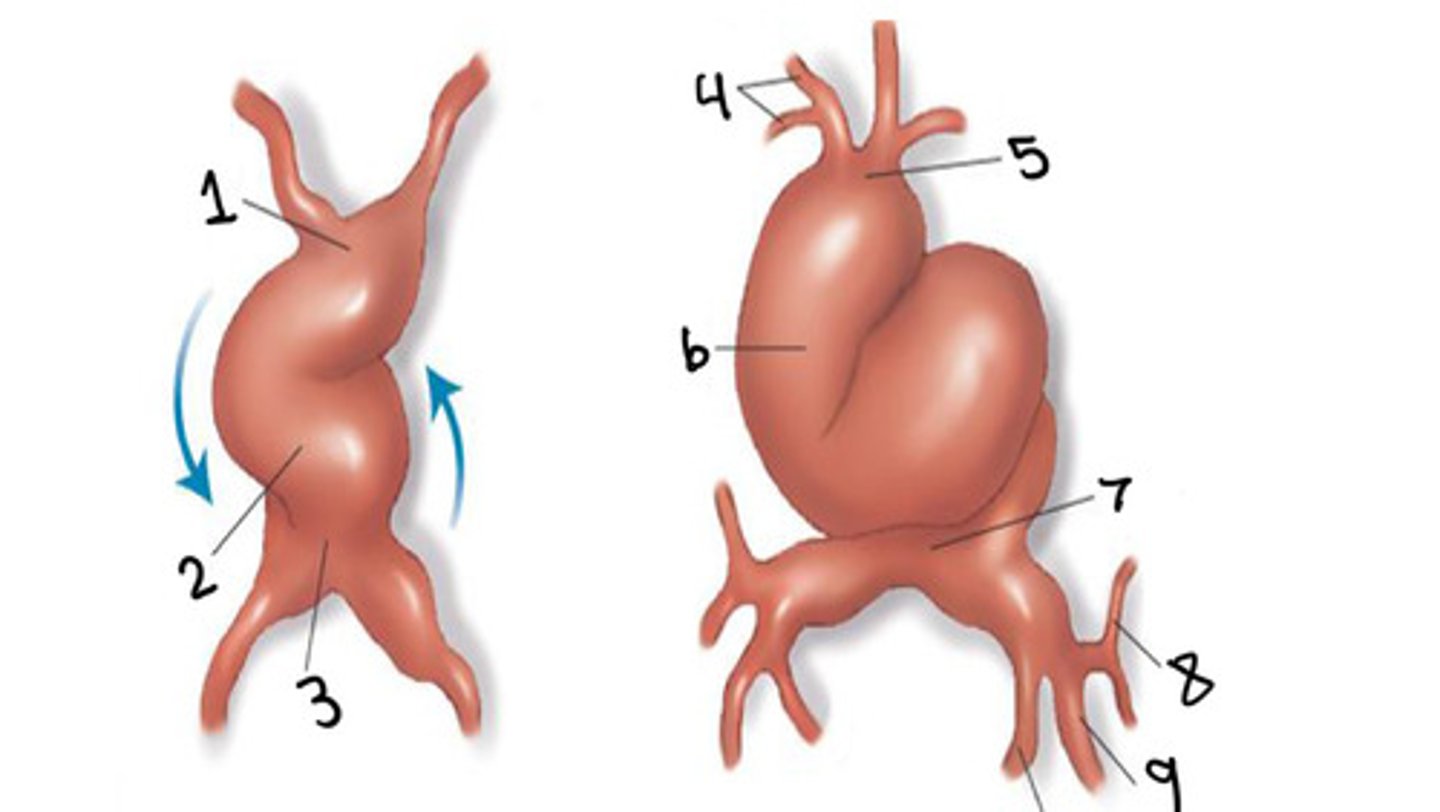
Truncus arteriosus (asc ao + pulm trunk)
What is 1
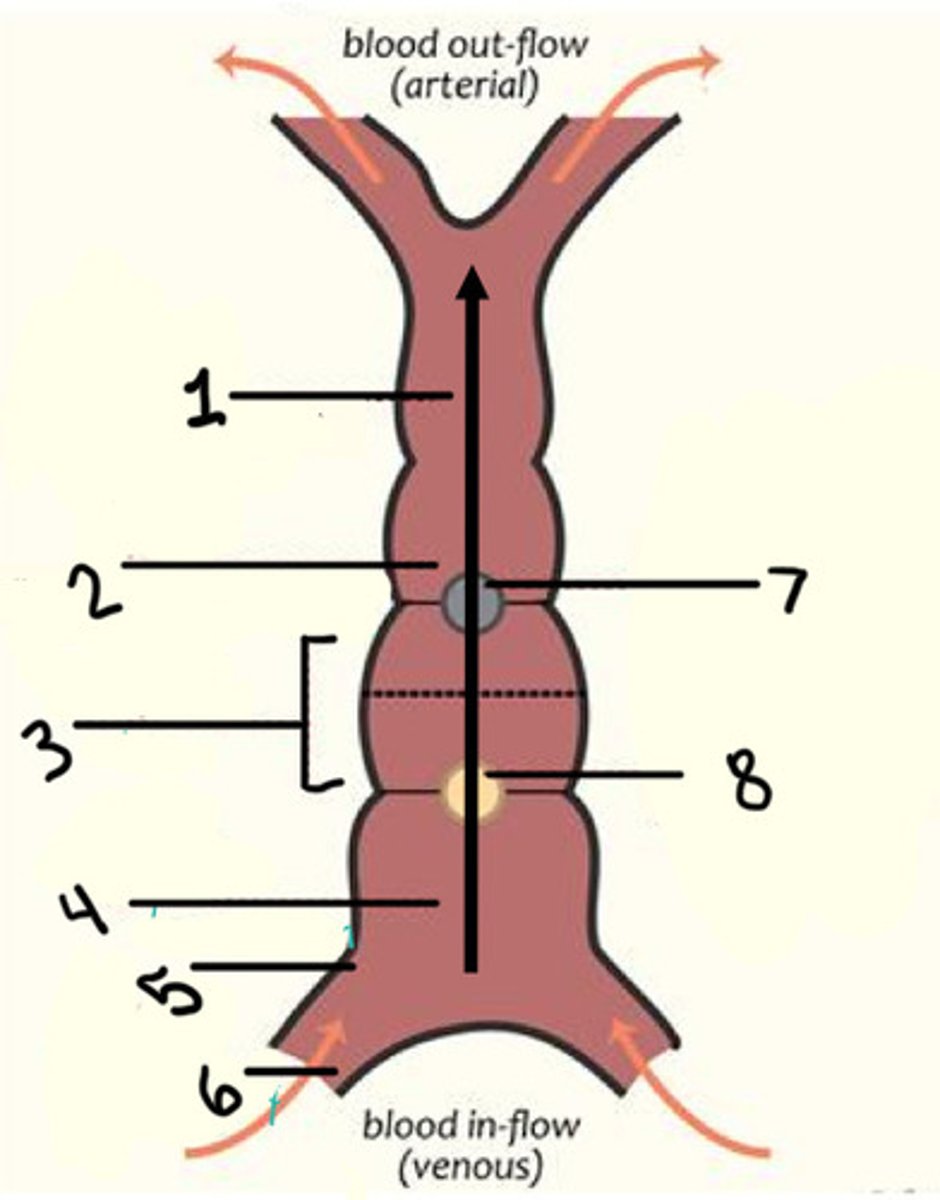
Bulbus cordis (infundibulum + LVOT)
What is 2
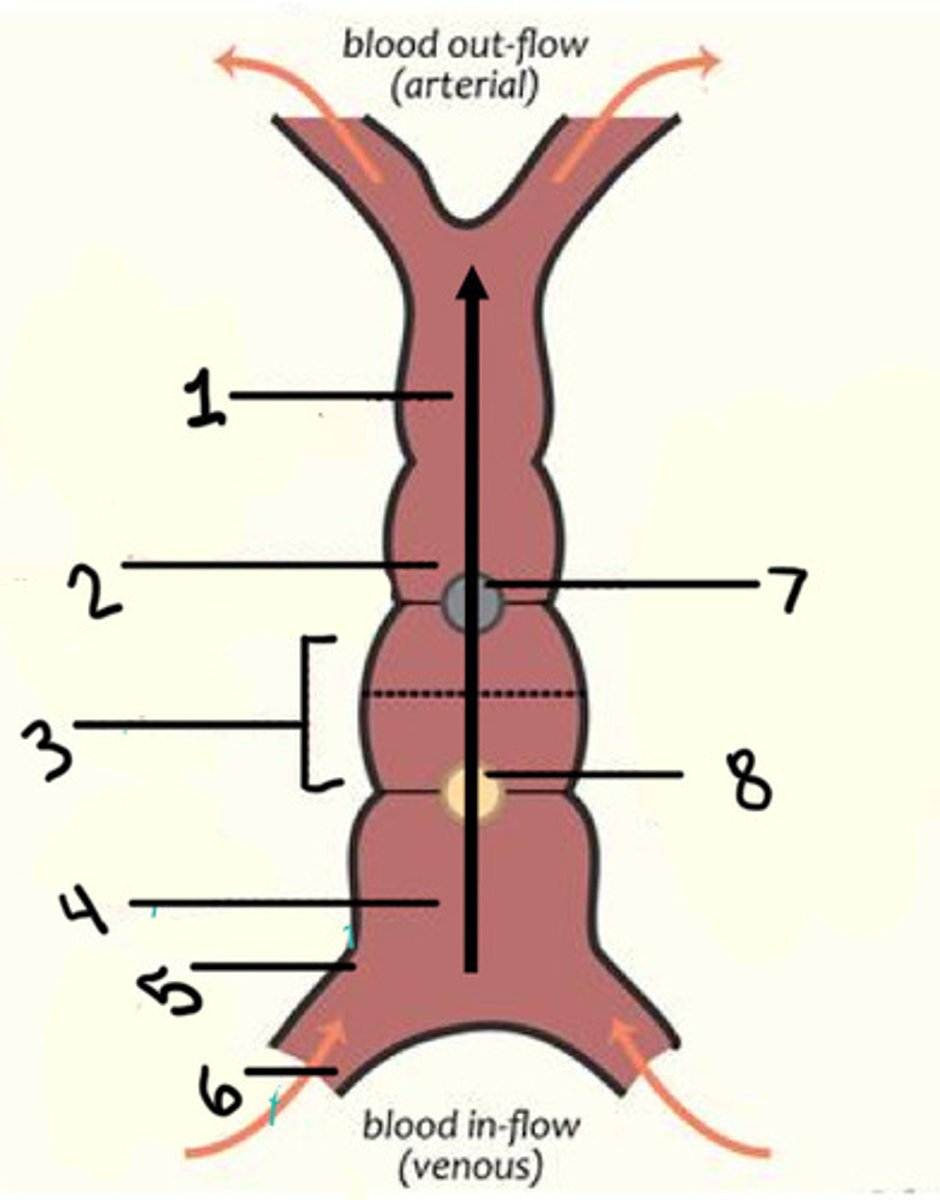
Primitive ventricle (LV/RV?)
