Geology 209 Final Chapters 8 & 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Last updated 12:34 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Fossils
________ represent the vestiges of ancient life forms.
2
New cards
Body fossils
Most frequent, has part or whole of organism preserved, includes hard parts, palaeontology
3
New cards
Trace fossils
Represents organism’s activities, original organism left traces of moving and feeding, sedimentary petrology
4
New cards
Chemical fossils
Represents chemical combinations of certain substances produced by an organism or existing in its body and the minerals in the surrounding environments, geo chemistry
5
New cards
Recrystallization
The conversion of original minerals of the test into different minerals, common transformation is aragonite to calcite
6
New cards
Moldic preservation
The original test or shell dissolves after being embedded into the rock, creates an empty space that preserves external and internal features
7
New cards
Moldic preservation replacement
Particular case of moldic preservation, new space from dissolution is filled with new material
8
New cards
Pyritization
Most frequent case of replacement
9
New cards
Permineralization
Results from the filling of pore spaces by opal, or chalcedony, trees are prone to this
10
New cards
Carbonization
Occurs when fossils are buried into Earth’s crust, organic material is expelled except for carbon, frequent in plants
11
New cards
Congealment
Occurs at high latitudes, thick layer of frozen soil and rock and the uppermost part of the Earth’s crust, fossilized soft tissue
12
New cards
Amber
Fossilization happens in natural resin, allows three dimensional fossilization when resin was liquid, fossilized soft tissue
13
New cards
Tar pits
Occurs in in zones with oil seeps, organisms stuck in viscous fluids
14
New cards
Metasomatosis
Complete replacement of the chemical and mineralogical composition of a fossil
15
New cards