What is 3
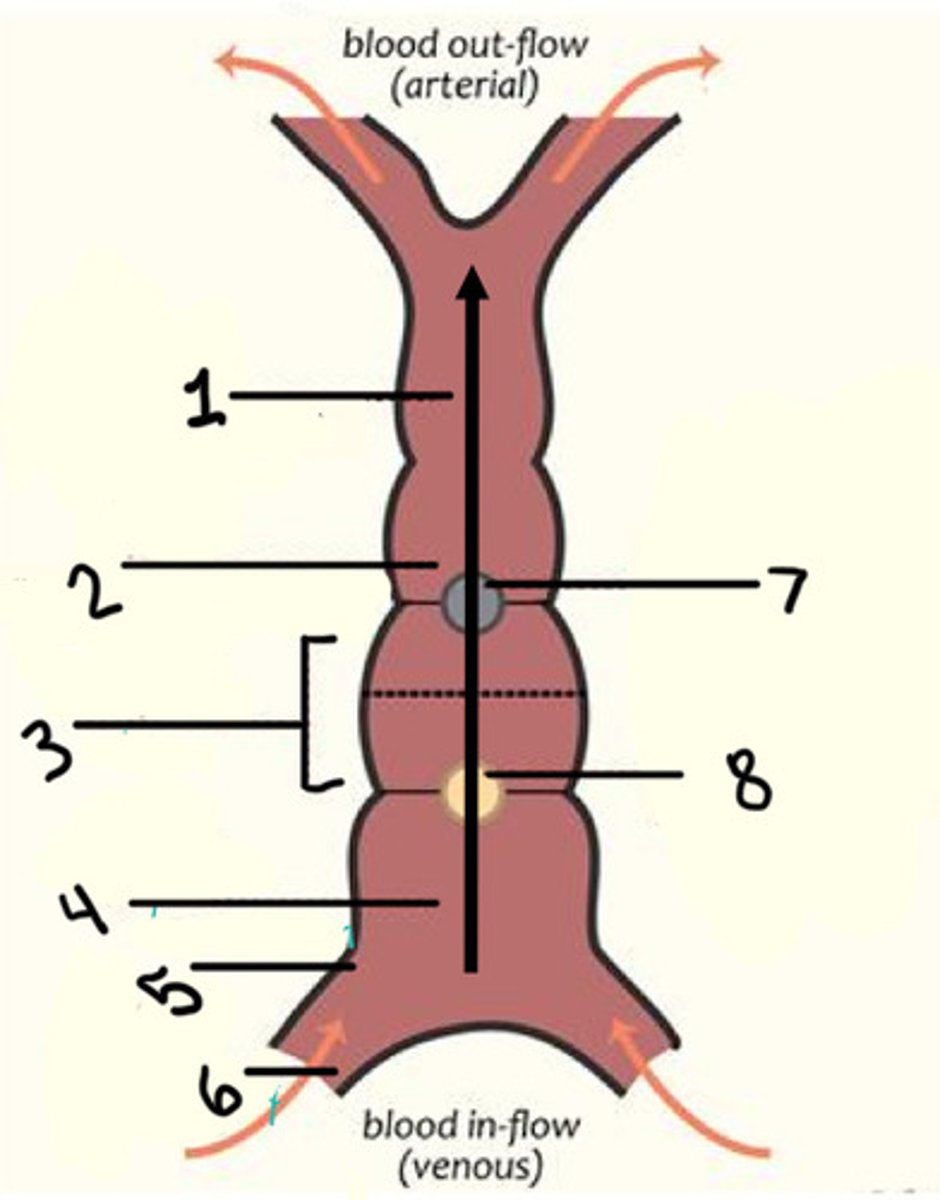
Primitive atrium (atrium)
What is 4
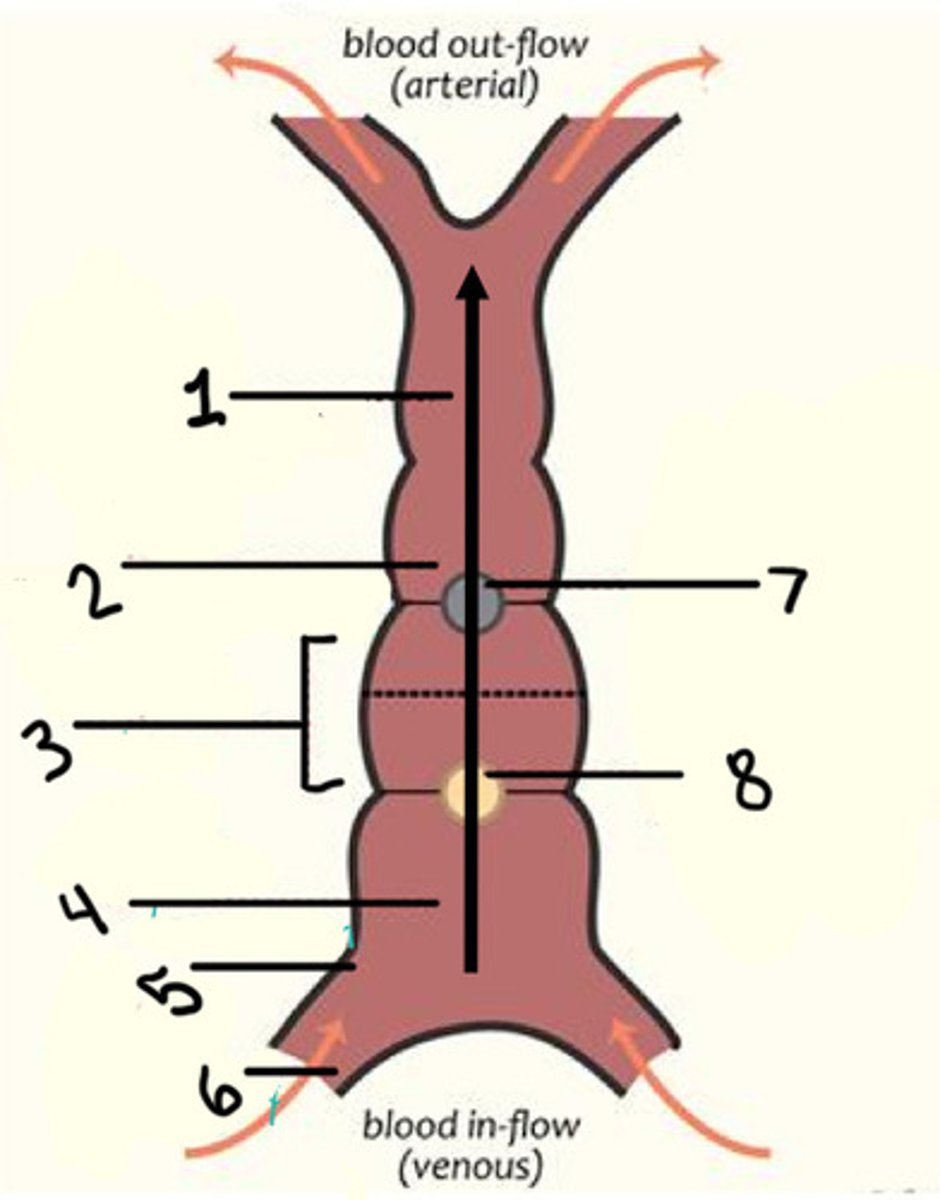
Sinus venosus (coronary sinus)
What is 6
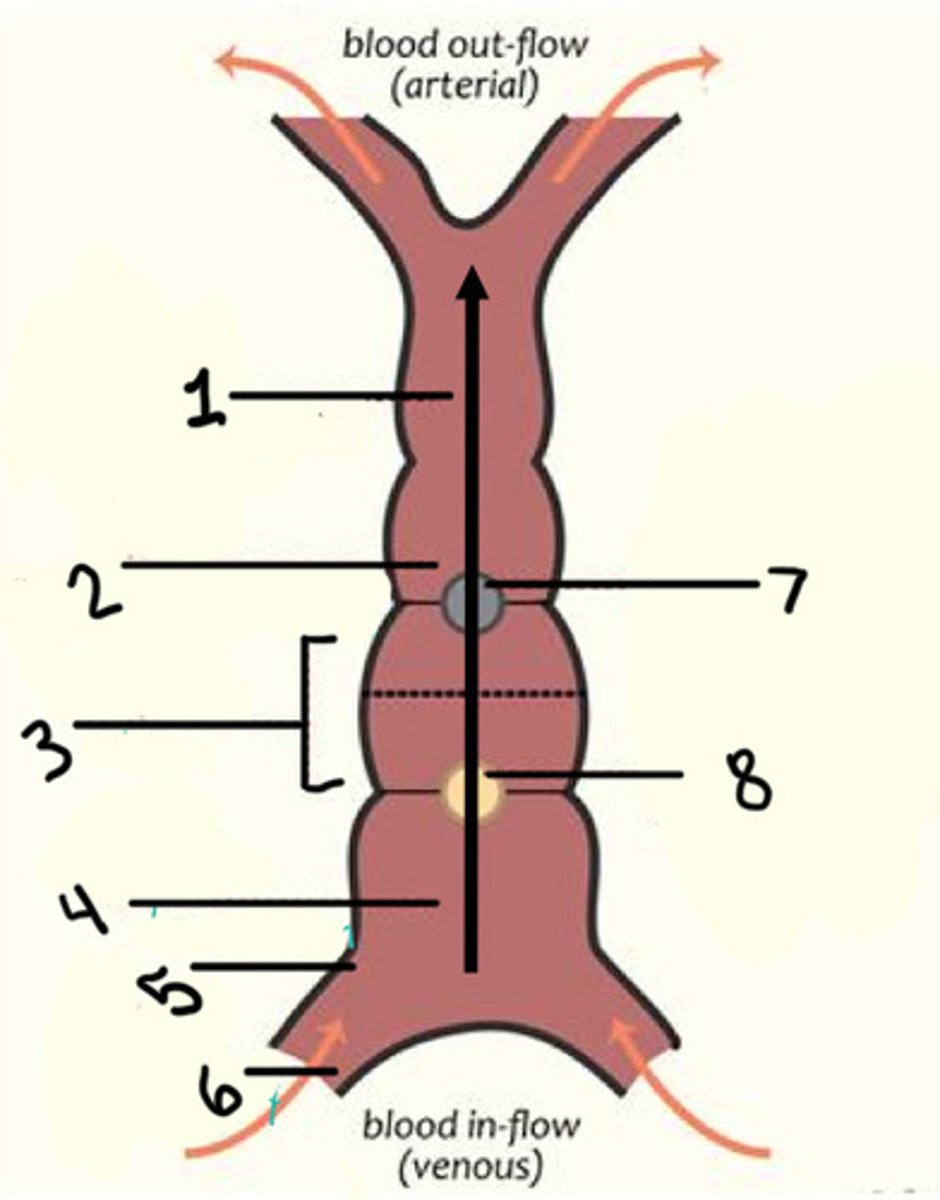
Interventricular secular (IVS)
What is 7
Atrioventricular sulcus (AVS)
What is 8
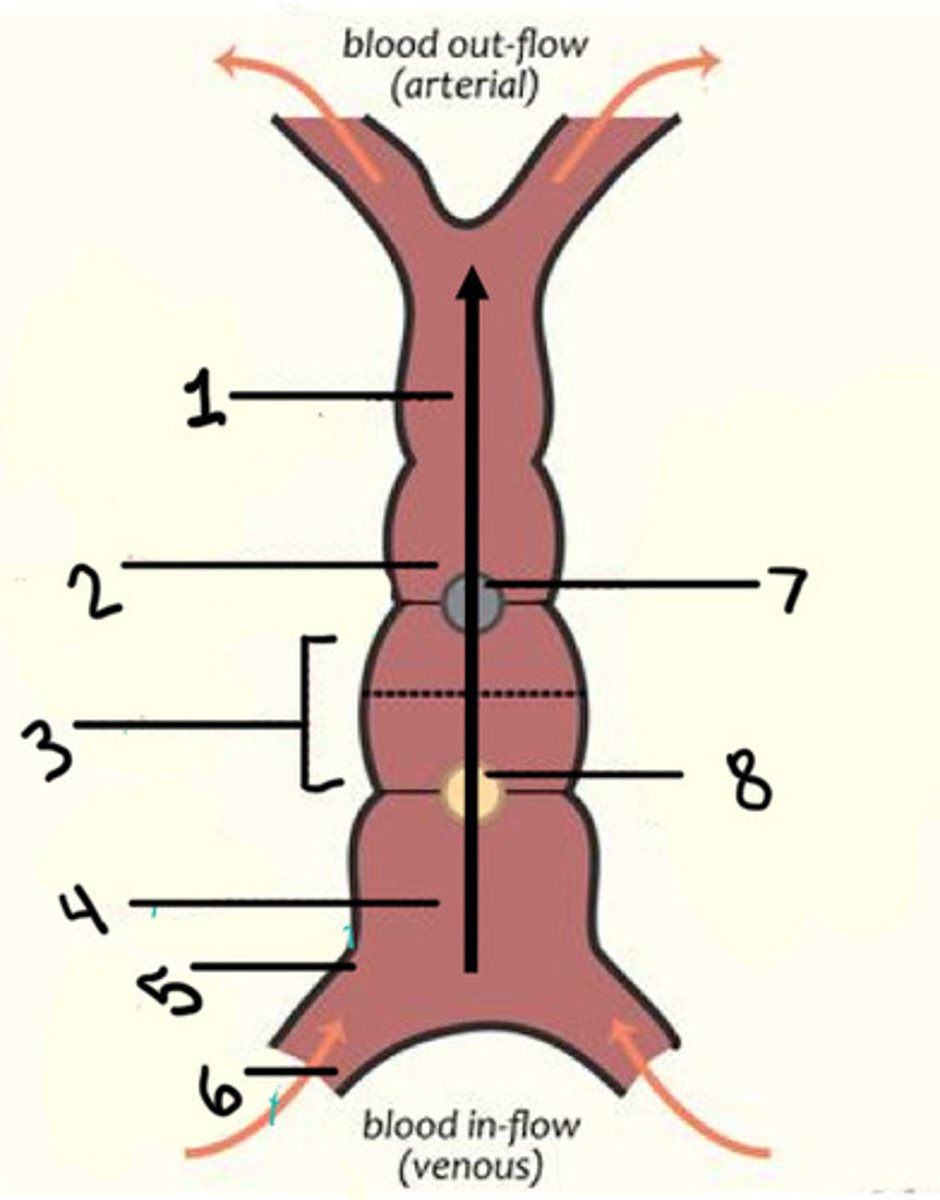
LT transposition of the great arteries
What does leftwards folding result in
LT transposition of the great arteries
What does L-TGA stand for
Separates
What does septum mean
Hole
What does foramen mean
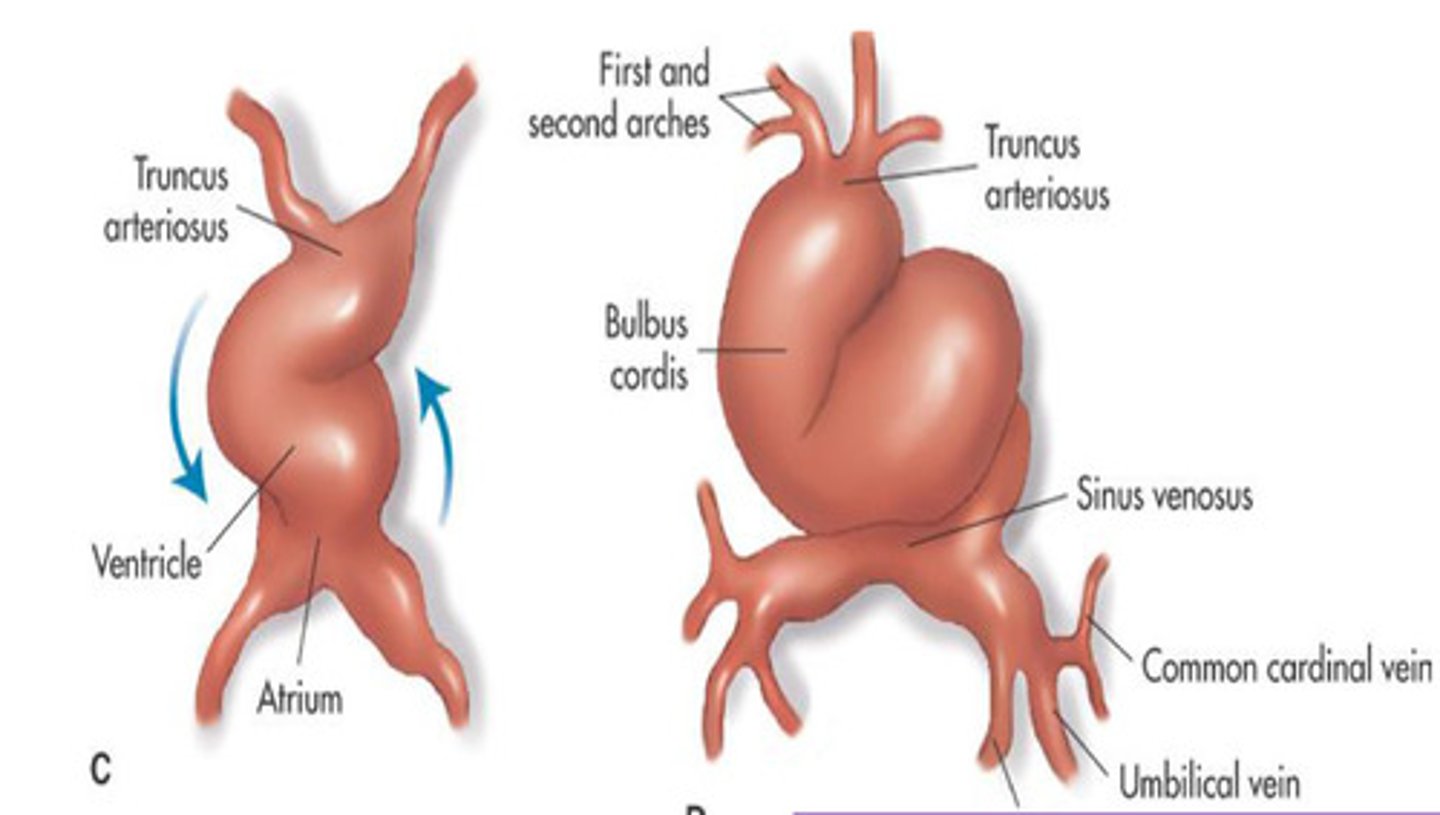
Truncus arteriosus
What is 1
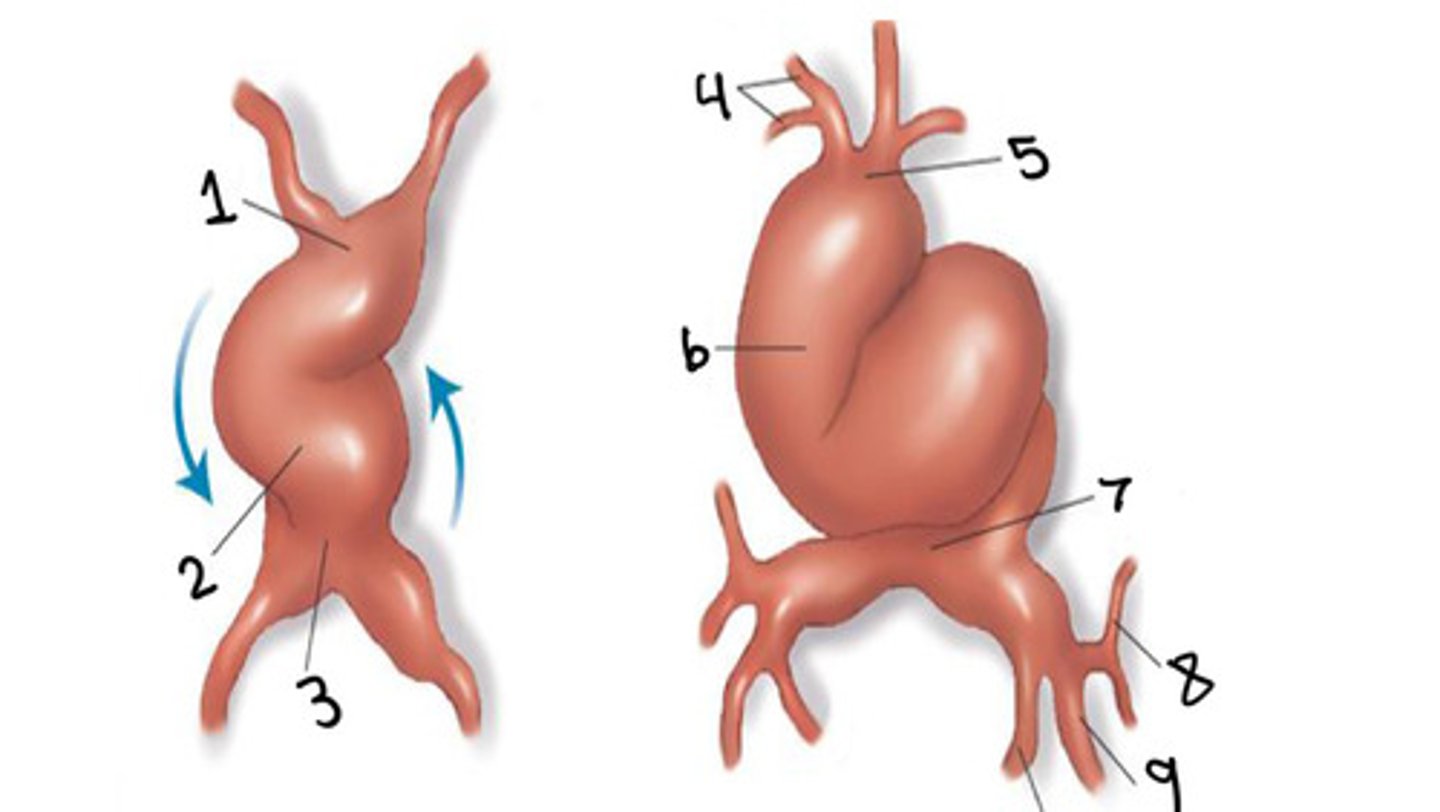
Ventricle
What is 2
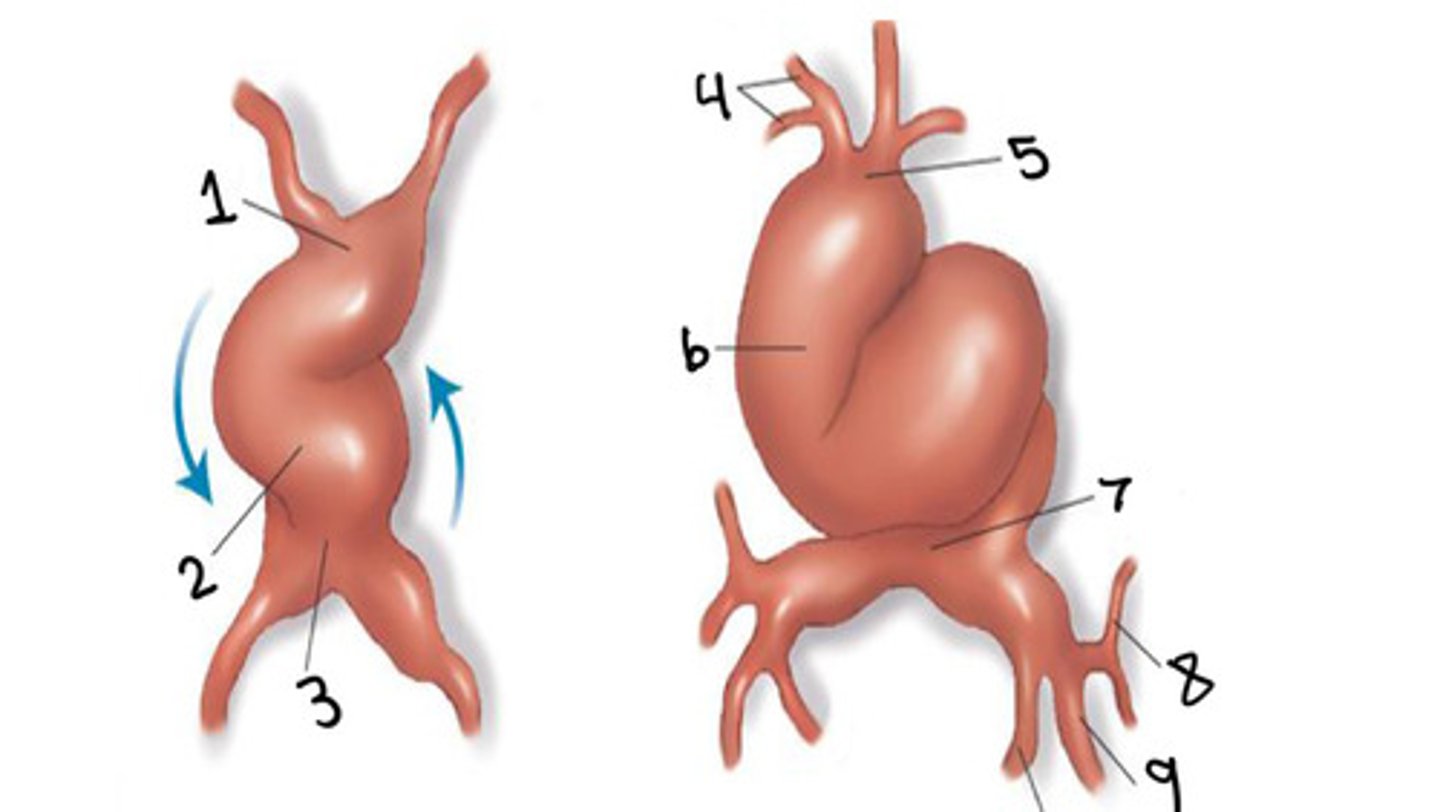
Atrium
What is 3
First and second arches
What is 4
Truncus arteriosus
What is 5
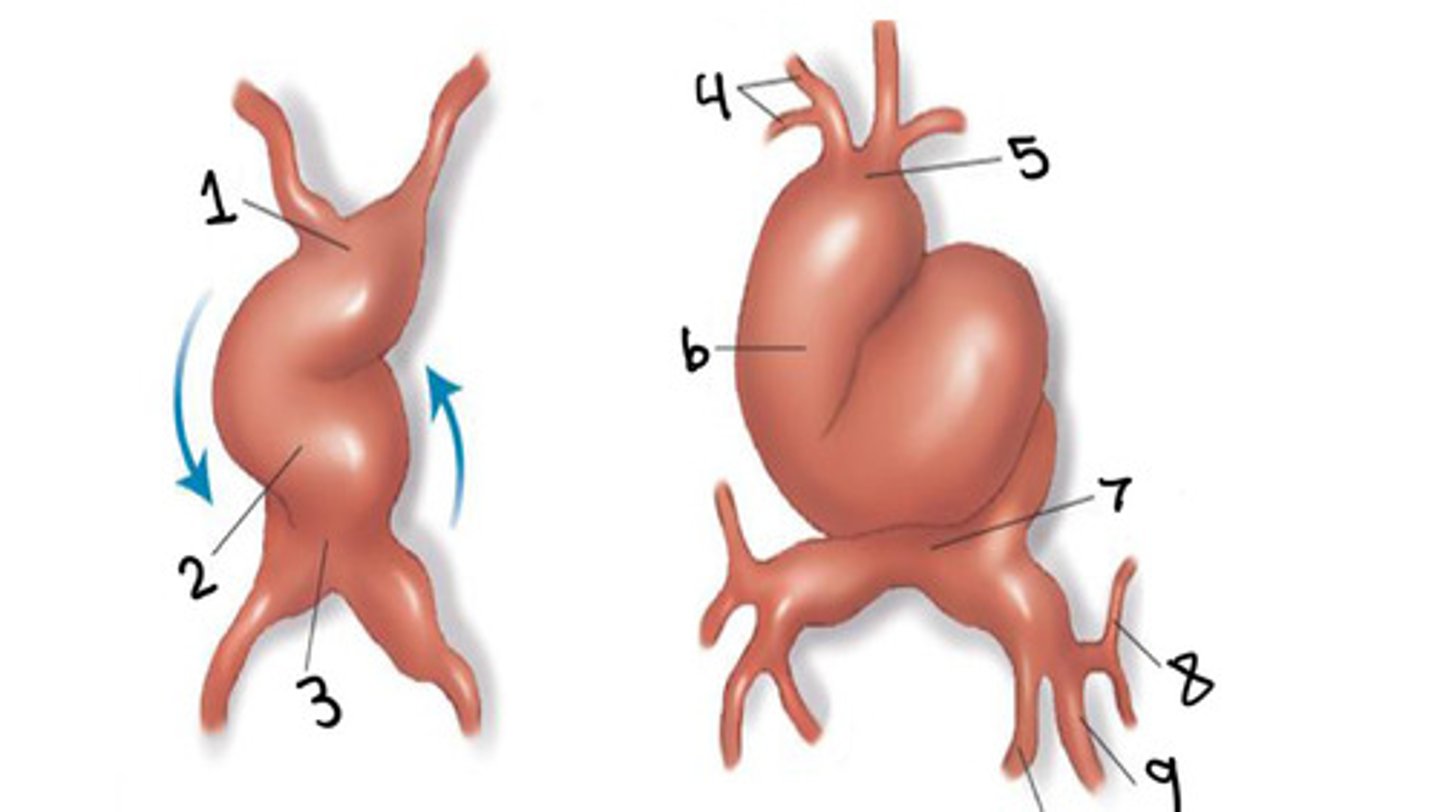
Bulbus cordis
What is 6
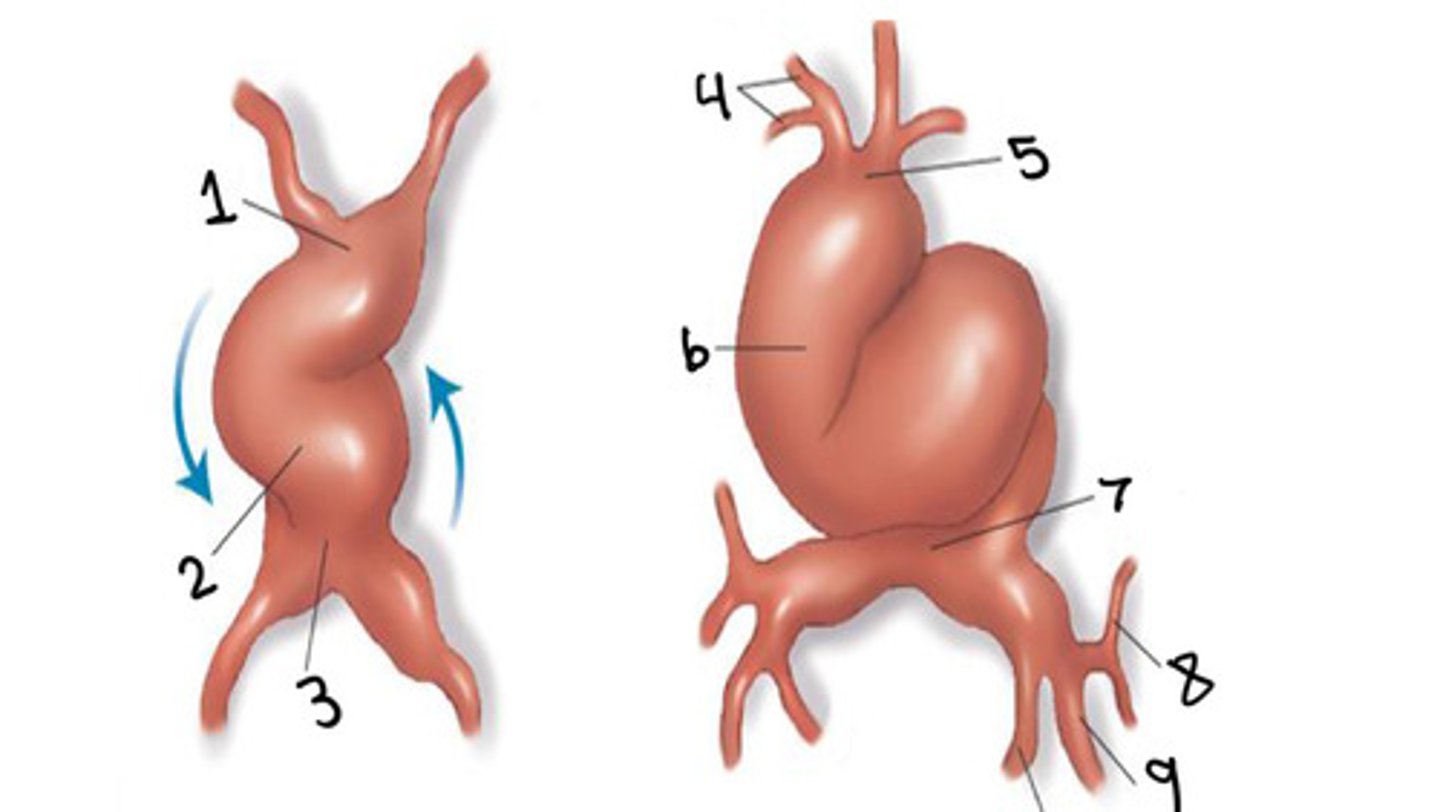
Sinus venosus
What is 7
Common cardinal vein
What is 8
Umbilical vein
What is 9
1st (think primary)
What does primum means
2nd
What does secundum mean
Normal rightward looping of the heart tube
What does this image show
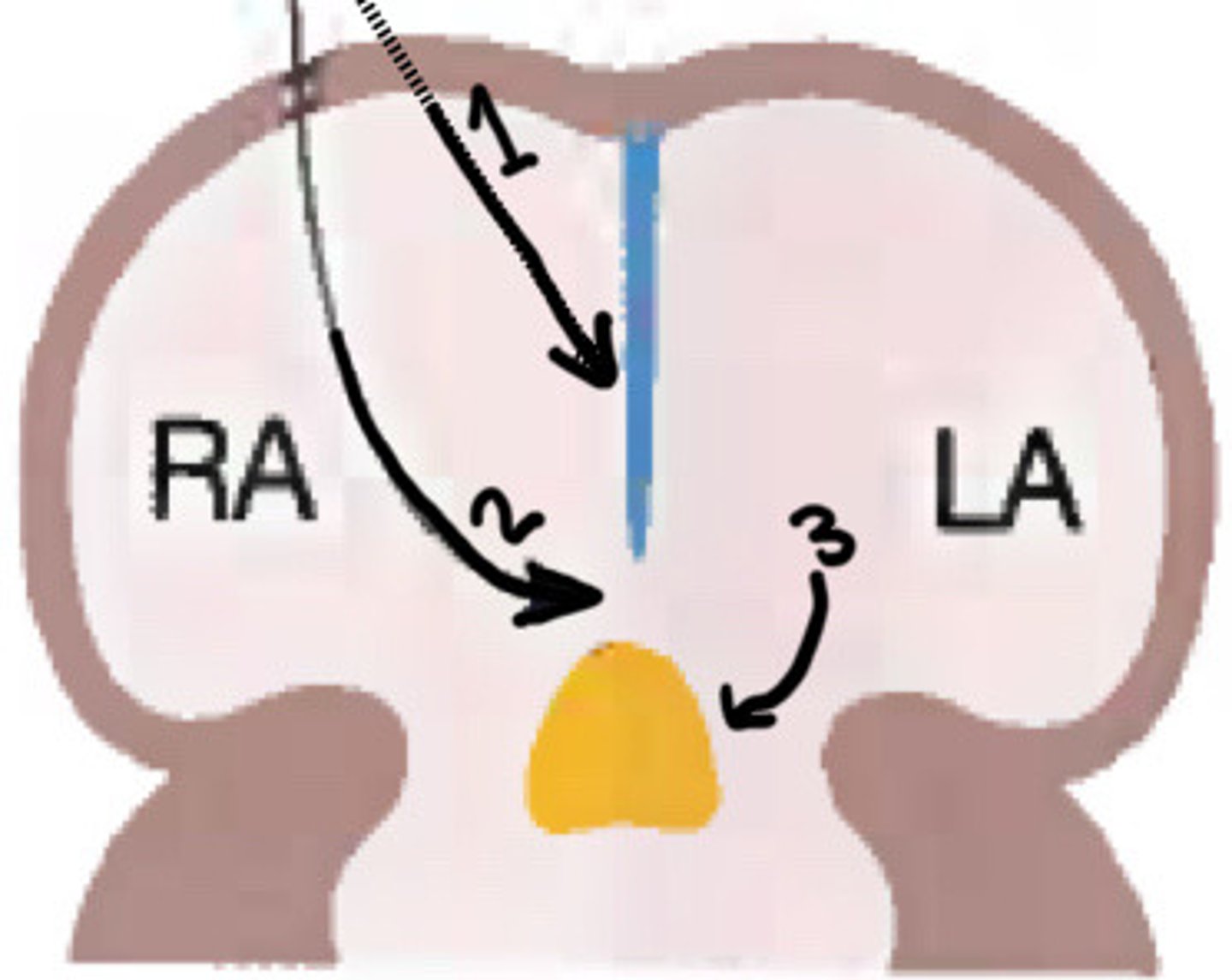
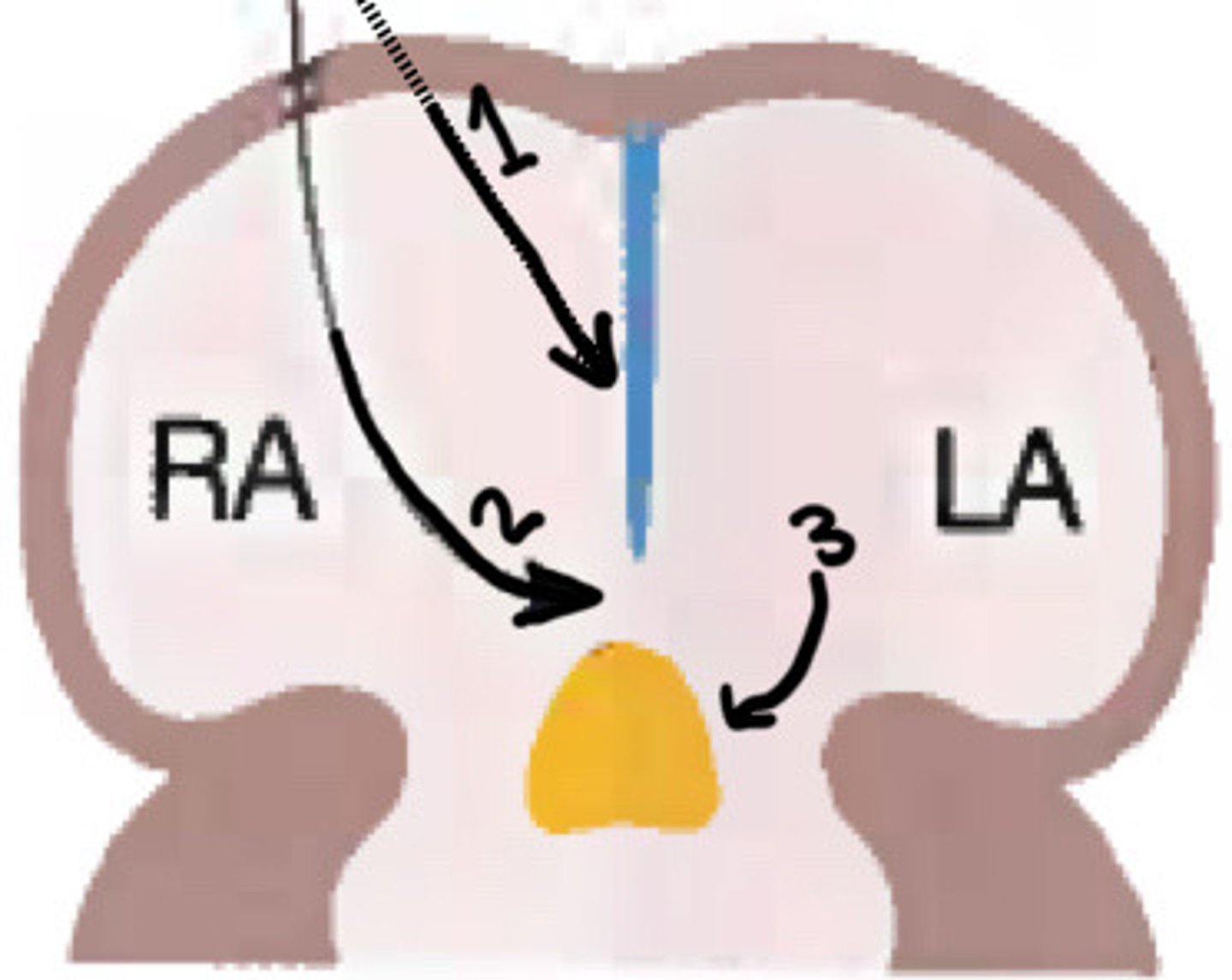
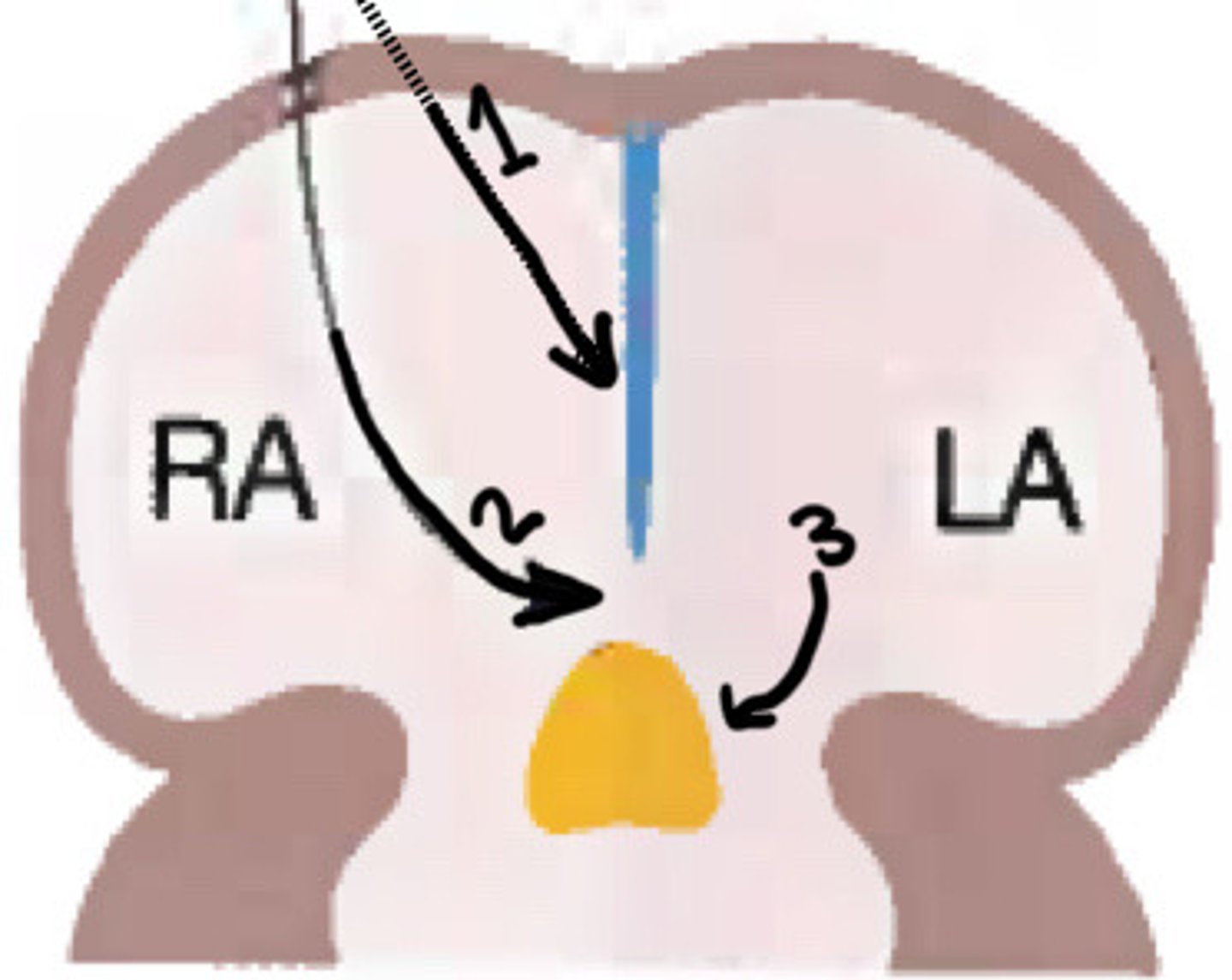
Primitive atrium
What does the yellow circle indicate
Septum primum
What is stage 1 of atrial septal formation
Divides atrium into RT and LT
What does septum primum do
Extends down from the roof of the common atrium toward endocardial cushion
How does the septum primum develop
No
Does septum primum fully connect to the endocardial cushions and close off the IAS