Structural geology
Represents the study of rock deformation in response to applied force
16
New cards
Principle of original layer horizontality
Deformed and tilted layers are the result of crustal movements
17
New cards
Force
The push or pull that result in a change in the motion of a physical body of given mass
18
New cards
Stress
The amount of force per unit area
19
New cards
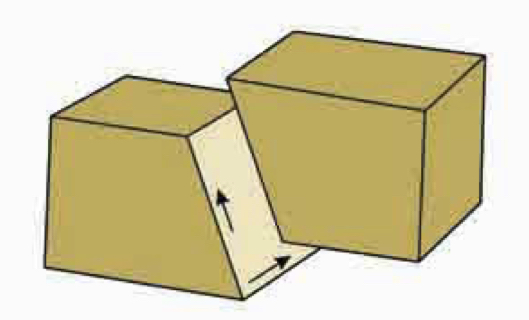
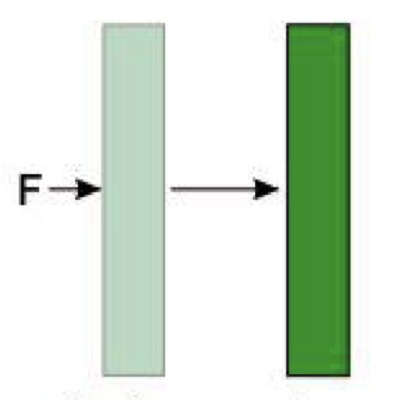
Change in place (displacement)
A rock volume is moved from one place to another
20
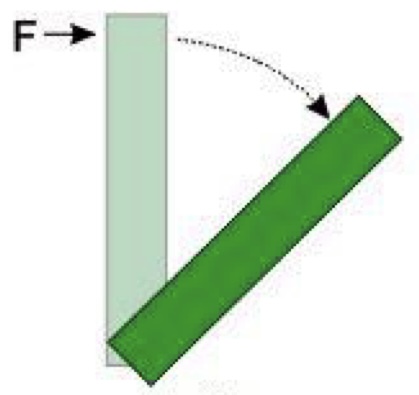
New cards
Change in position (rotation)
Occurs when a rock spins around a center or an axis
21
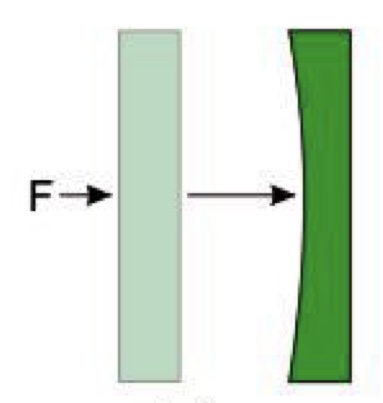
New cards
Change in shape (strain)
Represents the internal deformation of a rock response to force or stress
22
New cards
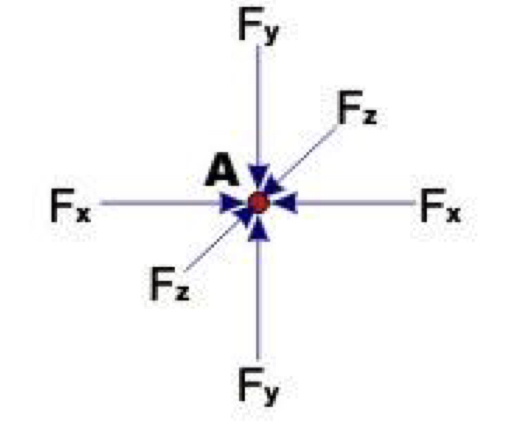
Confining stress
Equal in all three directions of the space for a certain point in the Earth’s crust, occurs in rock burial
23
New cards
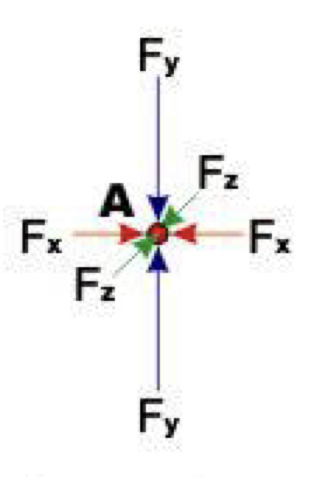
Differential stress
The amount of stress is higher in certain directions, occurs in crustal movements
24
New cards
Compression
Stress pushes on a rock
25
New cards
Tension
Stress stretches a rock
26
New cards
Shear
Stress is applied in two opposite directions
27
New cards
Fluid pressure
Is given by the fluids in rock pores and occurs mostly in the case of sedimentary rocks, pressure is opposite to general stress and reduced effects of total stress
28
New cards
Brittle deformation
Upper portion of crust, rocks are weak due to low pressure, fractures are dominant structures
29
New cards
Ductile deformation
Occurs with depth increase, rocks are strong due to high pressure, folds are dominant structure
30
New cards
Folds
Structures that result from lateral compression of the Earth’s crust
31
New cards
Branches
The two convergent or divergent sides of the fold, aka limbs
32
New cards