Foramen primum
What is the gap between the septum primum and endocardial cushions
Primum ASD
What ASD does the foramen primum turn into if this gap does not close off after baby is born
Septum primum
What is 1
Foramen primum
What is 2
Endocardial cushions
What is 3
Septum primum grows toward endocardial cusions
What is step 2 of atrial septal formation
Foramen primum closes
Besides growing inferiorly towards the endocardial cushions, what else does the stage 2 involve (what does this growth result in)
Perforations
What appears in the upper portion of the septum primum after its inferior growth in stage 2
Foramen secundum
What does these perforations result in
Secundum ASD
What ASD would these perforations lead to if it doesn't close up properly
Septum primum growth
What is 1
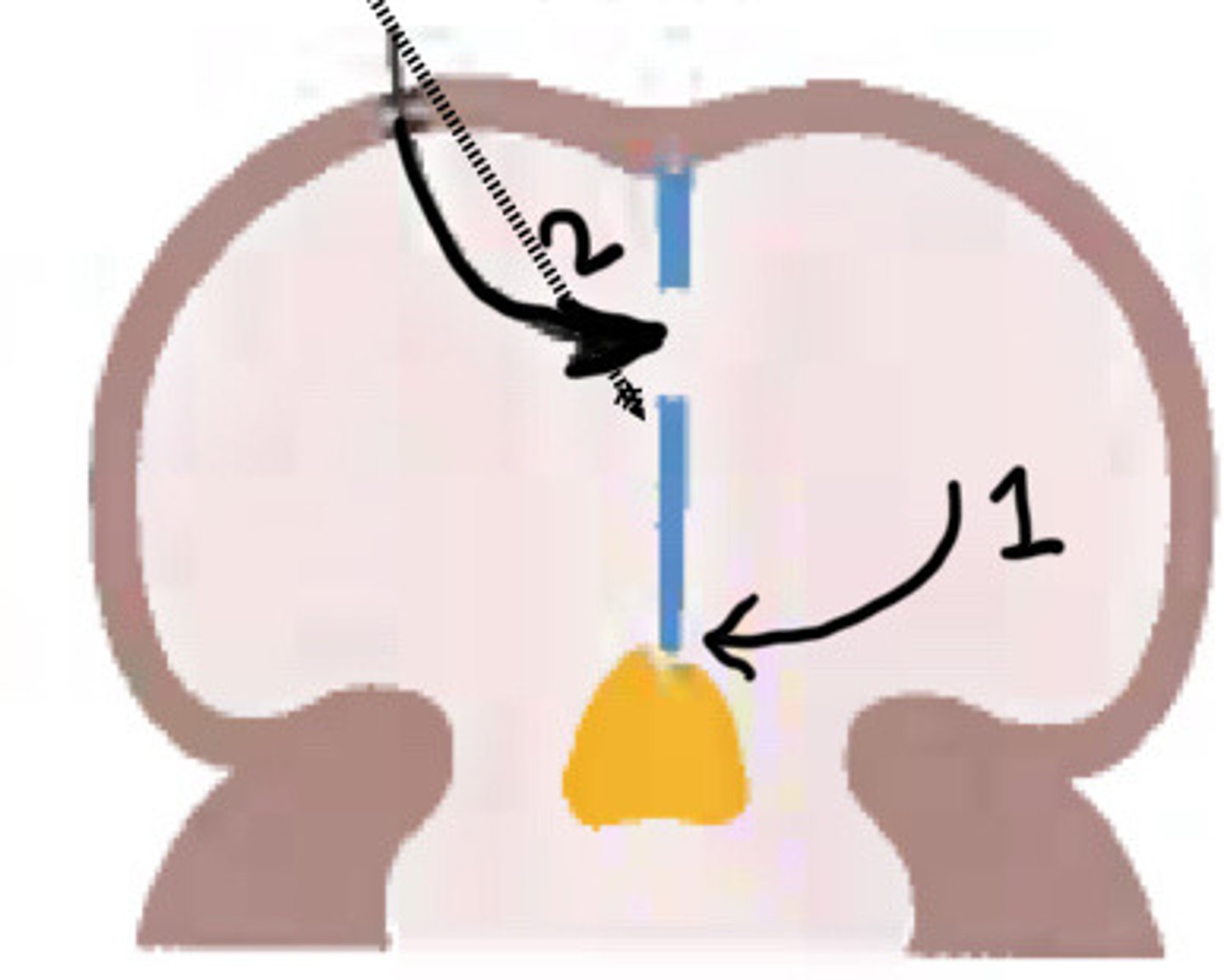
Foramen secundum
What is 2
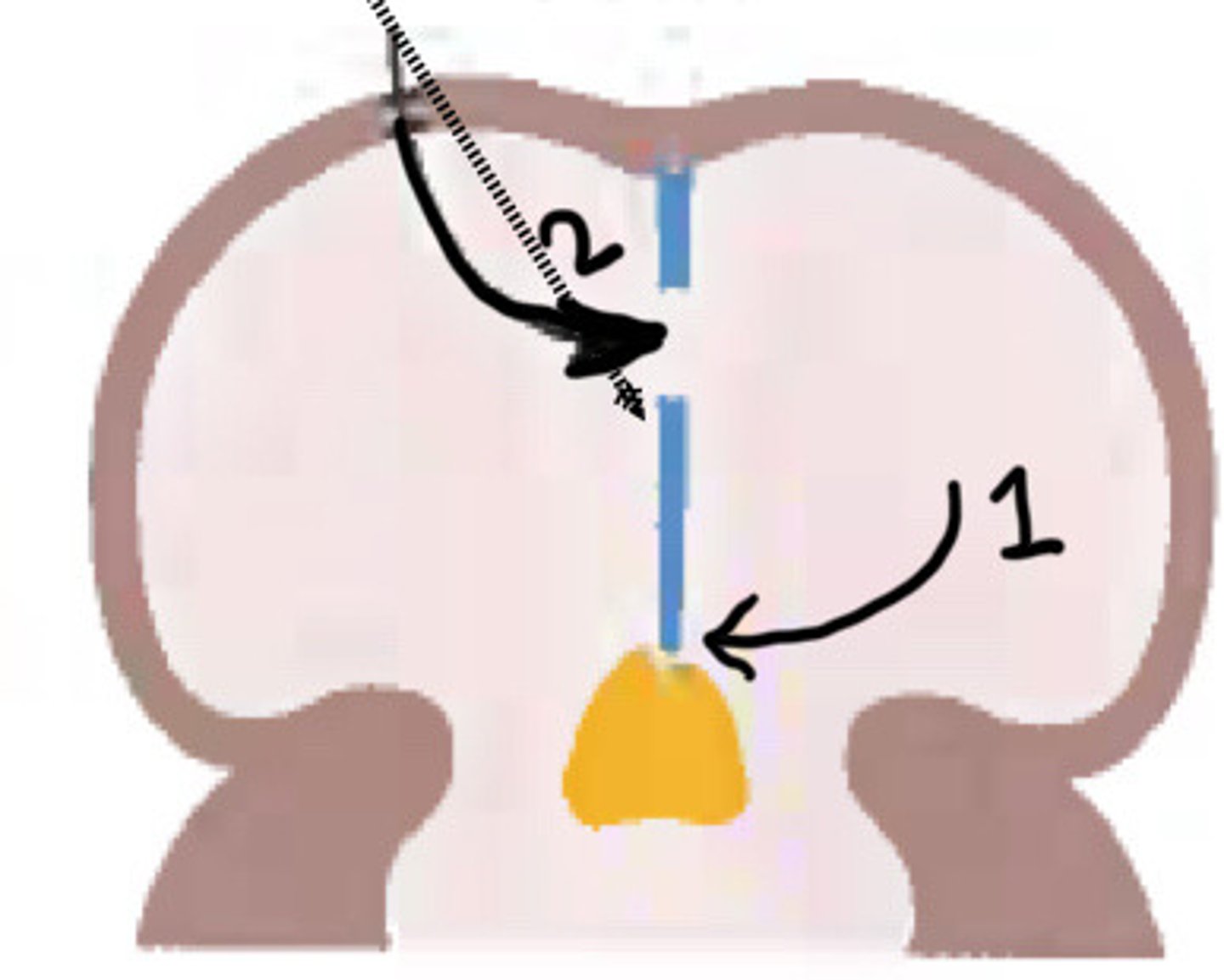
Septum secundum
What is the 3rd stage of atrial septal formation
Adjacent and to the right of septum primum (superior atrium)
How does septum secundum grow
Foramen secundum
What does septum secundum partially overlap
Foramen ovale
What does septum secundum creat by partially ovale flapping foramen secundum
PFO
What ASD does foramen ovale form if not closed fully
Septum secundum
What is 1
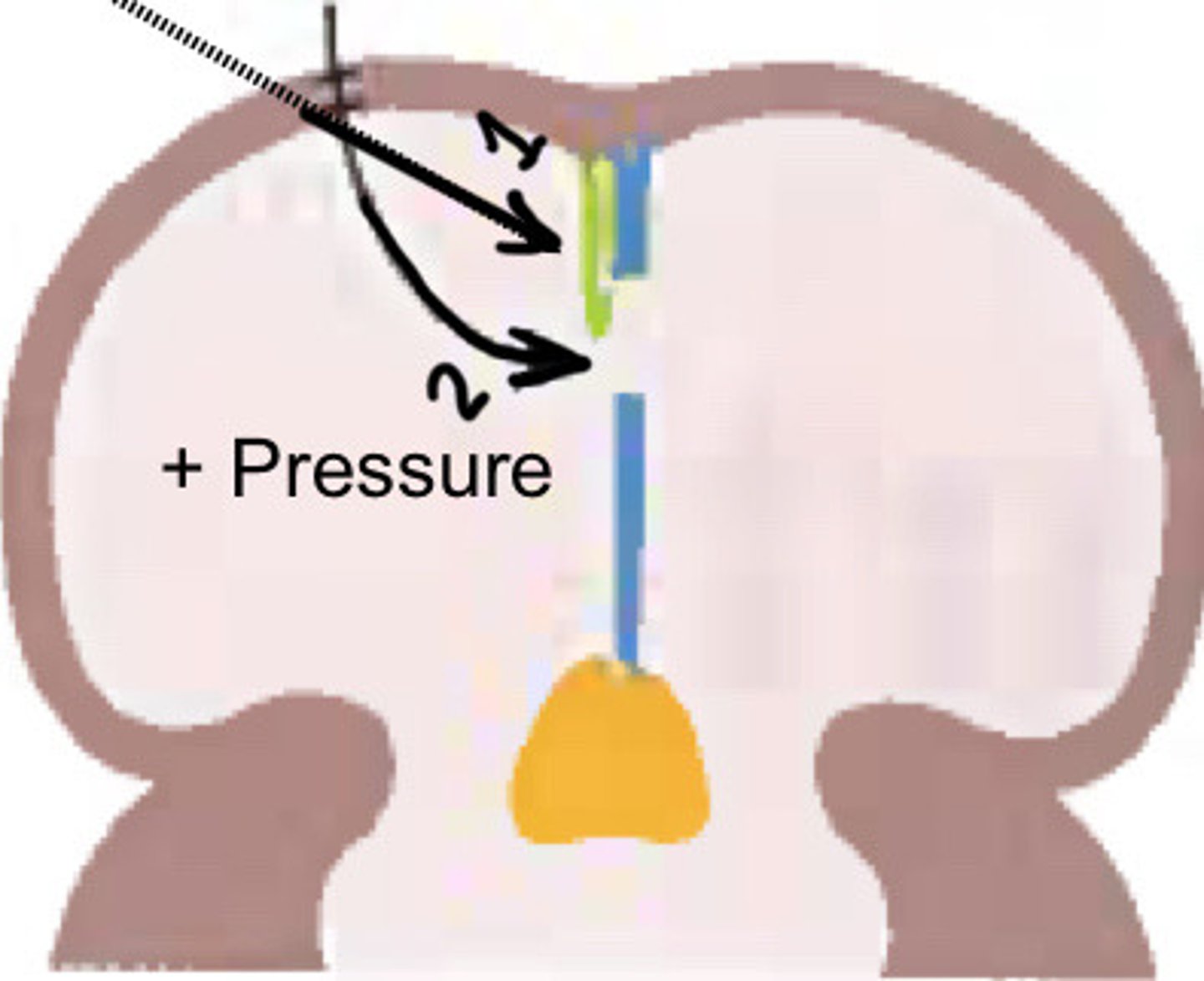
Foramen ovale
What is 2
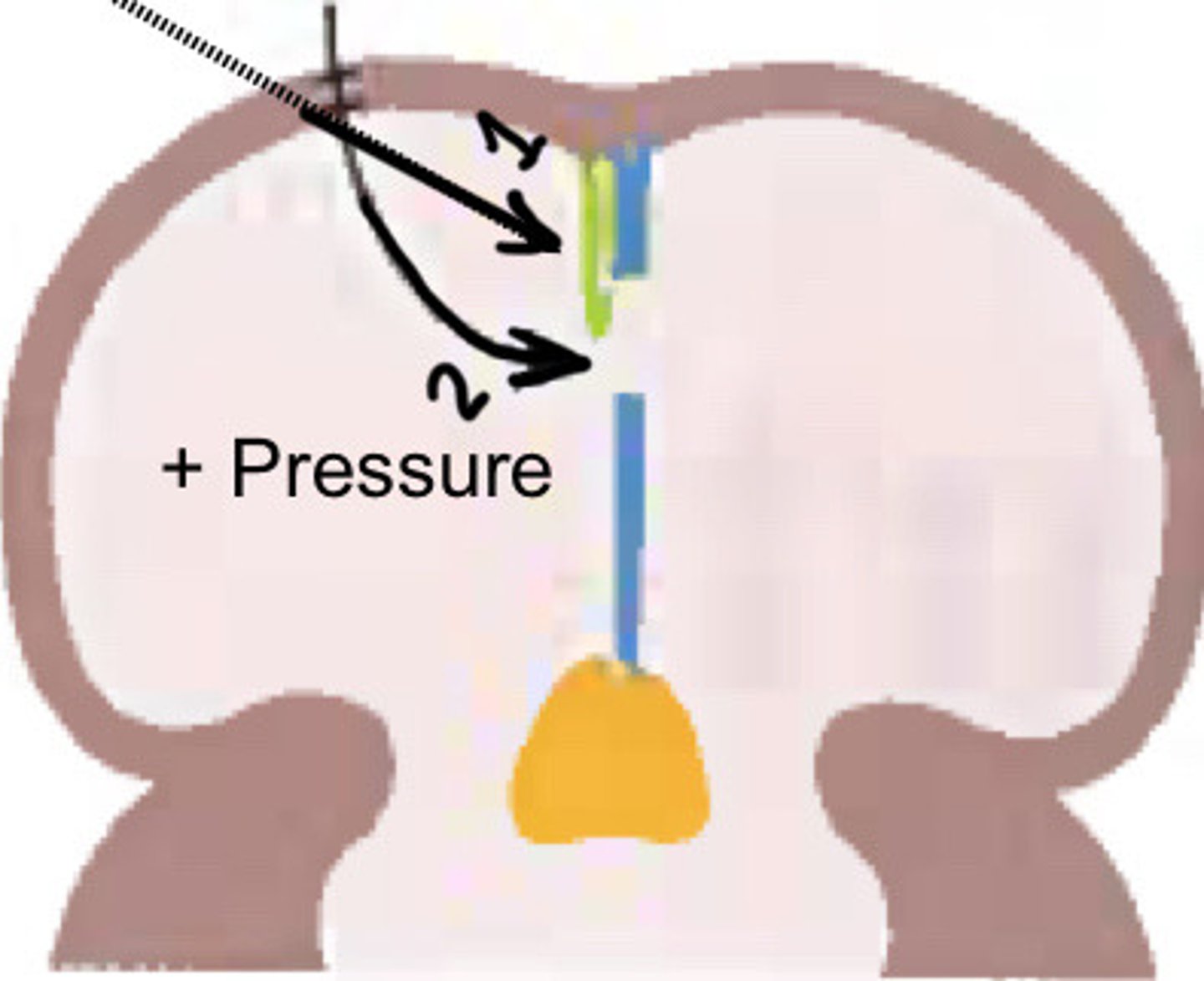
Foramen ovale
What is stage 4 of atrial septal formation
Upper septum primum
What disappears in stage 4 of atrial septal formation
Valve of foramen ovale
What does the lower part of septum primum become (once the upper part disappears
RA>LA pressure
What keeps the foramen ovale open during gestation
Septum secundum grows superior from the AV cushions
What happens to septum secundum as well during stage 4
Original growth of septum secundum
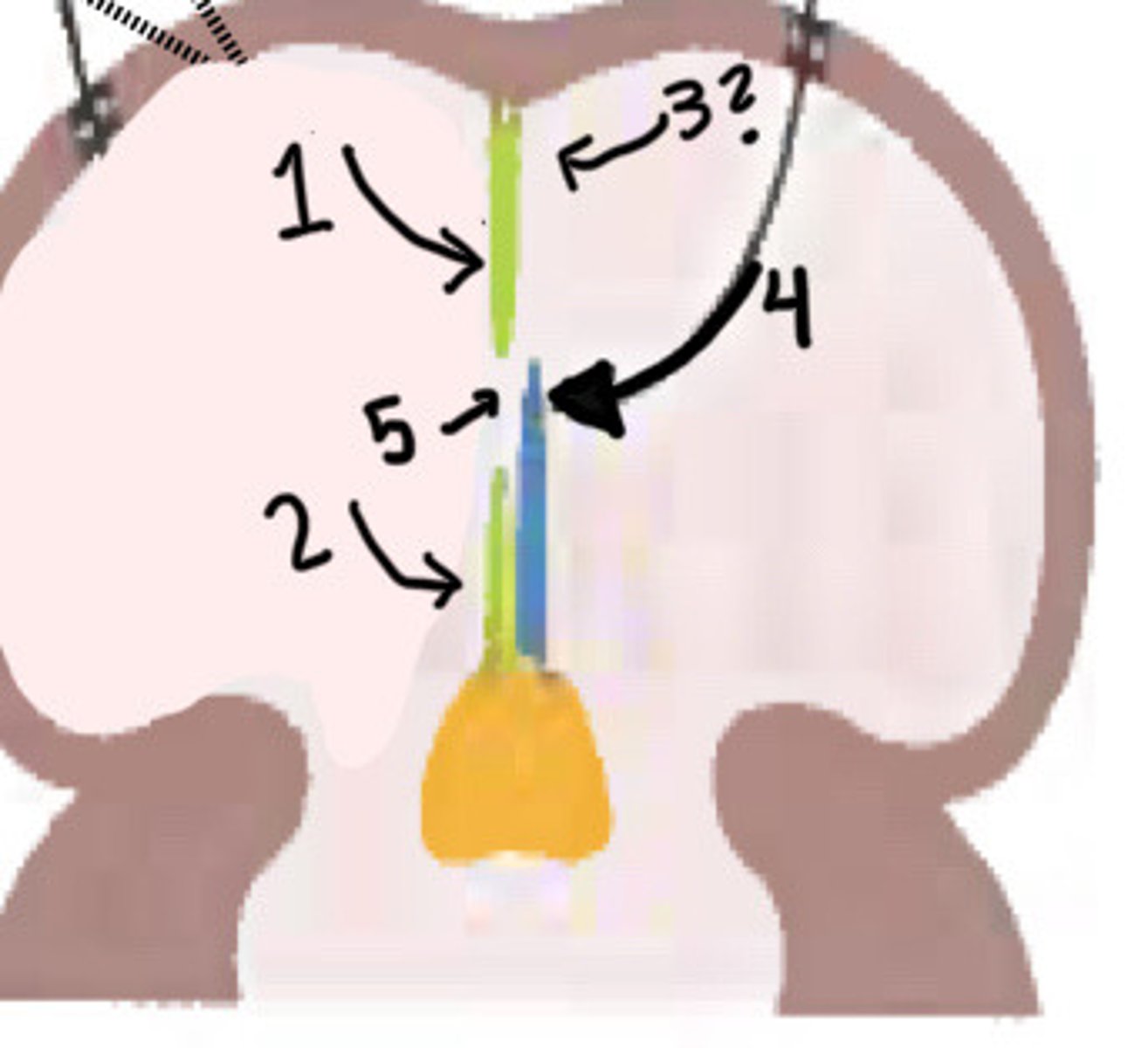
What is 1 pointing to
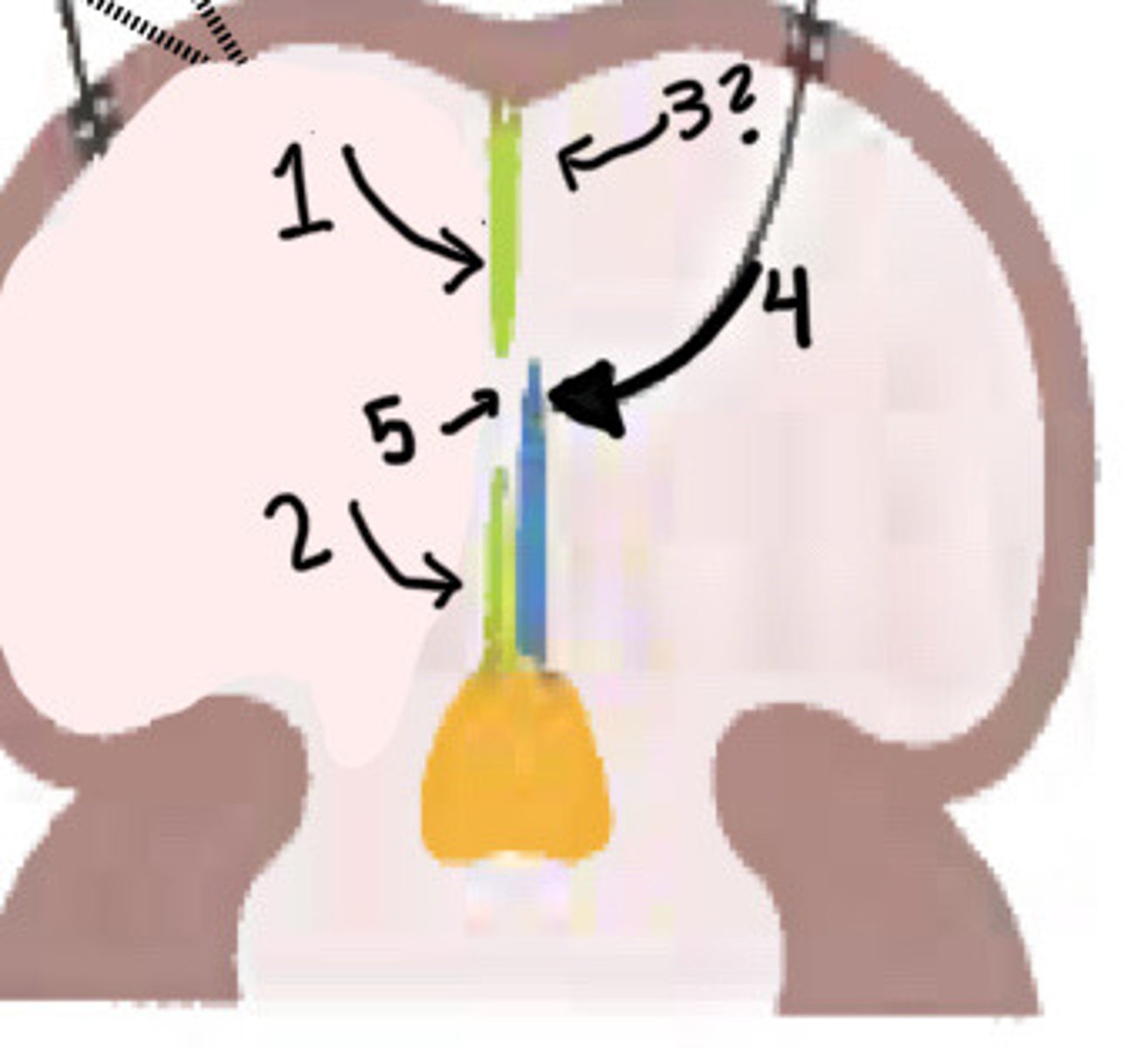
New growth of septum secundum
What is 2 pointing to
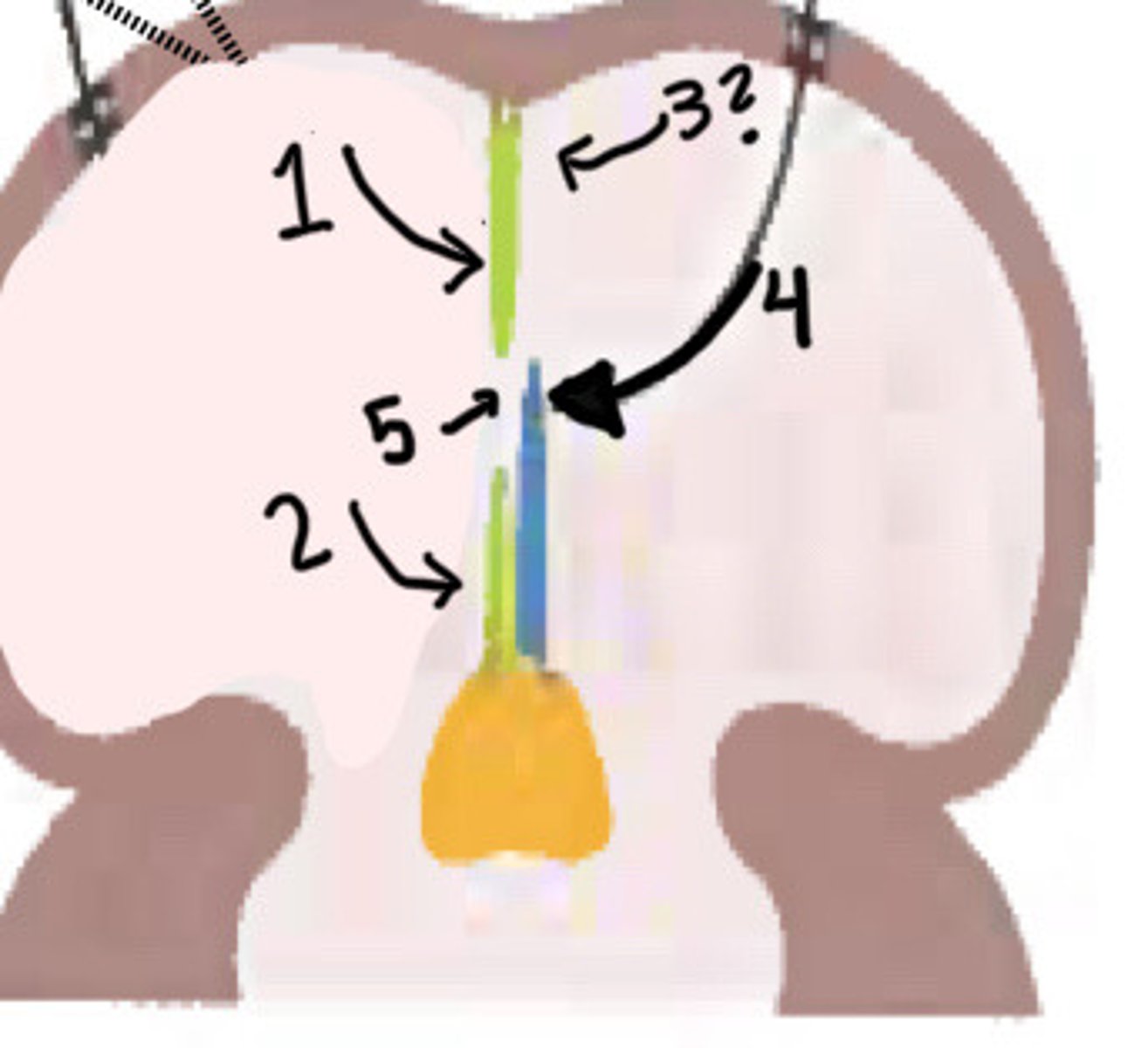
Disappearance of upper septum primum
What is 3 pointing to
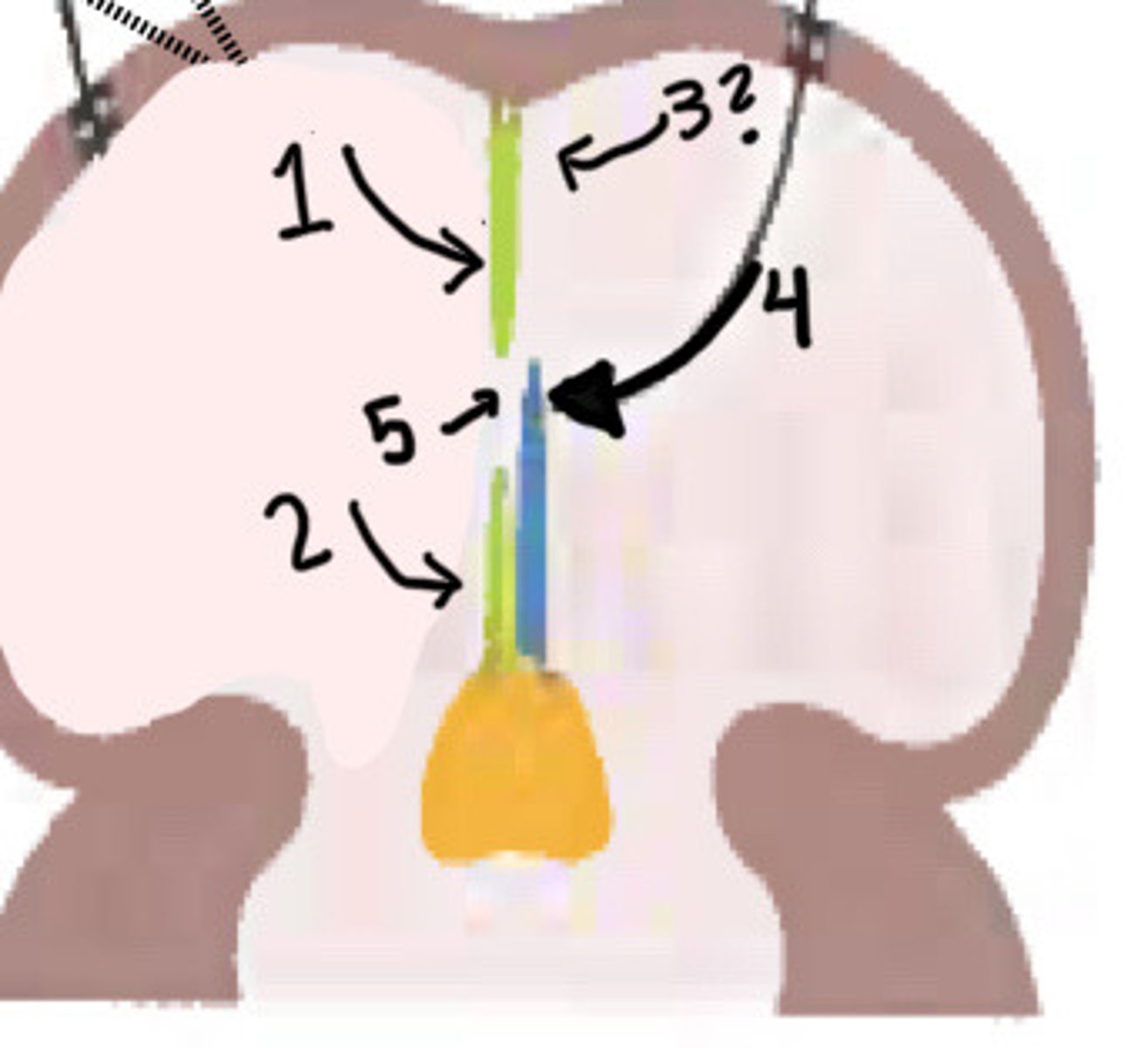
Valve of foramen ovale (lower part of septum primum)
What is 4 pointing to
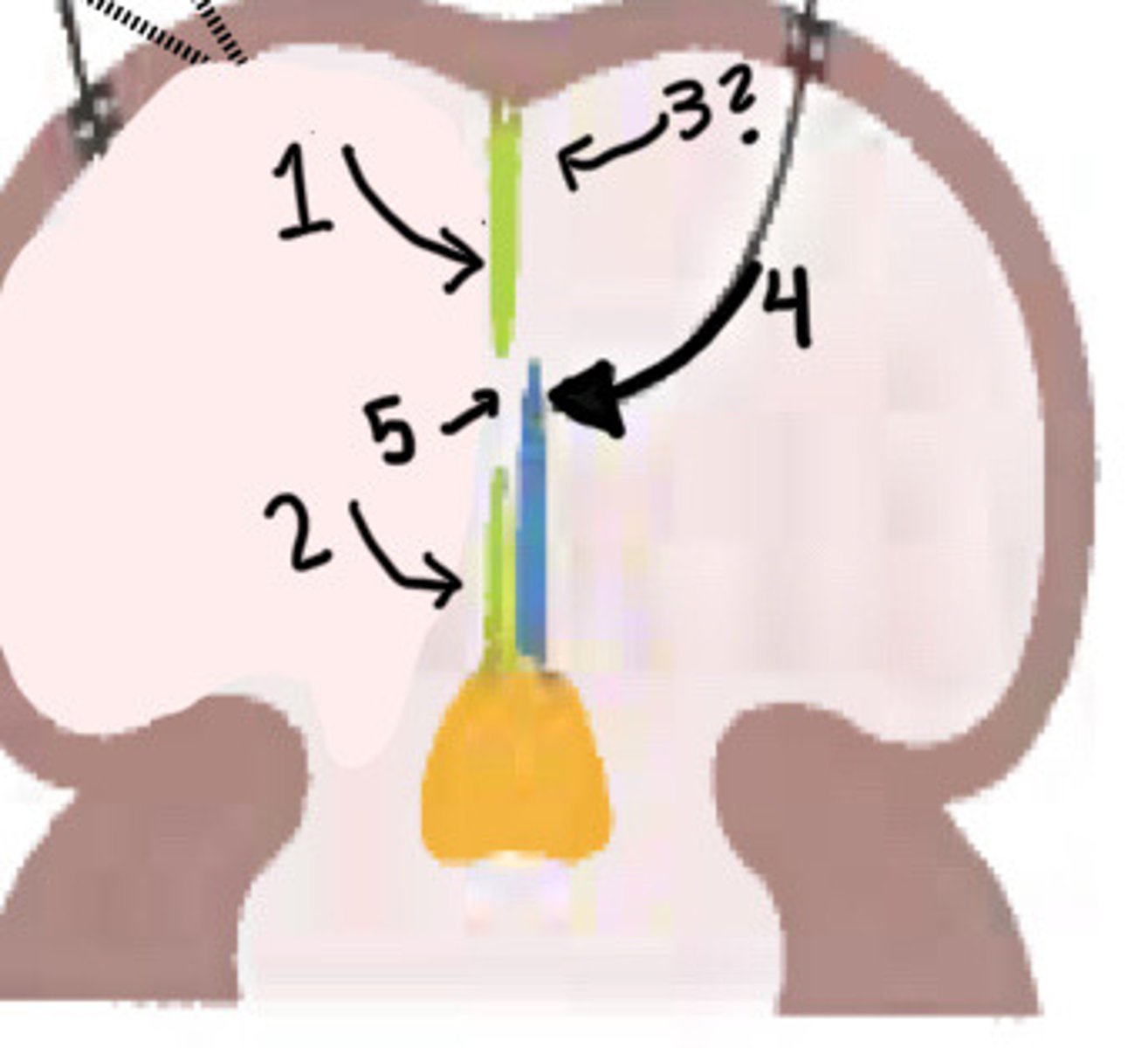
Foramen ovale
What is 5 pointing to