Fold crest
Highest part of fold
33
New cards
Trough
Lowest part of fold
34
New cards
Fold axis
A line defined by the points of maximum curvature
35
New cards
Axial plane
Defined by the axes that subdivide the fold into two equal parts
36
New cards
Anticline
Branches converge upwards

37
New cards
Syncline
Branches converge downwards

38
New cards
Monocline
One branch going downwards

39
New cards
Upright
Axial plane is vertical, the two limbs dip in opposite directions
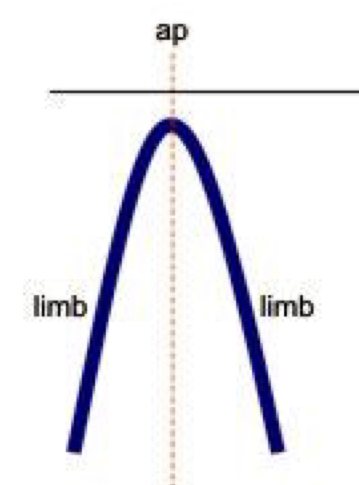
40
New cards
Inclined
Axial plane is inclined, the two limbs dip in opposite directions
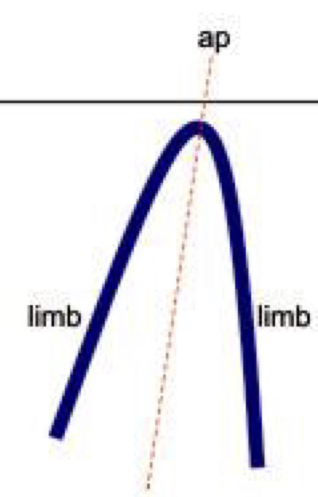
41
New cards
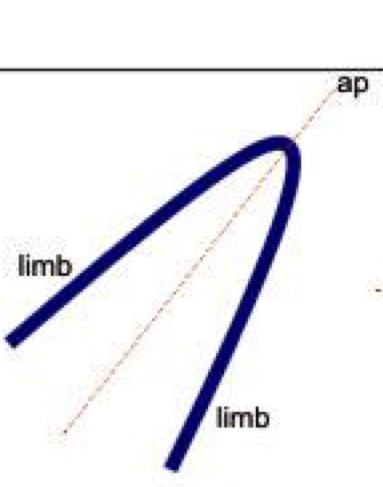
Overturned
Axial plane is inclined, the two limbs dip in the same directions
42
New cards
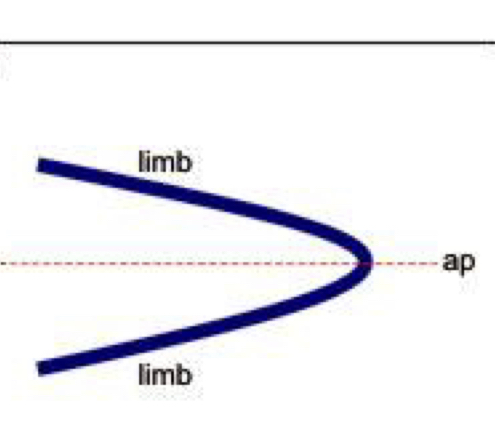
Recumbent
Axial plane is horizontal, the two limbs dip in opposite directions
43
New cards
Joints
Fractures in which the two resulting blocks present no movement with respect to each other
44
New cards
Faults
Fractures in which two resulting blocks present a significant displacement
45
New cards
Footwall
Situated below the fault plane
46
New cards
Hanging wall
Situated above the fault plane
47
New cards
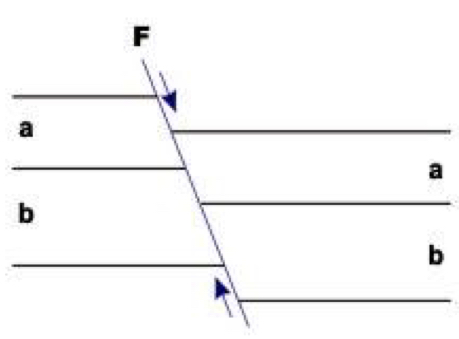
Normal faults
The hanging wall presents a downward displacement when compared to the footwall
48
New cards
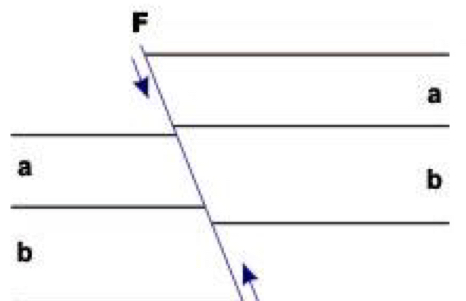
Reverse fault
The hanging wall presents an upward displacement when compared to the footwall
49
New cards
Thrust faults
Reverse faults which dip at a low angle
50
New cards
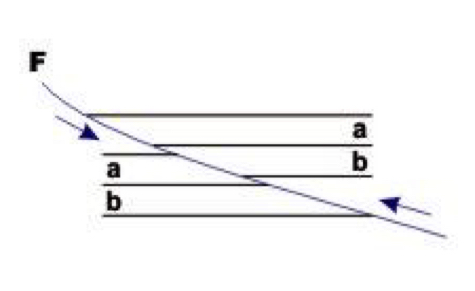
Strike-slip faults
The displacement is horizontal, along the strike
51
New cards
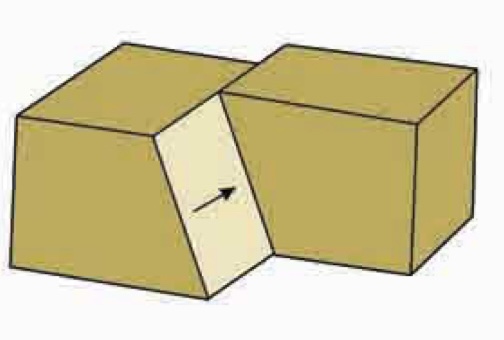
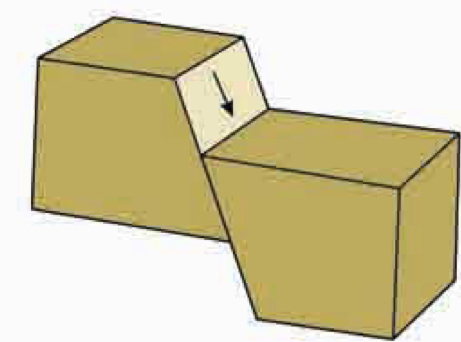
Dip-slip faults
There is only vertical displacement, along the dip
52
New cards
Oblique-slip faults
Most common, both horizontal and vertical displacement