Increase in systemic vascular resistance and decrease in RA pressure results in the LA pressure rising higher than the RA pressure
Describe the changes of pressure at brith in te heart
Pushes the valve of foramen ovale against the septum secundum, closing the foramen ovale hole
What does this increase in LA pressure at birth result in
Fuse
Over time, the valve of foramen ovale and septum secundum should _____________
25%
What % of people is it estimated that the flaps of foramen ovale don't fully fuse together
Ostium primum ASD
What is 1
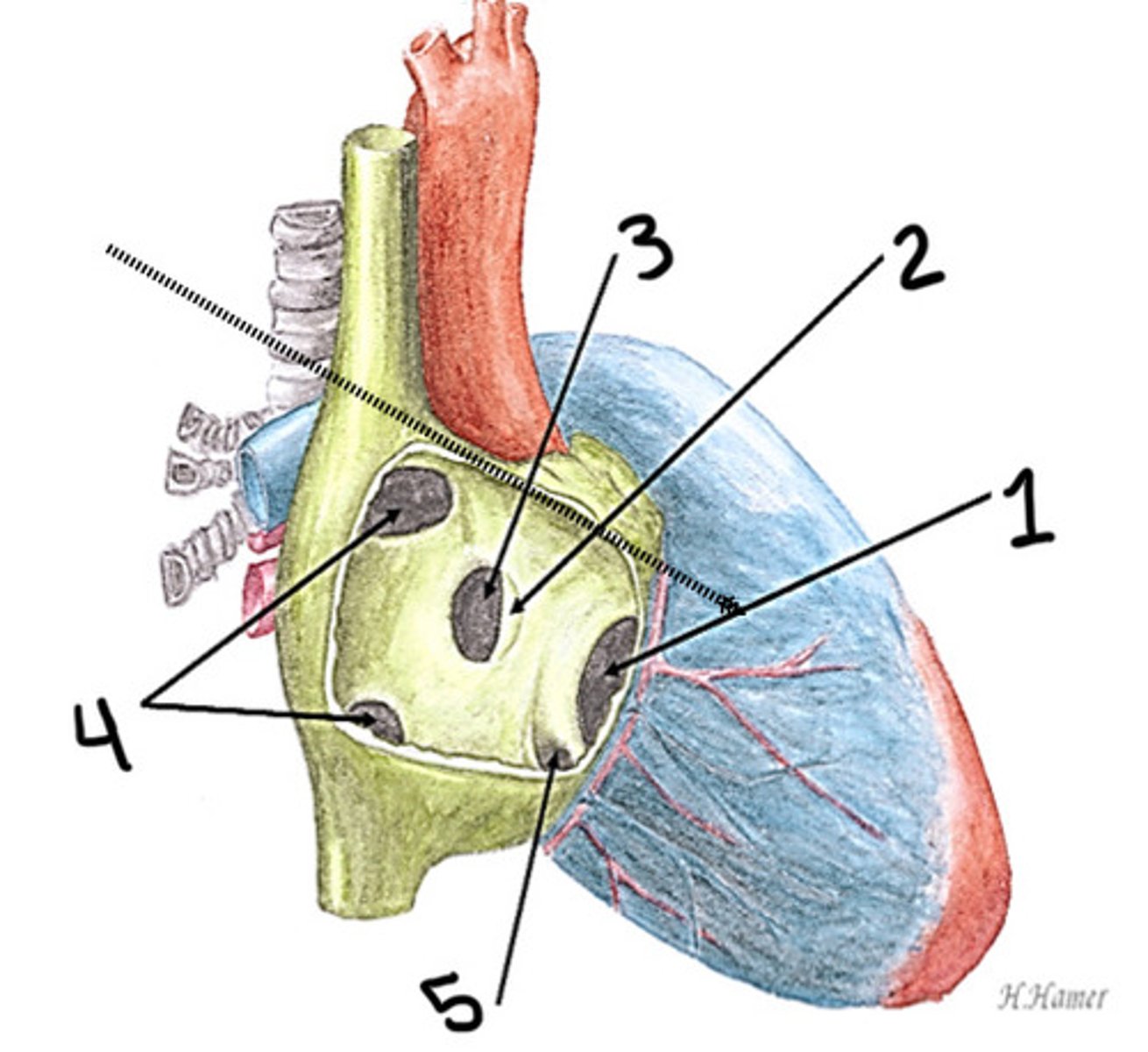
PFO (fossa ovalis)
What is 2
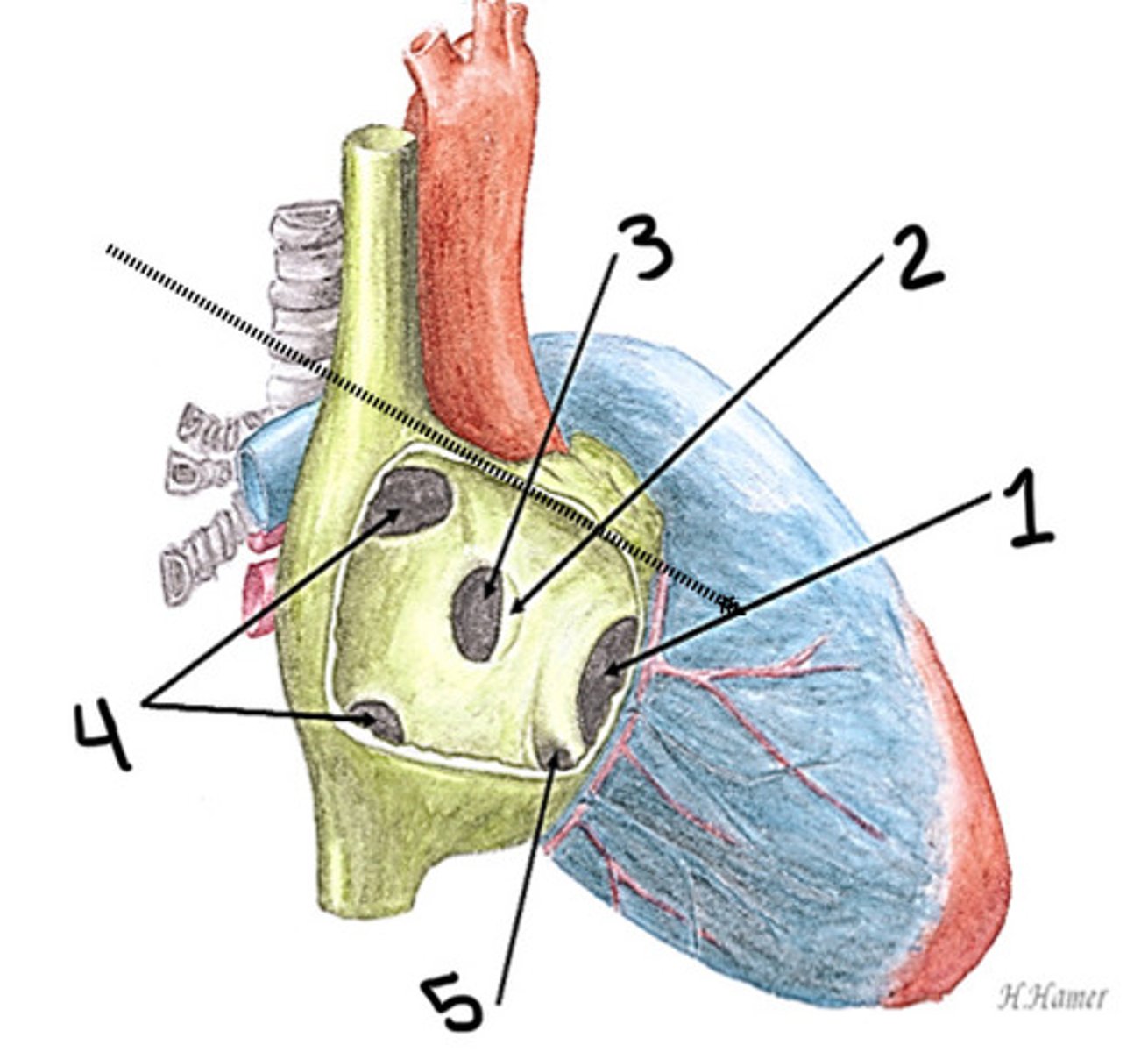
Ostium secundum ASD
What is 3
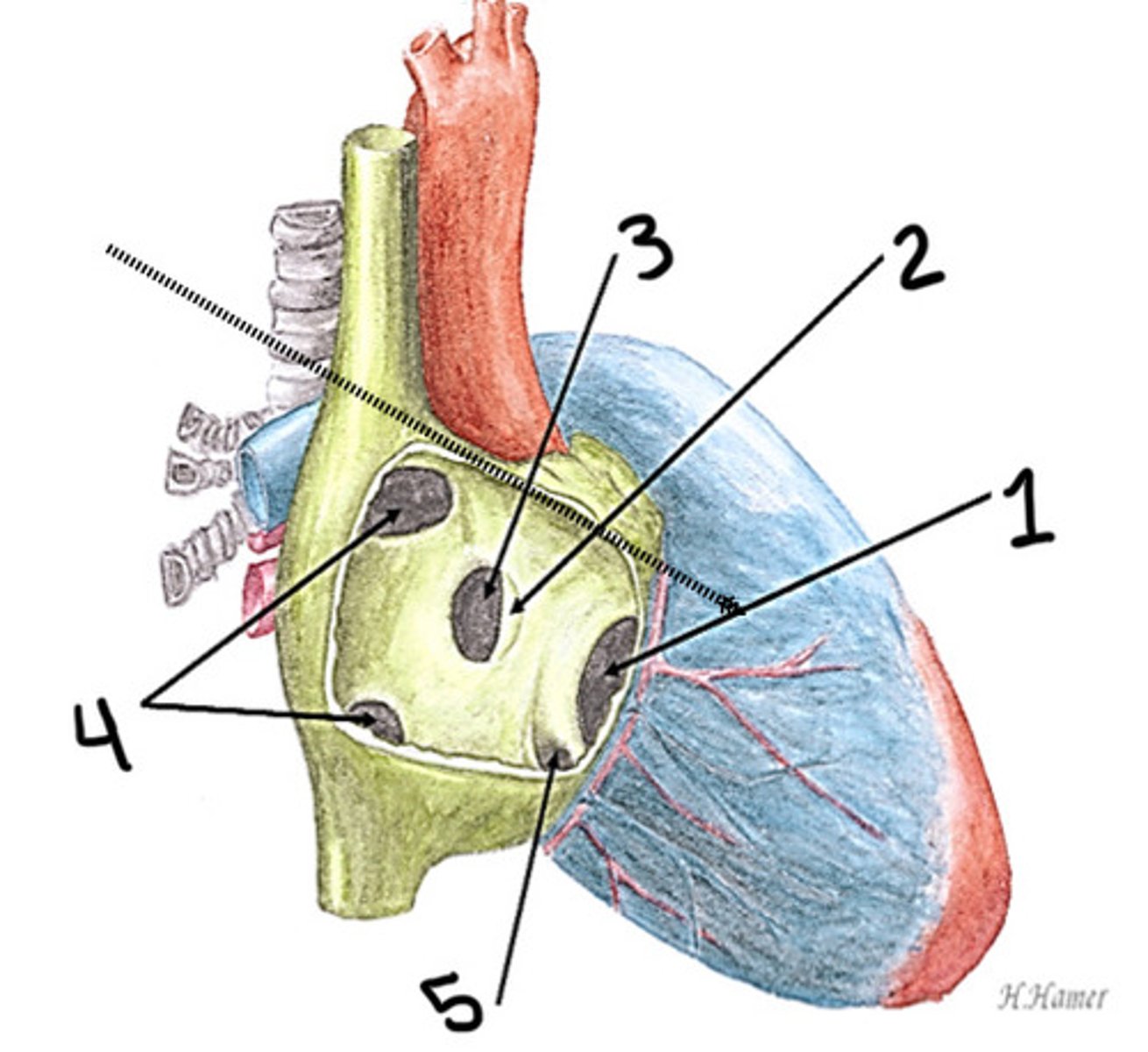
Sinus venous ASD (superior and inferior)
What is 4
Fossa ovalis
What is another term for a PFO
Patent foramen ovale
What does PFO stand for
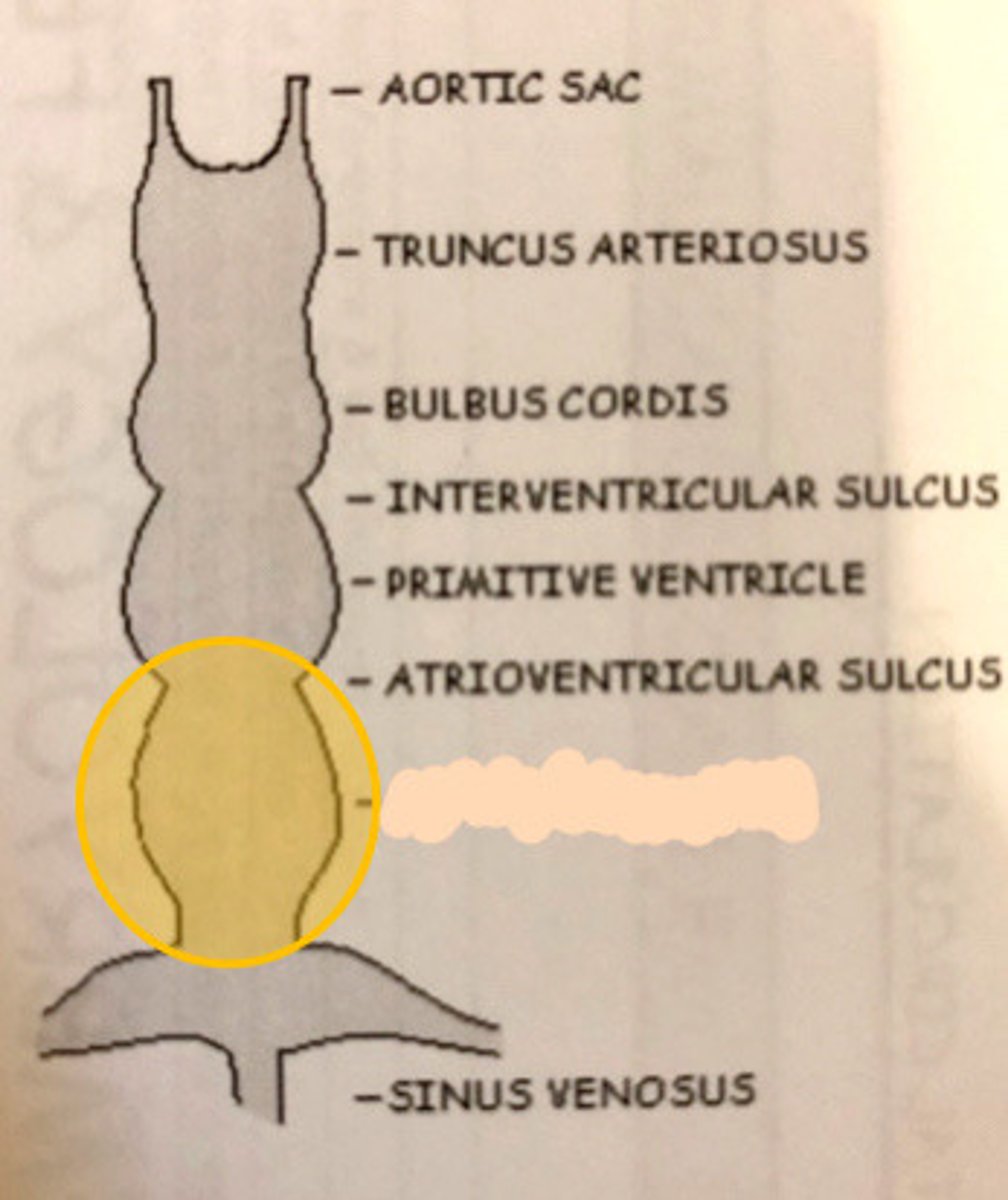
Primitive ventricle/bulbus cordis
What does the yellow circle indicate
Atrioventicular
What does AVC stand for
Bulbus cordis
What does BC stand for
Primitive ventricle
What does PV stand for
Trabecular IVS
What is stage 1 of ventricle septal formation
Part of the RV
What does the bulbus cordis become in stage 1
LV and the rest of the RV
What does the primitive ventricle become in stage 1
Trabecular IVS (muscular)
What part of the IVS grows in stage 1
Grows from apex to base but stops part way
Describe how the trabecular IVS grows in stage 1
Allows blood flow from both ventricles to exit the truncus arteriosus through the interventricular foramen
Why does the trabecular IVS stop partway while growing in stage 1